New Discovery: Protein AP2A1 May Hold the Key to Reversing Aging at the Cellular Level
New Discovery: Protein AP2A1 May Hold the Key to Reversing Aging at the Cellular Level
A groundbreaking new study has uncovered a protein that could revolutionize our understanding of aging — and potentially how we fight it. Scientists have identified AP2A1, a protein that plays a critical role in how cells age and, more importantly, how they might reverse the aging process.
As we age, many of the cells in our body begin to function less efficiently. One common sign of cellular aging is an increase in cell size. These enlarged, non-functioning cells contribute to many age-related diseases, but until now, the reason behind this change was poorly understood.
AP2A1 and Its Surprising Role in Aging
The researchers focused on human fibroblast cells, which are commonly used in aging studies because they mirror many of the changes seen in older cells. They found that AP2A1 activity was significantly higher in aging cells, especially in parts of the cell that help maintain its structure and shape.
What’s more intriguing is what happened when scientists reduced AP2A1 levels. The aging cells began to shrink back to a more youthful size and regain function, essentially reversing some of the hallmarks of aging. Conversely, when AP2A1 levels were increased in younger cells, those cells aged faster, showing clear signs of decline.
Effects Seen Across Multiple Cell Types
This wasn’t a one-time fluke. The study found similar results in other types of cells, including those artificially aged by UV radiation or drugs. That means AP2A1’s role in aging could be much broader than previously thought.
The researchers also discovered that AP2A1 works closely with another protein called integrin β1. Integrin β1 is responsible for helping cells anchor themselves to their environment, a key part of maintaining cellular structure. The duo of AP2A1 and integrin β1 strengthens the cell’s internal support system — specifically along structures called stress fibers — allowing the cells to stay more firmly attached.
This stronger attachment may be the reason aging cells become larger, as it helps lock them in place and makes them more resistant to change.
Could Controlling AP2A1 Reverse Aging?
This discovery suggests a powerful new possibility: regulating AP2A1 levels could be a way to control or even reverse cellular aging. Unlike other theories that propose aging happens randomly, this study points to a more targeted, structural process — one that could potentially be interrupted or reversed with the right treatment.
The implications of this are enormous. If scientists can find safe ways to manipulate AP2A1, it might lead to future therapies for age-related diseases, improved cell regeneration, and even anti-aging treatments that work at the root cellular level.
Conclusion: A Promising Step Toward Anti-Aging Therapies

The discovery of the AP2A1 protein and its impact on aging cells opens the door to a new era in anti-aging research. It highlights the potential to not only slow down the aging process but possibly reverse it at the cellular level. While more research is needed, especially in live organisms, this study represents a major step forward in understanding how aging works — and how we might one day stop it.
Stay tuned — the future of anti-aging science just got a lot more exciting.
News in the same category
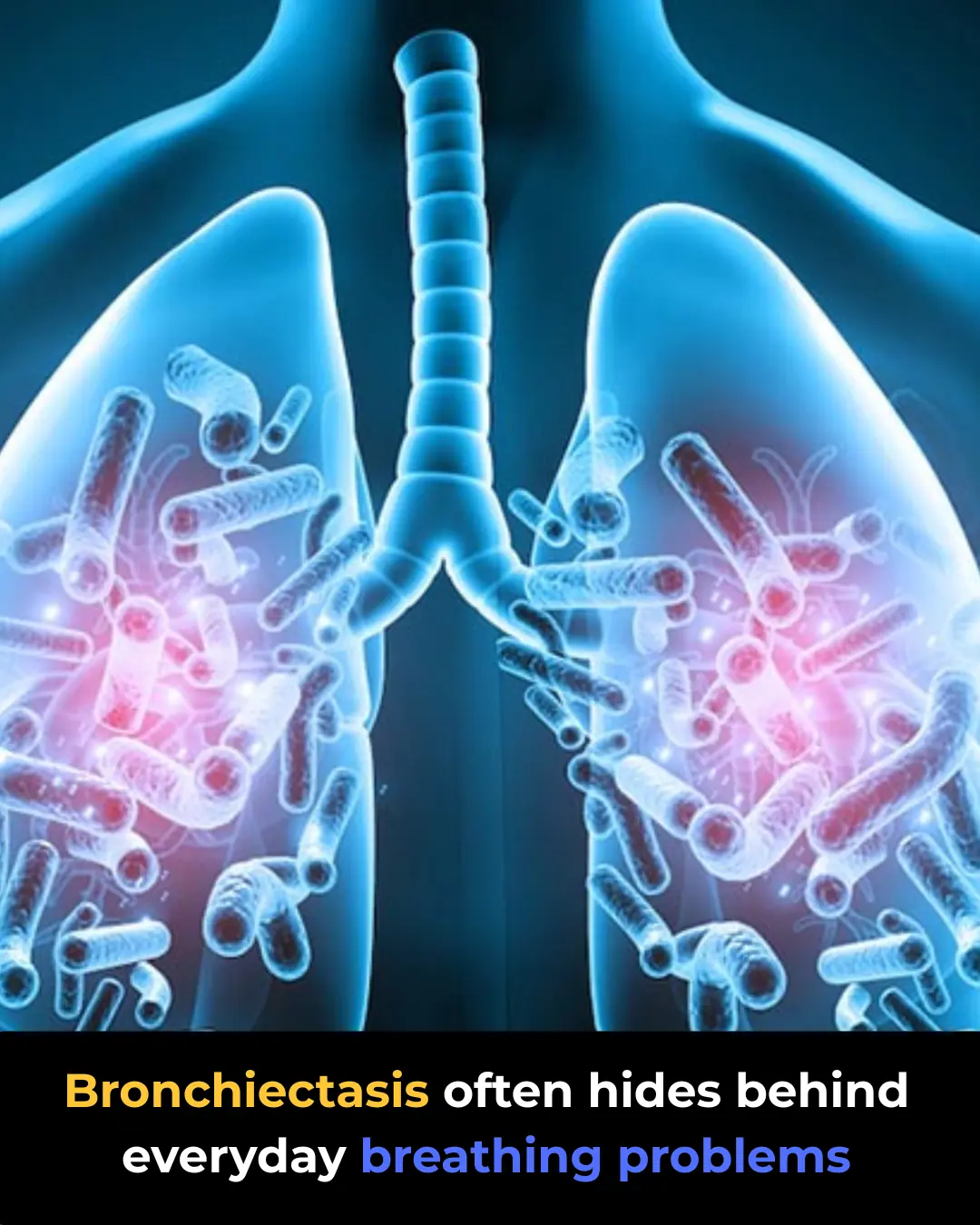


