New research discovers unexpected benefits of lard
Pork Fat: From Suspected Villain to Unexpected Benefits

For a long time, pork fat has been viewed with suspicion regarding its health effects. While it has often been blamed for negative impacts, a new study may help clear its name and reverse its bad reputation.
A recent study from the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences found that adding pork fat to the diet can have surprising positive effects on digestion. According to QQ, researchers compared two groups of mice: one group fed pork fat and another fed vegetable oils (corn or canola oil). The results showed that mice consuming pork fat had lower body weight, less fat accumulation, and notably lower serum cholesterol. Scientists suggest these effects may be due to several factors:
Pork Fat Supports a Healthy Gut Microbiome — A Key Factor in Weight Control
Experts explain that the difference is closely related to gut health. Mice fed pork fat had a more diverse gut microbiome — a sign of a healthy digestive system and better weight control. Moreover, pork fat affects bile acid metabolism, a cholesterol byproduct, which aids fat digestion, balances energy, and reduces inflammatory responses.
Fatty Acid Structure in Pork Fat Promotes Efficient Absorption
Another noteworthy point is the structure of the fat in pork fat. Pork fat contains three “chains” of fatty acids, with palmitic acid positioned in a way that the body can absorb efficiently. This makes pork fat not only easy to digest but also helps the body absorb other nutrients more effectively.
A Natural Source of Nutrients
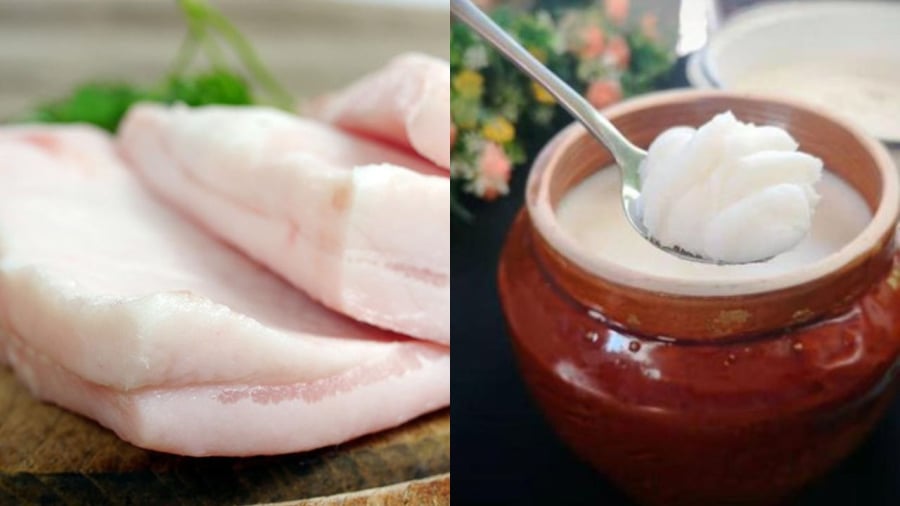

In addition to being energy-rich, pork fat provides vitamin E, antioxidants, and plant sterols — components that can help reduce the risk of obesity and certain chronic diseases. Pork fat is also high in saturated fatty acids (40–50%), which make it stable at high temperatures, resistant to oxidation, and give it a high melting point. These properties allow pork fat to retain its smooth texture even after melting.
Consumption Should Be Controlled
Despite its benefits, pork fat is still high in saturated fat. Excessive intake of saturated fat can raise LDL (“bad cholesterol”), contribute to plaque buildup, block blood vessels, and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. By contrast, most vegetable oils contain less than 20% saturated fatty acids. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that saturated fat should not exceed 10% of daily energy intake — roughly 22 grams for a 2,000-calorie diet.
It’s important to note that the current research is based on animal experiments, so it cannot definitively confirm that pork fat reduces weight or blood fat in humans. However, these findings suggest that pork fat is not necessarily the “health enemy” that many people assume. A balanced approach — combining pork fat with vegetable oils, controlling portions, and following nutritional guidelines — can allow you to enjoy the rich flavor of pork fat while maintaining heart health.
News in the same category


Why You Shouldn’t Wash Rice in the Inner Pot of an Electric Rice Cooker

Turns out I've been using it the wrong way for a long time

🥚 5 Simple Ways to Tell if Your Eggs Are Fresh or Rotten 🚫

Crush a handful of these leaves and drop them into the pot.

Mix banana peel with this and keep it in the corner of the house

The house is full of dust even if cleaned regularly, apply these 3 tips for a whole week and the house will still be clean

You’re doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to use baking soda around home

Don’t Soak Frozen Pork in Water — Try This 10-Minute Thawing Trick for Fresh, Tender Meat

Hotel Room Red Flags You Should Never Ignore

🔌 3 Mistakes to Avoid When Charging Your Phone — And How to Extend Its Life

You’re doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to clean air vents
You’re doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to wash pillows

Wow, I never knew this!

