
How Guyana Became the Only Nation Fully Self-Sufficient in All Seven Major Food Groups
Guyana's Agricultural Self-Sufficiency: A Model for Food Security in the 21st Century
Guyana, a small yet rapidly developing country in South America with a population of less than one million, has recently garnered significant attention for its remarkable achievements in agricultural self-reliance and food security. This small nation, nestled along the northeastern coast of South America, has proven that even countries with limited resources can achieve impressive levels of food self-sufficiency when backed by strategic government policies, sustainable practices, and strong local agricultural traditions.
Achieving Full Food Self-Sufficiency
Recent reports from international development agencies, including the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), highlight Guyana as one of the few countries in the world that has succeeded in producing enough food to meet all the dietary needs of its population. Notably, Guyana has been recognized as the only country among 186 surveyed to be self-sufficient in all seven major food groups: grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy, protein, oils, and legumes. This achievement is especially impressive considering that many nations, particularly in the industrialized world, struggle to meet their food demands domestically due to climatic, economic, or logistical challenges.
The self-sufficiency claim made by Guyana has been substantiated by assessments conducted by international organizations and regional think tanks that study food security. These reports reveal that Guyana’s agricultural output includes large-scale production of key staples such as rice, vegetables, fruits, and livestock, as well as seafood. Additionally, the country is known for its vibrant, sustainable fishing industry, which plays a crucial role in the nation's overall food production system. Guyana’s diverse farming methods, which blend traditional agricultural practices with modern techniques, have enabled it to produce an impressive variety of foods, ensuring that all major food groups are met locally.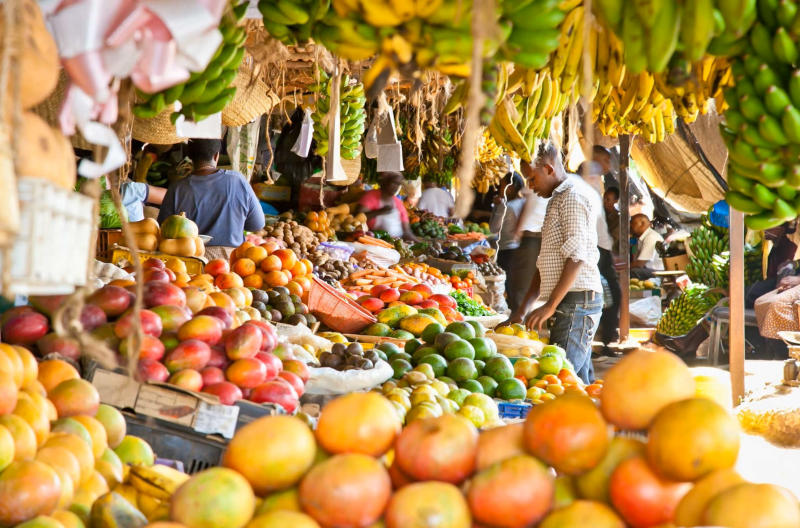
Government Policy and Investments in Agro-Processing
One of the main driving forces behind Guyana’s success in food self-sufficiency is its government-led food policies. These policies have encouraged investment in agro-processing and sustainable agricultural practices. The government has placed a strong emphasis on land use management and the promotion of environmentally friendly farming techniques. Additionally, infrastructure projects aimed at improving access to markets for farmers have played a pivotal role in boosting agricultural productivity and food security.
Another key component of Guyana's food security strategy is its participation in CARICOM’s “25 by 2025” initiative, a regional effort aimed at reducing food imports in the Caribbean by 25% by the year 2025. This initiative not only promotes food self-sufficiency within the region but also underscores Guyana’s commitment to sustainable agricultural practices and regional collaboration.
