
Eating Just One Bite is Already Harmful, But Many Still Eat It Without Worry
Introduction:
Foodborne parasites pose a significant threat to food safety. These microscopic organisms, including amoebas, roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, can lead to a wide range of health problems once they enter the human body. Symptoms of parasitic infections may include digestive issues, gastrointestinal infections, anemia, and colitis. Although parasites are often invisible to the naked eye and undetectable by smell, they can be eradicated through proper hygiene practices and thorough cooking. To protect yourself and your loved ones, it’s important to be aware of foods that can carry harmful parasites. This article will highlight common foods that require extra caution to prevent parasite-related health risks.
Common Foods at Risk for Parasitic Infections:
Undercooked Meat (Pork, Beef, and Fish):
Raw or undercooked meat, particularly pork, beef, and fish, can harbor parasites such as tapeworms and roundworms. These parasites are transmitted when meat is not cooked to the proper internal temperature. For example, undercooked pork can contain the Trichinella parasite, which causes trichinosis, while fish may carry Anisakis worms, which can lead to a condition known as anisakiasis. These parasites can cause severe health issues, so ensuring that meat is cooked thoroughly is vital.
Raw or Undercooked Shellfish:
Shellfish, including oysters, clams, and mussels, are filter feeders that accumulate parasites from contaminated water. These shellfish can harbor trematodes, a type of flatworm that can lead to infections in humans. Consuming raw or undercooked shellfish significantly increases the risk of ingesting these harmful parasites, potentially leading to long-term health consequences.
Unwashed Fruits and Vegetables:
Fresh produce that is not properly washed or peeled can carry parasites such as Toxoplasma gondii, which causes toxoplasmosis, and Giardia, responsible for giardiasis. The soil in which fruits and vegetables are grown can be contaminated with these parasites, and improper handling during transportation or at the market can lead to contamination. A proper washing routine is essential for reducing the risk of infection.
Unpasteurized Dairy Products:
Unpasteurized dairy products, including milk, cheese, and yogurt, can harbor dangerous parasites like Cryptosporidium and Giardia. These parasites are resistant to typical cleaning and sanitizing methods, making raw dairy products a significant health risk. Pasteurizing dairy products kills these harmful microorganisms, making them safer to consume.
Contaminated Water:
Drinking or using contaminated water for washing food can introduce parasites into the human body. Water sources can be contaminated with Giardia, Entamoeba histolytica, and other harmful microorganisms. It is essential to always drink clean, filtered, or boiled water, especially when traveling in areas with poor sanitation.
Instructions for Safe Consumption:
Proper Cooking of Meat:
-
Ensure that pork is cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C).
-
Beef should reach an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C) to kill any parasites present.
-
Fish should be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C), or until the flesh is opaque and flakes easily with a fork.
Cooking Shellfish Thoroughly:
-
Shellfish should be cooked at a high temperature to kill parasites. Methods like steaming, boiling, or grilling ensure thorough cooking. Always discard any shellfish that does not open during cooking.
Washing Produce:
-
Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly under running water before eating, cutting, or cooking. Use a vegetable brush for produce with thicker skins, such as potatoes or cucumbers. Whenever possible, peel the outer layers of produce to further reduce contamination risks.
Avoiding Raw Dairy Products:
-
Opt for pasteurized dairy products to ensure they are free from harmful microorganisms. Always check labels to confirm that the product has been pasteurized before purchasing.
Ensuring Clean Water:
-
Always drink water from trusted sources, especially when traveling. If local water quality is uncertain, use bottled or filtered water. Boiling water for at least one minute can help eliminate parasites and other harmful microorganisms.
Tips for Serving and Storing:
Storing Meat Properly:
-
Store raw meat separately from ready-to-eat foods in the refrigerator. Use airtight containers to prevent cross-contamination and ensure meat is cooked thoroughly before serving.
Freezing Fish:
-
If consuming raw or lightly cooked fish, freeze it for at least 24 hours before consumption to kill parasites like Anisakis. Freezing is an effective method for parasite control, especially in sushi-grade fish.
Washing Hands and Surfaces:
-
Always wash your hands with soap and water before preparing food, and after handling raw meat or seafood. Clean and sanitize all surfaces and utensils that come into contact with raw foods to prevent cross-contamination.
Storage for Produce:
-
Store unwashed produce in a cool, dry place. After washing, refrigerate fruits and vegetables to extend their shelf life. Always wash produce right before consumption, not before storing it.
Variants to Reduce Risk:
Cooked or Pasteurized Alternatives:
-
If you enjoy sushi, oysters, or other raw delicacies, consider switching to cooked alternatives to minimize the risk of parasites. Many restaurants now offer safe, cooked sushi rolls or grilled shellfish to reduce parasite exposure.
Grow Your Own Produce:
-
Growing your own fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk of contamination from external sources. If you cultivate your own produce, ensure it is thoroughly washed before consumption. Regularly inspect your garden for potential contaminants that may affect food safety.
By following these guidelines and being cautious about food safety, you can significantly reduce the risk of parasitic infections. Always prioritize cleanliness and proper cooking methods to protect yourself and your family from the dangers posed by foodborne parasites.
News in the same category

