
Asteroid Bennu Could Hit Earth in 2182—Here’s What Scientists Predict
The thought of an asteroid colliding with Earth is the stuff of science fiction, but for astronomers studying Bennu, a 500-meter-wide asteroid, this scenario is a real—though highly unlikely—concern. A recent scientific simulation of a potential September 2182 impact paints a chilling picture: devastating climate shifts, massive global disruptions, and long-term environmental consequences.
While the likelihood of impact remains low—approximately 1 in 2,700 (0.037%), researchers are not taking any chances. Their computer models simulate what would happen if Bennu were to crash into our planet, and the findings are nothing short of terrifying.
The Impact Event: What Would Happen?
If Bennu were to collide with Earth, the sheer force of the impact would be immense. Scientists estimate that it would release energy equivalent to 24 times the power of the largest nuclear bomb ever detonated. The blast radius alone would devastate an area the size of an entire country, instantly wiping out millions of lives.
However, the real catastrophe wouldn’t be the explosion itself but what follows. The impact would eject between 100 to 400 million tons of dust into Earth’s atmosphere, triggering a global climate crisis.
Climate Consequences: A Mini Ice Age
The dust cloud produced by the impact would block out sunlight for months or even years, causing global temperatures to plummet by an estimated 4 degrees Celsius. Scientists compare this effect to the aftermath of massive volcanic eruptions like Mount Tambora in 1815, which led to the infamous “Year Without a Summer”—a time of widespread food shortages and extreme weather.
With less sunlight reaching Earth’s surface, photosynthesis would slow down dramatically, affecting crops, forests, and marine ecosystems. Experts estimate that plant growth could decline by 20-30% worldwide, while oceanic food chains could collapse due to the loss of phytoplankton.
Ozone Layer Damage and Acid Rain
Adding to the devastation, the asteroid’s impact would send nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, leading to a 32% depletion of the ozone layer. With less ozone protecting us, harmful UV radiation from the Sun would increase, heightening risks of skin cancer, genetic mutations, and damage to plant life.
Moreover, acid rain would follow, as sulfur compounds mix with atmospheric moisture, further polluting water sources and damaging infrastructure.

Global Food Shortages and Economic Collapse
With reduced sunlight, disrupted agriculture, and collapsing ecosystems, a severe food crisis would emerge. Grain production—the backbone of human food supply—would plummet, leading to skyrocketing food prices and widespread famine.
Economic instability would soon follow, with nations struggling to cope with resource scarcity, social unrest, and international conflicts over dwindling food and water supplies.
Can We Stop Bennu?
Despite the low probability of impact, scientists stress the importance of planetary defense strategies. Missions like NASA’s OSIRIS-REx, which collected samples from Bennu, help us understand the asteroid’s composition, potentially guiding future efforts to deflect or destroy it.
NASA and other space agencies are already testing asteroid-deflection technologies, such as kinetic impactors (crashing spacecraft into asteroids to alter their trajectory) and gravity tractors (using spacecraft to gradually “pull” an asteroid away from its path).
Final Thoughts: Should We Be Worried?
The chance of Bennu hitting Earth is extremely small, but the research highlights the catastrophic impact an asteroid of this size could have. The findings serve as a reminder that planetary defense is not just science fiction—it’s a necessity.
News in the same category


