Scientists reveal that consumption of TOMATO causes
Tomatoes are a staple in many diets around the world, loved for their vibrant color, juicy texture, and wide range of health benefits. They’re packed with vitamins, antioxidants, and plant compounds that support overall wellness.
However, as with most healthy foods, too much of a good thing can sometimes cause problems. Overeating tomatoes—whether fresh, cooked, or in sauces—may lead to several unwanted side effects due to their acidity, fiber, and natural bioactive compounds.
🍅 Possible Side Effects of Excessive Tomato Consumption
1. Digestive Issues
Tomatoes are naturally high in citric acid and malic acid, which give them their tangy flavor. Unfortunately, these acids can also irritate the stomach lining and worsen acid reflux or heartburn, especially in people prone to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
In addition, the fiber content in tomatoes—while generally beneficial—can cause bloating, cramps, or diarrhea when consumed in large amounts.
If you often feel stomach discomfort after tomato-heavy meals (like pasta sauce, ketchup, or salsa), it may be worth reducing your intake or balancing it with less acidic foods.
2. Kidney Problems
Tomatoes contain potassium and oxalates, both essential in moderation but potentially problematic when consumed excessively.
For individuals with kidney disease or impaired kidney function, excess potassium may lead to hyperkalemia, a condition where potassium levels become dangerously high and can affect heart rhythm.
Likewise, the oxalates in tomatoes can contribute to kidney stone formation in those who are genetically predisposed or already have a history of stones.
If you fall into one of these categories, talk to your healthcare provider before significantly increasing your tomato consumption.
3. Joint Pain and Inflammation (Rare Cases)
Tomatoes belong to the nightshade family, which also includes potatoes, peppers, and eggplants. These plants contain solanine, a natural compound that, in rare cases, may aggravate inflammation or joint pain in sensitive individuals.
While scientific evidence is mixed, some people with arthritis report feeling better when they limit nightshade vegetables. If you suspect tomatoes are triggering discomfort, consider keeping a food diary and tracking your symptoms.
4. Excessive Lycopene Intake
Lycopene is the powerful antioxidant that gives tomatoes their rich red color and many of their health benefits. However, too much lycopene isn’t necessarily better.
Overconsumption can cause lycopenodermia, a harmless but odd-looking condition where the skin takes on a slightly orange or reddish tint.
In very high doses, lycopene might also lead to nausea, digestive discomfort, or low blood pressure, particularly when combined with certain medications or supplements.
To stay safe, enjoy tomatoes regularly but don’t rely on them as your only source of antioxidants—variety is key.
5. Allergic Reactions
Although relatively uncommon, tomato allergies can cause noticeable symptoms such as skin rashes, itching, swelling, or respiratory difficulty.
For those with mild sensitivities, eating too many tomatoes can intensify these reactions. If you suspect an allergy, consult an allergist before including tomatoes in your diet again.
Sometimes, cooked tomatoes may cause fewer symptoms than raw ones, as heat breaks down some of the allergenic proteins.
🍅 How Many Tomatoes Should You Eat?
Moderation is the golden rule.
For most healthy adults, a daily serving of 1–2 medium-sized tomatoes (about 150–200 grams) or a handful of cherry tomatoes is considered safe and beneficial.
This amount provides a balanced intake of nutrients—without overwhelming the body with acids, potassium, or oxalates.
In general, 7–10 tomatoes per week is a reasonable and healthy target for maintaining all the benefits without the potential downsides.
🍅 The Benefits of Eating Tomatoes in the Right Amount
When eaten in moderation, tomatoes are incredibly nutritious and support multiple aspects of health:
1. Rich in Antioxidants
Tomatoes are a leading source of lycopene, which protects cells from oxidative damage and may reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers, especially prostate cancer in men.
2. Supports Heart Health
Their combination of potassium, folate, and vitamin C helps regulate blood pressure, improve blood vessel flexibility, and lower cholesterol levels—making tomatoes a friend to your cardiovascular system.
3. Good for Skin and Eyes
Lycopene and beta-carotene shield your skin from UV-related aging and damage. These same nutrients also protect your eyes, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and improving overall vision health.
4. Boosts Immunity
The vitamin C in tomatoes enhances the body’s ability to fight infections and promotes faster healing. Regular consumption can strengthen your immune defenses naturally.
5. Aids Digestion (When Eaten in Moderation)
Tomatoes provide dietary fiber, which supports smooth digestion and maintains gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria. Just be mindful not to overconsume, as too much fiber can cause the opposite effect.
6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Tomatoes contain phytonutrients such as flavonoids and carotenoids that help reduce chronic inflammation—one of the root causes of diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis.
✅ Summary: The Tomato Balance
| Aspect | Too Many Tomatoes | Right Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Potential Risks | Acid reflux, kidney strain, digestive upset, allergic reactions, lycopenodermia | — |
| Recommended Intake | — | 1–2 medium tomatoes per day or 7–10 per week |
| Benefits | — | Stronger immunity, heart health, glowing skin, better vision, and reduced inflammation |
🌿 Final Thoughts
Tomatoes are among the healthiest and most versatile foods you can add to your diet—but balance is everything. Listen to your body, diversify your fruit and vegetable intake, and enjoy tomatoes as part of a colorful, well-rounded diet.
When eaten wisely, these juicy red fruits can enhance your meals—and your health—for years to come.
News in the same category


