
12 Common Household Items That Are Slowly Killing Us
12 Common Household Items That Are Slowly Killing Us: Hidden Dangers in Everyday Products
Our homes are meant to be safe havens, but some common household items may be exposing us to hidden dangers that slowly impact our health. Many of these items, which we use daily without a second thought, contain chemicals or materials that can disrupt our health over time. From the air we breathe to the food we eat, the things we interact with at home can contribute to long-term issues like hormone disruption, respiratory problems, and even certain cancers. This article explores 12 household items that may be more dangerous than we realize.
-
Scented Candles
While they create a pleasant atmosphere, many scented candles release harmful substances like benzene, toluene, and synthetic fragrances. These chemicals can irritate the lungs and disrupt hormone function when inhaled over time. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), benzene is a carcinogen, which makes regular exposure to such candles potentially dangerous, especially for those with respiratory issues (EPA, 2020). The American Lung Association also warns that using candles with artificial scents may exacerbate asthma and other respiratory conditions (American Lung Association, 2022).
-
Old Carpets or Rugs
Old carpets and rugs may seem harmless, but they can harbor dust, mold spores, flame retardants, and chemicals that slowly release into the air. These substances can contribute to indoor air pollution, which has been linked to a variety of health issues, including respiratory problems and allergies. The chemicals in carpets, especially those treated with flame retardants, can linger in the home for years, affecting the quality of the air and the health of the inhabitants. Studies have shown that flame retardants can disrupt hormonal functions and even cause developmental issues in children (Environmental Working Group, 2021).
-
Non-Stick Cookware (Teflon)
Non-stick cookware, often made with Teflon, has become a staple in many kitchens due to its convenience. However, when overheated, Teflon can release harmful PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), which have been linked to thyroid issues, inflammation, and metabolic problems. Research published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives has shown that exposure to these chemicals can accumulate in the body over time, leading to serious long-term health risks (Environmental Health Perspectives, 2018). Cooking at high temperatures with non-stick pans can significantly increase the release of these chemicals into the air, making it important to avoid overheating.
-
Cheap Cookware (Aluminum)
While aluminum cookware is inexpensive and widely used, uncoated aluminum can leach trace metals into food, especially when cooking acidic foods like tomatoes. This can lead to the ingestion of aluminum, which has been associated with potential neurotoxic effects and cognitive decline. Studies have shown that long-term exposure to high levels of aluminum may contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer's Society, 2021). To avoid these risks, it’s advisable to opt for cookware made from safer materials such as stainless steel.
-
Air Fresheners
Air fresheners are commonly used to mask odors and freshen up the home, but they often contain phthalates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These chemicals can interfere with hormone regulation and worsen indoor air quality. Studies have found that VOCs can contribute to respiratory irritation and even trigger asthma attacks in sensitive individuals. A report by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that exposure to common air fresheners could lead to increased levels of indoor air pollution and higher rates of respiratory problems, particularly in children (NIH, 2019).
-
Plastic Food Containers
Plastic containers, especially those made with BPA (bisphenol A), can leach harmful chemicals into food when exposed to heat. BPA is known to disrupt hormones and negatively impact digestion. When plastic containers are used to store food, especially when they are microwaved, the heat causes BPA to seep into the food, increasing the risk of digestive and metabolic issues. Recent studies have highlighted the dangers of BPA exposure, linking it to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2020).
-
Cleaning Sprays
Many cleaning sprays contain ammonia, bleach, or strong synthetic fragrances. While they may seem effective at keeping surfaces clean, frequent use of these chemicals can irritate the lungs and increase the risk of chronic inflammation. Long-term exposure to ammonia and bleach fumes has been linked to respiratory issues such as bronchitis and asthma. According to the American Lung Association, cleaning products containing VOCs can significantly degrade indoor air quality, exacerbating existing respiratory conditions (American Lung Association, 2021).
-
Fabric Softeners
Fabric softeners are commonly used to make clothes feel softer and smell better, but they often contain quaternary ammonium compounds (quats) and artificial scents that can trigger asthma, skin irritation, and respiratory inflammation. The chemicals in fabric softeners may also contribute to indoor air pollution, particularly when the scent lingers in the fabric. Inhaling these substances over time can lead to chronic respiratory conditions, making it essential to choose natural alternatives when possible.
-
Microwave Popcorn Bags
The lining of microwave popcorn bags often contains PFAS, which are chemicals that break down into toxic compounds when heated. These compounds can be harmful when ingested, and studies have shown that they can accumulate in the body, leading to long-term health risks such as kidney disease, liver damage, and increased cancer risk. A study published in Environmental Science & Technology found that consuming microwave popcorn regularly could lead to significant PFAS exposure (Environmental Science & Technology, 2020).
-
Antibacterial Soaps
Many antibacterial soaps contain triclosan and similar chemicals that can disturb the microbiome and weaken the skin's natural defenses. Research has shown that triclosan can interfere with hormone regulation, particularly thyroid hormones, and may contribute to antibiotic resistance. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has even issued warnings about the potential dangers of antibacterial soaps, advising consumers to avoid products containing triclosan (FDA, 2016).
-
Synthetic Pillows & Mattresses
Synthetic pillows and mattresses often contain chemicals like formaldehyde and flame retardants, which can off-gas into the air. These chemicals can affect sleep quality, breathing, and long-term health. Studies have shown that exposure to flame retardants can disrupt hormone levels and lead to respiratory problems, particularly during sleep. The use of synthetic materials in bedding has also been linked to allergic reactions and skin irritation. Opting for organic, chemical-free bedding materials can significantly reduce exposure to these harmful substances.
In conclusion, while many of these household items are widely used and often seen as harmless, they can pose significant health risks over time. By being more mindful of the products we use in our homes and making informed choices, we can reduce our exposure to these harmful chemicals and create a safer, healthier living environment. Consider replacing some of these everyday products with safer, eco-friendly alternatives to protect both your health and the environment.
Sources:
-
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 2020. "Indoor Air Quality."
-
American Lung Association, 2022. "The Health Effects of Scented Candles."
-
Environmental Health Perspectives, 2018. "The Impact of PFAS Chemicals in Teflon Cookware."
-
Alzheimer's Society, 2021. "The Link Between Aluminum and Alzheimer's Disease."
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH), 2019. "The Dangers of Air Fresheners."
-
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2020. "Plastic Containers and BPA."
-
American Lung Association, 2021. "The Effects of Household Cleaning Products on Respiratory Health."
-
Environmental Science & Technology, 2020. "Microwave Popcorn and PFAS Exposure."
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 2016. "Antibacterial Soap: FDA's Final Rule."
News in the same category

