The Vitamin and Tea Combo Linked to Alzheimer’s Protection
The Vitamin and Tea Combo Linked to Alzheimer’s Protection
What if two simple, everyday compounds—one found in your vitamin cabinet and the other in your morning cup of green tea—could help your brain fight back against Alzheimer’s disease? It sounds almost too easy, yet emerging research is revealing a fascinating link between a form of Vitamin B3 and EGCG, the potent antioxidant in green tea. Together, they may hold clues to protecting brain cells from the kind of damage that underlies one of the world’s most feared neurodegenerative disorders.
With Alzheimer’s now affecting 1 in 10 people over the age of 65 worldwide, the global search for preventive strategies has never been more urgent. While pharmaceuticals and lifestyle interventions like diet and exercise have dominated the spotlight, scientists are increasingly turning to nutrient-based therapies that support the brain’s own repair mechanisms. A new study from the University of California, Irvine, shines light on a promising partnership: nicotinamide (a form of Vitamin B3) and EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate, the key antioxidant in green tea).
In this expanded breakdown, we’ll explore what makes these two compounds so special, how they appear to work together at the cellular level, and what this might mean for the future of Alzheimer’s prevention—and for your own long-term brain health.

Key Takeaways
-
Early lab studies suggest that combining Vitamin B3 (nicotinamide) and EGCG may help neurons resist the cellular damage associated with Alzheimer’s.
-
The duo works on two major fronts: boosting cellular energy production and defending against oxidative stress—the cellular equivalent of rust.
-
Together, they helped lab-grown neurons clear out toxic amyloid plaques, a defining feature of Alzheimer’s pathology.
-
This research is still in its early laboratory phase, done on mouse brain cells—not humans.
-
Always consult your healthcare provider before considering any supplements. This is promising science, not a treatment.
1. The Growing Concern: Why Brain Health Is Everyone’s Business
You’ve probably noticed how often brain health headlines dominate the news—and for good reason. Alzheimer’s disease doesn’t just steal memories; it erodes a person’s sense of self. Behind every diagnosis lies a family struggling to cope with the slow disappearance of a loved one’s personality and independence.
Scientifically speaking, Alzheimer’s is a story of communication breakdown between the brain’s billions of neurons. Two culprits are at the center of this story:
-
Amyloid plaques, sticky clumps of protein that build up between neurons and interfere with signaling.
-
Tau tangles, twisted protein fibers that form inside neurons and disrupt their internal transport system.
As these abnormal proteins spread, brain cells die, brain tissue shrinks, and cognitive function declines. For decades, researchers have sought ways to stop—or even reverse—these processes. That’s where the new findings about nicotinamide and EGCG come in.
2. The Brain’s Hidden “Energy Crisis”: The Role of GTP
To understand this study, think of your brain as a high-energy city—constantly active, processing information, and maintaining millions of connections every second. To keep this city running, brain cells rely on energy molecules like ATP, which you may recognize as the body’s main fuel source.
But ATP isn’t the only player. Another molecule, GTP (guanosine triphosphate), powers critical neuron-specific processes like cell signaling, protein transport, and waste removal. In aging brains, GTP levels naturally decline, triggering what scientists call an “energy crisis.”
When neurons don’t have enough GTP, they can’t perform vital cleanup tasks. It’s like a city where the power grid flickers—traffic lights fail, garbage trucks stall, and chaos slowly builds. This sets the stage for the toxic buildup of amyloid proteins that drive Alzheimer’s progression.
3. When the Brain’s “Garbage Disposal” Shuts Down
Your brain has its own internal recycling system called autophagy—literally “self-eating.” This essential process breaks down old or damaged cellular material so new, healthy components can take their place.
When GTP levels dip, autophagy slows dramatically. The “trash collectors” of the brain lose their fuel, and waste starts piling up in the form of misfolded proteins. Over time, this buildup turns into the amyloid plaques that choke neuronal communication and cause brain cell death.
This led researchers to ask a powerful question: If we could restore GTP levels and restart autophagy, could neurons begin cleaning up the toxic debris that drives Alzheimer’s?
4. The First Hero: Vitamin B3 (Nicotinamide) – The Cellular Power Booster
Enter nicotinamide, a special form of Vitamin B3. Unlike niacin, which is often used to manage cholesterol, nicotinamide plays a key role in boosting NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)—a molecule that fuels virtually every cellular process.
