
80% of Heart Attacks Are Preventable: Embrace These 5 Simple Habits
80% of Heart Attacks Are Preventable: Embrace These 5 Simple Habits
Heart attacks remain the leading cause of death in the United States, a startling statistic given that most are largely preventable. While some individuals experience symptoms of heart disease before a cardiac event, others have no warning signs until their first heart attack strikes. The remarkable truth is that nearly 80% of heart attacks could be avoided by adopting just a few straightforward lifestyle changes.

Understanding Heart Attack: Causes and Warning Signs
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, most commonly due to the narrowing of coronary arteries from plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), a condition known as coronary artery disease. Less common causes include spasms of a coronary artery (often linked to tobacco or illicit drug use) or a tear in the artery wall (spontaneous coronary artery dissection).
While the classic signs like crushing chest pain or sudden shooting pain in the left arm are widely recognized, it's crucial to be aware of other subtle indicators of heart trouble, which can be easily overlooked.
The Overlooked Heart Risk: The Impact of Sugar
Before diving into the five proven habits, it's essential to highlight a powerful yet frequently underestimated factor in heart disease: sugar.
Recent research unequivocally demonstrates that high sugar consumption directly contributes to heart disease, even in individuals who otherwise appear healthy:
-
A 2014 study in JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who consumed 25% or more of their daily calories from added sugar were over twice as likely to die from heart disease compared to those who kept sugar intake below 10%.
-
A comprehensive 2023 review in the British Medical Journal confirmed a significant association between added sugar and increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and metabolic disorders.
-
The American Heart Association (AHA) explicitly warns that excess sugar, especially from sugary drinks, elevates triglyceride levels, lowers "good" HDL cholesterol, and promotes inflammation—all factors that damage the cardiovascular system.
The bottom line? Reducing your intake of added sugars is one of the simplest and most impactful steps you can take to safeguard your heart.
5 Lifestyle Changes to Drastically Reduce Heart Attack Risk
A landmark 11-year study from Sweden's Karolinska Institute, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology in 2014, identified five powerful lifestyle factors that collectively reduced the risk of heart attack by a remarkable 79% (1):
-
A Healthy Diet: Emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods.
-
No Smoking: Complete abstinence from tobacco products.
-
Physical Activity: Engaging in brisk walking/bicycling for more than 40 minutes daily AND exercising for more than 1 hour per week.
-
Healthy Waist Circumference: Maintaining a waist circumference of less than 95 cm (approximately 37.4 inches).
-
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake to specific recommended levels.
These findings are corroborated by earlier research from 2004, published in the British Journal Lancet, which examined individuals from over 50 countries. This study found similar results, additionally highlighting the importance of managing diabetes and psycho-social factors, collectively accounting for a 90% reduced risk in men and 94% in women (2).
The consistent message from both recent and older research is clear: our lifestyle choices play an enormous role in determining our risk of heart problems. By making a few simple—though sometimes challenging—changes, the risk of a heart attack can be reduced by 79-90%.

Actionable Steps to Boost Your Heart Health:
Here are concrete ways to incorporate these heart-protective habits into your life:
-
Embrace Healthy Eating: A heart-conscious diet is paramount. Focus on:
-
High Fiber: From fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Low Trans Fat: Avoid processed and fried foods.
-
Lean Protein: Choose poultry, fish, or plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds.
-
Healthy Fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, and seeds.
-
Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
-
-
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: The Swedish study specifically noted a reduced heart attack risk for those consuming 10-30 grams of alcohol per day. However, the American Heart Association provides more conservative guidelines: no more than two drinks per day for men and no more than one drink per day for women. (One drink is typically defined as 1.5 fl oz of 80-proof spirits, 5 fl oz of wine, or 12 fl oz of regular beer.) Excessive alcohol intake can elevate blood pressure and triglyceride levels, and contribute to weight gain.
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a severe detriment to heart health, alongside its well-known damage to the lungs. Quitting cigarettes is one of the most impactful steps you can take for your cardiovascular system. Seek support or explore natural remedies to aid your journey to a smoke-free life.
-
Tackle Belly Fat: Both studies underscored "abdominal adiposity"—belly fat, particularly visceral fat (fat around internal organs)—as a significant contributor to heart attack risk. Visceral fat can be deadly, regardless of whether it feels solid or soft. Aim for a waist circumference smaller than 95 cm (approx. 37.4 inches). Focus on reducing visceral fat by making dietary changes (e.g., avoiding certain processed foods and incorporating belly-fat-burning foods) and increasing physical activity.
-
Get Physically Active: Regular exercise is critical for robust heart health. The studies advocate for at least 40 minutes of walking/bicycling daily and over an hour of more vigorous exercise per week. The National Heart, Blood, and Lung Institute recommends at least 2 hours and 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (like brisk walking) or 1 hour and 15 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise per week. The more active you are, the greater the benefits for your heart and overall well-being.
Additional Factors for Heart Protection:
-
Manage Stress: Chronic and acute stress negatively impact heart health. The AHA notes a link between stress and increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Learn stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, regular exercise, hobbies, or talking with supportive friends and family.
-
Control Diabetes and High Blood Pressure: These are major risk factors. Over 68% of people under 65 with diabetes die from some form of heart disease (3). Managing blood sugar levels through diet (e.g., specific foods, herbs, apple cider vinegar, okra water) and controlling high blood pressure are essential for cardiovascular protection.
Remember, your lifestyle choices are your most powerful defense against heart disease and heart attack. Taking responsibility for these habits can lead to a healthier, longer life.
News in the same category