My Mom's Simple Recipe That Banished Worms and Boosted Health – A Natural Remedy Worth Trying
What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know
Painful Red Bumps on Skin? It Might Be Dyshidrotic Eczema

Shocking Simulation Reveals The Effects Of Plucking A Hair From Your Skin

Scientists Discover Body’s ‘Kill Switch’ Capable of Destroying Cancer Cells

A Legacy Of Health: Soong Mei-Ling’s Longevity And Struggle Against Cancer

Prostate Cancer – Warning Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection
Mite Bites: Warning Signs and Natural Treatments

14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It

Effective Home Remedies for Lice (Based on Evidence)

Here’s How to Go to Sleep Fast (in Under 1 Minute)

Unexplained Bruising on Your Body: Causes and Treatments
11 Simple Steps to Slash Your Risk of Colorectal Cancer

Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence Based)
Mother’s Ultrasound Reveals Baby ‘Blowing Bubbles’
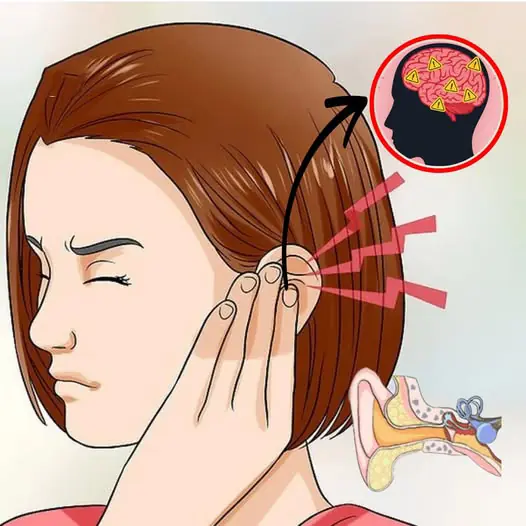
If you hear ringing in your ear, this is a sign that you will suffer from…

Man With Severe Anger Issues Cries After Seeing What Brain Scan Reveals
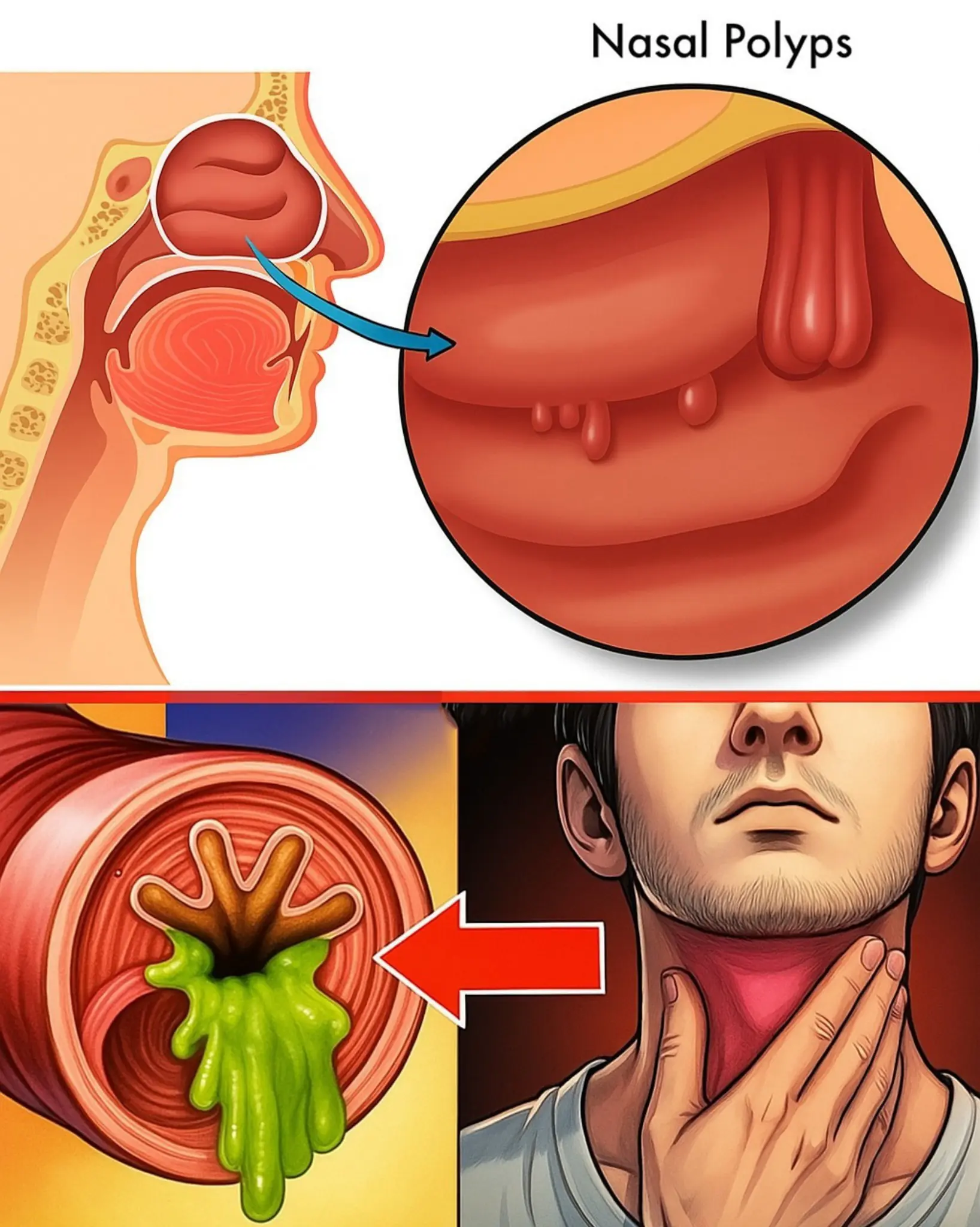
4 Effective Home Remedies to Eliminate Mucus and Phlegm from the Throat, Sinusitis, and Rhinitis
News Post