NAD+ acts like the master regulator of energy metabolism. Without it, both ATP and GTP production grind to a halt. Unfortunately, NAD+ levels decline sharply as we age—by about 50% by midlife. This drop leaves brain cells starved for energy and less able to repair DNA or maintain healthy communication.
By supplementing with nicotinamide, researchers were able to replenish NAD+ and, in turn, restore the neurons’ capacity to produce GTP. The “power plants” of the cells came back online, giving them the energy needed to resume normal maintenance and waste-clearing functions.
5. The Second Hero: EGCG – Green Tea’s Defense Shield
Energy is only half the story. Aging neurons are also under siege from oxidative stress—a relentless bombardment of free radicals that damages cell membranes, proteins, and DNA. Think of it as biological rust forming inside your brain.
EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate), the star antioxidant in green tea, is famous for its ability to neutralize these harmful molecules. But it doesn’t stop there. EGCG also activates a powerful internal defense system known as the Nrf2 pathway, which tells cells to produce their own protective antioxidants.
It’s a two-tiered protection plan: EGCG extinguishes the immediate “fires” of oxidative damage while simultaneously training cells to become more resilient against future stress. That’s why regular green tea consumption has been linked in population studies to better cognitive performance and reduced age-related decline.
6. The Power of Synergy: When Vitamin B3 and EGCG Join Forces
In the UC Irvine study, mouse neurons engineered to mimic Alzheimer’s pathology were treated with both nicotinamide and EGCG. The results were striking:
-
Energy Restored: Nicotinamide replenished NAD+ and boosted GTP production.
-
Damage Reduced: EGCG neutralized oxidative stress, protecting neurons from further harm.
-
Autophagy Reactivated: With energy restored and oxidative stress reduced, the cells’ cleanup machinery roared back to life.
-
Plaques Cleared: Amyloid proteins were broken down and removed more effectively.
-
Cell Survival Improved: Neurons treated with the combo lived longer and functioned more normally.
What made this so impressive wasn’t just the individual benefits—it was the synergy. Vitamin B3 powered the cleanup, while EGCG protected the machinery doing the cleaning. Together, they created a biological environment where damaged neurons could begin to heal themselves.
7. A Word of Caution: Promising, But Early Days
Before anyone rushes out to buy supplements, perspective is essential. This research is in vitro—conducted in glass dishes using isolated mouse brain cells. The human brain, protected by the blood-brain barrier and influenced by countless variables, is far more complex.
Moreover, both compounds face a delivery problem. When taken orally, much of the nicotinamide and EGCG is broken down by the digestive system and liver long before it reaches the brain. Scientists are now exploring advanced delivery methods—like nanoparticle formulations or intranasal sprays—to bypass this limitation.
So, while the early data are exciting, they represent a first step, not a medical solution. More animal studies and human clinical trials are needed before this combination can be recommended for Alzheimer’s prevention or therapy.
Conclusion: Hope in the Details
The combination of nicotinamide and EGCG offers an intriguing new lens on how to approach Alzheimer’s—by restoring energy balance and protecting neurons from oxidative decay. It’s an elegant example of systems biology in action, where two simple, natural compounds complement each other to target multiple aspects of cellular dysfunction.
But the most important takeaway is this: science is revealing that brain health is deeply connected to cellular energy and oxidative balance—factors we can already influence through our daily habits.
While we wait for further research, you can strengthen your brain’s defenses by doing what’s already proven to work:
-
Eat a nutrient-rich diet filled with colorful fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
-
Stay physically active, as movement naturally boosts both blood flow and NAD+ production.
-
Get enough restorative sleep, which allows your brain to clear out metabolic waste.
-
Keep your mind and social connections active, since mental stimulation supports neural plasticity.
And finally, if you’re curious about Vitamin B3 or green tea supplements, talk to your healthcare provider before starting anything new. This research gives us a hopeful glimpse into what might come next—but for now, smart lifestyle choices remain our best defense.
News in the same category


How to cleanse your kidneys using this natural, home made drink

Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight liver fat, regulate sugar and cholesterol

People whose mouths feel dry when sleeping at night need to know these 8 reasons
Scientists explain shocking reality of what your brain sees right before you die