5 great foods that should not be stored in the refrigerator - the risk of aflatoxemia that causes cancer
❤️ 5 Subtle Signs That May Suggest Heart Trouble – And When to See a Doctor

Eat these 3 foods to strengthen them…
Neckline Wrinkles 5 Tips to Prevent and Eliminate Them
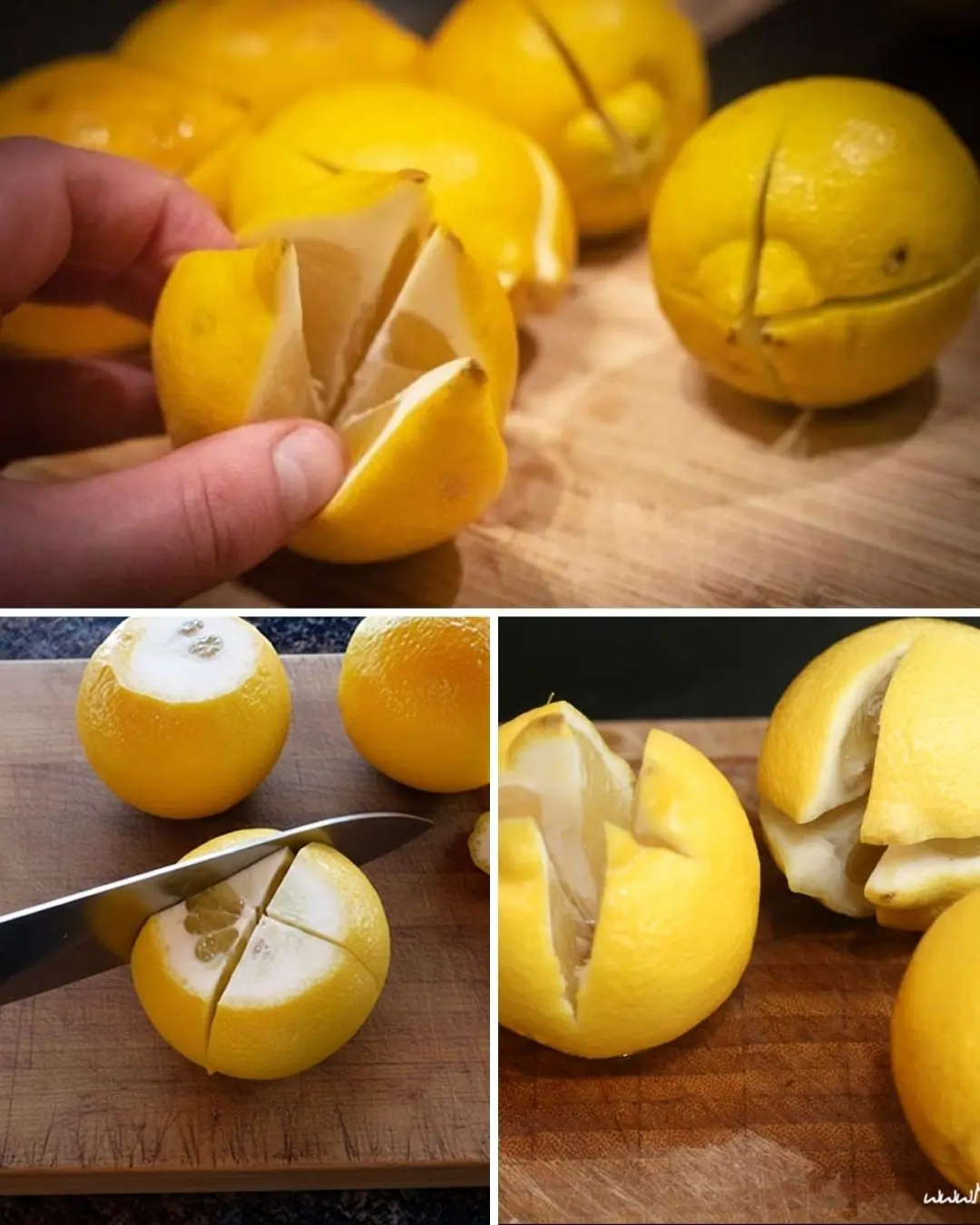

