
Doctors Reveal What Eating Peanuts Can Really Do to Your Body

Doctors Reveal What Eating Peanuts Can Really Do to Your Body
Peanuts are one of the world’s most beloved snacks, and their appeal goes beyond their delicious taste. In many cultures, including Brazil, peanuts are integral to traditional treats such as paçoca, pé-de-moleque, cakes, and festive desserts. While these little legumes (yes, technically not a nut!) are a treat to the taste buds, their health benefits might surprise you. According to doctors, peanuts offer a range of positive effects on the body—but not without some potential downsides.
If you are someone who enjoys peanuts often, you’re in for a detailed exploration of what they can do for your health.
Why Peanuts Deserve Your Attention
Native to South America, peanuts are not just a simple snack; they are packed with an array of nutrients that offer a wide range of health benefits. They are rich in:
-
High-quality plant protein
-
Healthy fats
-
Vitamins A, B6, and E
-
Minerals like calcium, iron, and phosphorus
-
Lecithin, amino acids, carotenoids, and choline
These compounds support everything from your heart health to metabolic function and brain activity. Recent studies also highlight the potential benefits of regular peanut consumption, including reducing cardiovascular risk, helping to regulate cholesterol levels, improving satiety, and even protecting against some diseases (Source: American Heart Association).
Top Health Benefits of Eating Peanuts
1. They Keep You Feeling Full Longer
One of the most well-known benefits of peanuts is their ability to keep hunger at bay. A small handful of peanuts or a tablespoon of peanut butter with your morning breakfast can help control your hunger for hours. The combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats slows digestion and provides a steady release of energy throughout the day. Nutritionists often recommend peanuts as an easy and satisfying snack to prevent overeating while maintaining balanced nutrition (Source: Harvard Medical School).
2. They Help Stabilize Blood Sugar Levels
Substituting red meat with peanuts several times a week may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by up to 21%. Peanuts are particularly beneficial because they slow the absorption of carbohydrates, preventing spikes in blood sugar. Consuming a small portion of peanuts in the morning can also help maintain steady blood sugar levels, support insulin regulation, and provide consistent energy (Source: Journal of Nutritional Science).
3. They May Reduce the Risk of Rectal Cancer
Research suggests that regularly consuming peanuts may lower the risk of rectal cancer. Studies show that women who eat peanuts at least twice a week have a 58% lower risk of developing this type of cancer, while men experience a 27% reduction in risk. This protective effect is attributed to the high levels of folic acid and antioxidants found in peanuts, which play a crucial role in cell regeneration and the repair of damaged DNA (Source: National Cancer Institute).
4. They Can Help Prevent Gallstones
Regular peanut consumption has also been linked to a reduced risk of developing gallstones. Experts suspect this is because peanuts help regulate cholesterol levels, which are a major contributor to gallstone formation. While more research is required to confirm this association, the current evidence points to peanuts as a helpful addition to a balanced diet for reducing the risk of gallstones (Source: British Journal of Nutrition).
Important Precautions When Eating Peanuts
While peanuts can be incredibly beneficial, there are some important precautions to keep in mind when consuming them.
✔ Don’t Eat Too Much
While peanuts are highly nutritious, they are also calorie-dense. Eating more than 50 grams per day may lead to weight gain, bloating, and digestive discomfort. Despite their health benefits, moderation is key when incorporating peanuts into your diet.
✔ Avoid Eating Peanuts on an Empty Stomach
Due to their high fat content, peanuts can be hard on an empty stomach and may cause cramps or discomfort. It is advisable to eat them with other foods or after a meal to avoid digestive issues.
✔ Never Eat Moldy Peanuts
Moldy peanuts can contain aflatoxin, a potent carcinogenic compound that can be harmful to your health. Always ensure that peanuts are fresh and not moldy before consuming them to avoid any potential toxicity (Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration).
✔ Be Cautious if You Use Blood Thinners
Peanuts are a rich source of Vitamin E, which may interfere with blood clotting. If you are taking anticoagulant medications, it is crucial to monitor your peanut intake to avoid interactions with your medications. Always consult a healthcare professional if you're unsure about how peanuts may affect your health in combination with prescribed treatments (Source: National Institutes of Health).
Who Should Avoid Peanuts?
1. People With Peanut Allergies
Peanut allergies are one of the most serious food allergies, and even small amounts of peanuts can trigger severe reactions, including:
-
Hives and itching
-
Throat swelling and difficulty breathing
-
A sudden drop in blood pressure
-
Dizziness
-
Life-threatening anaphylactic shock
If you are allergic to peanuts, you should avoid them completely and be aware of potential cross-contamination with other foods (Source: Mayo Clinic).
2. Individuals With Gout or High Uric Acid
While peanuts contain fewer purines than red meat, they still contain plant-based proteins that can raise uric acid levels in some individuals. While small amounts of peanuts are generally safe for people with gout or high uric acid levels, it is best to avoid peanuts during an active gout attack. Always consult a doctor if you have concerns about uric acid levels and peanut consumption (Source: American College of Rheumatology).
3. People With Sensitive Digestion
Even boiled peanuts can lead to digestive issues like gas, bloating, and discomfort, especially for individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Caution is advised for:
-
Young children (under 2 years old)
-
Elderly individuals
-
People recovering from illness
-
Anyone who frequently experiences digestive discomfort
If you have digestive sensitivities, it’s best to consume peanuts in small amounts and monitor how your body reacts.
Final Thoughts
Peanuts can be a delicious, nutrient-dense addition to your diet. From heart protection and blood sugar stabilization to potential cancer prevention, peanuts offer numerous health benefits. However, like any food, they must be consumed responsibly. If you have allergies, digestive issues, or chronic health conditions, consult with a healthcare provider before making peanuts a regular part of your diet.
When eaten in moderation and with consideration for individual health conditions, peanuts are one of nature’s most powerful—and delicious—superfoods.
Sources:
-
American Heart Association
-
Harvard Medical School
-
Journal of Nutritional Science
-
National Cancer Institute
-
British Journal of Nutrition
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
-
National Institutes of Health
-
Mayo Clinic
-
American College of Rheumatology
News in the same category