The Role of Indigenous Knowledge
In addition to modern farming methods, indigenous and traditional farming knowledge has played a crucial role in Guyana’s agricultural success. Indigenous communities in Guyana have long relied on a combination of farming, fishing, and forest management practices that have been passed down through generations. These practices, which emphasize the use of local resources and sustainable methods, have contributed to the country's agricultural resilience. As part of this, Guyana has also embraced agroforestry, integrating tree planting with crop production to enhance biodiversity and protect soil health.
The blending of modern science and indigenous wisdom has helped Guyana maintain a sustainable food system capable of meeting the needs of its growing population. The country’s agriculture ministry has worked closely with indigenous groups to integrate their knowledge into national policies and agricultural projects, ensuring that the benefits of these practices are shared across the population.
A Contrasting Global Landscape
While Guyana's achievements in agricultural self-sufficiency are notable, they are in stark contrast to many highly industrialized nations, which continue to rely heavily on food imports. Industrialized countries often depend on global supply chains to meet their food demands, especially for products such as dairy, fruits, and grains, due to climate or land limitations. In many parts of the world, land degradation, water scarcity, and climate change further complicate efforts to increase food production domestically.
For example, countries in Europe and North America, despite their advanced agricultural systems, import large quantities of food to ensure that their diverse populations have access to all the necessary food groups. By contrast, Guyana has largely avoided such dependencies, making it an exceptional case of food sovereignty in today’s interconnected world.
The Global Implications for Food Security
Guyana’s model of food self-sufficiency offers valuable lessons for other nations struggling with food security, particularly as climate change increasingly disrupts global agricultural patterns. Guyana’s ability to adapt to challenges by combining sustainable farming with government investment and indigenous knowledge could serve as a blueprint for countries seeking to strengthen their own food systems in the face of global uncertainties.
While Guyana's agricultural success is undeniably impressive, it also raises important questions about the future of food production and consumption on a global scale. How can other nations replicate Guyana’s success? What role will sustainable farming and local food systems play in ensuring food security for all?
As the world’s population continues to grow, and as climate change intensifies, countries like Guyana may become increasingly important models for promoting food sovereignty and sustainable agriculture on a global scale.
News in the same category


