
7 best foods to rebuild your muscle strength after 50
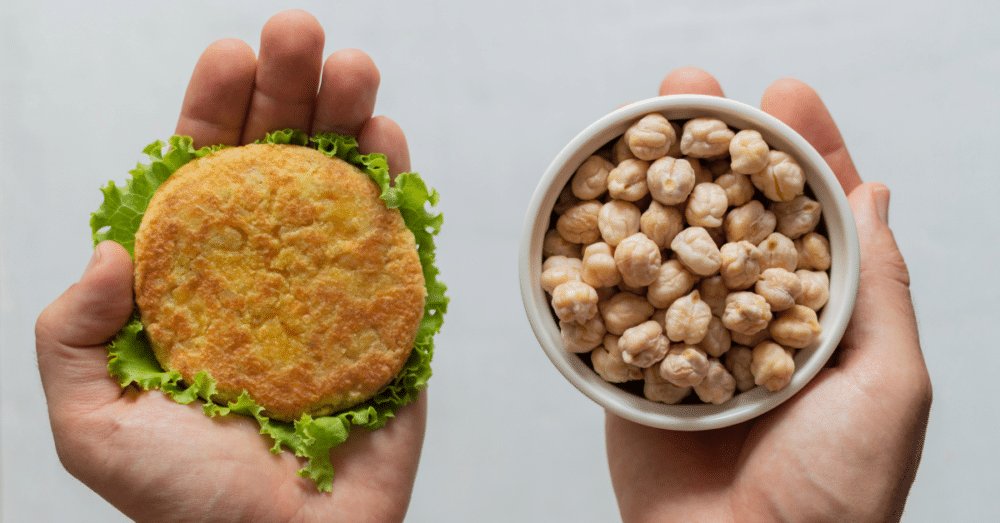