Mold Illness: What It Is, Hidden Signs, and How to Protect Your Home
Is Cancer Hereditary? Helpful Tips to Prevent the Growth of Cancer Cells
3 Pain Areas on the Body That Could Signal Early-Stage Cancer: Don’t Delay, or It Could Spread
Natural Solutions for Gout: Tackling Uric Acid to Prevent Pain
Don't Ignore These 15 Common Cancer Symptoms: A Guide to Early Detection
5 Hidden Nutritional Deficiencies You Likely Have (and How to Fix Them)
3-Year-Old Girl Bites and Swallows Mercury from a Broken Thermometer — Her Mother’s Quick Thinking Saves Her Life and Earns Praise from Doctors
More and More Young People Are Suffering from Colon Cancer — Doctors Warn: Eat Less of These 3 Things!
Diagnosed with Late-Stage Stomach Cancer, I Painfully Realized: 3 Foods Left Too Long in the Fridge Were the "Accomplices"
Waking Up to Shoulder Pain: Causes, Solutions, and How to Sleep Soundly
Your Lymphatic System: A Hidden Key to Lifelong Health

Doctors Issue Urgent Warning: Weight-Loss Jab Users Risk Malnutrition and Muscle Loss Amid Diet Concerns

You Should Never Ignore These 9 Things Your Fingernails Reveal About Your Health
6 Foods That Are Not Compatible with Tumors, Remember to Eat Them Regularly
Before Cancer Knocks: 4 Signs on Your Hands and Feet Not to Be Ignored