Simple way to get rid of ants from sugar jar, everyone should know clearly

Put the entire roll of toilet paper in the refrigerator
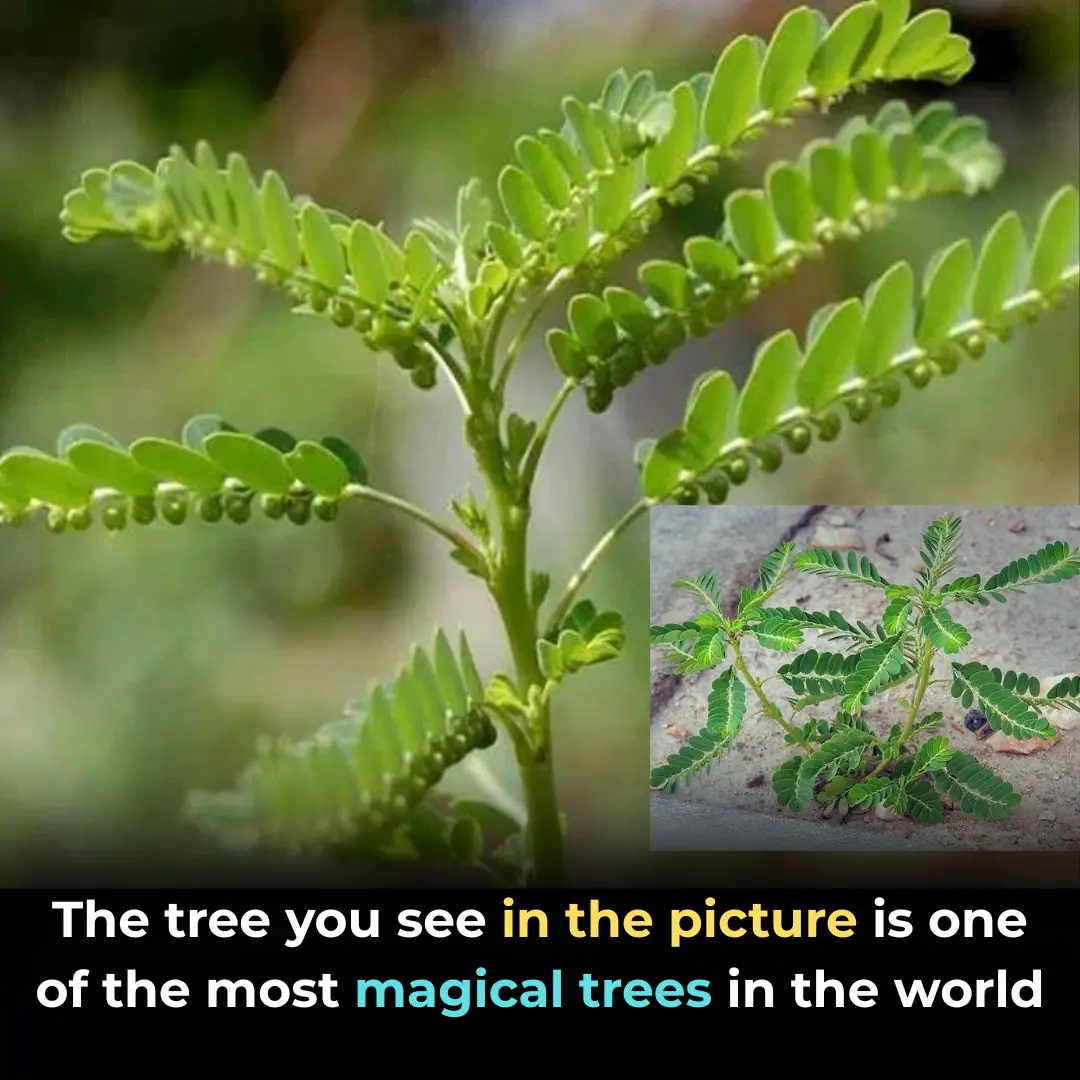

Serrated Leaf Motherwort: A Precious Herb with Many Benefits

Banana flowers and their little-known uses

Eat these 5 fruits to avoid magnesium deficiency, keep your heart healthy and your bones strong.
News Post