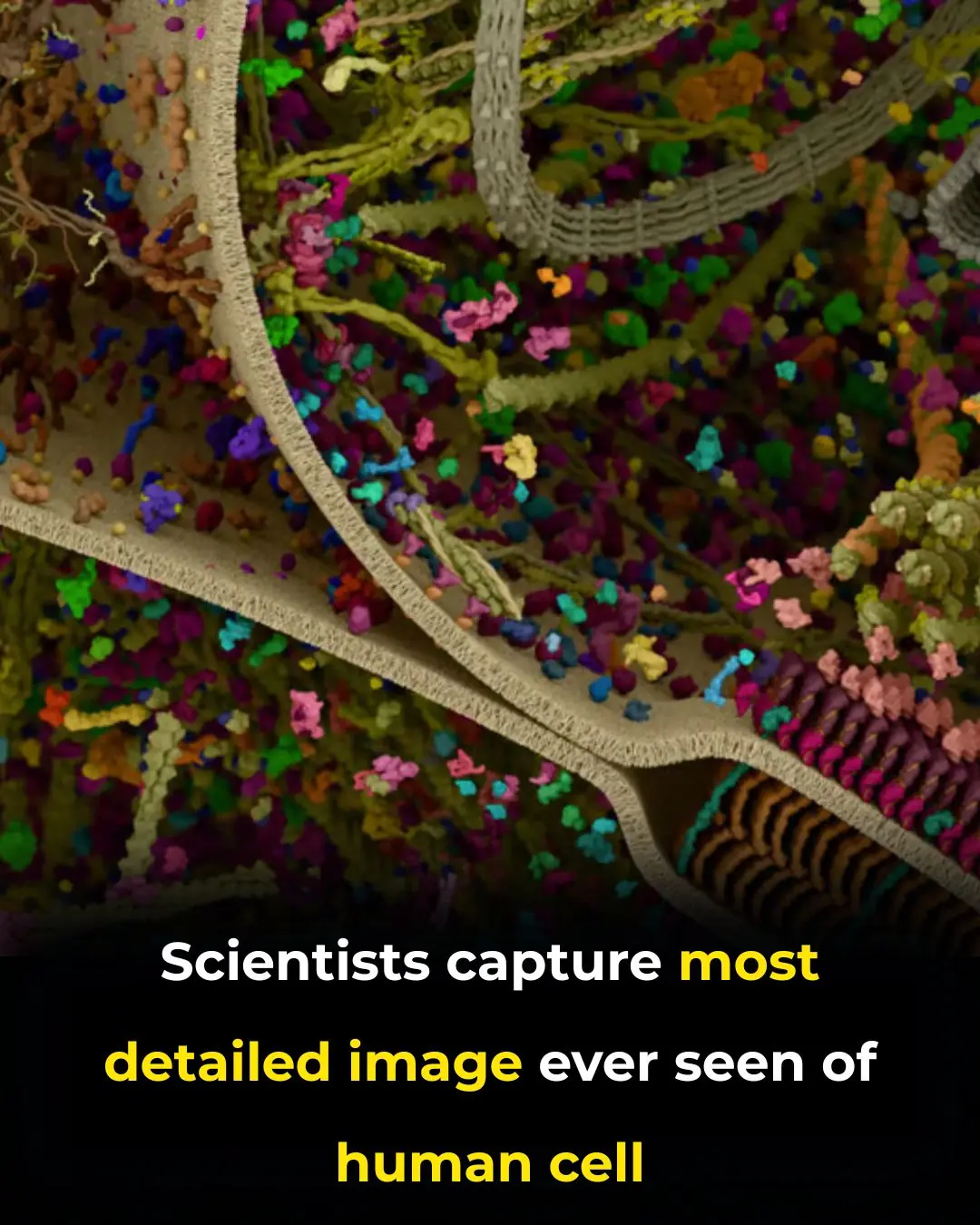
Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Capture the Most Detailed 3D Image of a Human Cell

