Nikola Tesla X-Rayed His Own Foot in 1896 — Pioneering the Future of Medical Imaging
In 1896, just months after Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery of X-rays, the brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla took it upon himself to build a high-voltage imaging device and test it by x-raying his own foot. What followed was a haunting "shadowgraph" image, capturing not only the bones of his foot but also the metal eyelets of his shoe, marking a significant moment in the history of medical imaging.
Tesla’s Bold Experimentation with X-rays
Tesla, known for his groundbreaking work in electrical engineering and technology, was not one to shy away from pushing the limits of new discoveries. After hearing of Röntgen's accidental discovery of X-rays in late 1895, Tesla quickly recognized their potential and immediately set to work on creating his own version of a high-voltage X-ray machine. This was an era when understanding of X-rays was in its infancy, and protective measures for radiation exposure were not yet a concern.
Tesla’s motivation wasn’t just curiosity; he sought to explore the potential applications of X-rays, particularly in the realm of medical imaging. His self-experimentation with the technology led to the creation of one of the first detailed radiographs in history, predating the more commonly known medical X-rays by several years. The "shadowgraph" Tesla created was one of the earliest clear images of bones captured using X-ray technology.
The Risks Tesla Recognized Early On
Tesla’s involvement in X-ray experimentation was not without its risks. During his tests, he began to notice the harmful effects of radiation exposure, such as skin burns and irritation. These signs, observed long before the dangers of radiation were widely understood, led him to warn about the potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to X-rays. Tesla’s early recognition of these dangers marked him as a visionary, as he was among the first to highlight the need for protective measures in X-ray technology—a concern that would not become standard practice until decades later.
Tesla’s Contribution to Modern Medical Imaging
While Wilhelm Röntgen is widely credited with the discovery of X-rays and the initial photographic images of bones, Tesla's work in refining and applying the technology played a crucial role in the development of modern medical imaging techniques. His contributions were not limited to theoretical work; he actively worked on improving the technology and bringing it closer to practical use. Tesla’s innovations in high-voltage devices and electromagnetic principles provided foundational knowledge that would influence the future of medical and scientific imaging.
Although Tesla’s early experiments did not result in the immediate widespread application of X-ray technology in medicine, his pioneering work undoubtedly laid the groundwork for future advancements. Tesla was a true visionary—a scientist and inventor willing to take immense personal risks in the name of progress. His experiments with X-rays not only expanded the possibilities of modern technology but also pushed the boundaries of what could be achieved in science and medicine.
Legacy of a Risk-Taking Genius
Nikola Tesla’s willingness to experiment with groundbreaking technology, even at the expense of his own safety, showcases his relentless pursuit of knowledge and innovation. His work with X-rays was just one of many instances where he placed himself at the forefront of discovery, constantly challenging established norms and shaping the future of science and technology.
Tesla’s legacy lives on in numerous fields, from electrical engineering to wireless communication, and his contribution to the development of medical imaging remains an important chapter in the history of science.
News in the same category


12 Probiotic Foods That Heal

Experience the Journey of a Lifetime: Ride Across America for Just $213 with Amtrak

12 Common Household Items That Are Slowly Killing Us

Magpie The Spiritual Meaning of an Unusual Encounter

Humanity’s Farthest Traveler Still Hasn’t Reached One Light-Year

The Vaquita: Earth's Most Endangered Marine Mammal Fights for Survival

AI Drones Are Rebuilding Australia’s Forests, One Seed Pod at a Time
A World Without Cavities? Scientists Have Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel!

