Acid Reflux (GERD): When Should You See a Doctor?
Acid reflux is a common condition, but when it becomes frequent or severe, it may indicate a more serious issue known as GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease). While many people brush off heartburn as something normal, chronic reflux can damage the esophagus and affect long-term health.
This guide explains the symptoms, causes, dangers, and — most importantly — when to seek medical attention.
What Is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid moves backward into the esophagus. This causes burning, discomfort, and irritation in the chest and throat.
Occasional reflux is normal. Chronic reflux is not.
Signs of Acid Reflux
-
Heartburn
-
Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
-
Chest burning after meals
-
Bloating
-
Belching
-
Regurgitation of food
-
Difficulty swallowing
If reflux happens twice a week or more, it may be GERD.
Common Causes of Acid Reflux
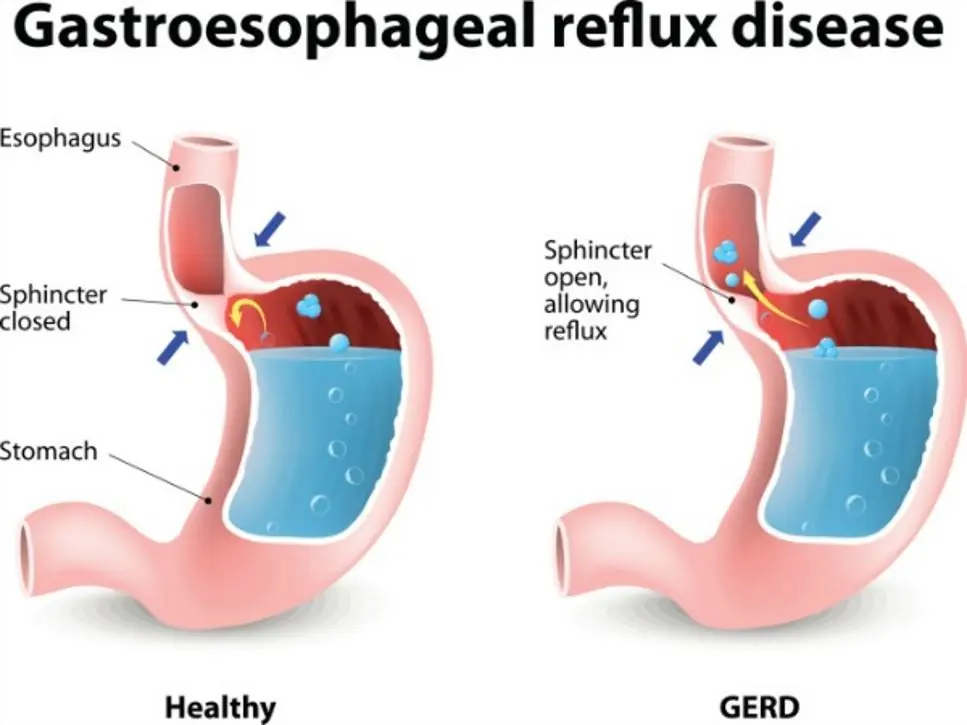
1. Weak Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
This valve normally keeps stomach acid from rising. Weakness leads to reflux.
2. Poor Diet
Triggers include:
-
Spicy foods
-
Fatty foods
-
Chocolate
-
Coffee
-
Alcohol
-
Citrus fruits
3. Eating Late at Night
Lying down soon after eating worsens reflux.
4. Obesity
Extra abdominal pressure pushes stomach acid upward.
5. Smoking
Weakens the LES and increases stomach acid.
6. Pregnancy
Hormonal and physical changes often cause reflux.
When Acid Reflux Becomes Dangerous
Untreated GERD can lead to:
-
Chronic inflammation
-
Esophagitis
-
Strictures (narrowing of the esophagus)
-
Barrett’s esophagus
-
Increased risk of esophageal cancer
When Should You See a Doctor?
Seek medical care if you experience:
1. Frequent Heartburn
More than two times per week.
2. Pain That Mimics a Heart Attack
Chest pain must be evaluated immediately.
3. Difficulty Swallowing
A sign of esophageal damage.
4. Persistent Hoarseness or Chronic Cough
Reflux can irritate the throat and vocal cords.
5. Vomiting or Blood in the Stool
May indicate internal irritation or bleeding.
6. Unintended Weight Loss
A warning sign of complications.
7. Symptoms That Don’t Improve With Lifestyle Changes
Medication or further diagnostic tests may be required.
Home and Natural Remedies
1. Elevate the Head of Your Bed
Prevents acid from rising at night.
2. Avoid Trigger Foods
Identify patterns and adjust your diet.
3. Eat Smaller Portions
Large meals increase pressure on the stomach.
4. Lose Weight if Needed
Just 5–10% weight loss reduces GERD symptoms significantly.
5. Drink Ginger or Chamomile Tea
These soothe the digestive tract.
6. Don’t Lie Down After Eating
Wait at least 2–3 hours.
7. Reduce Alcohol and Caffeine
Both relax the LES and worsen reflux.
Medical Treatments
-
Antacids
-
H2 blockers
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
-
Surgery (for severe cases)
Conclusion
Acid reflux becomes dangerous when ignored. Understanding when it’s time to see a doctor can help prevent long-term complications and protect your digestive health.
News in the same category