When a Woman Bites Her Lip While Staring at You, It Means She Is ...

3 flowers that make snakes tremble with fear — beautiful and safe to plant around your home

Meet Jonathan: The 192-Year-Old Tortoise Who Has Witnessed History and Continues to Inspire

Retired Couple in UK Successfully Nurtures 90-Million-Year-Old Wollemi Pine, Leading to Its First Reproduction Outside Australia

Stem Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Shows Promise in Human Clinical Trials
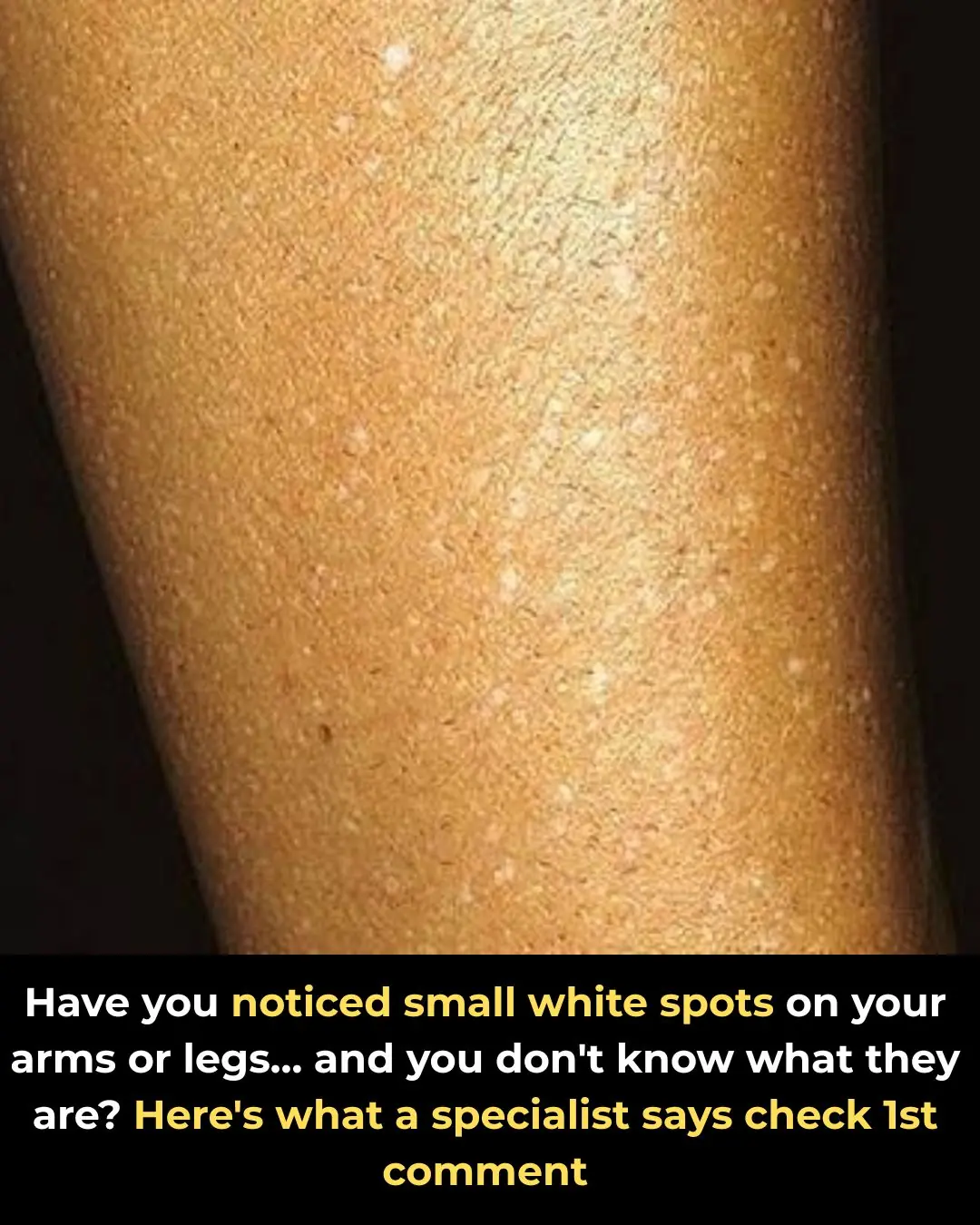
Have you noticed small white spots on your arms or legs… and you don't know what they are?

Donald Trump's new scarf leaves everyone saying the same thing

Scientists May Have Just Found a Breakthrough Hair-Loss Treatment

Genetic Evidence Links Icelanders to Native Americans, Suggesting Viking Contact with the Americas

Vietnam Approves Russian-Made Cancer Immunotherapy ‘Pembroria’ for Multiple Cancer Types

Hayli Gubbi Volcano Erupts in Ethiopia for First Time in 12,000 Years

Mia Khalifa at Oxford: A Controversial Talk on Redemption, Reinvention, and Second Chances

Breaking Bob: How a 75-Year-Old Turned a Five-Minute Smoke Break into a Viral NYC Spectacle

The Night Google.com Was Accidentally Sold for $12: A Story of Integrity and Goodwill

After 12 Millennia of Silence, Ethiopia’s Hayli Gubbi Volcano Erupts Dramatically

When a Woman Bites Her Lip While Staring at You, It Means She Is ...

How Europe Says "Street": A Multilingual Journey Through Language and Culture
News Post

How to Get Rid of Bad Breath (Halitosis): Scientifically Proven Home Remedies

Frozen Pork? Don’t Soak It in Water! Use This Trick to Thaw in 10 Minutes and Keep It Fresh