Have you been feeling that your strength just isn’t what it used to be? Perhaps carrying groceries feels heavier, or climbing stairs requires more effort than before. This gradual decline is often the result of sarcopenia—age-related muscle loss that commonly begins after the age of 50. While it’s a natural physiological change, it’s not an inevitable decline you must simply accept. In fact, with the right nutrition and daily habits, you can significantly slow down muscle deterioration and in many cases even rebuild the strength you thought was gone for good.
Yet the modern food industry has turned “protein” into a profitable marketing slogan. Shelves are lined with bars, shakes, and powders that claim to boost muscle, but many of these products are so heavily processed that they may create more inflammation than rebuilding. That’s exactly why today we’re going to cut through the confusion and highlight seven powerful whole foods that actually support muscular regeneration. Even better, I’ll explain how to prepare them properly so your body can absorb the maximum benefits.
(Inspired by the expertise of Dr. Iñigo Martín.)
Key Takeaways
Prioritize Whole Foods
Real strength comes from nutrient-dense, unprocessed foods—not overpriced protein bars or artificial shakes filled with additives that stress your digestive system.
Complete Proteins Matter
Foods like quinoa and tofu provide all nine essential amino acids necessary for repairing muscle tissue, giving them an advantage over many traditional grains.
Choose Smart Carbohydrates
Sweet potatoes, oats, and similar foods provide a slow and steady release of energy, supplying your muscles with consistent fuel without blood-sugar spikes.
Don’t Ignore Minerals
Potassium, magnesium, iron, and manganese are essential for muscle contraction, relaxation, oxygen delivery, and energy production. Almonds, chickpeas, lentils, and greens are rich in these vital compounds.
Preparation Maximizes Nutrition
Simple habits like soaking grains, activating nuts, pressing tofu, and combining certain foods help neutralize anti-nutrients and unlock their full nutritional value.
The Billion-Dollar Trap: How Processed Proteins Slow You Down
Before we examine the foods that genuinely rebuild strength, it’s crucial to expose the trap many people unknowingly fall into. The food industry has transformed protein into a billion-dollar marketing concept, convincing you that you need “fast,” “convenient,” or “ready-to-drink” protein to stay strong. But what they rarely mention is that these ultra-processed products can impair your muscle recovery while draining your budget.
Protein Bars: Candy Bars in Disguise
Look at the ingredient list on most protein bars and you’ll notice something alarming: glucose syrup, fructose, maltodextrin—the very sugars responsible for insulin spikes and fat storage. You might think you’re fueling your muscles, but your body often reacts as if you’ve just eaten a candy bar. That rapid rise in insulin can temporarily shut down muscle-building pathways. No wonder so many people feel bloated, tired, or mentally foggy after eating one.
Processed Meats and “Healthy” Veggie Sausages
These products often contain staggering amounts of sodium—sometimes 400 mg in just a small serving. Too much sodium increases water retention, strains your cardiovascular system, and reduces nutrient delivery to muscle cells. Even worse are nitrites, preservatives that can convert into inflammatory nitrosamines during digestion. While occasional consumption isn’t dangerous, regular intake increases long-term gastrointestinal risk. The truth is, these products offer convenience, not nourishment.
Supermarket Protein Shakes: A Chemical Cocktail
Even when the main protein source is decent (soy, whey, or pea), many commercial shakes include artificial sweeteners, gums, thickeners, and synthetic flavorings. These substances often irritate the gut lining. When your gut is inflamed, nutrient absorption drops significantly. Symptoms like gas, stomach pain, or sudden fatigue after a shake are not normal—they’re a message from your body. A clean protein powder should contain one ingredient: the protein itself.
Instead of paying premium prices for packaged “protein,” you can make your own nutrient-dense energy balls with dates, almonds, seeds, and pure cocoa. They give you clean fuel, natural minerals, and real fiber at a fraction of the cost.
7. Quinoa: The Complete Plant-Based Protein
Quinoa is one of the rare plant foods that contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a true complete protein. Think of quinoa as a microscopic muscle-repair system. Each seed supplies the raw building blocks your muscles need to recover from daily wear—whether from walking, lifting, or simply maintaining posture throughout the day.
Unlike pasta or white rice, which primarily provide quick energy, quinoa simultaneously fuels and repairs. Its low glycemic index means it releases energy slowly over several hours, stabilizing both blood sugar and energy levels. Just half a cup at breakfast can help you avoid those mid-morning slumps that sap productivity.
How to Make It More Effective:
-
Rinse the grains for at least 30 seconds to remove bitter saponins.
-
Cook it in vegetable broth for richer flavor.
-
Mix with legumes like lentils or chickpeas for an even more complete amino acid profile.
This combination becomes a nutritional powerhouse that supports strong, resilient muscles.
6. Sweet Potato: The Intelligent, Long-Lasting Energy Source
If quinoa supplies the building materials, sweet potatoes provide the long-lasting fuel. Their slow-releasing carbohydrates give your body consistent energy without the crashes that come from refined grains. It’s the difference between driving on a full tank versus stopping for fuel every 30 minutes.
But the real secret lies in their mineral content.
Potassium: The Trigger for Muscle Contraction
A medium sweet potato offers more potassium than a banana. Potassium regulates each muscle contraction, and deficiency often leads to cramps, weakness, or fatigue.
Magnesium: The Relaxation Mineral
Paired with potassium, magnesium helps muscles relax properly after contracting. Without this balance, muscles become stiff, tight, or prone to spasms.
The carotenoids in sweet potatoes also act as antioxidants that protect muscle cells from oxidative stress. Think of them as microscopic shields preserving your strength.
Best Preparation:
Bake whole sweet potatoes at 400°F (200°C) for 45 minutes. Leave the skin on—it's loaded with fiber and minerals.
5. Chickpeas: The Budget-Friendly Muscle Builder
Chickpeas are one of the most economical sources of clean, high-quality protein. A single cup provides about 15 grams of protein and a wide spectrum of amino acids essential for repairing daily micro-tears in muscle fibers.
Every movement—walking, climbing stairs, lifting objects—creates tiny tears in your muscle tissue. This is normal, but without adequate protein and minerals, your body cannot rebuild these fibers stronger.
The Hidden Power of Manganese
Chickpeas are extremely rich in manganese, a mineral that activates enzymes responsible for converting nutrients into usable energy. Without manganese, protein synthesis slows dramatically—even if you’re eating enough protein.
Folate for Cellular Regeneration
Folate plays a key role in forming new cells, including muscle cells. Low folate can lead to slow recovery after workouts or physical exertion.
How to Prepare Them Properly:
-
Soak dried chickpeas with a pinch of baking soda to reduce gas and remove phytates.
-
Use them to make hummus, stews, salads, or homemade veggie patties.
They’re inexpensive, versatile, and remarkably effective for muscle support.
4. Lentils: The Muscle-Building Activation Switch
Lentils are one of the richest natural sources of leucine—the amino acid responsible for activating muscle protein synthesis. Leucine turns on the mTOR pathway, the biochemical switch that signals your body to start building new muscle tissue.
A cup of cooked lentils provides approximately 1.3 grams of leucine. To fully activate muscle growth, your body typically needs around 2.5 grams per meal. By pairing lentils with brown rice, quinoa, or a handful of nuts, you hit that threshold easily and naturally.
Why This Matters Daily
Add a cup of lentils to your lunch, and your body enters muscle-building mode for the next several hours. The combination of protein and fiber releases amino acids at a slow, steady pace, ensuring that your muscles receive what they need without spikes or crashes.
A Quiet Superpower: Iron
If you often feel tired even after a good night’s sleep, low iron may be playing a role. Lentils contain a high level of plant-based iron, and cooking them with tomatoes or lemon juice can triple absorption thanks to vitamin C.
Preparation Tip:
Soak dry lentils for four hours with a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar. This makes them easier to digest and increases mineral availability.
News in the same category