This Homemade Coffee & Turmeric Eye Cream Will Erase Your Dark Circles
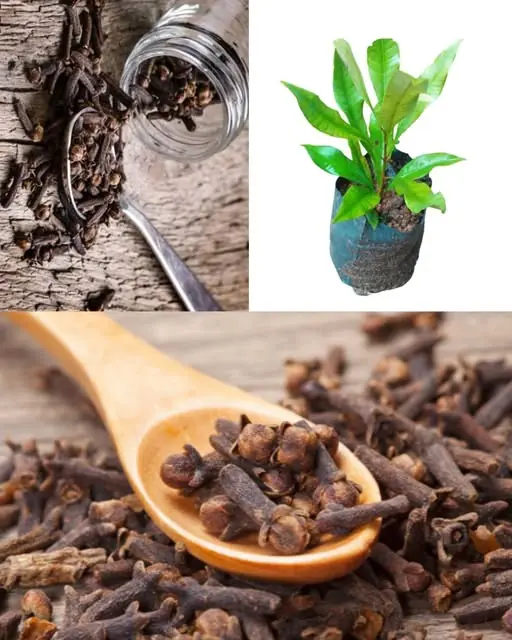

How to grow clove plant at home – from seed to spice
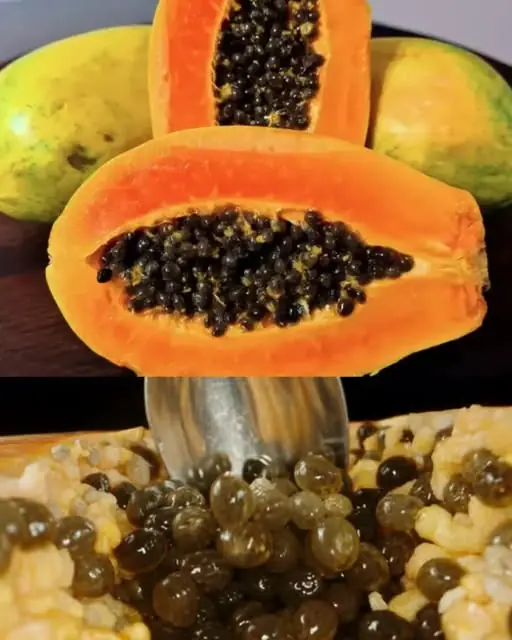

7 Benefits Of Papaya Seeds & How To Consume Them Correctly
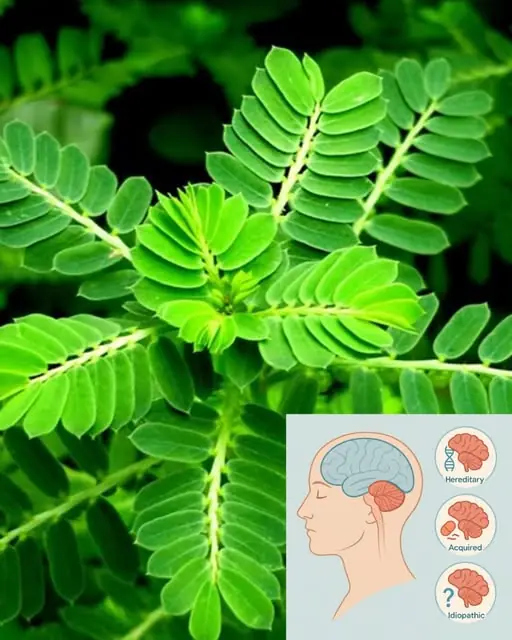

Chanca Piedra (Stonebreaker): Benefits and Uses

Nerve damage? 6 best oils to help repair your nerves

Red Onion for Hair Growth: How This Overlooked Natural Remedy Can Stop Hair Fall and Boost Thickness Fast