Clothes Turning Yellow? This Simple Trick Will Make Them Bright White Again

Tried this the other day and it did wonders!
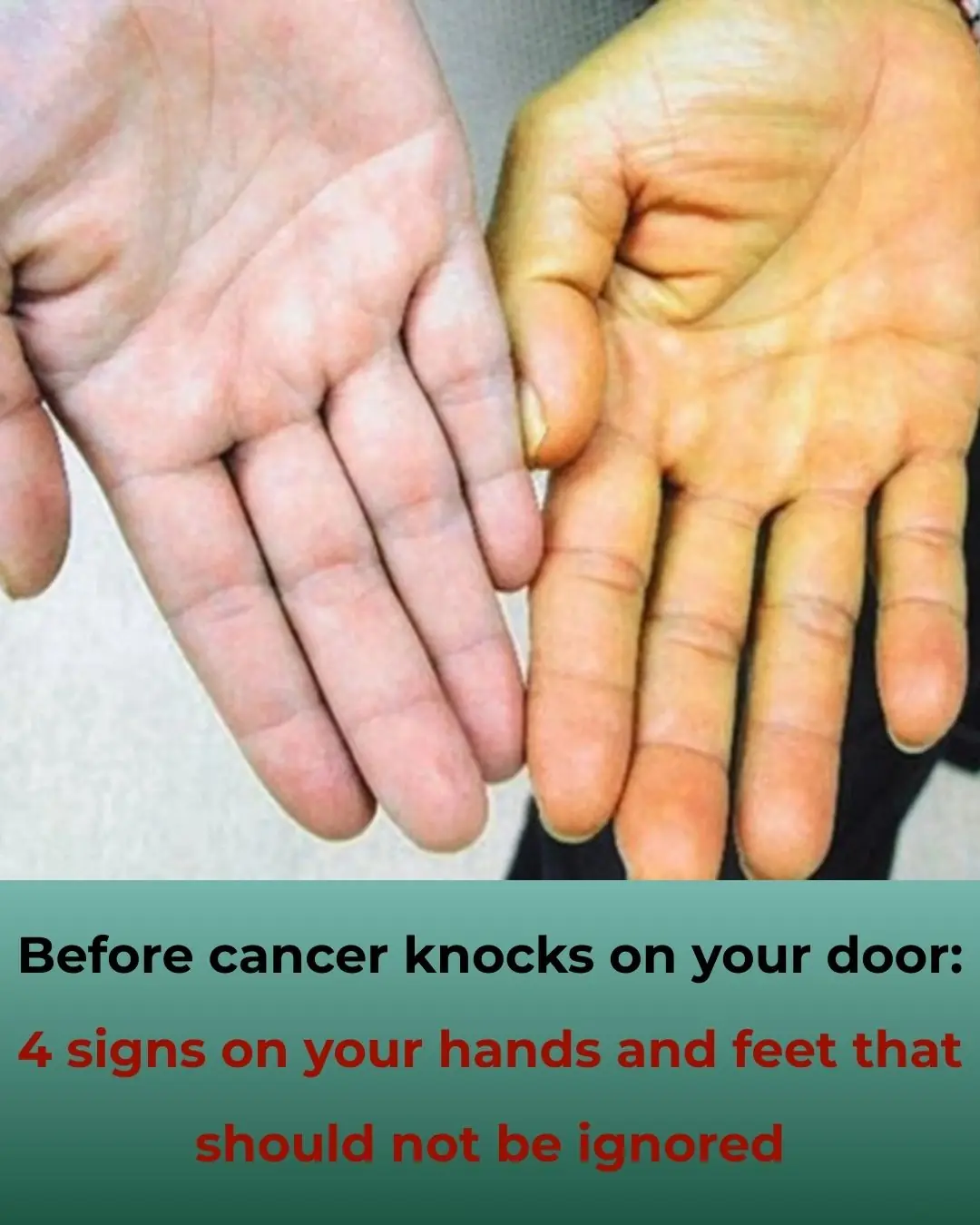
4 Warning Signs on Hands and Feet You Should Not Ignore Before Cancer Strikes