Bamboo and Hemp: The Future of Sustainability

The “Anti-AI Mask” Is Not What It Claims – Here’s What It Actually Does

Chuck Feeney: The Billionaire Who Gave It All Away Before He Died

How to React If You Get Bit by This Bug

China’s Giant Inflatable Dome Redefines Urban Construction and Environmental Protection in Jina
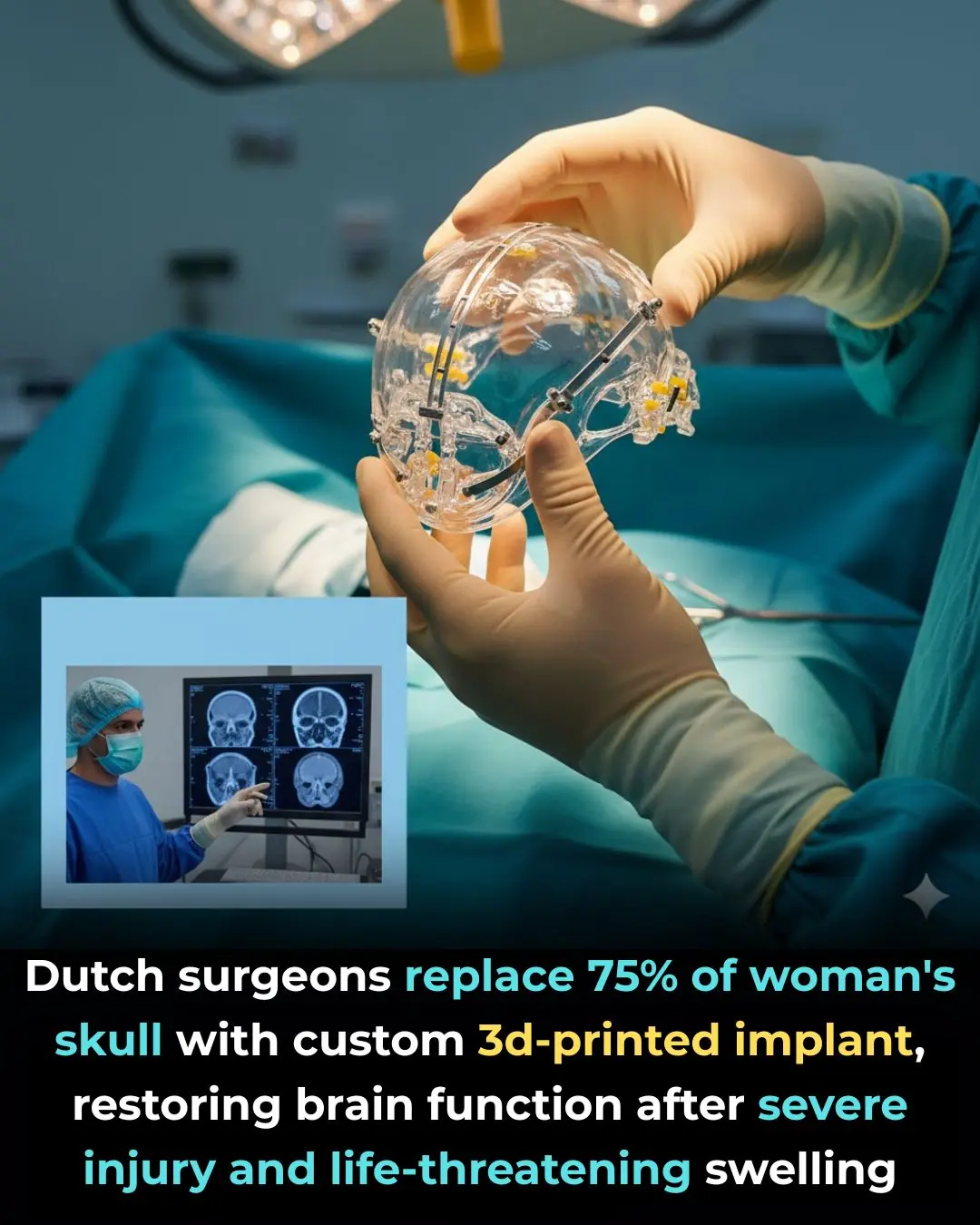
Groundbreaking Surgery in the Netherlands Uses 3D-Printed Implant to Save Woman's Life After Traumatic Brain Injury
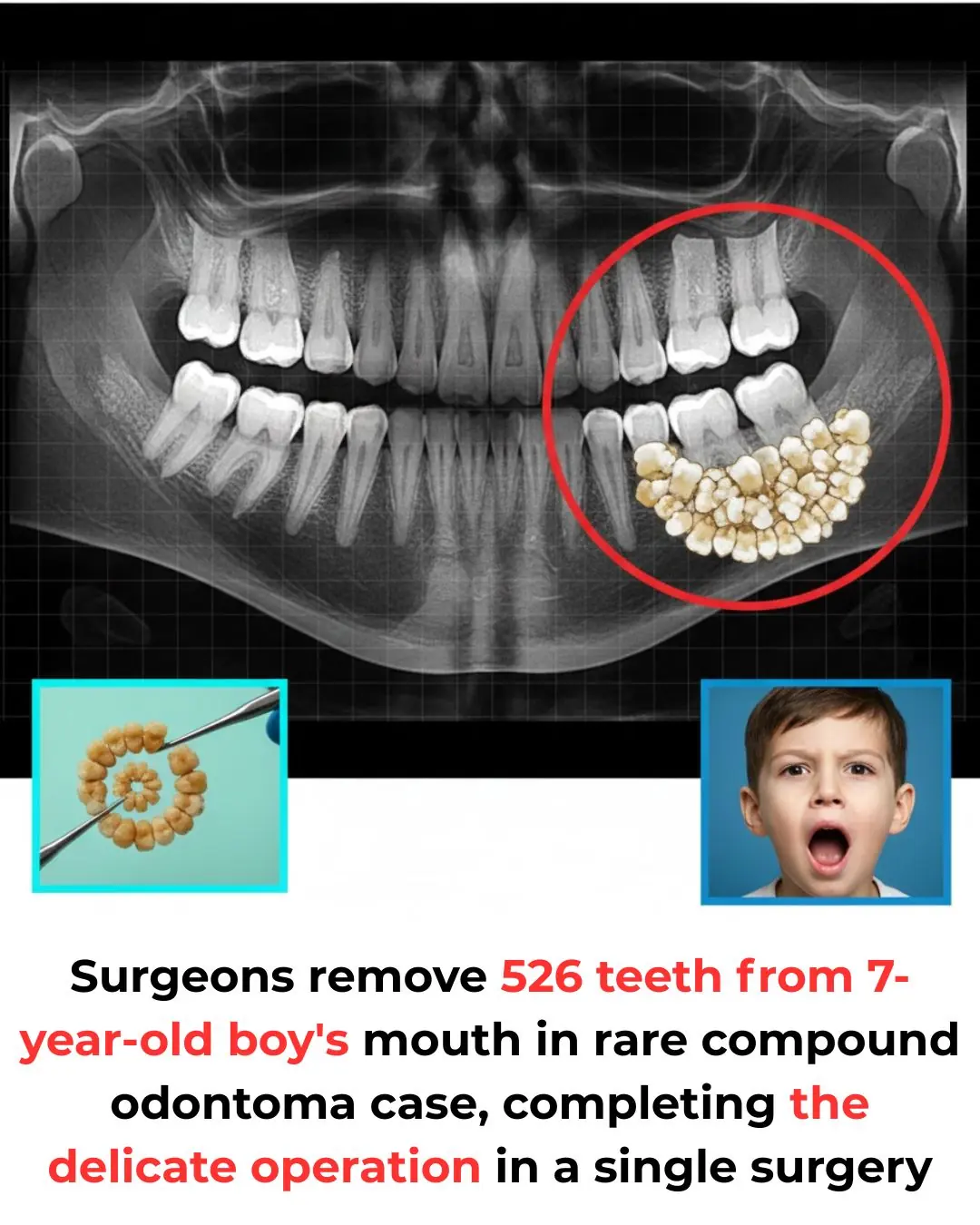
Seven-Year-Old Boy in India Undergoes Surgery to Remove Rare Jaw Tumor Containing 526 Tiny Teeth