Banana and Coffee: Powerful combination with surprising benefits

1 cup to protect the pancreas (and reduce blood sugar)
Manraj’s Journey: A Brave Little Fighter Who Beat Cancer
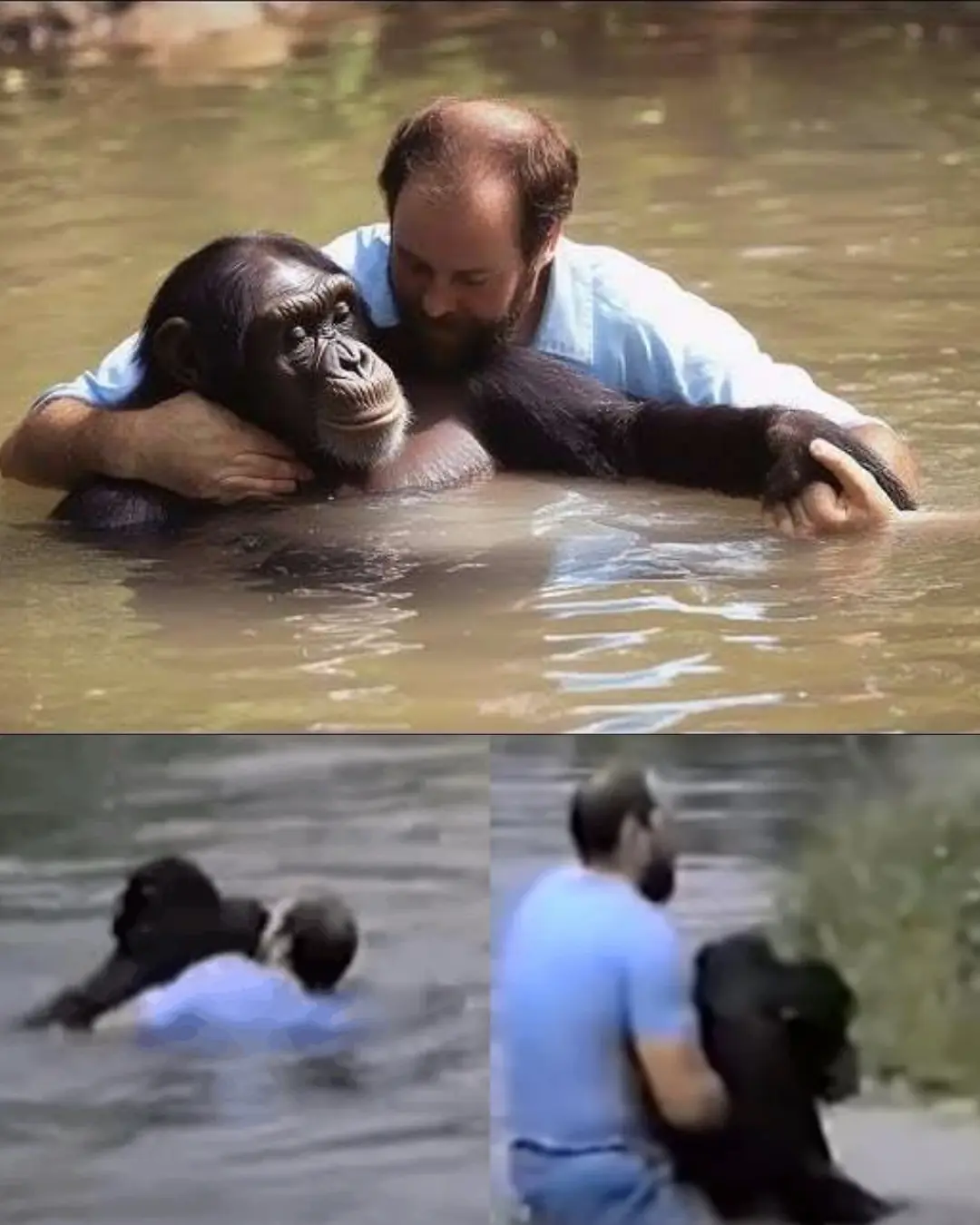