12 Probiotic Foods That Heal

Connecting Consumers to Farmers: The Trend of Personalized Food Packaging in Japan

Experience the Journey of a Lifetime: Ride Across America for Just $213 with Amtrak

Magpie The Spiritual Meaning of an Unusual Encounter

Humanity’s Farthest Traveler Still Hasn’t Reached One Light-Year

The Vaquita: Earth's Most Endangered Marine Mammal Fights for Survival

AI Drones Are Rebuilding Australia’s Forests, One Seed Pod at a Time
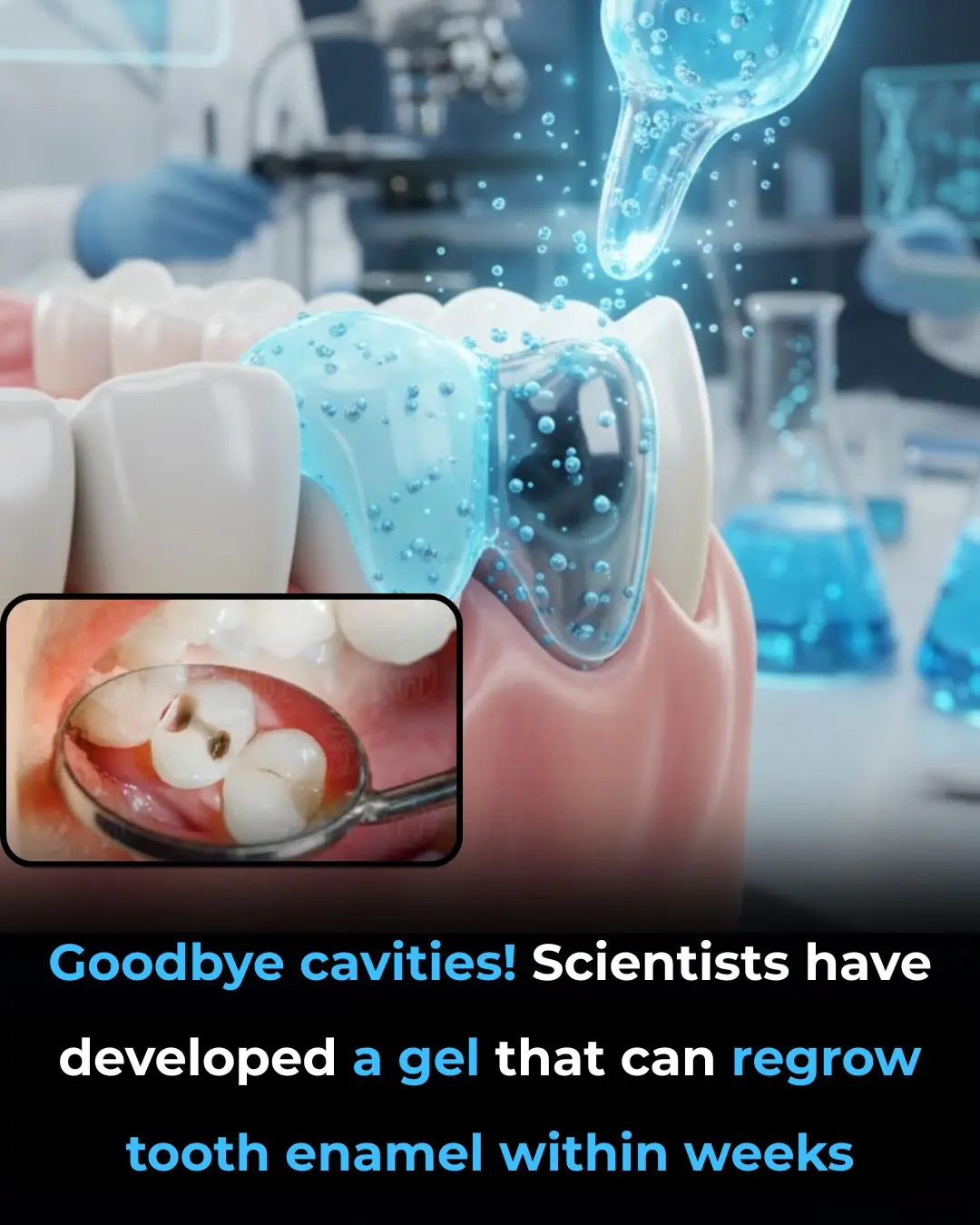
A World Without Cavities? Scientists Have Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel!