Stop counting calories — the “100g protein rule” people swear helps with energy and cravings

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

How to Detect and Eliminate Eyelash Mites (Demodex Mites)
1 simple move to cleanse your lymphatic system and revitalize heart, skin, and blood sugar
5 common habits that quietly damage your kidneys
The best way to lower blood pressure fast!

🌱 The Power of Chia Seeds: Tiny Superfoods with Massive Health Benefits
4 hidden signs of iodine deficiency in your skin, hair & nails

Crabgrass: The “Weed” That Could Be a Wellness Wonder
Fatty Liver Disease: A Growing Silent Health Concern – And How Turmeric May Support Liver Health
Foods and Lifestyle Choices That May Influence Cancer Risk

Drink one cup daily of this juice to UNCLOG arteries?

Don’t ignore your legs: the surprising early signs of pancreatic cancer

12 medications you should never mix with coffee

WARNING: This common pill causes dementia

This Is One Of The Most C.ancer-Causing Foods – Stop Eating It!

Improve Eyesight Naturally With Onion Tea: Benefits, Uses & How to Make It

Roll your feet daily—unlock rapid healing throughout your body!
News Post

You’re Doing It All Wrong: Here’s the Right Way to Warm Up a Cold Bed

How to Remove Stubborn Toilet Water Rings: Simple, Effective, and Science-Backed Solutions

They Just Opened Newark, New Jersey’s First Black-Owned Drive Thru Movie Theater To Celebrate Black Culture

You’re Doing It All Wrong: Here’s the Right Way to Drink 8 Glasses of Water a Day

Will Smith Shares Heartwarming Moment With 10th Grade Teacher at Street Renaming Ceremony

My nana taught me a hack to remove sticky jar labels in 1 minute with zero effort — here’s how it works

Meet the First Black Person to Receive a Doctorate in Computer Science at the University of Florida

Lizzo to Star as the Godmother of Rock & Roll In Upcoming Sister Rosetta Tharpe Biopic

Meet Pancho & Kristyn Patterson, the Father-Daughter Duo Renovating Detroit Homes on HGTV

DC Man Gifts Woman With Hair Salon After She Donates One Of Her Kidneys To Him

The Powerful Health Benefits of Papaya Seeds: Why You Should Include Them in Your Diet

Viola Davis Shares how Cicely Tyson Paved the Way for Her and Black Girl Magic in TV and Film

Morehouse College Makes History as First HBCU to Compete & Win National Boxing Tournament

7 Natural Remedies to Beat Constipation Fast — The Fig Trick You Shouldn’t Ignore

The Magic in Disney Dreamers Academy Isn’t Just in the Parks, It’s in the Representation

DHT Blocking Gel For Thick Hair Growth

Stop counting calories — the “100g protein rule” people swear helps with energy and cravings

This old school home remedy will soothe your back, joints & knee pain in just 7 days!

How to Detect and Eliminate Eyelash Mites (Demodex Mites)
