
12 Probiotic Foods That Heal
12 Probiotic Foods That Heal: A Guide to Boosting Your Gut Health
Probiotics are live microorganisms that offer a variety of health benefits, particularly for our gut health. These beneficial bacteria help balance the gut microbiome, improve digestion, and support immune function. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can play a vital role in maintaining digestive health, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall well-being. Here are 12 probiotic foods that not only enhance your gut flora but also offer a range of healing benefits.
-
Yogurt (with live cultures)
Yogurt is one of the most well-known sources of probiotics. The live bacterial cultures in yogurt, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, help restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut. Consuming yogurt regularly can reduce bloating, improve digestion, and enhance the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. It has been shown to support the immune system and even alleviate symptoms of lactose intolerance (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2021). For maximum benefits, choose unsweetened yogurt with live and active cultures. -
Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential health benefits. This drink is rich in probiotics, particularly beneficial for replenishing gut flora. Additionally, kombucha is known for supporting liver detoxification and boosting energy levels due to its high content of antioxidants and organic acids. Research suggests that kombucha can also reduce inflammation and improve digestion (National Institutes of Health, 2020). It is a refreshing way to introduce probiotics into your diet while also reaping the benefits of natural detoxification. -
Fermented Pickles (not vinegar pickles)
Unlike commercially pickled vegetables that are preserved with vinegar, fermented pickles are made through natural fermentation, which helps cultivate beneficial bacteria. These pickles provide probiotics that contribute to a healthy gut by reducing bloating and stabilizing gut pH levels. They also support digestive health and help in balancing the microbiome. Studies have shown that fermented foods like pickles can improve the body's ability to digest food and absorb nutrients (University of California, 2021). -
Kefir
Kefir is a fermented milk drink that contains up to three times more probiotic strains than yogurt. It is a potent source of beneficial bacteria that support immunity, aid in digestion, and promote skin health. Kefir is also a good option for those who are lactose intolerant, as its probiotics help break down lactose, making it easier to digest. In addition to its digestive benefits, kefir contains vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall well-being, including calcium, magnesium, and B vitamins (Cleveland Clinic, 2021). -
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is a fermented cabbage dish that is rich in probiotics. This food is known for its ability to heal the gut lining, reduce inflammation, and promote better nutrient absorption. The beneficial bacteria in sauerkraut can also support immune function and aid in the treatment of digestive disorders such as IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome). The fiber content in sauerkraut further supports digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2021). -
Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean fermented food made from vegetables, especially napa cabbage and radishes, flavored with chili pepper, garlic, and other spices. It is an excellent source of Lactobacillus, a type of probiotic that supports healthy digestion, improves metabolism, and reduces markers of inflammation. Kimchi has been found to support immune function and may even have anticancer properties due to its high levels of antioxidants and bioactive compounds (Journal of Food Science, 2020). -
Natto
Natto is a Japanese fermented soybean product known for its potent health benefits. It is a rich source of vitamin K2, which plays an essential role in bone health, heart health, and supporting proper blood circulation. The probiotics in natto, specifically Bacillus subtilis, contribute to the balance of gut bacteria, enhancing digestion and gut health. Regular consumption of natto can improve bone density and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (Nutritional Research Reviews, 2018). -
Buttermilk (cultured)
Buttermilk, particularly cultured buttermilk, is gentle on the stomach and provides a rich source of probiotics that help restore good bacteria after illness or antibiotic use. This fermented dairy product can alleviate digestive issues such as bloating, indigestion, and constipation. In addition to its probiotic content, buttermilk is also an excellent source of vitamins such as B12 and riboflavin, which are important for overall health and energy (Cleveland Clinic, 2020). -
Miso
Miso is a fermented soybean paste commonly used in Japanese cuisine. It contains live probiotics that help support gut health, hormone balance, and immune function. The fermentation process also makes miso a great source of natural enzymes that aid in digestion. Miso’s ability to repair the gut lining and improve nutrient absorption is particularly beneficial for individuals with digestive disorders. Studies have also shown that miso may help prevent certain types of cancer due to its high levels of antioxidants (Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 2019). -
Tempeh
Tempeh is a fermented soybean product that provides a natural source of plant-based protein and beneficial bacteria for gut health. It contains probiotics that help strengthen the gut microbiome and support digestion. Tempeh is also rich in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium, making it a great option for vegetarians and vegans. The fermentation process also enhances the digestibility of tempeh, making it easier for the body to absorb essential nutrients (The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2020). -
Fermented Coconut Yogurt
For those who are dairy-free, fermented coconut yogurt is an excellent alternative. This yogurt is made by fermenting coconut milk with probiotic cultures, providing similar benefits to traditional dairy yogurt. It helps heal the gut, reduces inflammation, and supports skin clarity. Coconut yogurt is also rich in healthy fats, which support heart health and improve brain function. It is an ideal choice for individuals with lactose intolerance or those following a plant-based diet (Cleveland Clinic, 2021). -
Sourdough Bread
Sourdough bread is made from naturally fermented dough, which makes the gluten in the bread easier to digest. The fermentation process helps break down phytic acid, improving the absorption of minerals such as calcium, iron, and zinc. Sourdough is also beneficial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, as it contains probiotics that support digestion. Studies have shown that regular consumption of sourdough can improve gut health and reduce bloating and discomfort associated with gluten sensitivity (Journal of Food Science, 2020).
Conclusion
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can offer numerous health benefits, particularly for your digestive system and overall well-being. From improving gut health to boosting immunity and reducing inflammation, these foods provide a natural way to support your body’s microbiome. By adding a variety of these fermented foods to your meals, you can promote a healthier gut, improve digestion, and support long-term health.
Sources:
-
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, 2021. "The Benefits of Probiotics."
-
Cleveland Clinic, 2021. "Kefir: A Probiotic-Rich Drink."
-
National Institutes of Health, 2020. "Kombucha and Its Health Benefits."
-
Journal of Food Science, 2020. "Kimchi and Its Impact on Gut Health."
-
Nutritional Research Reviews, 2018. "The Benefits of Natto and Vitamin K2."
News in the same category

