
Honeybee Venom Shows Promise Against Aggressive Breast Cancer Cells: What Scientists Have Discovered
Honeybee Venom Shows Promise Against Aggressive Breast Cancer Cells: What Scientists Have Discovered
Australian scientists have uncovered a remarkable finding that may shape the future of cancer research. A new study from the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and The University of Western Australia reveals that honeybee venom—specifically a compound within it called melittin—can rapidly destroy aggressive breast cancer cells in laboratory tests. Although this research is still in its early stages, it opens the door to exciting possibilities for developing new, targeted cancer treatments.
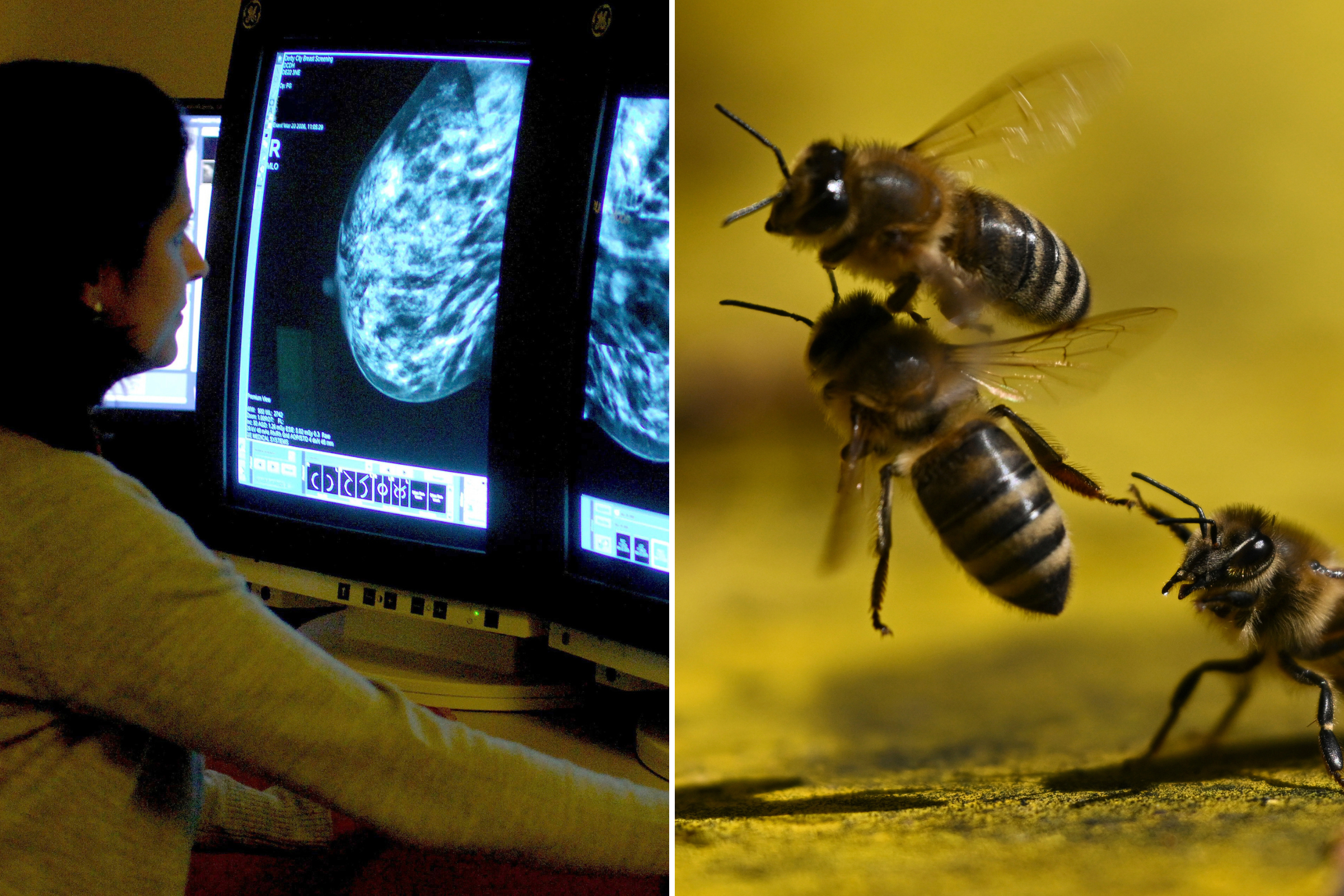
A Breakthrough for Hard-to-Treat Breast Cancer Types
The researchers focused on some of the most challenging forms of breast cancer, including:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
-
HER2-positive breast cancer
These cancer subtypes are known for their resistance to many standard therapies, leaving patients with fewer treatment options. According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), triple-negative breast cancer, in particular, tends to grow and spread more aggressively than other forms, making it a major priority for new drug development.
In controlled laboratory experiments (in vitro studies), the venom and melittin demonstrated the ability to break down the membranes of cancer cells, effectively killing them. Even more promising, the melittin peptide showed a level of selective toxicity, damaging cancer cells while leaving most healthy cells unharmed.
Why This Discovery Matters
The potential of honeybee venom lies in several key advantages:
-
Rapid action: Melittin worked quickly in lab tests to disrupt cancer cell survival.
-
Targeted potential: Scientists hope melittin could eventually be engineered to target tumor cells more precisely.
-
Natural compound innovation: The study highlights how naturally occurring substances may complement modern cancer therapy approaches.
Organizations such as Cancer Research UK and the American Cancer Society have long emphasized the importance of investigating natural compounds, as many current cancer drugs were originally derived from plants, microbes, or other organisms.
This research adds honeybee venom to the growing list of natural substances with potential medical value.
Still Early—But Filled With Promise
Although the results are impressive, it's important to understand the context:
-
The findings are limited to laboratory (in vitro) experiments.
-
The method has not been tested in animals or humans yet.
-
There is no evidence that raw bee venom or bee stings offer any medical benefit—these can be dangerous and cause severe allergic reactions.
Experts from the Harry Perkins Institute emphasize that much more work is needed before this approach can be translated into safe cancer therapies. Additional research will determine how melittin can be delivered, how it interacts with other treatments, and whether it can be used without harming healthy tissues.
A Growing Role for Nature-Derived Cancer Innovations
This study strengthens the argument that nature-based compounds may inspire the next generation of cancer medicines. By examining molecules like melittin, scientists hope to develop:
-
More precise and less toxic cancer treatments
-
New therapeutic options for resistant cancer types
-
Safer ways to target tumor growth without damaging healthy tissue
As oncology research continues to evolve, discoveries like this help fuel scientific innovation, offering hope for advancements that could one day lead to life-saving therapies.
News in the same category