Sugar Apple (Annona squamosa): A Sweet Fruit with Powerful Health Benefits

Burning Garlic at Home: What Happens After 15 Minutes

Why Do People Put Butter on a Date? The Ancient Energy Mix Making a Modern Comeback

Rosemary: The Ancient Herb With Powerful, Little-Known Benefits for the Human Body

The #1 cheap food packed with natural probiotics (and how to prepare it)

American Sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua): Health Benefits and Easy Ways to Use It at Home

Boost Low Platelets Naturally: The Papaya–Beet Smoothie That Strengthens Your Blood and Immunity

What’s Behind Those White Spots on Your Skin? Possible Causes You Should Know

Why Every Woman Over 35 Needs to Boil Aidan Fruit Today (You’ll Wish You Knew This Sooner)

The Power of Castor Leaves: Nature’s Hidden Gift

12 Benefits of Bull Thistle Root and How to Use It Naturally

7 Colorful Smoothies for a Healthy Week + MORNING DETOX DRINK

Boosting Hair Growth Naturally with Red Onion, Cloves, and Rosemary

The Best Tea to Start Your Morning and After Dinner: A Powerful Blend for Wellness

Store Homemade Apple Pie in a Jar for a Quick Dessert — Here’s How You Do It
Don’t Toss Those Onion Peels — They’re Nature’s Hidden Remedy

The Plaster That Re-Grows Teeth – The Revolution That Changes Dentistry

Eat Eggs but NEVER Make These 7 Mistakes — They Can Be Dangerous for Seniors
News Post