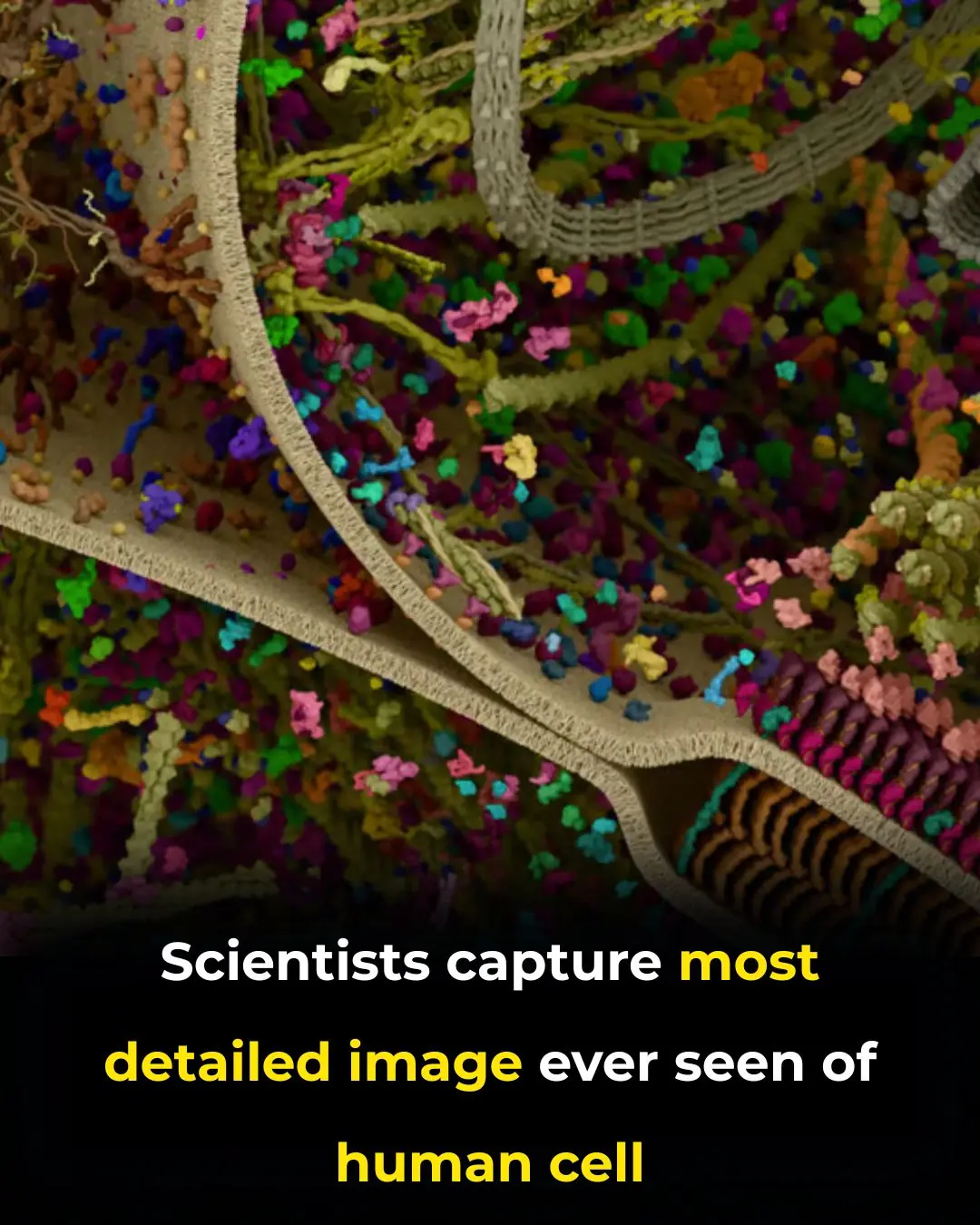
Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Capture the Most Detailed 3D Image of a Human Cell