5 early signs of poor circulation & how to boost blood flow

How to Use Garlic to Get Rid of Pests: Mice, Flies, Lice, Cockroaches, Lizards, Mosquitoes, and Kitchen Cockroaches
5 early warning signs of pancreatic cancer, according to survivors

Drink this to STOP joint pain naturally
Top 6 Neuropathy Remedies (Peripheral Neuropathy Home Remedies)

10 daily habits that are silently destroying your kidneys

Saffron boosts mood and libido naturally

How to Support Your Kidneys Naturally Using 1 Teaspoon of Baking Soda
The surprising power of 4 seeds to repair your nerves naturally

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Canned Tuna Every Day

Doctors warn: these everyday antacids could be putting your heart in danger
Doctors Reveal What Really Happens When You Use Castor Oil
The Natural Secret Doctors Never Tell You That Melts Away Uric Acid Fast

9 Convincing Reasons to Consume More Dates

Two handfuls of peanuts daily boost memory in 4 months

Prunes and bone health: surprising benefits beyond constipation relief
12 Weird Diabetes Skin Problems You Need To Know
High Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Natural Ways to Lower It
News Post

The Surprising Heart-Healing Power of Olive Oil, Chia Seeds, and Cayenne Pepper

5 early signs of poor circulation & how to boost blood flow

How to Use Garlic to Get Rid of Pests: Mice, Flies, Lice, Cockroaches, Lizards, Mosquitoes, and Kitchen Cockroaches

5 early warning signs of pancreatic cancer, according to survivors

Drink this to STOP joint pain naturally

Top 6 Neuropathy Remedies (Peripheral Neuropathy Home Remedies)

10 daily habits that are silently destroying your kidneys

Pineapple Mango Ginger Lemon Juice: Benefits, Nutrition & How to Make It

Saffron boosts mood and libido naturally

How to Support Your Kidneys Naturally Using 1 Teaspoon of Baking Soda

Can a Honey–Chia Drink Support Kidney Health? Benefits, Recipe & Daily Tips

Euphorbia Hirta (Asthma-Plant): Traditional Uses, Applications & Emerging Insights
Nails: What Do They Reveal About Your Health

The surprising power of 4 seeds to repair your nerves naturally

Don’t Throw Away Date Seeds – Here’s Why They’re So Powerful

Avocado Seed: Cleanse Your Body and Strengthen Your Heart Naturally

Stop Shaving! Discover Natural & Long-Lasting Hair Removal for Face & Body

Why wood—not diamonds—is the universe’s rarest treasure

A Nearby Earth-Sized World Raising New Hopes for Habitability