Bamboo and Hemp: The Future of Sustainability

The “Anti-AI Mask” Is Not What It Claims – Here’s What It Actually Does

Chuck Feeney: The Billionaire Who Gave It All Away Before He Died

How to React If You Get Bit by This Bug

China’s Giant Inflatable Dome Redefines Urban Construction and Environmental Protection in Jina
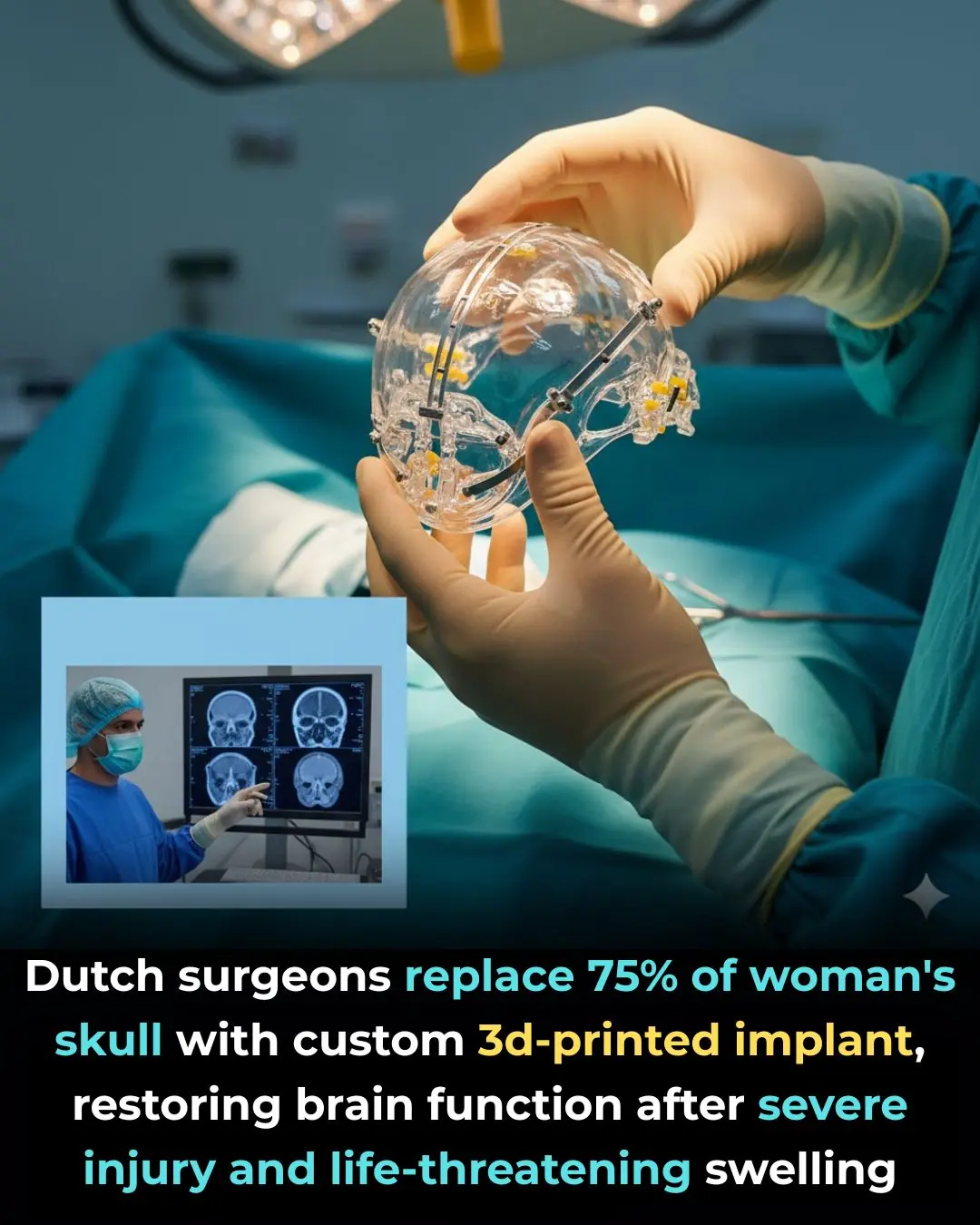
Groundbreaking Surgery in the Netherlands Uses 3D-Printed Implant to Save Woman's Life After Traumatic Brain Injury
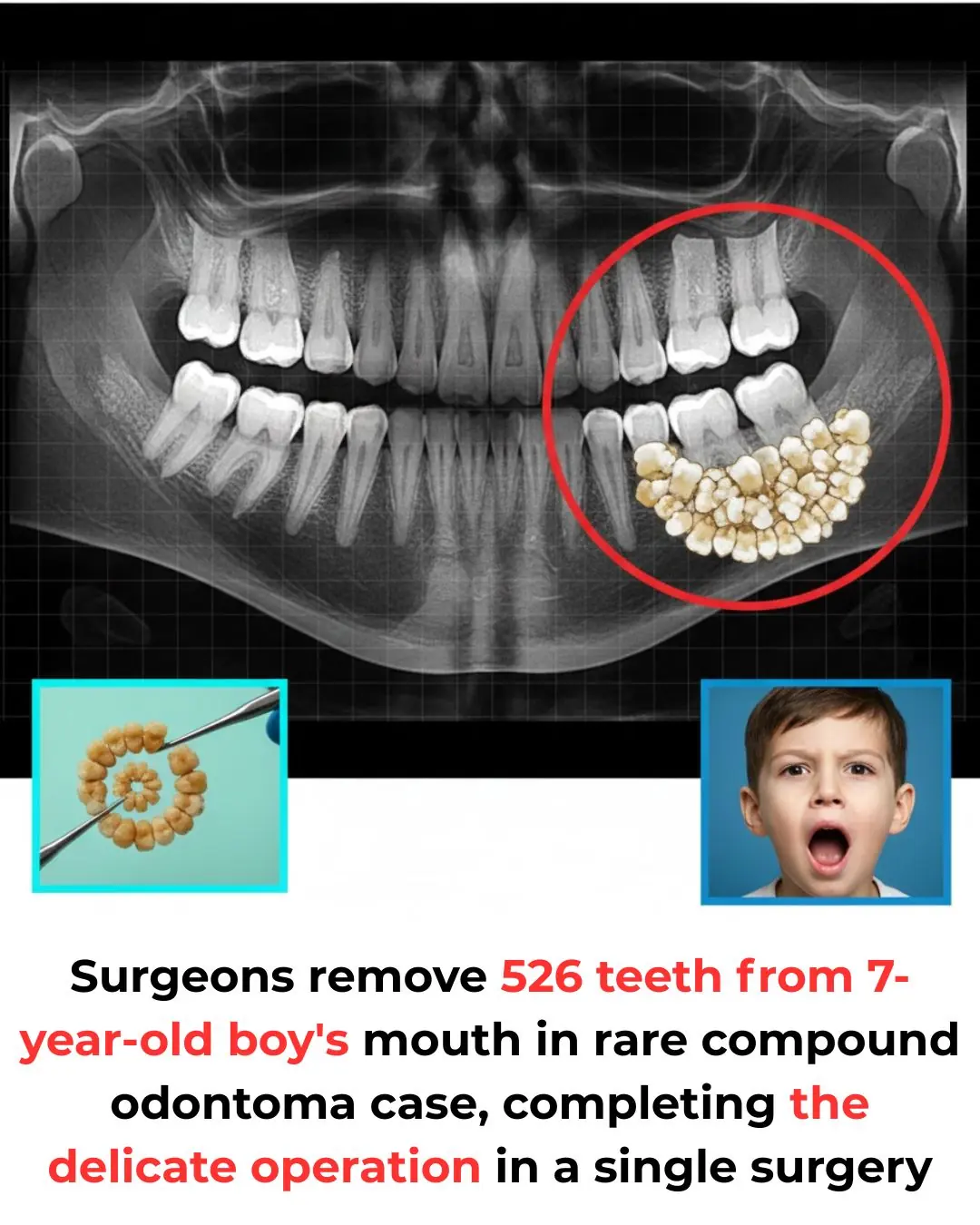
Seven-Year-Old Boy in India Undergoes Surgery to Remove Rare Jaw Tumor Containing 526 Tiny Teeth