Neurologist Advises Ceasing Beer Consumption by Age 65

Drinking Water on an Empty Stomach: Japanese Water Therapy, What Science Says, and More
Eat This — It Opens Arteries to Your Heart and Brain

Eat this before bed? Doctors are stunned by the results
The 7 Silent Causes of Poor Leg Circulation — And How to Fix Them Naturally
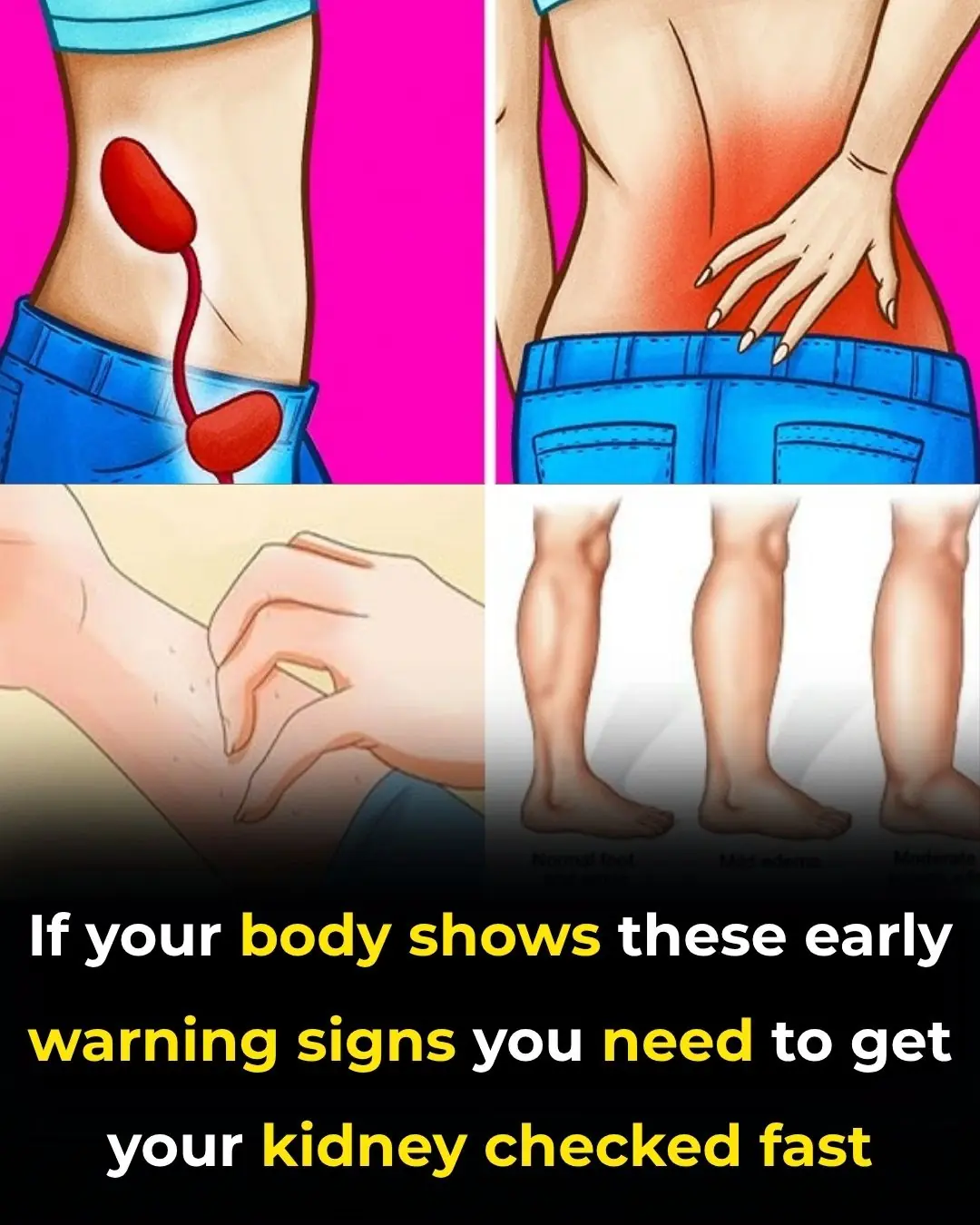
Early Signs of Kidney Disease & How to Protect Your Kidneys (Evidence Based)