My Father-in-Law Gave Me a Pillow as an Anniversary Gift – I Was Shocked When I Learned His True Intentions
When a mysterious package arrives at Kate and Josh's home, they are confused to see that the sender is Josh's estranged father. But things get even stranger when Josh finds a ticking box inside the gift — a beautiful pillow. A confrontation occurs, and
A Young Man Befriended Me at Work — I Didn't Realize He'd Change My Life Forever
I had spent years blending into the background, just another old man behind the register. Then one day, a young man walked into my grocery store and struck up a conversation like we were old friends. I never could have guessed how much he would change my

Doctors Issue A Warning About Hot Showers That Might Change How You Bathe

My Mom's Simple Recipe That Banished Worms and Boosted Health – A Natural Remedy Worth Trying

What Your Legs Can’t Say, Your Vagina Can — The Truth About the Female Body Most People Don’t Know

Painful Red Bumps on Skin? It Might Be Dyshidrotic Eczema

Shocking Simulation Reveals The Effects Of Plucking A Hair From Your Skin

Scientists Discover Body’s ‘Kill Switch’ Capable of Destroying Cancer Cells

A Legacy Of Health: Soong Mei-Ling’s Longevity And Struggle Against Cancer

Prostate Cancer – Warning Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

The Ultimate Guide to Vaseline: 10+ Beauty Hacks for Skin, Lips & Hair

The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

Mite Bites: Warning Signs and Natural Treatments

14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It

I FOUND A LACE ROBE HIDDEN IN MY HUSBAND’S CLOSET — THEN I SAW MY STEPMOTHER WEARING IT.

My Mother-in-Law Kicked My Parents Out of My Wedding Because They “Didn’t Pay for It”

I Decided to Surprise My Husband at Work and Uncovered a Secret That Changed Our Lives Forever.

My Husband’s Mistress Sent Me a Box on My Birthday – I Was Stunned by What I Found Inside.

While Decorating a Gingerbread House, My Daughter Said, 'It's Beautiful, like the Secret House Daddy Takes Me to Every Weekend'
When my daughter compared our gingerbread home to the "secret house Daddy takes me to every weekend," I laughed it off until she mentioned a pretty lady with candy. A few days later, I found myself following my husband, although I'd never been a suspiciou

I Heard a Young Woman on the Street Singing the Same Song My Daughter Sang Before Going Missing 17 Years Ago, So I Went Closer
I was walking home from work one day, thinking about the bills I had to pay that evening. But as I turned the corner onto the town square street, a familiar melody suddenly reached my ears and stopped me in my tracks.