Connecting Consumers to Farmers: The Trend of Personalized Food Packaging in Japan

Experience the Journey of a Lifetime: Ride Across America for Just $213 with Amtrak

12 Common Household Items That Are Slowly Killing Us

Magpie The Spiritual Meaning of an Unusual Encounter

Humanity’s Farthest Traveler Still Hasn’t Reached One Light-Year

The Vaquita: Earth's Most Endangered Marine Mammal Fights for Survival

AI Drones Are Rebuilding Australia’s Forests, One Seed Pod at a Time
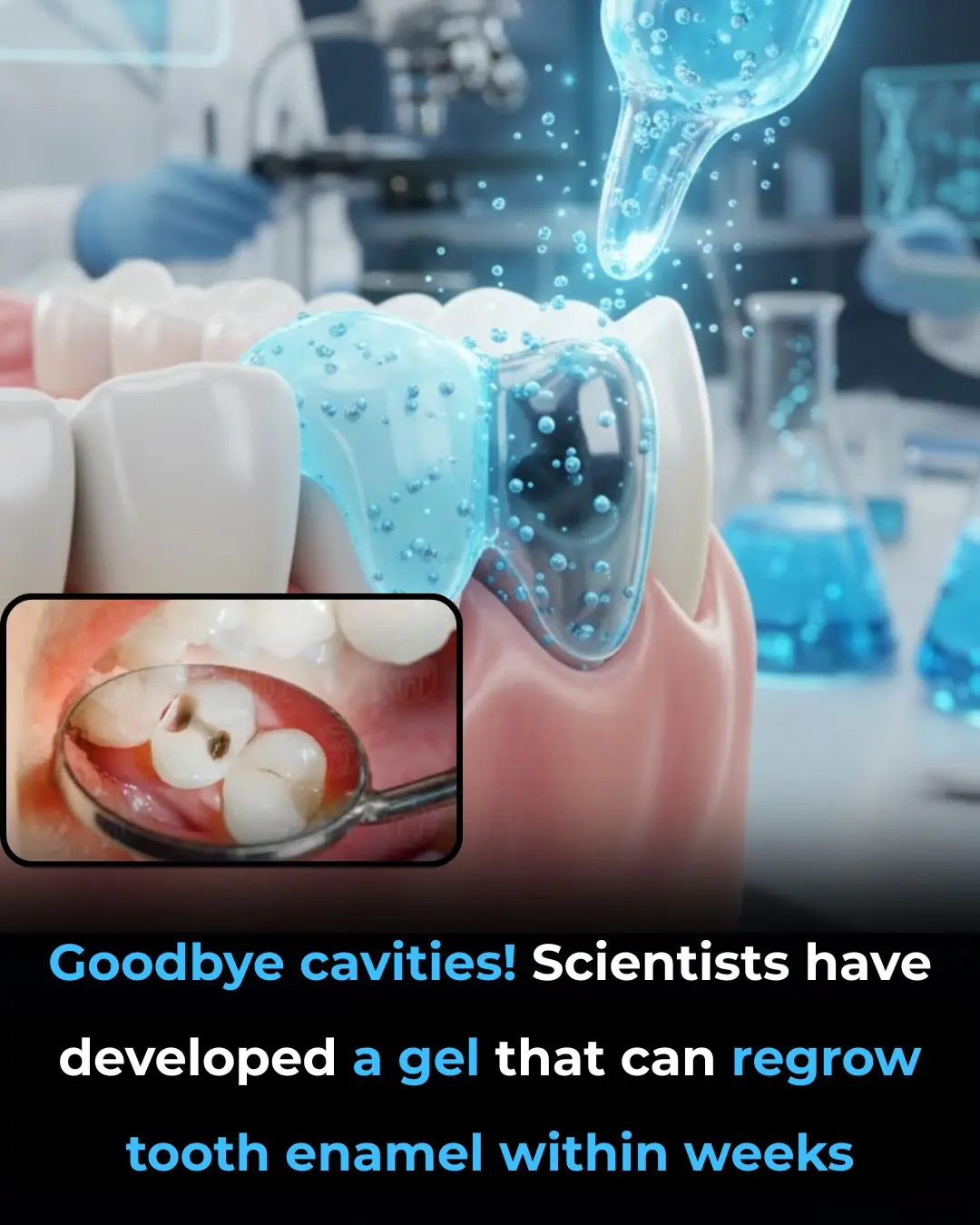
A World Without Cavities? Scientists Have Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel!

