
Revolutionary Light-Based Cancer Treatment Offers Precision and Fewer Side Effects
Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in the fight against cancer by developing a revolutionary method that uses light instead of traditional drugs or radiation. This new technique presents an innovative and non-invasive alternative to conventional cancer treatments. By utilizing light to target and break apart cancer cells, researchers have unlocked a promising approach that could transform cancer care as we know it.
The principle behind this light-based therapy revolves around harnessing specific wavelengths of light to disrupt the molecular structure of tumor cells. What makes this method particularly exciting is its ability to target cancer cells with high precision, without causing significant damage to the surrounding healthy tissues. This breakthrough is a major step forward in cancer treatment, as it offers a more targeted approach compared to existing therapies, which often damage healthy cells in the process of attacking cancer cells.
Early experiments have shown that this method can effectively destroy cancer cells while significantly reducing the harmful side effects commonly associated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Traditional treatments like chemotherapy can often lead to severe side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and immune suppression, as they affect both cancerous and healthy cells. Radiation therapy can also damage healthy tissues, leading to long-term complications. However, with the use of light, researchers are hopeful that this technique will allow for much more selective destruction of cancer cells, sparing healthy cells and potentially minimizing the long-term side effects that patients typically endure during treatment.
The potential applications of this light-based cancer treatment are vast. Unlike conventional therapies, this method has the ability to be faster, more precise, and less taxing on patients' bodies. Because it directly targets cancer cells and causes minimal collateral damage, it could also shorten recovery times and reduce the overall burden on patients. In addition, because this technique is non-invasive, it could be an option for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or who are looking for alternative treatment options that are less physically demanding.
While this discovery is still in its early stages, the implications for the future of cancer treatment are enormous. Researchers are optimistic that with further development and clinical trials, this innovative approach could lead to the creation of new, widely available treatments for various types of cancer. The hope is that this technique will provide a safer, more effective alternative for millions of cancer patients worldwide, offering them better quality of life and increasing their chances of recovery.
As research continues to advance in this area, experts believe that light-based therapies could complement or even replace traditional cancer treatments in the coming years. This breakthrough opens up exciting possibilities in the field of oncology, and the continued development of light-based treatments could lead to a new era in cancer care, where precision, safety, and efficacy are the hallmarks of therapy.
In conclusion, the discovery of light-based cancer therapy represents a significant leap forward in oncology. This technique could revolutionize cancer treatment by offering a more precise, non-invasive alternative to current therapies, significantly reducing side effects while improving patient outcomes. Although still in its infancy, the potential of this method to transform cancer care is immense, and further research will likely lead to the development of safer and more effective treatments for cancer patients around the world.
News in the same category


Breakthrough in Burn Treatment: Lab-Grown Skin with Functional Sweat Glands

Australia's Undersea Solar Cable: A Groundbreaking Step Toward Global Renewable Energy

The London Bus Driver Who Jumped Tower Bridge and Became a Legend

Honoring the Heroism of Saman Kunan: A Legacy of Courage and Sacrifice

How Two Quiet Hours a Day Can Rebuild Your Brain

How Cats Use Smell and Earth’s Magnetic Field to Navigate Home Over Long Distances