1 cup a day takes joint pain away naturally

Feeling sluggish after meals? 7 natural ways to improve bile flow and boost digestion
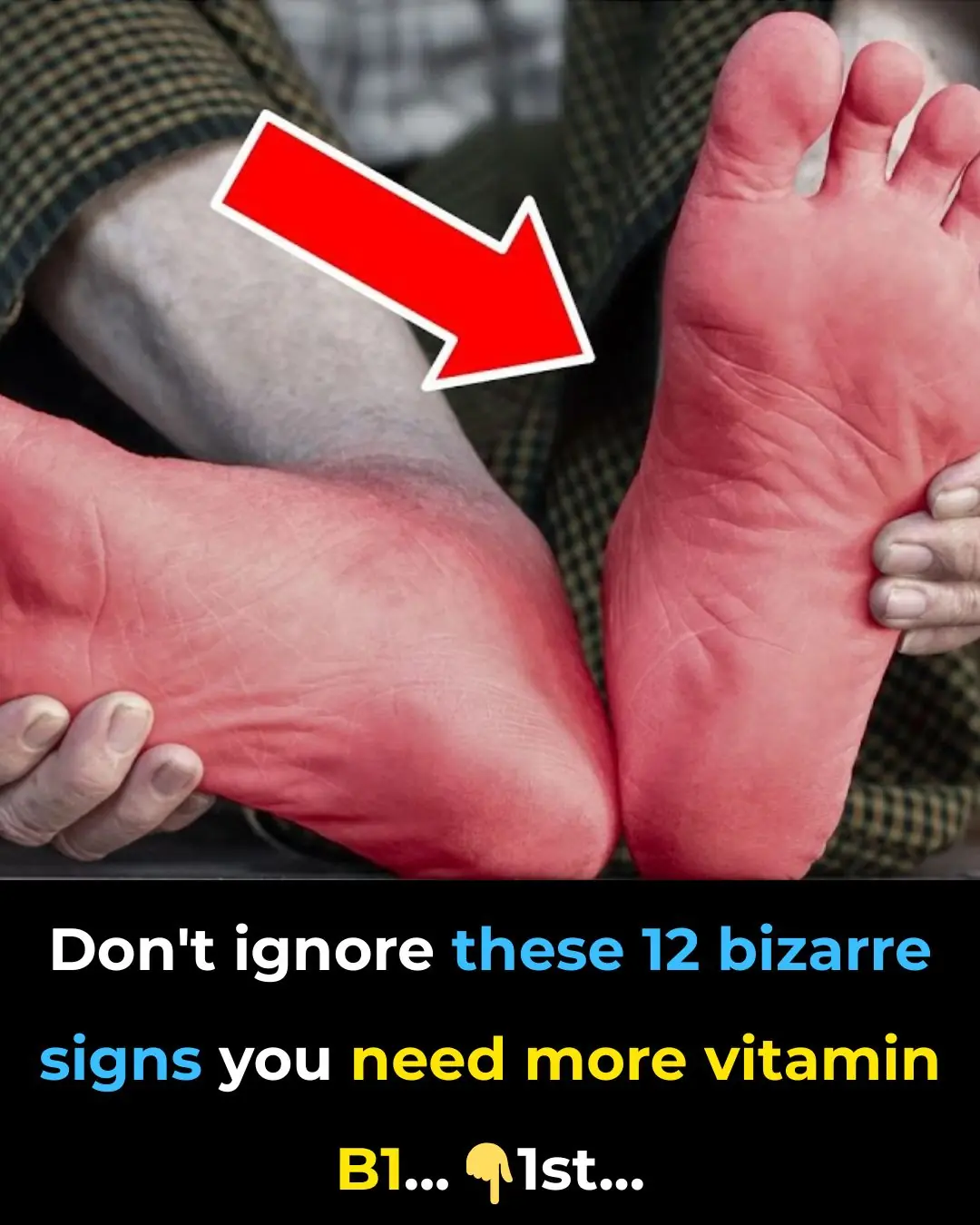
Don’t ignore these 12 bizarre signs you need more vitamin B1!

