Leftovers may seem harmless, but in some cases, they can turn into hidden health risks. A tragic case has recently drawn attention to how certain foods, when stored improperly or left too long, may lead to life-threatening consequences.
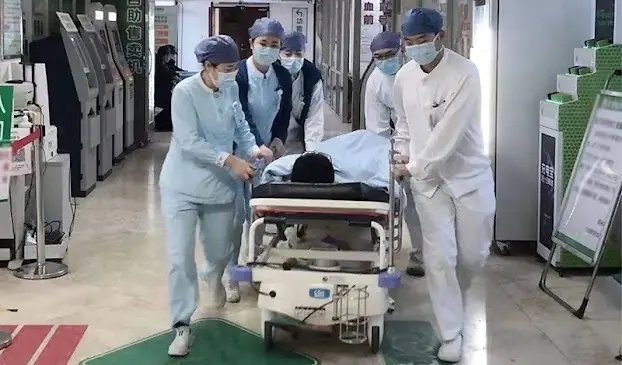
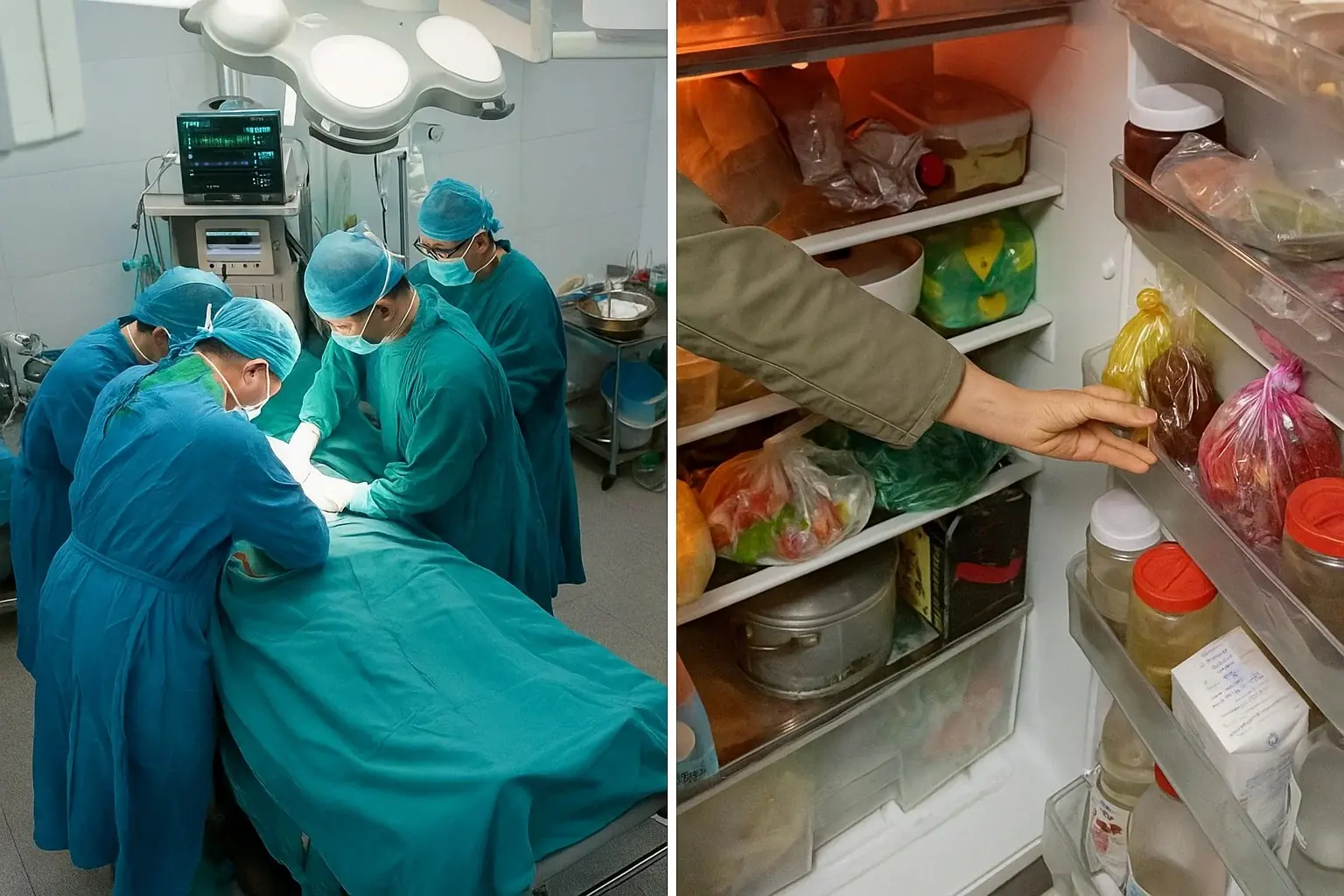
In China, a 50-year-old man was hospitalized after suffering severe diarrhea following the consumption of leftovers stored in his refrigerator. Despite being treated with IV fluids, he suddenly collapsed and was rushed to a higher-level hospital. Doctors attempted emergency resuscitation for nearly 40 minutes, but his heart stopped, and he did not survive.