The Day Rick Swope Saved Jo-Jo the Chimp: A Heroic Act of Compassion
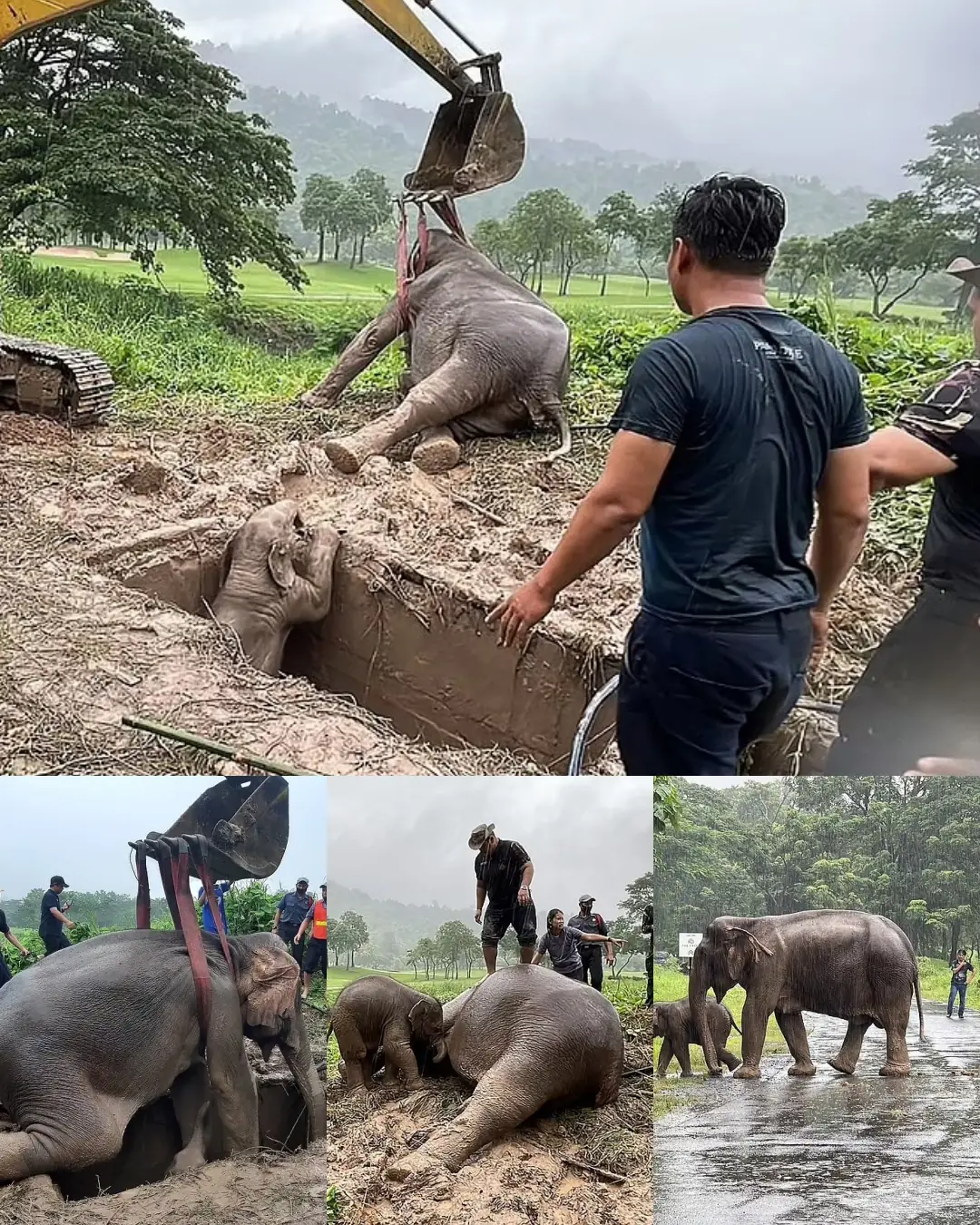

A Dramatic Rescue: The Courageous Effort to Save a Mother and Calf Elephant in Thailand
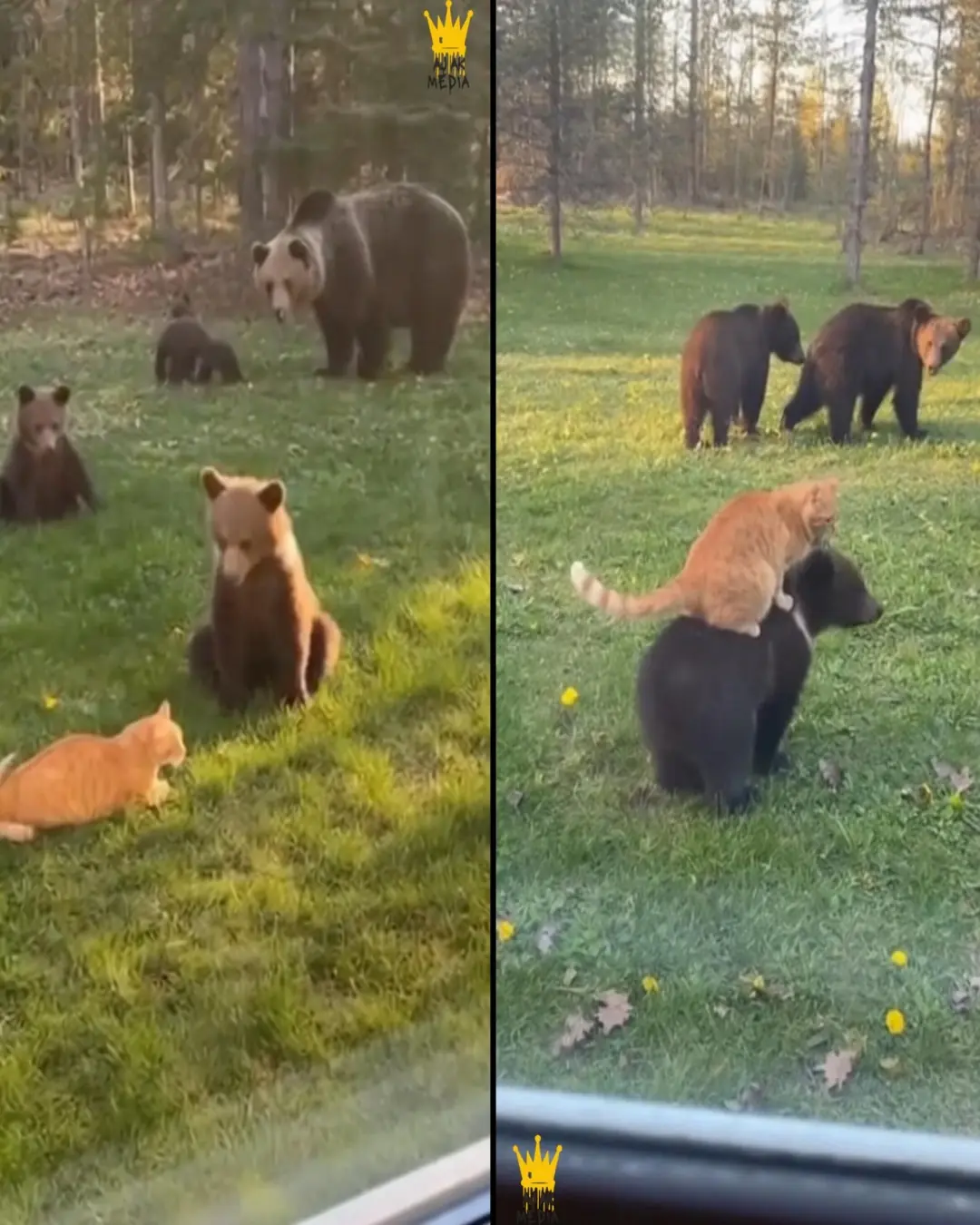