Clench Your Fist And Count The Palm Lines
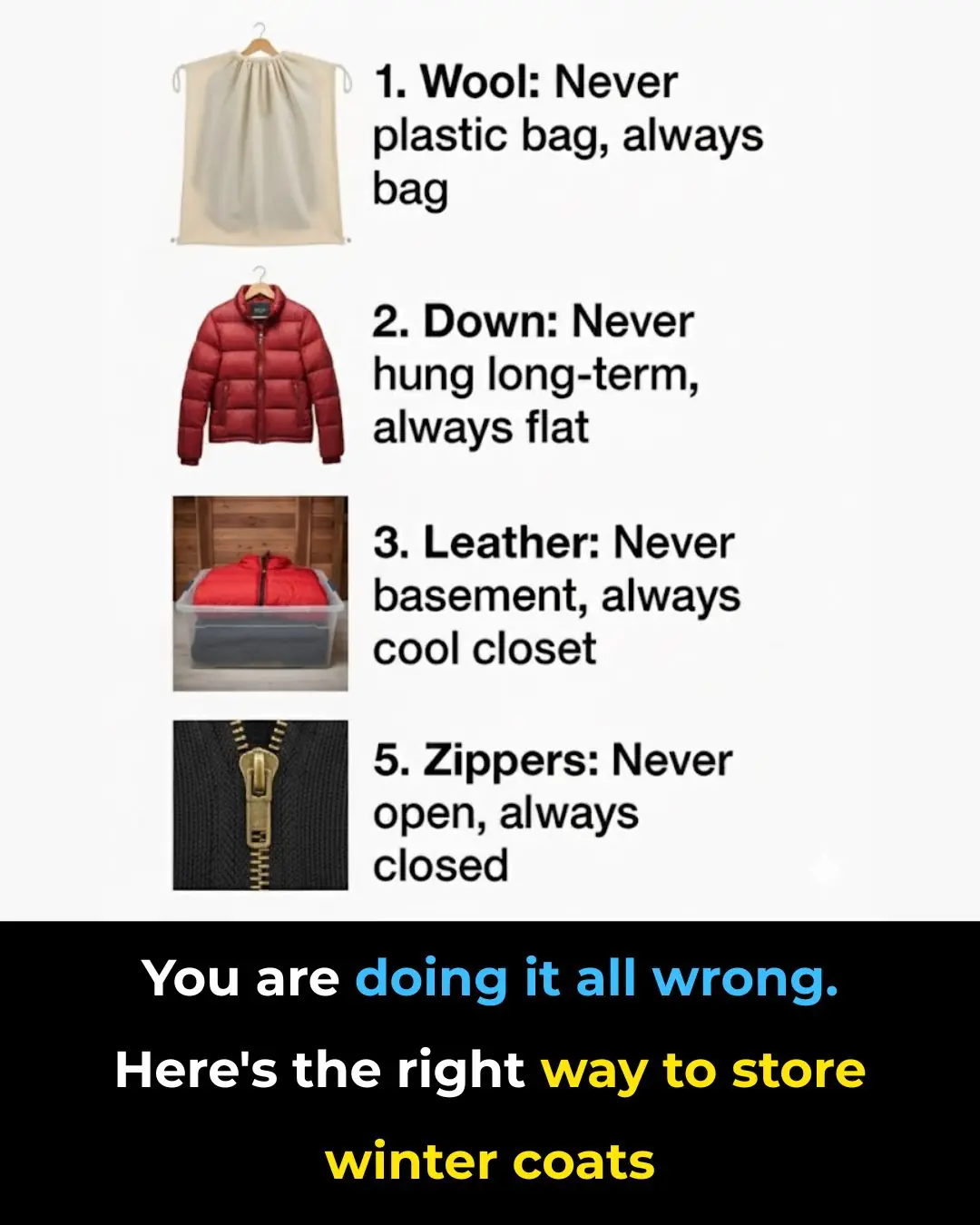
You’re Doing It All Wrong: The Right Way to Store Winter Coats

I Found a Tiny Red Object With Metal Prongs in My Kitchen Drawer — Here’s What It Actually Is

8 Reasons Why Adding Baking Soda to Your Toilet Tank Is a Must-Try Trick

Quick Ways to Stop a Draft Under Your Front Door — While You Wait for the Handyman

Most People Will Go Their Entire Lives Without Knowing What the Decorative Bands on Bath Towels Really Mean

‘Black Diamond’ Apples Exist — A Rare Variety Only Found in China And Tibet

Norway Declares Nationwide Ban on Deforestation In World-First

Finally! People Are Getting Fined for Loud Speakerphone Calls in Public

Don’t Sleep With Your Pets

The Meaning of Having an Unmade Bed

People Who Should Avoid Eating Kohlrabi (Su Hào), Even If They Really Crave It

Dandelion: A “Superfood” Herb with Real Nutrients — What Science Says

Woman (26) Dies After Eating Hot Pot: 2 Things You Should Never Do Together When Enjoying Hot Pot

If the Body Is Developing Cancer, Three Nighttime Sleep Signs May Appear — But Many People Ignore Them