Physicians later explained that the man likely developed acute enteritis after eating food that had been left for too long. The condition caused persistent diarrhea—over ten times in a single day—leading to dangerous electrolyte imbalances, severe metabolic acidosis, and hyperkalemia. These complications escalated quickly and ultimately proved fatal.
This case highlights that leftovers are not always safe, especially when kept beyond recommended storage times. In fact, certain foods are particularly risky to reheat and consume the next day.
What Science Says About Leftovers
Researchers at the Ningbo Institute of Food Safety conducted an experiment to better understand how leftovers change over time. They prepared 30 common household dishes—including meats, fish, vegetables, and mixed recipes—then stored them under two different conditions: refrigeration at 4°C and room temperature at 25°C.
The findings were eye-opening:
- Vegetables stored at 4°C for less than 6 hours showed little change in nitrite levels and minimal bacterial growth.
- Vegetables left at 25°C for more than 6 hours, however, experienced rapid bacterial proliferation, even if nitrite levels remained relatively stable.
In simple terms, food kept at safe refrigeration temperatures for no longer than 24 hours generally posed little danger. However, at room temperature or when stored improperly, harmful microorganisms could multiply quickly, raising the risk of foodborne illness.
The 5 Foods You Should Never Eat After Leaving Overnight
- Mushrooms and Wood Ear Fungus
These foods contain complex proteins that can become harmful to digestion once reheated after long storage. Mushrooms also naturally contain nitrates, which can convert into toxic nitrites if left for too long. Even when grown in controlled conditions, they degrade quickly. Experts recommend eating mushroom dishes the same day they are cooked.
- Leafy Green Vegetables
Spinach, bok choy, lettuce, and other leafy greens have naturally high nitrate content. When left overnight at room temperature, these nitrates can transform into nitrites, while vitamins and minerals are also lost. Eating reheated leafy greens regularly may place stress on the digestive system and should be avoided.
- Soy-Based Foods
Products like tofu, soy milk, and bean curd are rich in protein, making them fertile ground for bacterial growth. If stored for too long, they are at risk of contamination with Clostridium botulinum, a dangerous bacterium that can cause neurological damage. To stay safe, these should be consumed fresh and not reheated after prolonged storage.