7 Drinks to Cleanse Phlegm, Boost Lung Health, and Combat Bacteria and Viruses
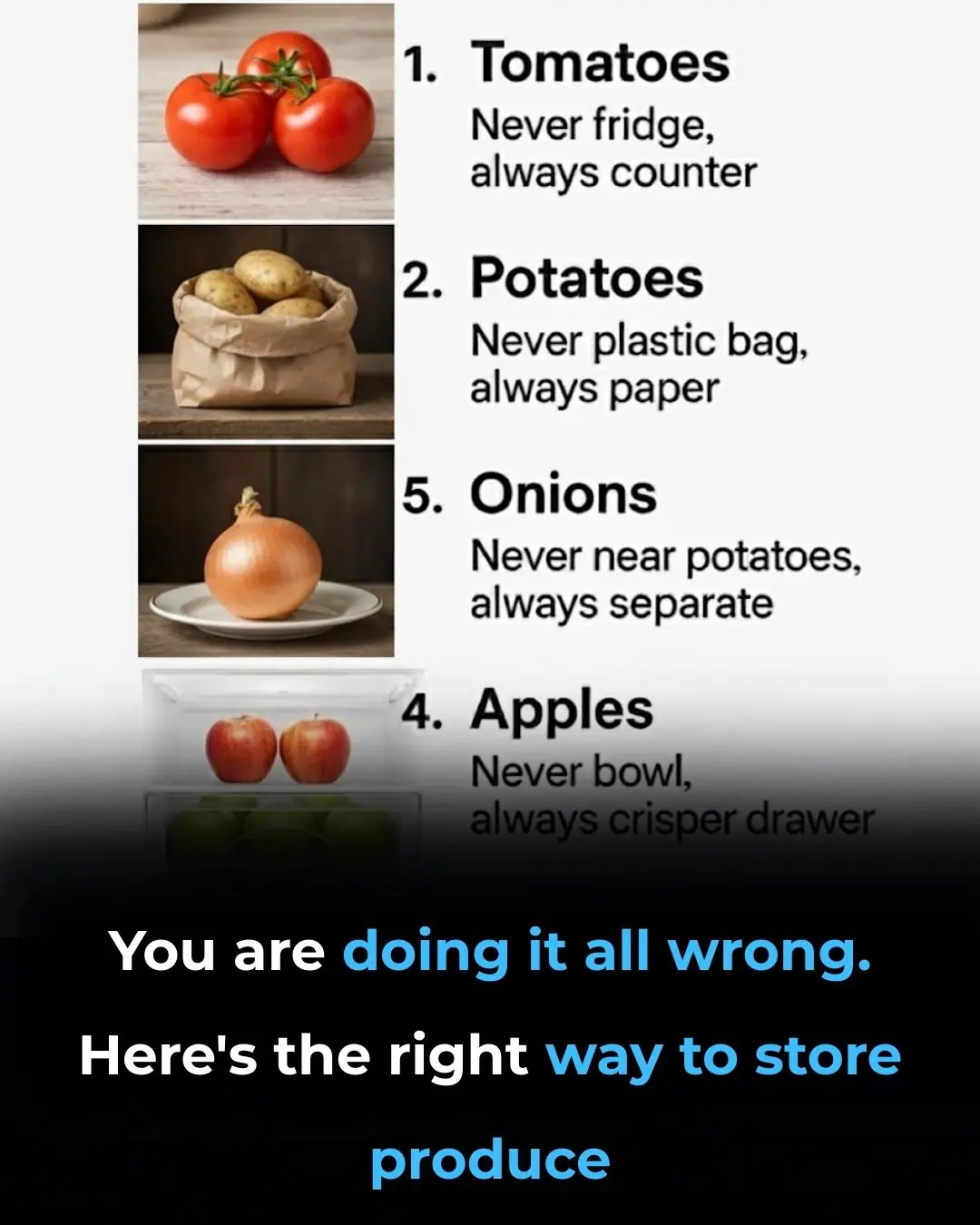
You are doing it all wrong. Here's the right way to store produce

How to Clean a Showerhead to Prevent Clogging: Simple Tips to Keep It Working Like New Without Spending on Replacements

The Health Benefits of Black Bean Soup with Chicken Feet: As Effective as Ginseng

Goodbye Cavities? A Future Where Teeth Heal Themselves May Be Closer Than We Think

Got High Blood Pressure? Try This 2-Ingredient Tea!

She Lost Half Her Brain — But Rebuilt an Entire Life

Bone Cancer: The Silent Destroyer That Strikes From Within

Put a drop of essential oil on clothes while soaking: "Special" use, not everyone knows how to apply it

Tips for using air conditioners, staying cool all day without worrying about skyrocketing electricity bills

How to stew delicious braised meat with Northern style, great to eat with rice in cold weather

10 ways to get rid of cockroaches from your home permanently, simple, safe and economical

How to fry delicious, crispy spring rolls that won't get soggy: Remember not to put them in boiling oil right away.

Smart people always put a towel in the refrigerator, knowing its uses everyone wants to learn from it.