Breakthrough in Burn Treatment: Lab-Grown Skin with Functional Sweat Glands
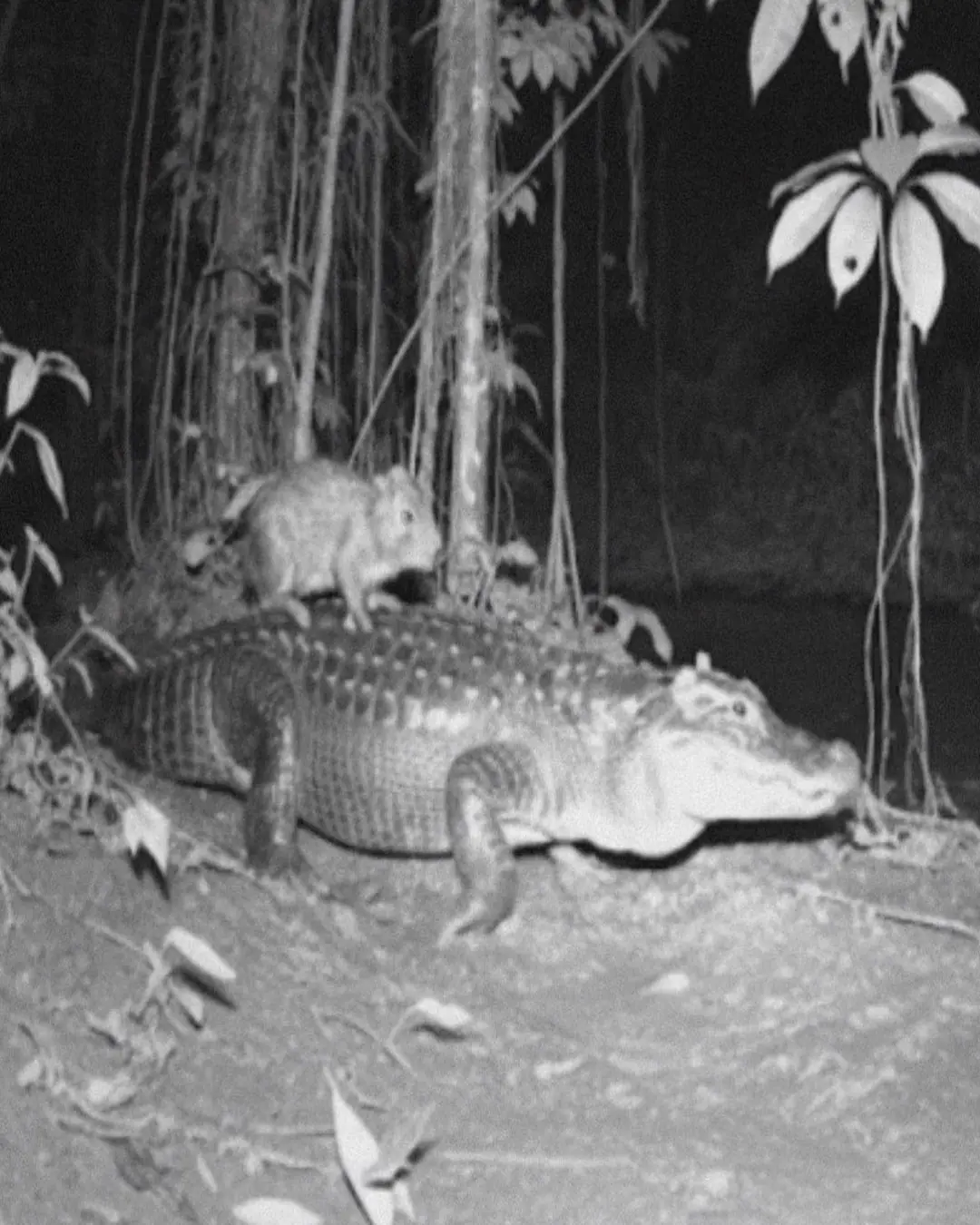

“The Unlikeliest Friendship in the Wild”: The Capybara Who Rode an Alligator.

7 powerful anti-cancer foods you should start including in your diet

A Mother Who Survived the Unsurvivable: The Story of Motola and Her First Steps Toward Hope.