The Orange Cat and the Bears: A Friendship You Have to See to Believe

Little-known wonderful uses of baking soda in gardening
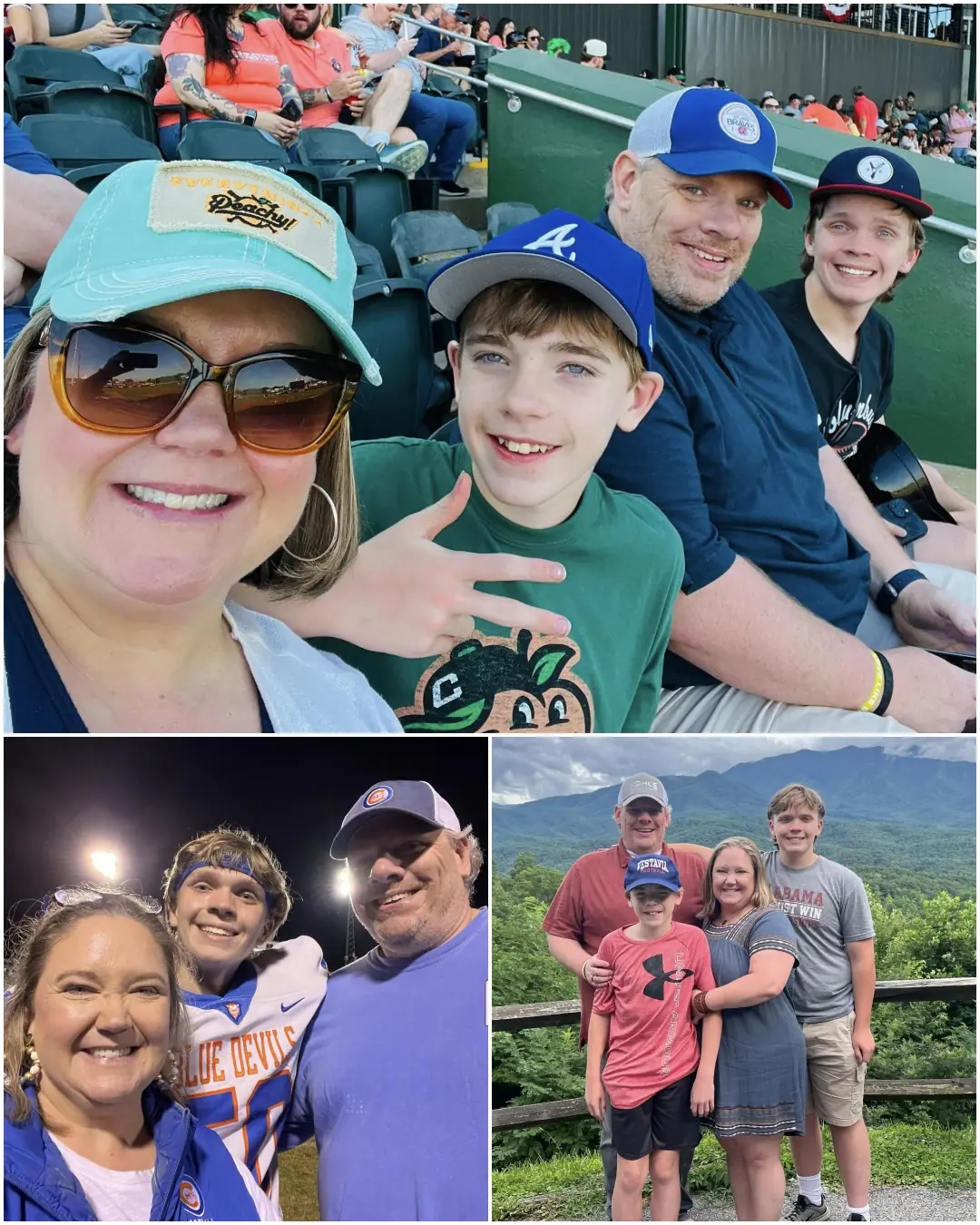