Innovative Heliostat Mirrors Bring Sunlight to Norwegian Towns Amid Winter Darkness

MIT Physicists Perfect the Double-Slit Experiment, Confirming Quantum Theory
News Post

The Hidden Power: How Green Papaya Sap Soothes Cracked Heels and Boosts Digestion

Anise Seeds: 8 Remarkable Benefits for Women – When Science Meets Ancient Tradition

Two Tablespoons in the Morning: The Power of Magnesium Chloride

Warning Signs of an Overworked Liver—and the Top Herbs to Help Restore Its Function

Drink Just 1 Glass Before Bed to Cleanse Your Entire Colon in 10 Minutes

New Research Shows Beta Blockers May Raise Heart Failure Risk in Women With Hypertension

The Power of Clove Steam Inhalation (Respiratory Relief You Can Feel Immediately)

13 Science-Backed Benefits of Drinking Lemon Water Daily

Doctors Reveal What Eating Cauliflower Really Does to Your Body — And Why You Shouldn’t Ignore It

Spray This 3-Ingredient Oil On Your Feet 10 Minutes Before Bed And You’ll Be Dozing Off In No Time!

Sniffing Rosemary Can Increase Memory by 75%

The 60-second trick to reset your nervous system

Cleanse Your Kidneys of Toxins With 2 Effective 1-Ingredient Drinks

The unexpected connection between morning blood flow and a stronger heart

Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Capture the Most Detailed 3D Image of a Human Cell

7 gentle balance moves seniors are using to feel steadier on their feet

12 Probiotic Foods That Heal

Connecting Consumers to Farmers: The Trend of Personalized Food Packaging in Japan
