
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer
Many people tend to overlook small, seemingly harmless changes in their mouths—thinking that a sore, a discolored patch, or slight numbness is nothing serious. However, these minor issues can sometimes signal a far more dangerous condition: oral cancer. This type of cancer often develops quietly, with few or no symptoms in its early stages, and by the time it's noticeable, it may have already progressed significantly.
People over the age of 40, especially those who smoke or consume alcohol regularly, are at higher risk. Even mild symptoms like persistent mouth sores, swelling, or difficulty swallowing should never be ignored. Early recognition and timely treatment can be the difference between life and death.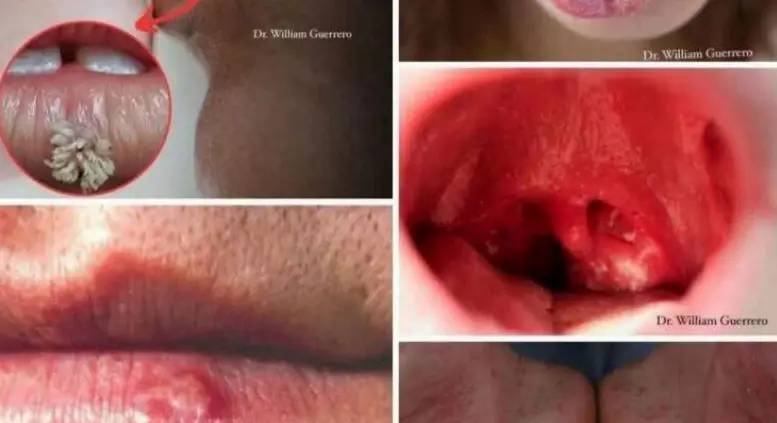
Understanding Oral Cancer: A Growing Concern in India
Oral cancer affects various parts of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, floor of the mouth, and the roof of the mouth. In India alone, over 77,000 new cases are reported annually, with more than 52,000 deaths—making it one of the country’s leading cancer-related causes of death. One major challenge is that oral cancer is often detected at a late stage, typically after it has spread to the lymph nodes or other nearby tissues.
That said, with early detection, the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival increase significantly. Awareness, regular check-ups, and attention to warning signs are crucial.
Types of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is not limited to one area. It can develop in different parts of the oral cavity, including:
-
Lip cancer
-
Tongue cancer
-
Gum cancer
-
Cancer of the inner cheek (buccal mucosa)
-
Floor of the mouth cancer
-
Cancer of the hard and soft palate
Each type may present slightly different symptoms, but all require immediate medical attention when signs appear.
When to See a Specialist
Prompt consultation with a dentist or oral cancer specialist is crucial if you notice any abnormal symptoms. Ideally, individuals should have oral check-ups at least twice a year, even if there are no apparent issues. Specialists like Dr. Sajjan Rajpurohit, a renowned expert in Delhi, offer comprehensive care focused on early detection and personalized treatment plans, which are key to improving patient outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer
While early-stage oral cancer may not show obvious signs, monitoring your oral health is particularly important if you fall into a high-risk category. Watch out for the following symptoms:
-
Persistent sores or blisters in the mouth that don’t heal
-
Red or white patches on the lips, gums, or inside the mouth
-
Swelling, lumps, or thickening in the mouth or neck
-
Unexplained bleeding
-
Loose teeth without clear dental causes
-
Difficulty or pain while chewing or swallowing
-
Numbness in the lips, tongue, chin, or neck
-
Chronic throat discomfort or hoarseness
-
Sudden and unexplained weight loss
-
Pain in the jaw or stiffness
-
Ear pain without hearing issues
-
Persistent dry mouth or burning sensation
-
Pain or discomfort in the tongue
If any of these symptoms persist for more than two weeks, seek a professional evaluation, especially if they do not respond to routine treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can significantly increase your risk of developing oral cancer:
-
Tobacco Use: This includes smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and chewing tobacco. Approximately 80% of oral cancer cases are directly linked to tobacco consumption.
-
Excessive Alcohol Use: Heavy drinking, especially when combined with tobacco use, multiplies the risk.
-
HPV Infection: Certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) are linked to oral cancers, especially in the back of the throat.
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Long-term neglect of oral health can increase vulnerability to infections and cancer.
-
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun without protection can lead to lip cancer.
-
Family History: A genetic predisposition to cancer may elevate the risk in some individuals.
-
Dietary Deficiencies: Low intake of fruits and vegetables can reduce the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
Stages of Oral Cancer
The stage of the cancer determines both the treatment approach and the likely prognosis:
-
Stage 1: Tumor is less than 2 cm (about 1 inch) and has not spread to lymph nodes.
-
Stage 2: Tumor measures 2–4 cm but still hasn't reached the lymph nodes.
-
Stage 3: Tumor is larger than 4 cm or has spread to one nearby lymph node.
-
Stage 4: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or distant organs, making treatment more complex.
Treatment Options
Oral cancer treatment varies depending on the type, location, and stage of the disease. Standard treatments include:
-
Surgery: Removal of the tumor is often the first line of defense. In some cases, reconstructive surgery may be necessary, using advanced techniques such as pedicle or free flap reconstruction.
-
Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to target and destroy cancer cells. Types include external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and brachytherapy, a more localized internal form.
-
Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs are used to kill cancer cells, often in combination with radiation for better results.
-
Targeted Therapy: This involves drugs designed to interfere with specific molecules involved in cancer growth, often producing fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
-
Immunotherapy: In some advanced cases, therapies that boost the body’s natural immune response to fight cancer may be recommended.
A multidisciplinary approach often yields the best outcomes, combining surgery, radiation, and drug therapy depending on the patient’s condition.
Key Facts and Statistics
-
Over 80% of oral cancer cases are preventable with lifestyle changes.
-
The average age of diagnosis is around 50 years, but younger individuals are increasingly being diagnosed, especially due to HPV-related cancers.
-
Men are twice as likely as women to develop oral cancer.
-
Early detection increases survival rates up to 82%, while late-stage detection drops survival rates to just 27%.
-
Regular screening can detect abnormalities long before symptoms appear.
Why Early Detection Matters
In countries like India, oral cancer often goes undiagnosed until it reaches an advanced stage—largely due to a lack of awareness, delayed medical consultation, and limited access to specialized care in rural areas. Educating the public and encouraging regular dental visits can play a major role in reversing this trend.
By paying attention to early warning signs, making smart lifestyle choices, and seeking prompt medical advice, individuals can drastically improve their chances of recovery and reduce complications.
Conclusion
Oral cancer is a silent but deadly disease that can affect anyone, but it’s also one of the most preventable and treatable cancers—if caught early. Don’t ignore persistent sores, unusual patches, difficulty swallowing, or any unexplained changes in your oral health. Regular dental visits, awareness of personal risk factors, and early screening are essential tools in the fight against oral cancer. Staying proactive is the most effective way to protect your health and your future.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with any concerns you may have regarding a medical condition.
News in the same category