The Reason Some People Keep Lemons on Their Nightstand While Sleeping
Ginger and Salt Teeth Whitening Remedy
The Pain Most People Brush Off That Signals Serious Trouble
Warning Signs Your Arteries Need Cleansing and The Foods That Do It Best
10 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It

The 5 fruits secretly damaging your brain after 50
The #1 silent sign your kidneys are in trouble (and it’s not your urine)

Why Some People’s Skin Turns Red When Drinking Alcohol
🩺 The #1 Silent Sign Your Kidneys Are in Trouble (And It’s Not Your Urine)

The 5 Fruits Silently Damaging Your Brain After 50 — And What to Eat Instead

Capsaicin: The Fiery Compound That Stops Heart Attacks and Destroys Cancer Cells

Flush Away the Hidden Toxins Damaging Your Kidneys — With These 13 Powerful Cleansing Foods

The surprising truth about eating eggs every day

Why You Should Stop Waking Up to Urinate
News Post
What Does Your Sitting Position Reveal About Your Personality

The Uses Of This Small Hole On a Padlock
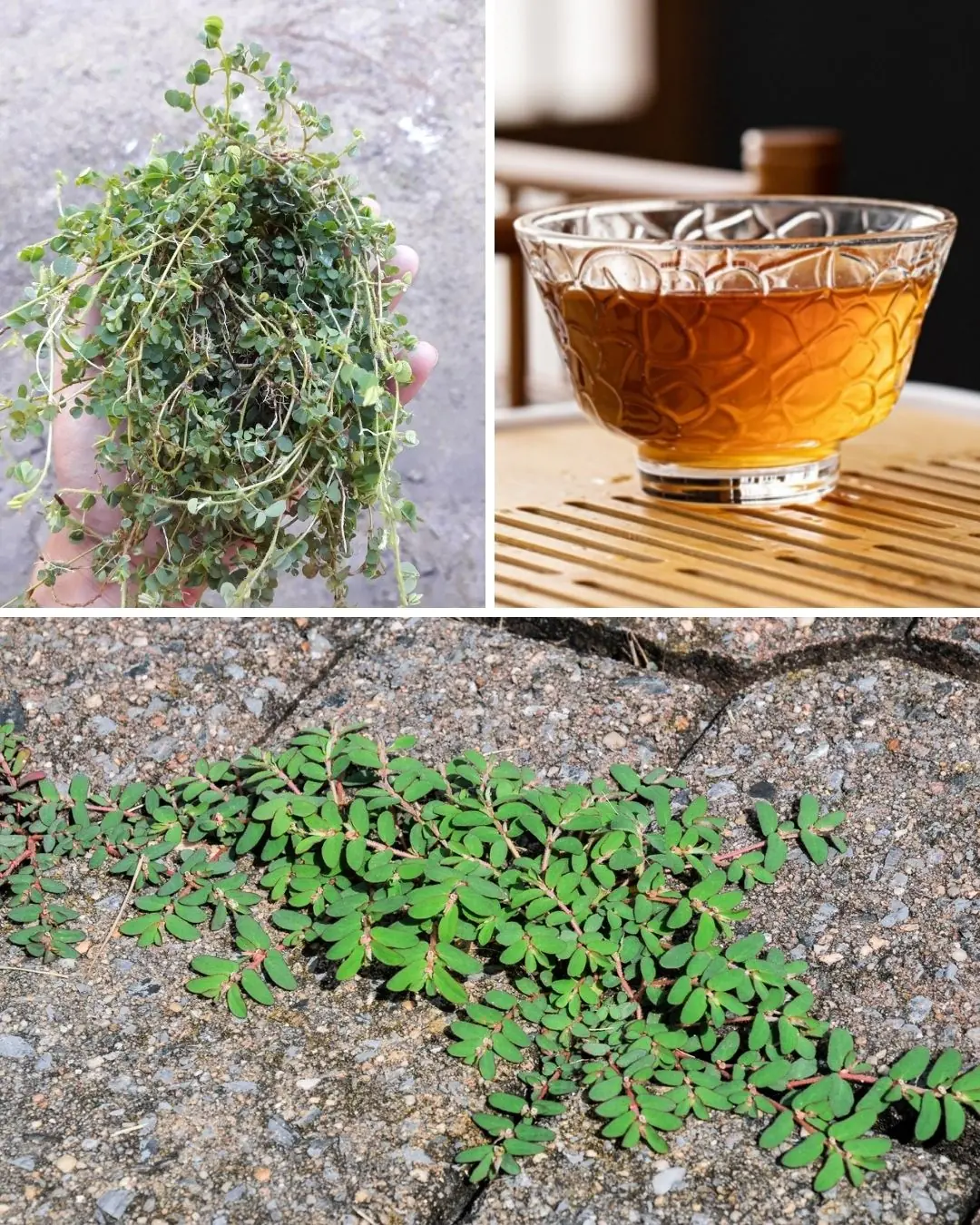

