
Merck Was Injecting Girls With Aluminum But Told Them It Was A Saline Placebo: This Is Why It's Called "Big Pharma"
The HPV Vaccine: Controversies, Misleading Practices, and Public Safety Concerns

The HPV vaccine, developed by Merck, stands as one of the pharmaceutical giant's highest-grossing products, generating billions of dollars in revenue every year. However, new revelations have come to light that cast a shadow on its development and clinical trials, pointing to a pattern of potentially misleading practices and concerning safety claims.
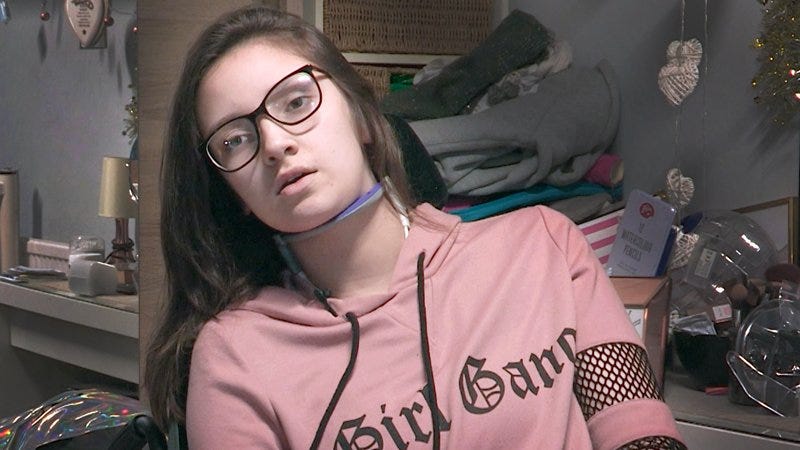
Ruby Shallom’s Story: A Personal Tragedy
Ruby Shallom’s life was dramatically altered by the HPV vaccine. In 2014, she suffered a severe reaction to the vaccine, and by 2016, she had become almost completely paralyzed, with only limited movement in her left hand. After enduring intense physical therapy, she has managed to regain some mobility, occasionally walking short distances. Her story, documented in the Sacrificial Virgins documentary, highlights the tragic side effects that some individuals have experienced after receiving the HPV vaccine.
The Dark Side of "Big Pharma"
The term “Big Pharma” is often dismissed by critics as mere rhetoric, but for many, it’s a term that captures the long history of criminal activities within the pharmaceutical industry. Merck, in particular, has faced scrutiny for its aggressive marketing and the questionable ethics surrounding its HPV vaccine.
For example, between 2002 and 2010, Pfizer was fined $3 billion for criminal activities, civil penalties, and jury awards, setting records for both criminal fines and total penalties. Despite these widespread transgressions, it wasn't until the COVID-19 pandemic that the general public became more aware of such practices. As Robert G. Evans, PhD, an emeritus professor at the Vancouver School of Economics, noted, large corporations often treat criminal and civil penalties as "business expenses," calculating them against the profits they gain from illegal behavior. In contrast, when individuals commit crimes, the consequences are far more severe, including imprisonment.
Merck's case isn't classified as "criminal" per se, as federal health authorities believe aluminum adjuvants, such as those used in vaccines, are completely safe, but troubling questions remain about the practices surrounding the HPV vaccine.
What Went Wrong in Merck's HPV Vaccine Trials?
A revealing study, published in the International Journal of Risk & Safety in Medicine, delves into Merck’s controversial clinical trials for its Gardasil vaccine. The study reveals how Merck misled participants in its Gardasil FUTURE II trial, leading them to believe that the placebo they were receiving was a harmless saline solution. However, the placebo actually contained an adjuvant called amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate (AAHS), which is far more potent and reactive than traditional aluminum adjuvants.
The trial's consent form clearly stated that one half of participants would receive the active vaccine while the other half would receive a "placebo vaccine," implying the placebo was inactive. Yet, the adjuvant used in the placebo was not inert at all. As a result, several participants experienced chronic and disabling symptoms, including those who were placed in the "placebo" group.
Merck’s misleading trial materials and failure to disclose the true nature of the placebo compromised the informed consent process, a critical ethical aspect of any clinical trial. Dr. Peter Doshi, a senior editor at the British Medical Journal, uncovered similar issues upon reviewing clinical trial reports from the European Medicines Agency, raising significant concerns about the transparency and integrity of these studies.
Merck’s Response to the Controversy
Merck’s official stance has been that its AAHS formulation is proprietary, and to this day, the company has refused to provide independent researchers with samples for further testing. As a result, the full composition of AAHS remains unknown, raising further questions about the safety and transparency of the HPV vaccine. Despite Merck’s assurances, independent experts, including Dr. Peter Doshi, have criticized the use of AAHS in placebo trials, calling it unethical and potentially misleading in assessing the safety of the vaccine.
The Hidden Dangers of Aluminum in Vaccines
Aluminum is a known neurotoxin, and its inclusion in vaccines as an adjuvant has raised alarms for decades. While aluminum is widely used in various industrial applications, its biological effects are a cause for concern when it is introduced into the human body via injection. Unlike aluminum consumed through food, which is processed and expelled by the digestive system, aluminum injected directly into the bloodstream behaves differently, accumulating in tissues and potentially causing long-term damage.