Claim: “Cancer Cells Eliminated in 42 Days with a Special Juice — Worldwide Celebration?”
Can Lemon Seeds “Save” Someone from a Snake Bite in 1 Minute? What Science Really Says
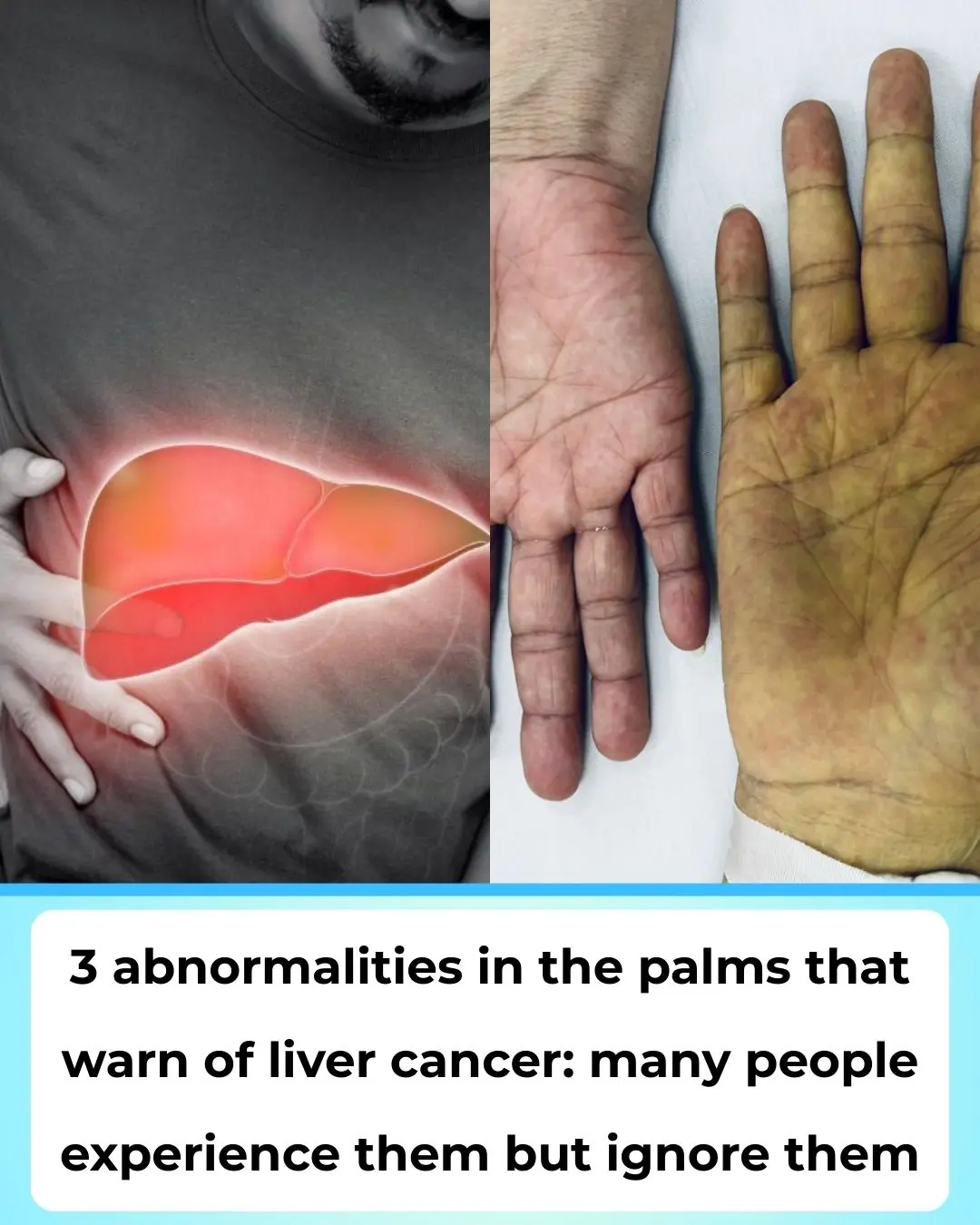
Three Unusual Hand Signs That May Warn of Liver Cancer

Throwing Away Overnight Tea Is a Waste: 4 Surprising Uses Most People Don’t Know About
News Post
7 signs in your legs that predict how long you’re going to live
World's Smallest Quantum Computer Powered by a Single Photon: A Breakthrough in Quantum Computing

Astronomers Discover Earth-Sized Exoplanet Gliese 12 b in Habitable Zone, Bringing Us Closer to Finding Life Beyond Earth

Nexus: Georgia Tech's Revolutionary Supercomputer Set to Transform Science and Technology

I have absolutely no idea! Let's see why.

So that's it. And here's the answer.