Doctors Warn: 4 Food Storage Habits in the Refrigerator That Can Cause Cancer

Doctors Said It Was Gallstones—But It Was Stage Four Cancer
News Post

AI is Finally Learning to Translate Cat Meows Into Human Speech. Here Are the Tools to Try
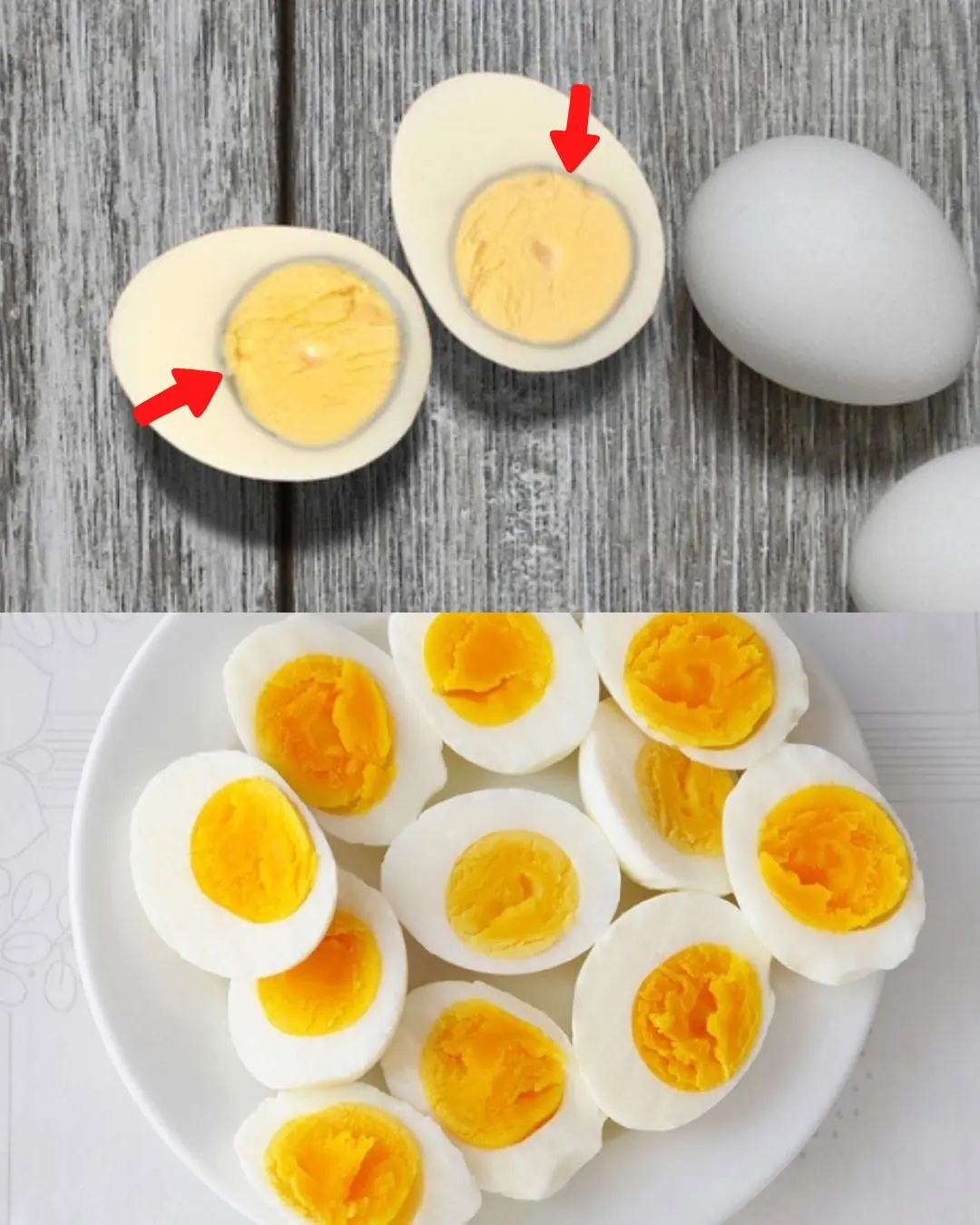

What causes the green ring around hard-boiled eggs?

Scientists Say More Animals Are Conscious Than We Ever Imagined—Even Insects
5 foods you should never keep overnight

63 Earths Can Fit Comfortably Inside Uranus

Scientists Develop Eco-Friendly Concrete Alternative From Sugarcane Waste, Called Sugarcrete

Mom Tells Boy He Can Pick Any Animal At Shelter. He Picked This Eldery, Overweight And Shy Cat

A New Study Suggests We Might Be Sitting Inside a Huge Cosmic Void and That Could Solve One of the Biggest Puzzles in Cosmology

Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutritional Facts (Evidence-Based)

Mold Illness: What It Is, Hidden Signs, and How to Protect Your Home

Is Cancer Hereditary? Helpful Tips to Prevent the Growth of Cancer Cells
Warning from Hospitals: Eating This Type of Meat Every Day Can Increase Cancer Risk – Don’t Be Complacent!

3 Pain Areas on the Body That Could Signal Early-Stage Cancer: Don’t Delay, or It Could Spread

What Your Ankle Bracelet Really Says About You — It’s More Than Just Jewelry

Truth behind viral statement after married CEO caught with employee on Coldplay kiss cam

DIY Okra Face Gel Recipe for Radiant, Firm Skin: Collagen Boosting Skincare Solution for Glowing Skin
By incorporating this okragel into your nightly skincare routine, you can enjoy smoother, firmer, and more radiant skin in just a few simple steps.

Homemade Rice Face Cream: A Simple, Natural Skincare Solution to Achieve Radiant Glass Skin in 7 Days
It’s time to create the DIY rice face cream that will help you achieve glowing, glass-like skin in just 7 days.

Natural Solutions for Gout: Tackling Uric Acid to Prevent Pain