Bronchiectasis: Symptoms Most People Overlook
Respiratory Failure: Causes and Emergency Signs

The Hidden Power of Nutrition: 14 Overlooked Nutrients That Transform Health
Lung Infections: Common Types and How to Treat Them

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Misunderstood Signs

Dizziness and Balance Problems: What They May Indicate
Nerve Damage: Common Causes and Recovery Tips

The 4 hidden causes of persistent phlegm in your throat (& how to fix it naturally)
4 popular supplements that rapidly drain potassium from your body

Turmeric and vitamin D are allies against high blood pressure in diabetes
This is How Headaches Reveal What is Wrong With Your Health

#1 best way to reverse & slow dementia
How to shrink thyroid nodules naturally with 2 key minerals
The Number One Deficiency Behind Aging Spots
If You Get These Bruises On Your Body

The hidden power inside celery that most people never hear about…

7 warning signs your potassium levels are dangerously low and what to eat to restore them

Ashwagandha Side Effects: What You Really Need to Know Before Taking It Daily
10 warning signs your body is running low on magnesium and how to get it
News Post

How to flush sugar out of your body fast

Mix rice with this and leave it in a corner of the house; mice will run away in terror and never dare to come near again.

Cut up some soap, mix it with sugar, and place it in a corner of the house: Mosquitoes will swarm, and the whole house will be clean and fragrant – everyone will love it!

Drivers Urged To Wrap Their Keys In Tinfoil

What’s That White Goo That Comes Out of Chicken After Cooking

Bronchiectasis: Symptoms Most People Overlook

Respiratory Failure: Causes and Emergency Signs

The Hidden Power of Nutrition: 14 Overlooked Nutrients That Transform Health

Lung Infections: Common Types and How to Treat Them

Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Misunderstood Signs

Dizziness and Balance Problems: What They May Indicate

Nerve Damage: Common Causes and Recovery Tips

10 DIY Storage Ideas to Quickly Organize Your Home

How to Remove Yellow and Brown Stains From a Toilet Seat Before Replacing It

It Takes 1–2 Years for a Woman’s Body to Fully Recover After Pregnancy — Not Just 6 Weeks
World’s First 3D-Printed Windpipe Successfully Implanted in South Korea

The Natural Glow: Yeast and Yogurt Mask for Radiant Skin

How a 20-Minute Walk Can Positively Transform Your Brain and Body

12 Common Kitchen Mistakes You Should Avoid for Better Health and Safety