The Health Benefits of Euphorbia Thymifolia: A Powerful Yet Overlooked Herb 🌿✨
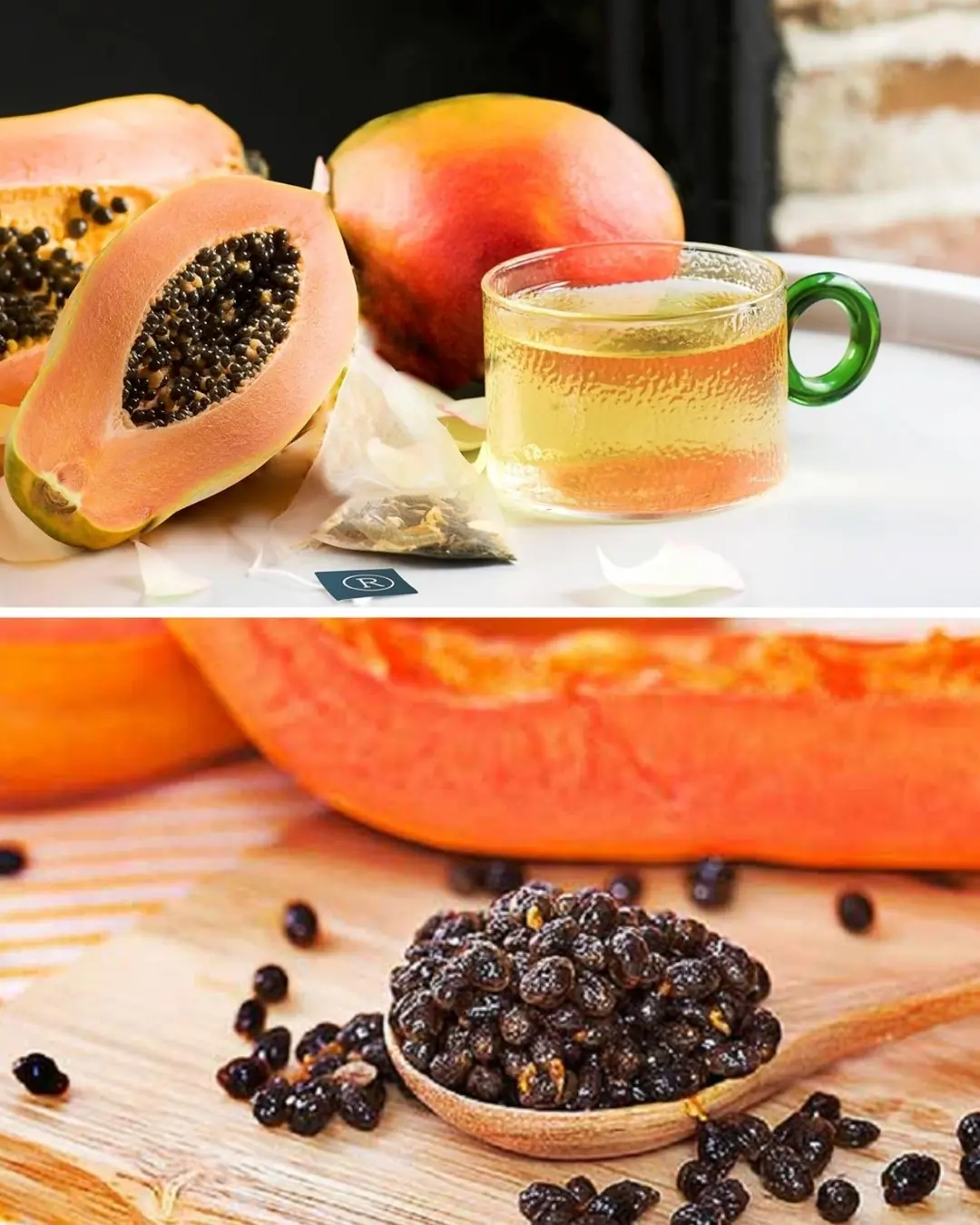

The Powerful Health Benefits of Papaya Seeds: Why You Should Include Them in Your Diet

10 Red Flags Your Body Is Begging You to Quit Caffeine

Father Gifts Daughter A House For Her 13th Birthday

DC Woman Wins Landmark Case After Suing Neighbor Over Overpowering Weed Smell

Bill Gates–Backed Beyond Meat Faces Collapse After Massive Stock Drop

Here’s the court order! And now get up and get out of my apartment,” she addressed her husband, mother-in-law, and sister-in-law.

The guy was amazed as to why his beloved was so interested in the well in the yard. He even decided to follow her.

Nastya had already approached the café when she heard familiar voices:

Having set out to clean before the April holidays, Olga found a strange letter in her husband’s office, and upon reading it, she couldn’t hold back her tears.

The Millionaire’s Daughter Pretended to be a Stuttering Cleaning Lady in Order to Uncover All the Scandals of Her Spouse

I’m not going to give you any money for your apartment!” Vera declared to her mother-in-law and father-in-law.

A girl was selling her deceased mother’s belongings at the market. One day, an expensive car pulled up nearby.

Our son returned from camp completely changed, as if something terrible had been done to him.

Your wife should move in with her mother, and you can come over here just to cook and clean,” declared my mother-in-law.

Son, you urgently need to file for divorce and divide the property!” These were the words that Katya accidentally overheard while helping her mother-in-law in the garden.