7 Signs of Arthritis You Shouldn't Ignore
When your liver is bad, these parts start to hurt
Top 12 ways to quickly improve blood circulation in legs
Tingling Sensation In Your Body: Why Does It Happen
5 Breast Cancer Signs You’ve Never Heard Of — But Shouldn’t Ignore

YOUR BODY’S SCREAMING FOR HELP — DON’T IGNORE THESE HIDDEN DEFICIENCY SIGNS
SUBTLE WARNING SIGNS OF CLOGGED ARTERIES AND HOW TO UNCLOG THEM NATURALLY

Scientists have just uncovered a game-changing reason to eat an egg every day

What Happens If You Eat 4 Whole Eggs a Day for 30 Days?

The Most Powerful Anti-Cancer Food You’ve Probably Never Tried

How to Use Frozen Lemon to Help Combat Malignant Tumors in the Body

Vitamin K2: The Underrated Nutrient That Protects Your Heart and Arteries
DENTISTS HATE HOW SIMPLE THIS TEETH WHITENING HACK IS

What Happens to Your Body When You Stop Eating

The #1 Drink to Prevent Foamy Urine — Plus 7 More Your Kidneys Will Thank You For
The #1 Most Effective Remedy for Dental Plaque (And How to Beat Tartar at Home)

JUST 1 CUP FLUSHES POUNDS OF TOXIC WASTE
News Post

The Powerful Health Benefits of Papaya Seeds: Why You Should Include Them in Your Diet

The Wonderful Hazel Tree (Corylus avellana): Nutrition, Healing, and Traditional Uses of Every Part

Boiling a Whole Avocado: The Secret to Softness, Nutrition, and a Delicious Baked Recipe

The Hidden Healing Power of Papaya Leaves

Sugar Apple (Annona squamosa): A Sweet Fruit with Powerful Health Benefits

If you find a centipede at home, here is what it means...

Why We Feel That Little Electric Sh0ck When We Touch Another Person—Science Explains

If a Man Doesn’t Appreciate You, Here’s What You Should Do
25 Worrying Signs Your Body Is Trying to Warn You of Serious Health Problems (and What to Do About Them)

The Hidden Power of Lactuca serriola Root (Prickly Lettuce Root)

Why You Should Stop Waking Up to Urinate

4 types of vegetables are full of parasites but many people still eat them raw every day

Maple Trees from Root to Crown: A Complete Guide to Every Edible Part

7 Signs of Arthritis You Shouldn't Ignore

California Poppy: Nature’s Gentle Remedy for Relaxation and More

What is its purpose. see details

When a woman stops loving a man, she begins…

5 hygiene mistakes that many people make... but no one dares to talk about...