Bamboo and Hemp: The Future of Sustainability

The “Anti-AI Mask” Is Not What It Claims – Here’s What It Actually Does

Chuck Feeney: The Billionaire Who Gave It All Away Before He Died

How to React If You Get Bit by This Bug

China’s Giant Inflatable Dome Redefines Urban Construction and Environmental Protection in Jina
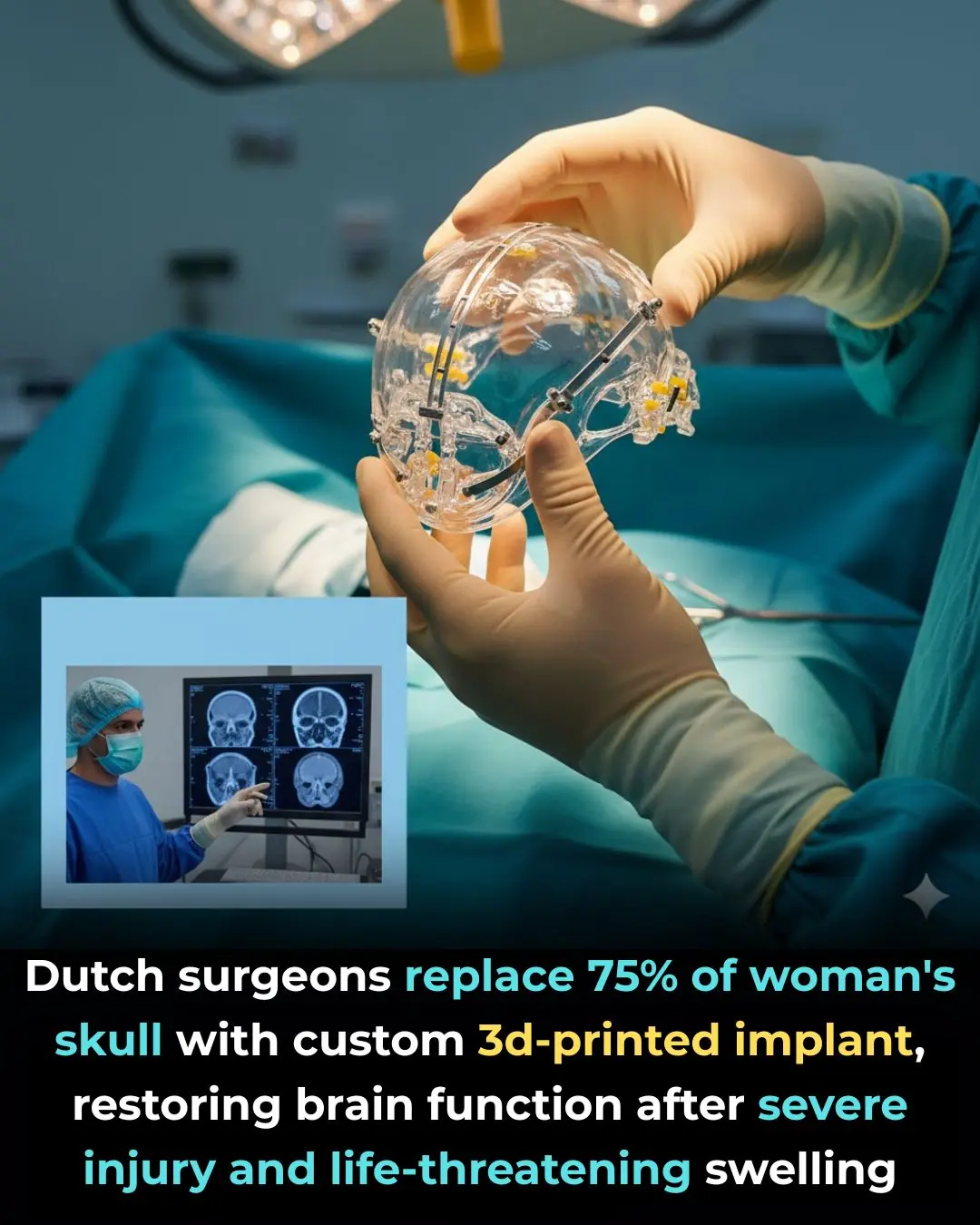
Groundbreaking Surgery in the Netherlands Uses 3D-Printed Implant to Save Woman's Life After Traumatic Brain Injury
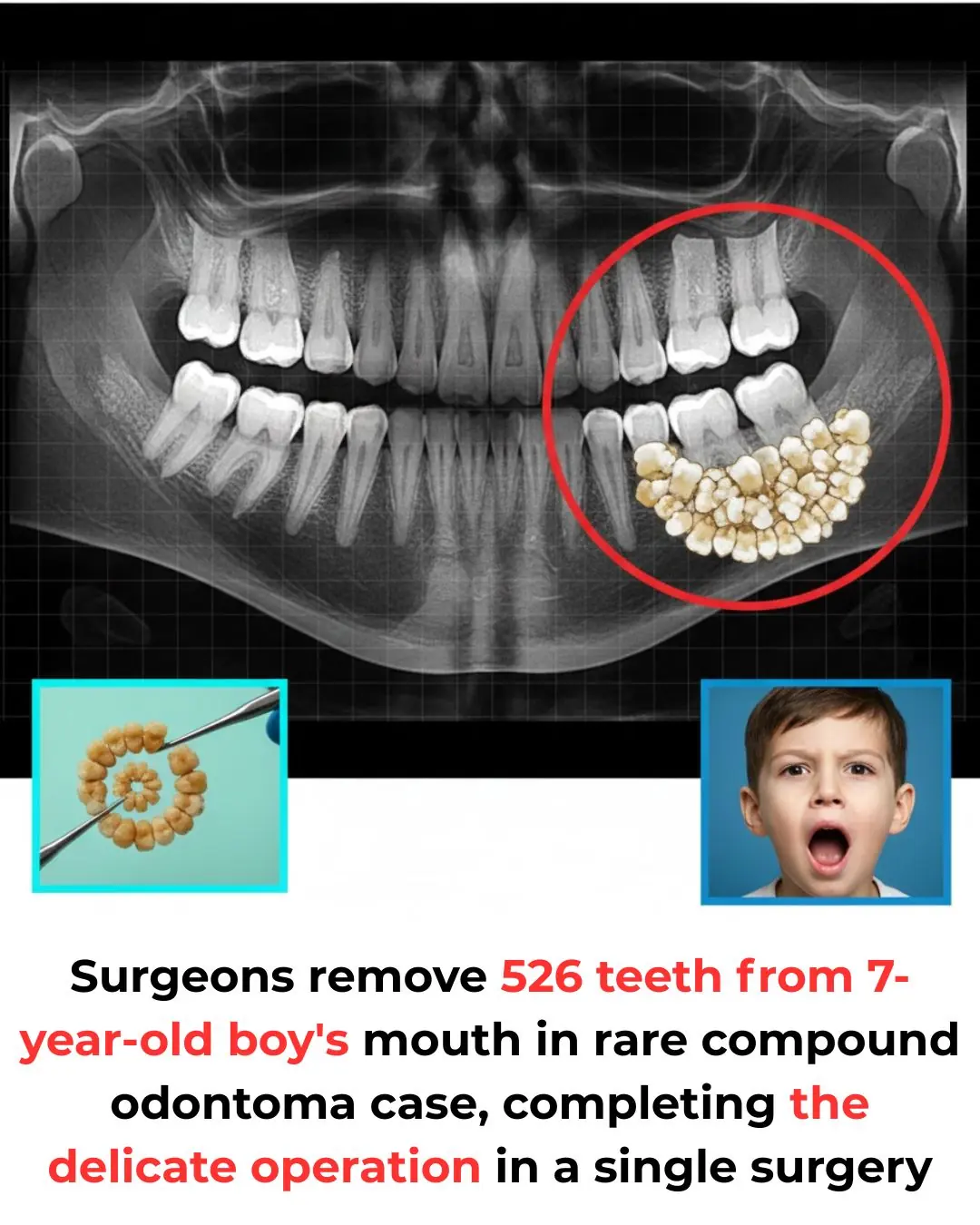
Seven-Year-Old Boy in India Undergoes Surgery to Remove Rare Jaw Tumor Containing 526 Tiny Teeth