Fact-checkers have often downplayed these concerns, comparing the amount of aluminum in vaccines to the aluminum found in canned food. However, this analogy is misleading, as it fails to account for the vastly different ways in which aluminum behaves in the body when injected versus ingested.
The concerns over aluminum's safety are not without merit. Researchers have found that aluminum adjuvants can trigger severe systemic adverse reactions, including chronic autoimmune disorders, neurological damage, and more. As Dr. Lucija Tomljenovic, one of the leading researchers in this area, points out, using an adjuvant that can independently cause adverse reactions invalidates the concept of a placebo-controlled trial, making it impossible to assess the vaccine’s true safety.
Questions About the Necessity of the HPV Vaccine
The HPV vaccine is heavily promoted as a preventive measure against cervical cancer, but several studies have cast doubt on the vaccine’s ability to prevent this disease. A study published in The Royal Society of Medicine analyzed the phase 2 and 3 trials conducted to assess the vaccine’s efficacy and found significant uncertainties in the data. The authors emphasized that the trials were not designed to detect cervical cancer, which typically takes decades to develop, and thus the vaccine’s long-term efficacy remains uncertain.
Moreover, it’s important to note that the vast majority of HPV infections do not lead to cancer. In fact, approximately 70% of women who contract an HPV infection will clear it naturally within a year, and 90% of infections resolve within two years. Only a small percentage of these infections progress into precancerous lesions, and even fewer will develop into invasive cervical cancer over the course of several decades.
Dr. Diane Harper, a leading expert in OB/GYN who helped design and carry out the clinical trials for Gardasil, stresses that the progression from CIN3 lesions to invasive cervical cancer is a slow process, taking decades in most cases. This suggests that the urgency surrounding the HPV vaccine may be overstated.
Adverse Reactions and Ongoing Injuries
Numerous reports of adverse reactions to the HPV vaccine have emerged over the years. Researchers at Mexico’s National Institute of Cardiology reviewed 28 studies, including randomized trials and post-marketing case series, and found evidence of severe injuries, including permanent disabilities and even deaths following vaccination with Merck's HPV vaccines.
The tragic case of 14-year-old Christopher Bunch, who passed away after receiving the HPV vaccine, exemplifies the risks some individuals face. His parents claim that the vaccine directly led to his death, and his mother even started a petition to raise awareness of the potential dangers of the vaccine. Despite these personal stories, Merck and health authorities continue to insist on the vaccine’s safety, pointing to evaluations conducted by organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). However, many question whether these evaluations are truly independent and comprehensive.
The Ongoing Controversy
The debate over the HPV vaccine has sparked numerous lawsuits and injury claims. Despite the mounting evidence of potential risks and the ongoing controversy, mainstream media often dismisses concerns as "anti-vaccine pseudoscience," while labeling legitimate scientific critiques as conspiracy theories. This pattern of suppressing dissenting voices is not new and mirrors the tactics used during the COVID-19 pandemic, when many experts and critics were silenced through media campaigns funded by pharmaceutical interests.
Dr. Arnold Seymour Relman, a Harvard professor of medicine and former editor-in-chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, famously said, “The medical profession is being bought by the pharmaceutical industry, not only in terms of the practice of medicine but also in terms of teaching and research.” His words reflect the growing influence of pharmaceutical companies on academic and medical institutions, raising serious ethical concerns about the integrity of health policy and research.
The Need for Informed Consent
As we continue to evaluate the benefits and risks of the HPV vaccine, it is crucial that we prioritize informed consent and open, transparent discussions. The risks and benefits should be weighed carefully, and individuals should have access to unbiased information to make informed choices about their health.
While vaccines undoubtedly play a crucial role in preventing diseases, it is equally important to address the ethical and safety concerns surrounding their development and administration. Informed consent is a fundamental human right, and it should never be compromised for the sake of profit or political agendas.
News in the same category