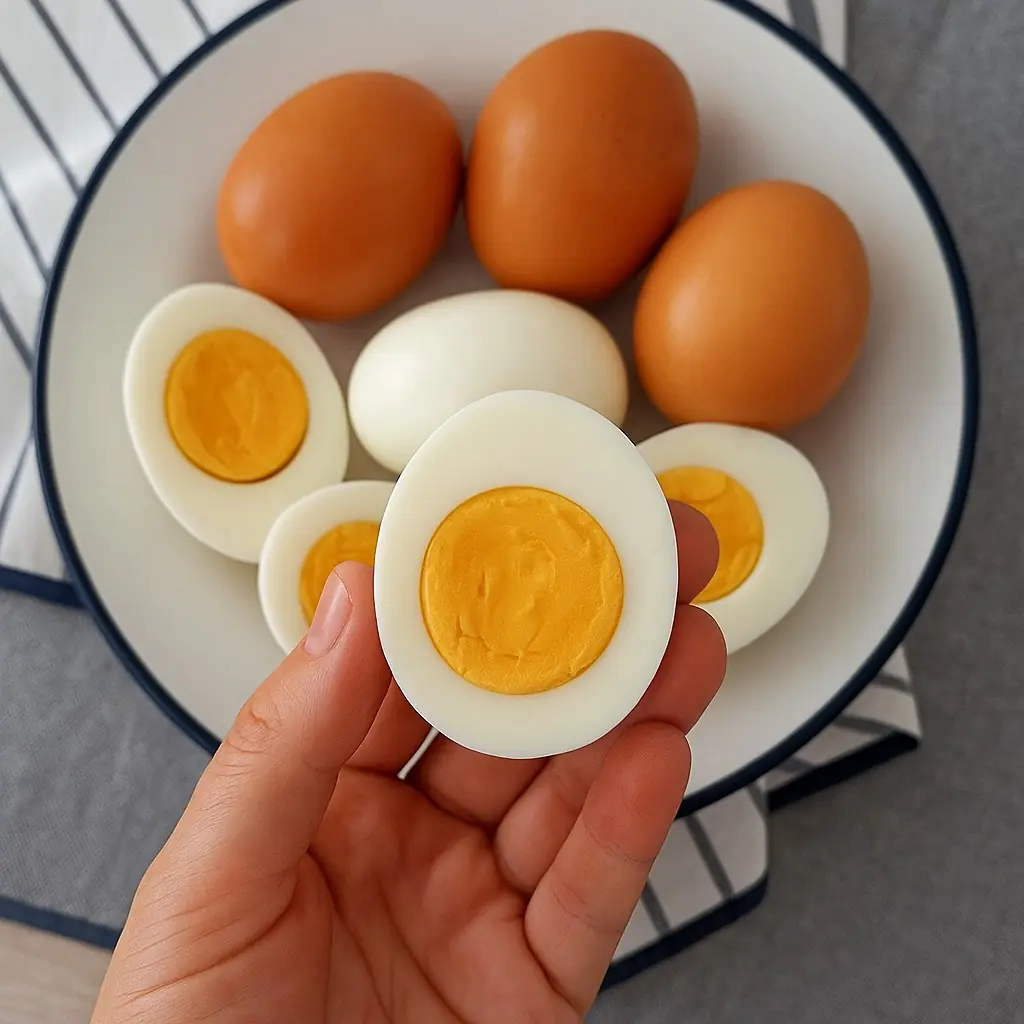
- Soft-Boiled or Half-Cooked Eggs
Eggs with partially cooked yolks are not fully sterilized. When left overnight, bacteria can multiply rapidly due to the nutrient-rich environment. This makes half-cooked eggs unsafe to reheat or eat the following day.
- Seafood
Fish, shrimp, clams, and other seafoods can harbor bacteria that survive cooking. Once refrigerated, these bacteria may regrow and produce protein breakdown products that can harm the liver and kidneys. For this reason, seafood should be eaten immediately after preparation rather than saved for later.
How to Store Leftovers Safely
If you must keep leftovers, follow these essential guidelines:
- Store food at low temperatures (around 4°C or below) as soon as possible.
- Use clean containers or wrap food tightly with plastic film to reduce contamination.
- Consume leftovers within 24 hours—beyond that, risks increase sharply.
- Reheat thoroughly before eating, ensuring food reaches safe internal temperatures.
The Bottom Line
While not all leftovers are dangerous, certain foods—particularly mushrooms, leafy greens, soy-based products, soft-cooked eggs, and seafood—carry higher risks if eaten after long storage. To protect yourself and your family, it’s better to cook smaller portions, eat fresh, and throw away what cannot be finished safely.
When it comes to health, the old saying applies perfectly: “Better safe than sorry.”