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs

Egg Yolk + Garlic + Honey: The 3-Ingredient Elixir You’ll Wish You Discovered Years Ago
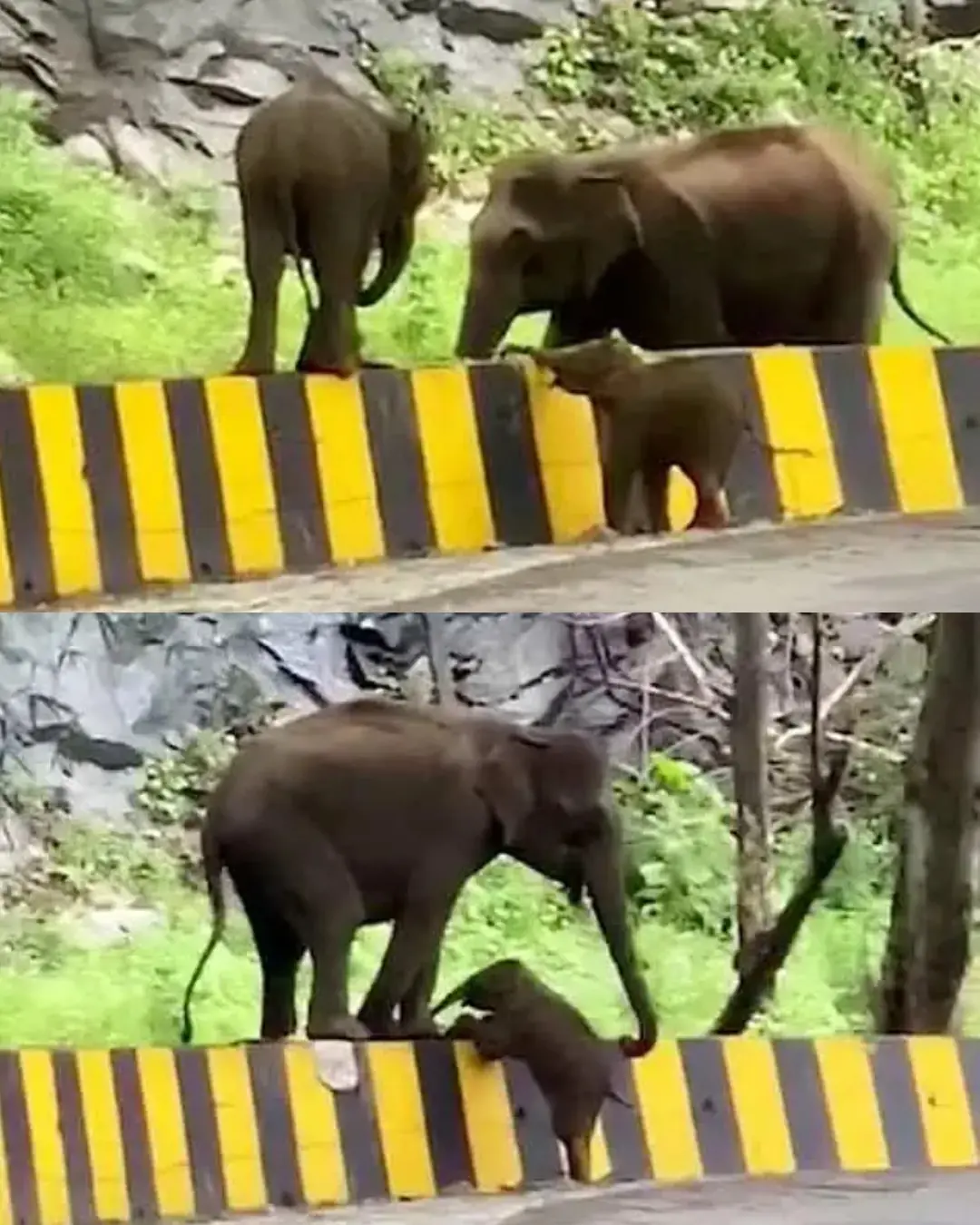

A Mother’s Promise: The Elephant Who Refused to Leave Her Baby Behind.

Australia's Undersea Solar Cable: A Groundbreaking Step Toward Global Renewable Energy

The London Bus Driver Who Jumped Tower Bridge and Became a Legend

Honoring the Heroism of Saman Kunan: A Legacy of Courage and Sacrifice

Sugar Apple (Annona squamosa): A Sweet Fruit with Powerful Health Benefits

Top 8 Foods for Stronger Legs (Seniors, Eat Daily!)

Burning Garlic at Home: What Happens After 15 Minutes

He thought it was just an allergy, until the diagnosis proved otherwise

3 Natural DIYs To Increase Breast Size Natually
One Miracle Oil to Remove Dark Spots “Overnight”!

The #1 seed flour people over 60 use for steady energy and strength

5 types of fish “loaded” with mercury – don’t be tempted even if they are cheap