Red and Processed Meat Consumption Increases Cancer Risk, Experts Warn

The Hidden Dangers of Eating Leftover Food Stored Overnight

Two Rare Neurologic Disorders Added to US Newborn Screening Panel

Intensive Long-Distance Running and Colon Health: Emerging Evidence of Increased Risk for Advanced Adenomas
After Many Years of Practice, Doctors Noticed Six Common Morning Habits Among Cancer Patients

Six Foods That May Help Prevent Colorectal Cancer — Especially After Age 45
How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs
Why Your Legs Cramp At Night And How To Stop It From Happening
1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally
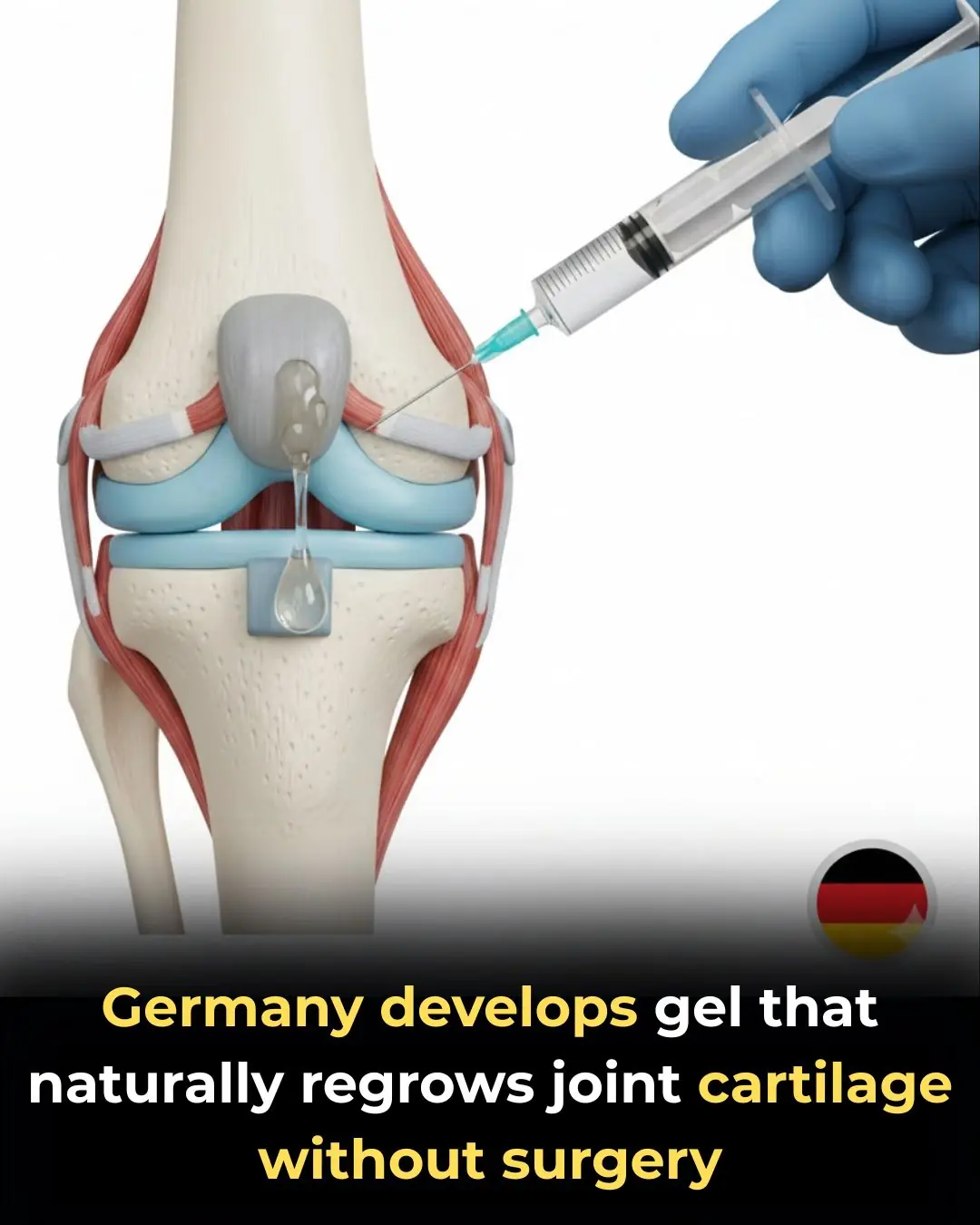
Revolutionary science is changing how we treat joint damage.

