
Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory
The hippocampus shrinks in late adulthood, leading to impaired memory and increased risk for dementia. Hippocampal and medial temporal lobe volumes are larger in higher-fit adults, and physical activity training increases hippocampal perfusion, but the extent to which aerobic exercise training can modify hippocampal volume in late adulthood remains unknown.
Here we show, in a randomized controlled trial with 120 older adults, that aerobic exercise training increases the size of the anterior hippocampus, leading to improvements in spatial memory. Exercise training increased hippocampal volume by 2%, effectively reversing age-related loss in volume by 1 to 2 y. We also demonstrate that increased hippocampal volume is associated with greater serum levels of BDNF, a mediator of neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.
Hippocampal volume declined in the control group, but higher preintervention fitness partially attenuated the decline, suggesting that fitness protects against volume loss. Caudate nucleus and thalamus volumes were unaffected by the intervention. These theoretically important findings indicate that aerobic exercise training is effective at reversing hippocampal volume loss in late adulthood, which is accompanied by improved memory function.
Deterioration of the hippocampus precedes and leads to memory impairment in late adulthood (1, 2). Strategies to fight hippocampal loss and protect against the development of memory impairment has become an important topic in recent years from both scientific and public health perspectives. Physical activity, such as aerobic exercise, has emerged as a promising low-cost treatment to improve neurocognitive function that is accessible to most adults and is not plagued by intolerable side effects often found with pharmaceutical treatments (3). Exercise enhances learning and improves retention, which is accompanied by increased cell proliferation and survival in the hippocampus of rodents (4–6); effects that are mediated, in part, by increased production and secretion of BDNF and its receptor tyrosine kinase trkB (7, 8).
Aerobic exercise training increases gray and white matter volume in the prefrontal cortex (9) of older adults and increases the functioning of key nodes in the executive control network (10, 11). Greater amounts of physical activity are associated with sparing of prefrontal and temporal brain regions over a 9-y period, which reduces the risk for cognitive impairment (12).
Further, hippocampal and medial temporal lobe volumes are larger in higher-fit older adults (13, 14), and larger hippocampal volumes mediate improvements in spatial memory (13). Exercise training increases cerebral blood volume (15) and perfusion of the hippocampus (16), but the extent to which exercise can modify the size of the hippocampus in late adulthood remains unknown.
To evaluate whether exercise training increases the size of the hippocampus and improves spatial memory, we designed a single-blind, randomized controlled trial in which adults were randomly assigned to receive either moderate-intensity aerobic exercise 3 d/wk or stretching and toning exercises that served as a control. We predicted that 1 y of moderate-intensity exercise would increase the size of the hippocampus and that change in hippocampal volume would be associated with increased serum BDNF and improved memory function.
News in the same category


11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending

Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence Based)
Occupational Bromide Exposure and the Development of Multiple Cherry Angiomas: Insights from a Case Report

How to Use Castor Oil to Regrow Eyelashes and Eyebrows

Three-Dimensional Video Gaming and Hippocampal Plasticity in Older Adults

Affectionate Touch, Oxytocin, and Women’s Stress and Cardiovascular Health

Raw Cabbage Juice and Rapid Healing of Peptic Ulcers: Early Clinical Evidence from Stanford

Montmorency Tart Cherry Juice as a Supportive Dietary Intervention in Ulcerative Colitis

Anemia: A Lesser-Known Side Effect of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?

Can Gray Hair Be a Sign That the Body Is Eliminating Cancer Cells?

A 95-Year-Old Cancer Expert with 60 Years of Research Reveals: Four Things You Must Avoid to Keep Cancer from Knocking on Your Door
Clinical Trials Show Meaningful Progress in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Medicinal Health Benefits of Garlic (Raw, Supplement) – Science Based
Colon Cleansing: How to Naturally Flush Your Colon at Home (Science Based)
7 Warning Signs of Lung Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

After a Stroke, Women Struggle With Daily Tasks for Longer Than Men
What causes night cramps and how to fix the problem

Thymoquinone and Breast Cancer Cell Suppression: Evidence from Preclinical Research
News Post