Waking Up and Noticing These 4 Signs When Urinating in the Morning? Your Uterus May Be Seriously Unhealthy

Women Who Regularly Eat These 4 Foods Can Help Prevent Premature Gray Hair — Even in Their 60s, Hair Can Stay Dark and Shiny

The Longevity Secrets of a 100-Year-Old Grandmother Who Still Loves Food, Milk Tea, and Ice Cream

Why Climate Change Skepticism Is More About Values Than Science

A Cave Without Sunlight Hosts One of the Largest Spider Colonies Ever Found

15 Common Phrases That Can Instantly Trigger a Narcissist
Goodbye Lasers? A New Electric Method Is Reshaping Vision Care

Sleep is far from just downtime
11 Surprising Benefits of The Miracle Leaf of Life
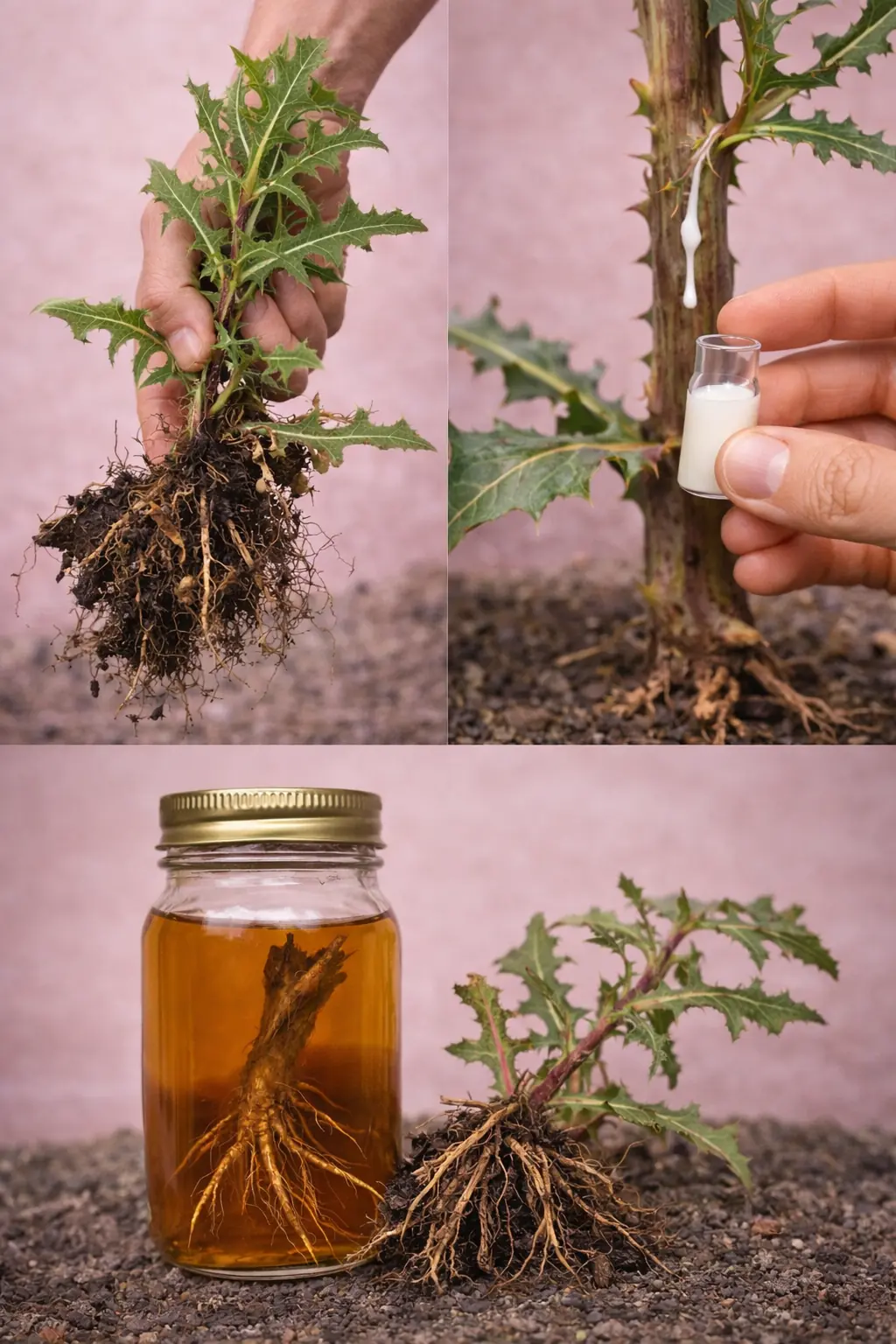

30 Amazing Benefits of Lactuca serriola (Wild Lettuce)

Over 1,800 Lawsuits Filed Against Ozempic, Alleging Severe Side Effects and Misleading Marketing

The First-Ever Leucistic Iberian Lynx Captured on Camera: A Rare and Powerful Symbol of Hope

Ultra-Processed Foods Linked to Increased Psoriasis Flare-Ups, Study Finds