Innovative Heliostat Mirrors Bring Sunlight to Norwegian Towns Amid Winter Darkness

MIT Physicists Perfect the Double-Slit Experiment, Confirming Quantum Theory
News Post

The Hidden Power: How Green Papaya Sap Soothes Cracked Heels and Boosts Digestion

Anise Seeds: 8 Remarkable Benefits for Women – When Science Meets Ancient Tradition

Two Tablespoons in the Morning: The Power of Magnesium Chloride

Warning Signs of an Overworked Liver—and the Top Herbs to Help Restore Its Function

Drink Just 1 Glass Before Bed to Cleanse Your Entire Colon in 10 Minutes

New Research Shows Beta Blockers May Raise Heart Failure Risk in Women With Hypertension

The Power of Clove Steam Inhalation (Respiratory Relief You Can Feel Immediately)

13 Science-Backed Benefits of Drinking Lemon Water Daily

Doctors Reveal What Eating Cauliflower Really Does to Your Body — And Why You Shouldn’t Ignore It

Spray This 3-Ingredient Oil On Your Feet 10 Minutes Before Bed And You’ll Be Dozing Off In No Time!

Sniffing Rosemary Can Increase Memory by 75%

The 60-second trick to reset your nervous system

Cleanse Your Kidneys of Toxins With 2 Effective 1-Ingredient Drinks

The unexpected connection between morning blood flow and a stronger heart

Nikola Tesla X-Rayed His Own Foot in 1896 — Pioneering the Future of Medical Imaging

Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Capture the Most Detailed 3D Image of a Human Cell

7 gentle balance moves seniors are using to feel steadier on their feet

Connecting Consumers to Farmers: The Trend of Personalized Food Packaging in Japan