Innovative Heliostat Mirrors Bring Sunlight to Norwegian Towns Amid Winter Darkness

MIT Physicists Perfect the Double-Slit Experiment, Confirming Quantum Theory
News Post

The Hidden Power: How Green Papaya Sap Soothes Cracked Heels and Boosts Digestion

Anise Seeds: 8 Remarkable Benefits for Women – When Science Meets Ancient Tradition

Two Tablespoons in the Morning: The Power of Magnesium Chloride

Warning Signs of an Overworked Liver—and the Top Herbs to Help Restore Its Function

Drink Just 1 Glass Before Bed to Cleanse Your Entire Colon in 10 Minutes

New Research Shows Beta Blockers May Raise Heart Failure Risk in Women With Hypertension

The Power of Clove Steam Inhalation (Respiratory Relief You Can Feel Immediately)

13 Science-Backed Benefits of Drinking Lemon Water Daily

Doctors Reveal What Eating Cauliflower Really Does to Your Body — And Why You Shouldn’t Ignore It

Spray This 3-Ingredient Oil On Your Feet 10 Minutes Before Bed And You’ll Be Dozing Off In No Time!

Sniffing Rosemary Can Increase Memory by 75%

The 60-second trick to reset your nervous system

Cleanse Your Kidneys of Toxins With 2 Effective 1-Ingredient Drinks

The unexpected connection between morning blood flow and a stronger heart

Nikola Tesla X-Rayed His Own Foot in 1896 — Pioneering the Future of Medical Imaging

Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Capture the Most Detailed 3D Image of a Human Cell

7 gentle balance moves seniors are using to feel steadier on their feet

12 Probiotic Foods That Heal

Connecting Consumers to Farmers: The Trend of Personalized Food Packaging in Japan