Japan’s Visionary Floating City: A Sustainable Urban Model for 2030 and Beyond
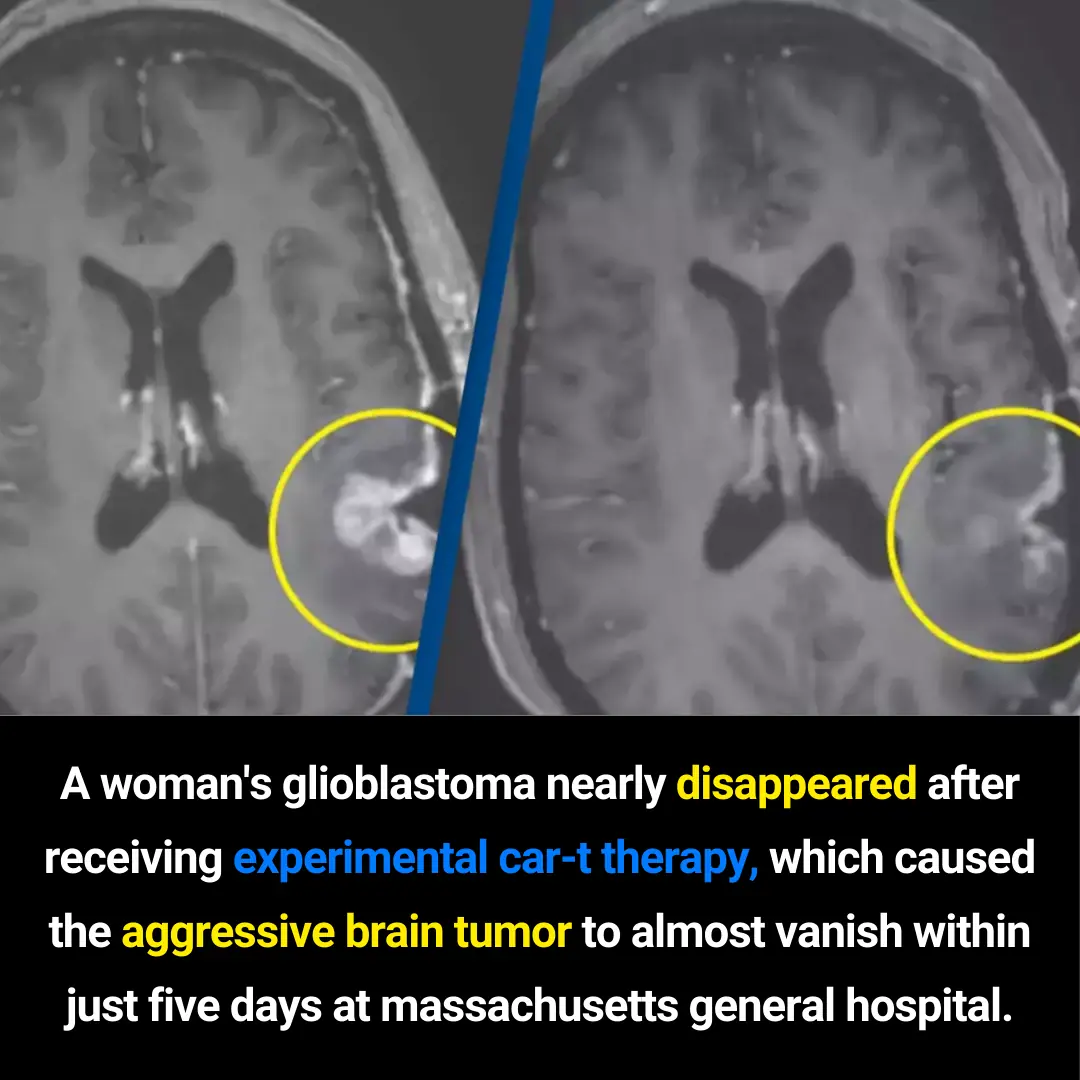
Experimental CAR-T Therapy Shows Dramatic 5-Day Regression of Glioblastoma at Massachusetts General Hospital

From Shortage to Supremacy: The Unexpected Rise of Vietnam’s Coffee Industry

Growing Concerns Over ADHD and Autism in Children: Insights, Challenges, and Evidence-Based Perspectives

Breakthrough Hydrogel Restores Damage in a Day, Mimicking Human Tissue

Inside the Science of Forgetting: How the Brain Downregulates Unwanted Memories
A New Era in Immunotherapy: MIT’s Synthetic Gene Circuit Hunts Cancer with Unmatched Precision

Surviving the Void: How Voyager 1 Still Operates Billions of Miles from Earth

The Bird’s Nest: A Tiny-Home Community Redefining Aging for Women in Texas

We Found Something Unexpected in the Garden

How to Know Your Rotisserie Chicken Is Truly Fresh

The HPV Vaccine Does Prevent Cervical Cancer, Scientists Confirm
News Post

The effortless daily trick people use to double their potassium

The Second Life of Lions — Finding Freedom After Rescue.

Aspirin saves lives— but here’s what most people still get wrong about it

“The Cry That Saved Us”: The Night Two Fort Worth Officers Refused to Give Up.

The top 10 foods people use to keep their blood sugar steadier

Collagen Powder 1 Spoon daily to Reverse your Age by 10 Years

Surge in Appendix Cancer Among Younger Adults Raises Alarms for Health Experts

Six Prisoners, One Fallen Officer, and a Choice That Revealed Their True Hearts.

The One Kitchen Ingredient That Makes Bedbugs, Mosquitoes, Cockroaches, Ants & Silverfish Disappear Like They Never Existed – And It Costs Less Than a Cup of Coffee

Doctors Reveal What Eating Peanuts Can Really Do to Your Body

Breakthrough in Burn Treatment: Lab-Grown Skin with Functional Sweat Glands

“The Unlikeliest Friendship in the Wild”: The Capybara Who Rode an Alligator.

7 powerful anti-cancer foods you should start including in your diet

A Mother Who Survived the Unsurvivable: The Story of Motola and Her First Steps Toward Hope.

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs

Egg Yolk + Garlic + Honey: The 3-Ingredient Elixir You’ll Wish You Discovered Years Ago

A Mother’s Promise: The Elephant Who Refused to Leave Her Baby Behind.

Australia's Undersea Solar Cable: A Groundbreaking Step Toward Global Renewable Energy