Don't be fooled by their supposed health benefits; these 3 fruits are secretly damaging your liver

Early signs of stroke should not be ignored, regardless of age

Surprising Health Benefits of Eating Ginger Every Day

Bizarre theories about people who have ‘never broken a bone’
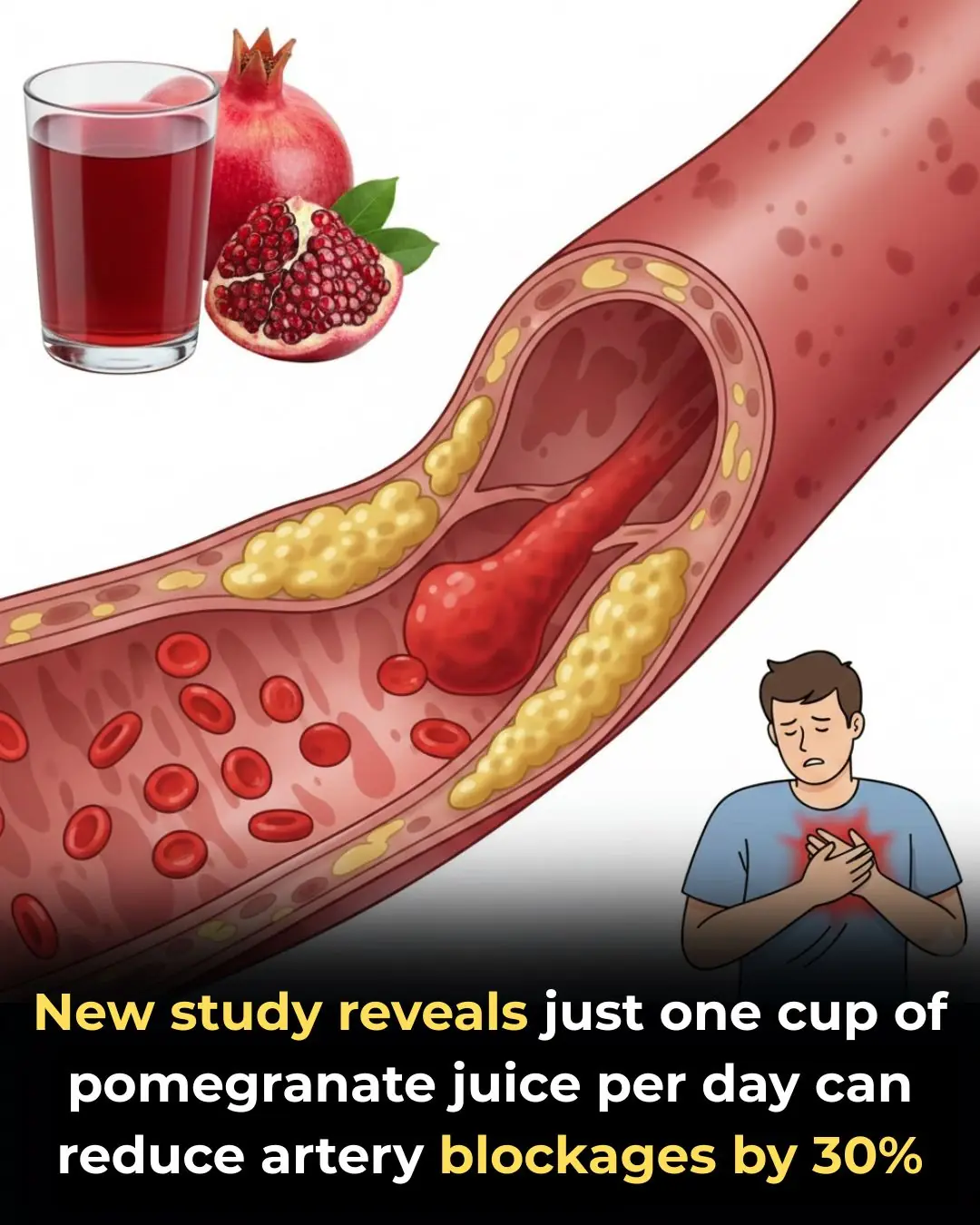
The Cardiovascular Benefits of Pomegranate Juice: Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms

One Person Washes the Dishes, the Whole Family Faces Cancer Risk?