Remembering Tim Franklin: A Husband, Father, and Friend Who Loved With His Whole Heart
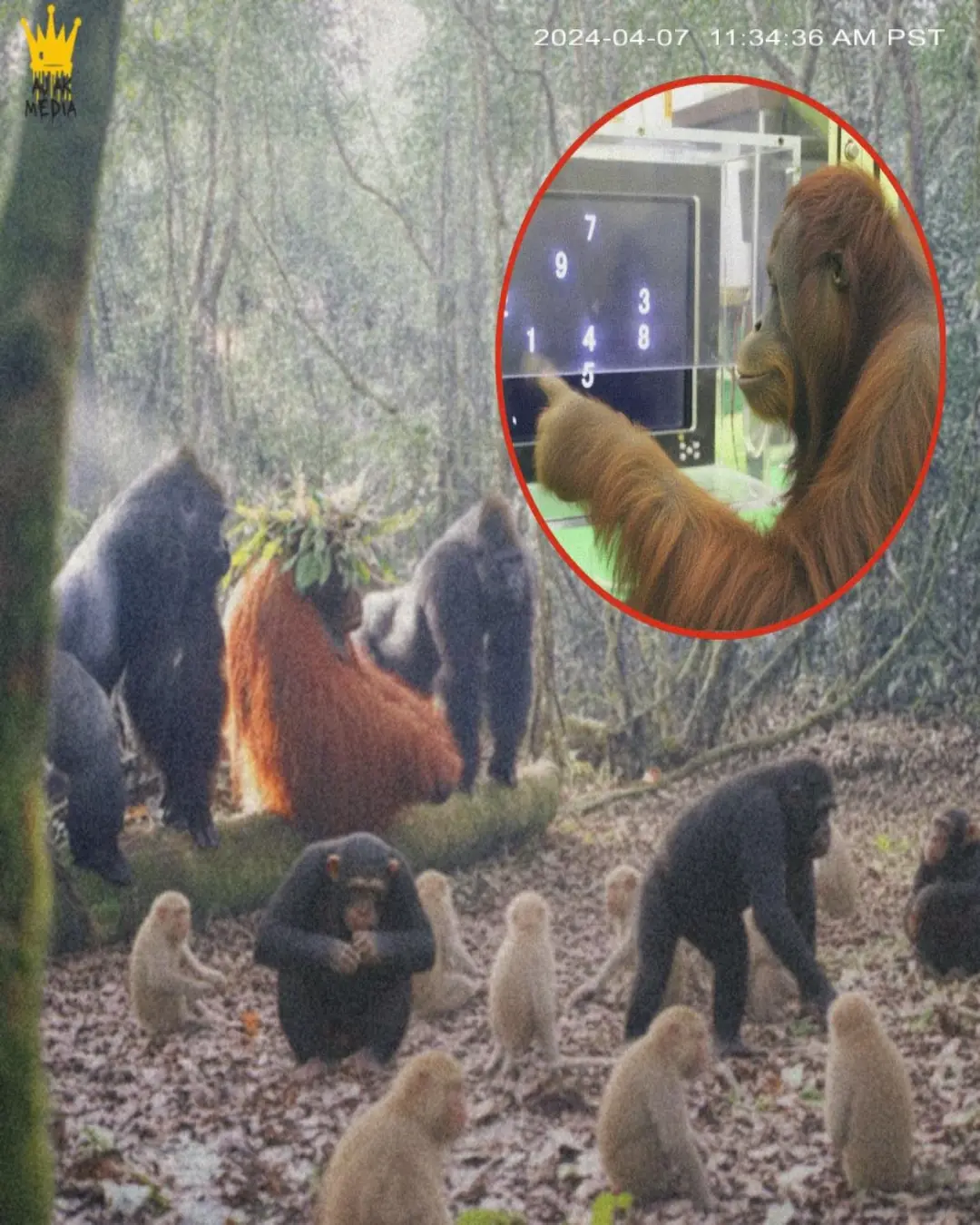