How Just Six Minutes of Reading Can Significantly Reduce Stress: What Science Really Says

Italy Becomes the First Country to Ban Cultured Meat: Tradition vs. Innovation

The Woman Who Donated Over 2,600 Litres of Breast Milk: Alyse Ogletree’s Record-Breaking Act of Compassion

How COVID-19 Vaccines Saved Millions of Lives: A Global Triumph of Science

Scarface: The Legendary Lion Whose Battle Scars Captivated the World

China Launches the World’s First Commercial 10G Home Broadband Network

New York City Is Gradually Sinking: Research Reveals Rising Risks from Subsidence and Sea-Level Rise

Japan's TRG 035 Drug Could Revolutionize Dental Care by Regrowing Human Teeth

Breakthrough Stem Cell Treatment Helps Paralyzed Man Stand and Begin Walking Again

Germany Develops AI-Enhanced Cockroach Bio-Robots for Advanced Surveillance

Guava Molecule Shows Promise in Fighting Liver Cancer, Researchers Find

Learning Without Stress: How Finland Built One of the World’s Best School Systems

Frog Weddings and Floods: Ancient Traditions in the Face of Nature's Power

Israel’s Innovative Smart Water Pipes: Revolutionizing Water Infrastructure and Renewable Energy Generation

Jorge the Loggerhead Turtle: A Story of Rehabilitation, Freedom, and Remarkable Resilience

Revolutionary Discovery: Reprogramming Cancer Cells to Restore Health and Transform Treatment

Canadian Scientists Develop Mini Robot to Treat Kidney Stones Without Surgery

🚿 8 Bathroom Habits That Ruin Your Feeling of Freshness (And How to Fix Them)
News Post

Gene Editing Shows Promise in Repairing Damaged Hearts

Your Skeleton Is Constantly Renewing Itself: The Hidden Power of Bone Remodeling

The Story of Two Exhausted Surgeons After a 32-Hour Operation: A Symbol of Sacrifice in Medicine
If I had insulin resistance again, here’s the exact plan I’d follow to fix it fast

How Just Six Minutes of Reading Can Significantly Reduce Stress: What Science Really Says

Octopuses Can Recode Their RNA: A New Frontier in Marine Adaptation and Intelligence

10 Easy Home Remedies to Help Alleviate Gum Disease

My Nana Shared This Trick That Stops Ants in the Garden in Just 1 Minute With Zero Effort — Here’s How It Works
Interesting

Meet Eva Woolridge, the Award-Winning Photographer Using Her Lens to Reclaim Power, Joy, & Identity
Health Alert: 6 Black-Colored Body Changes That May Signal a Serious Disease — Don’t Ignore Them

5th Grader Sports ‘Bigger and Better’ Afro After Being Teased About Her Hair At School

Principal Creates Barbershop In School To Connect With Students By Cutting Their Hair

My Nana’s 5-Minute Freezer Defrosting Hack (Zero Effort Needed)

You’re Doing It All Wrong: Here’s the Right Way to Warm Up a Cold Bed

How to Remove Stubborn Toilet Water Rings: Simple, Effective, and Science-Backed Solutions

They Just Opened Newark, New Jersey’s First Black-Owned Drive Thru Movie Theater To Celebrate Black Culture

You’re Doing It All Wrong: Here’s the Right Way to Drink 8 Glasses of Water a Day