Rising Stroke Rates: Doctors Warn Against Overusing Four Common Foods
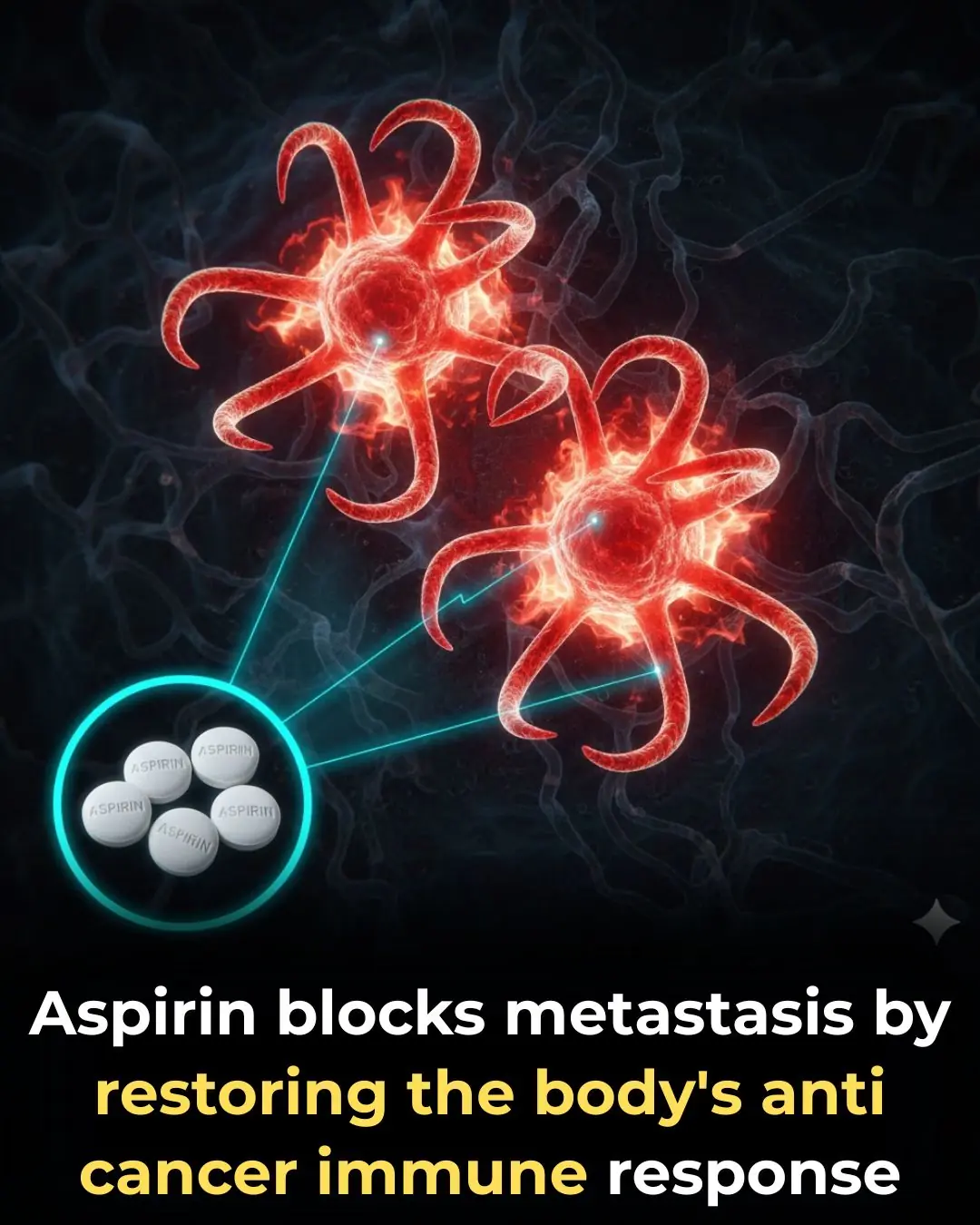
Aspirin May Help Stop Cancer From Spreading, Study Finds

A 53-Year-Old Man Diagnosed With Liver Cancer: Doctors Warn About the Top 3 Behaviors That Severely Damage the Liver
News Post

Measles Cases Hit 30-Year High in the US, Raising Urgent Public Health Concerns

Why Skipping Housework on New Year’s Day Might Bring You Good Luck

Five Simple Drinks That Help Eliminate Uric Acid and Prevent Gout Flare-Ups

Your method isn't quite right. Here's the correct way to maintain a clean home.

Red and Processed Meat Consumption Increases Cancer Risk, Experts Warn

The Hidden Dangers of Eating Leftover Food Stored Overnight

Two Rare Neurologic Disorders Added to US Newborn Screening Panel

Breaking Through the Stigma as Access to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Expands

Intensive Long-Distance Running and Colon Health: Emerging Evidence of Increased Risk for Advanced Adenomas

141 years, one legendary life 🐢💚 Read Gramma’s incredible

High school football coach facing charges for allegedly hitting and choking players

After Many Years of Practice, Doctors Noticed Six Common Morning Habits Among Cancer Patients

Six Foods That May Help Prevent Colorectal Cancer — Especially After Age 45

Don't put the scallions straight into the refrigerator after buying them; follow this method, and they'll last for a whole month without spoiling.

How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs

Why Your Legs Cramp At Night And How To Stop It From Happening

1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally

Revolutionary science is changing how we treat joint damage.

Millie Bobby Brown’s Reaction to Eleven’s Ending Goes Viral After Stranger Things Finale