Even old, non-stick pans can be "revived" with just a few simple tips that everyone should know.
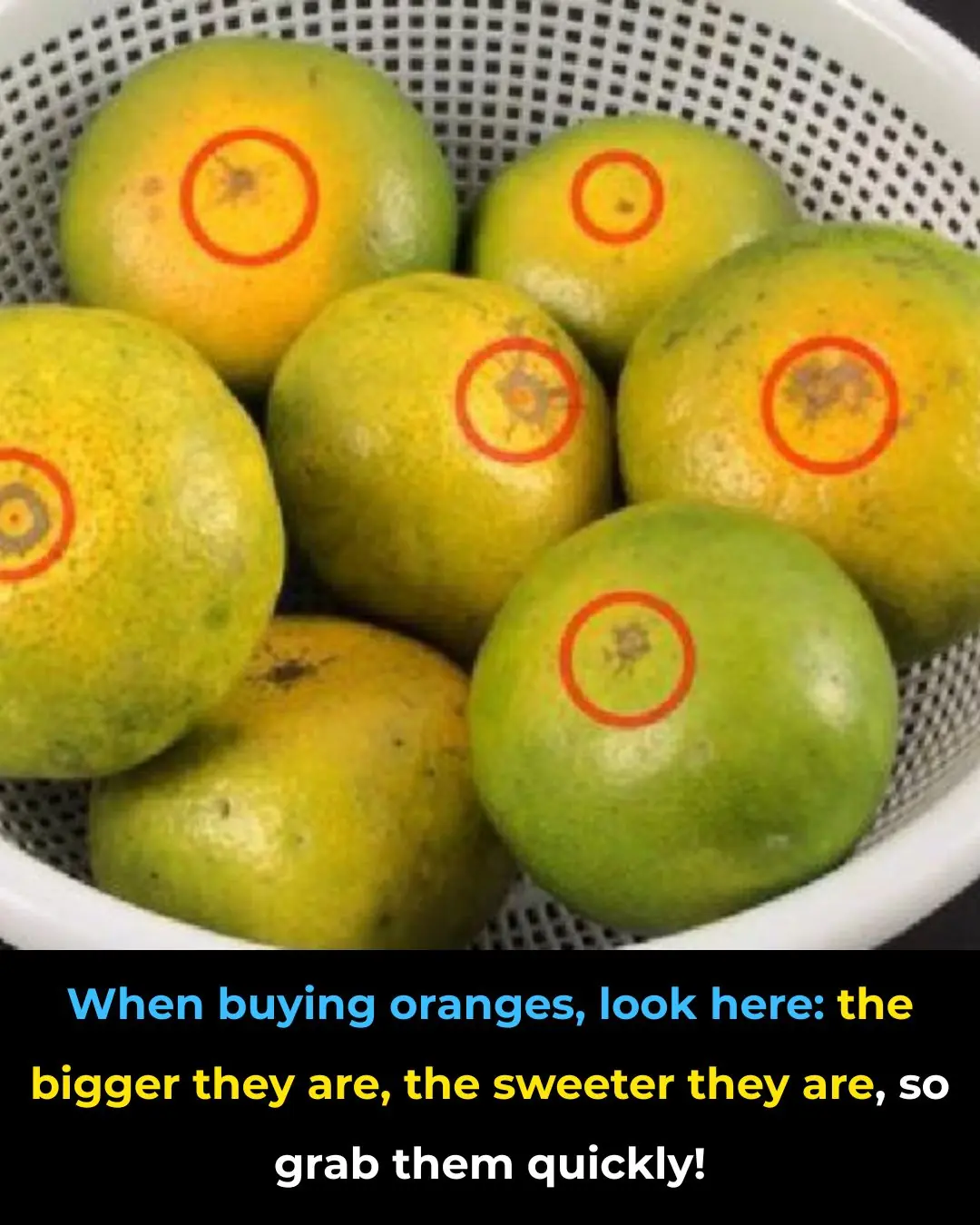

When buying oranges, look here: the bigger they are, the sweeter they are, so grab them quickly!

Tips for making sticky rice that cooks quickly without soaking the rice overnight, resulting in plump grains that remain soft and chewy even after a while.

10 signs you're not drinking enough water

Vinegar Consumption and Reduced Risk of Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stones: Evidence from a Pilot Human Study

11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending

Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence Based)

Occupational Bromide Exposure and the Development of Multiple Cherry Angiomas: Insights from a Case Report

How to Use Castor Oil to Regrow Eyelashes and Eyebrows

Three-Dimensional Video Gaming and Hippocampal Plasticity in Older Adults

Affectionate Touch, Oxytocin, and Women’s Stress and Cardiovascular Health

Raw Cabbage Juice and Rapid Healing of Peptic Ulcers: Early Clinical Evidence from Stanford

Montmorency Tart Cherry Juice as a Supportive Dietary Intervention in Ulcerative Colitis

DIY Flaxseed Gel Ice cubes for Clear Skin & Large Pores

Garlic and Honey for Cold, Cough & Acne

Beetroot Ice cubes for Glowing Skin

AN HOUR BEFORE THE CEREMONY, I OVERHEARD MY FIANCÉ WHISPER TO HIS MOM: ‘I DON’T CARE ABOUT HER—I ONLY WANT HER MONEY.’

AFTER 10 YEARS OF MARRIAGE, MY HUSBAND FOUND HIS ‘TRUE LOVE,’ HE SAYS. SHE’S DOWN-TO-EARTH AND DOESN’T CARE ABOUT MONEY. I JUST LAUGHED, CALLED MY ASSISTANT, AND SAID, ‘CANCEL HIS CREDIT CARDS, CUT OFF HIS MOTHER’S MEDICATION, AND CHANGE THE L

I had just landed, suitcase still in my hand, when I froze. There he was—my ex-husband—holding his secretary like they belonged together. Then his eyes met mine.