Abused Genius Turns King: The Lost Experiment That Became Legend of the Jungle

Why You Shouldn’t Wash Rice in the Inner Pot of an Electric Rice Cooker

Turns out I've been using it the wrong way for a long time
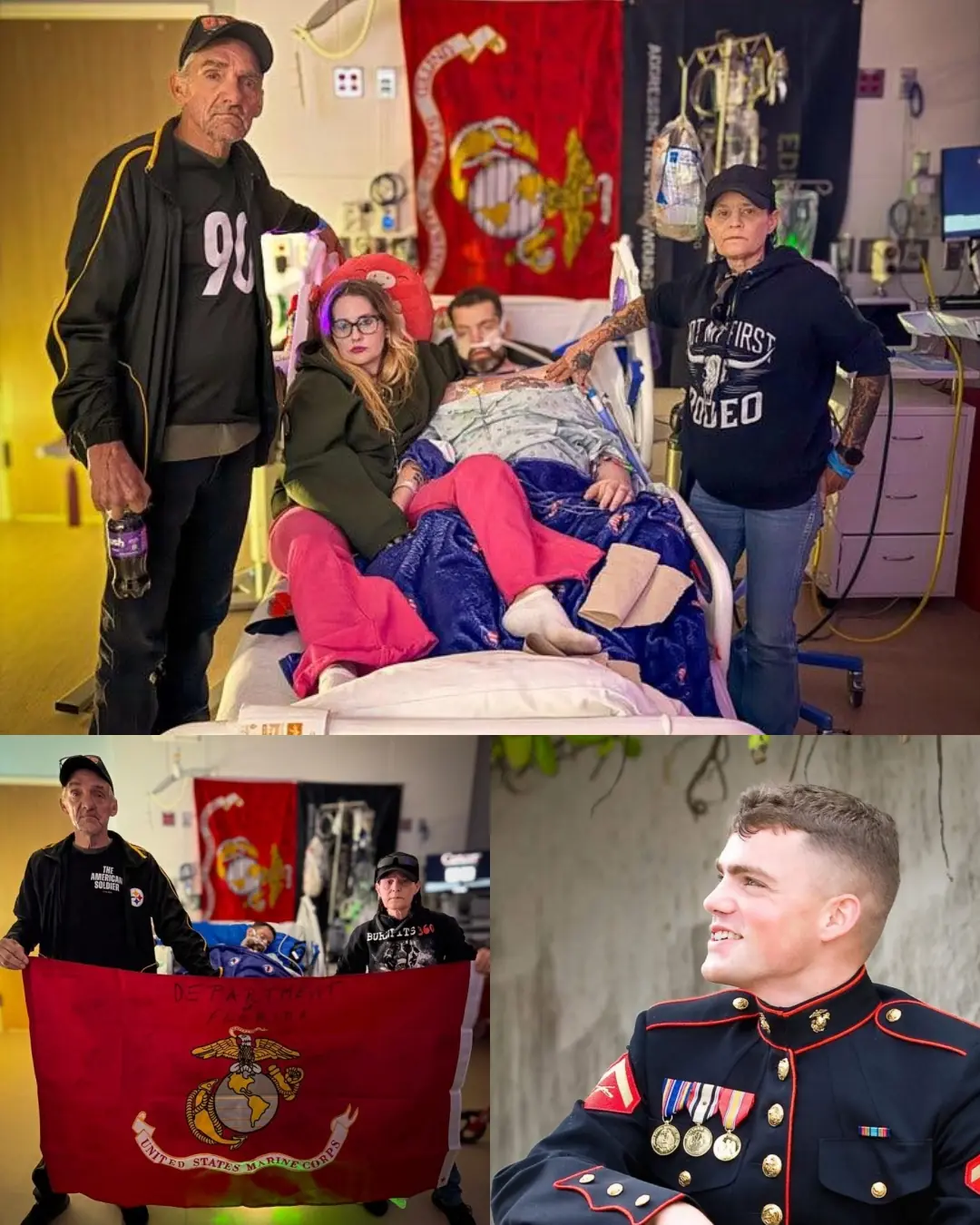

Semper Fi Until the End: Honoring Sgt. Kevin Lloyd, a True American Hero

🥚 5 Simple Ways to Tell if Your Eggs Are Fresh or Rotten 🚫