Orange & Ginger Cleanse Juice for Kidneys, Lungs & Liver

Thyme: The Natural Remedy for a Variety of Health Problems
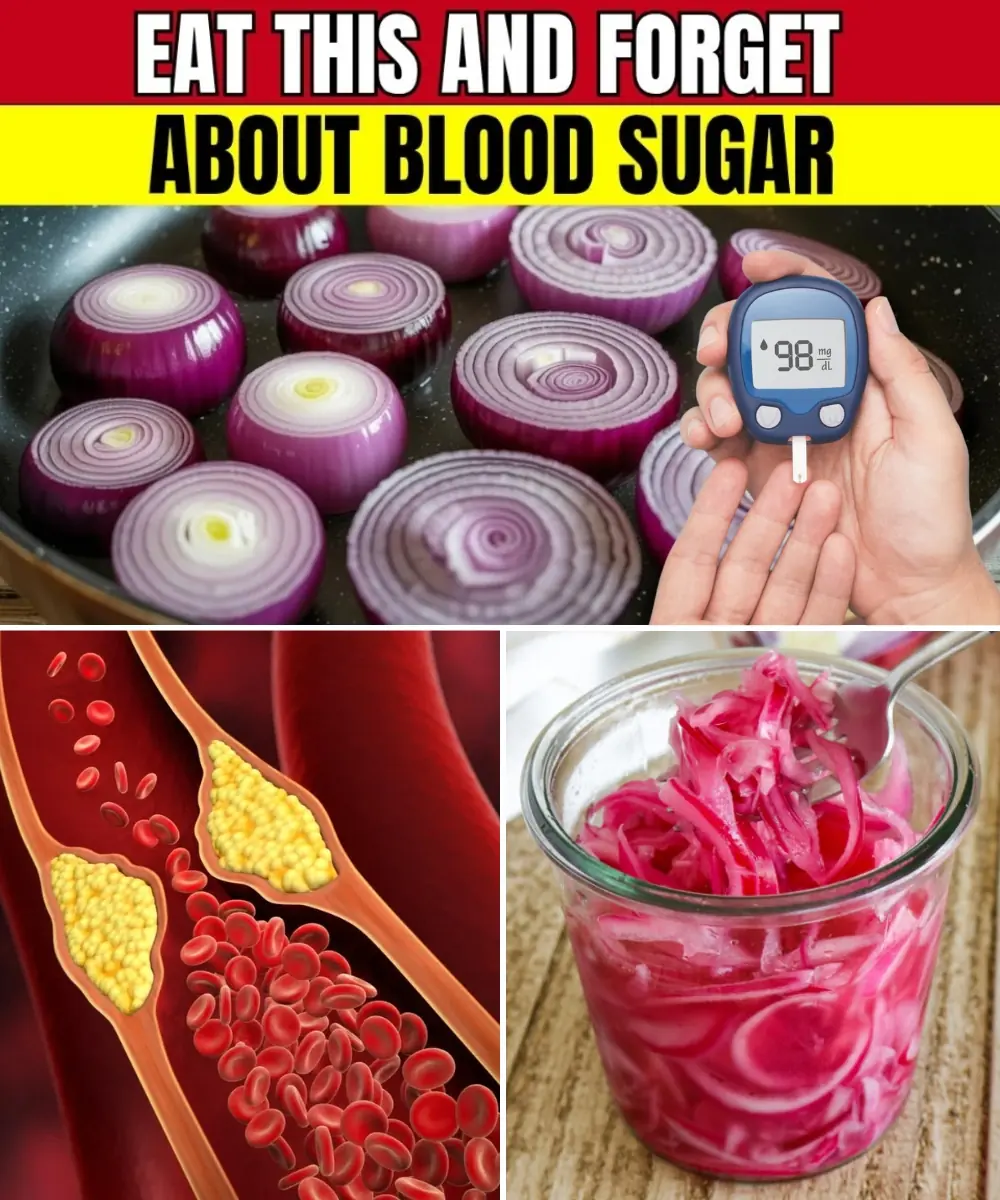
Red Onion for Instant Blood Sugar Drop: A Kitchen Secret Few Know
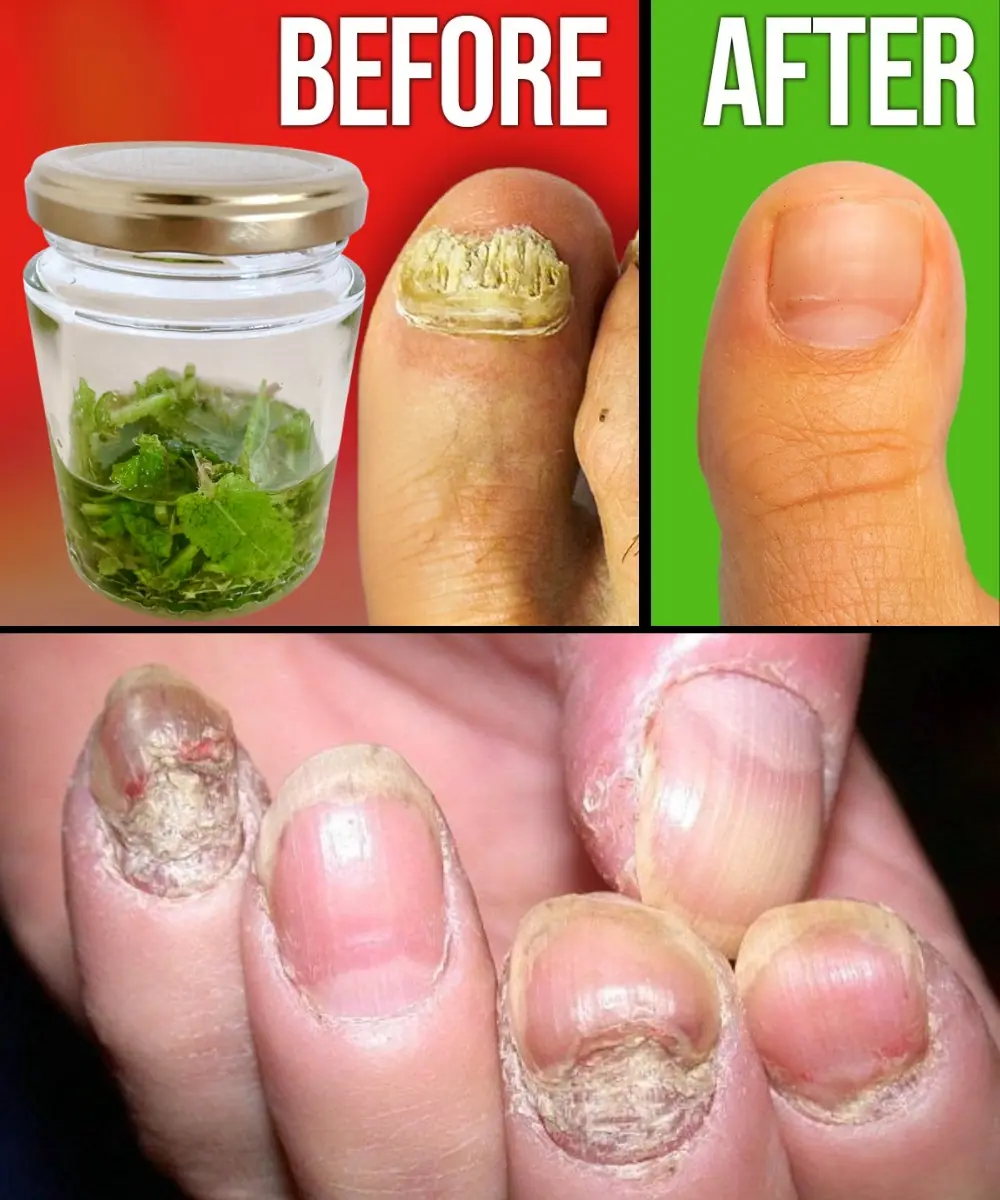
Discover the Secret of “Rompe Fungus”: Naturally Restore Healthy Nails!

Here’s How to Go to Sleep Fast (in Under 1 Minute)
News Post

10 genius tricks to revive your garden patio

You are doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to wash towels

They look so harmless

How to Remove a Fish Bone from Your Throat 🐟😮

You’re doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to store knives

You’re doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to unclog your drain

Detroit Man Went From Quitting His Job To Buying A Building For His Car Detailing Business After It Went Viral On TikTok

Thyme Essential Oil Shows Signs of Killing Lung, Oral and Ovarian Cancer

A Boy, A Bullet, and the Friend Who Saved Him

How to cleanse your kidneys using this natural, home made drink
A Heart of Gold: 5-Year-Old Danya Dudin’s Toy Drive Brings Joy to Kids with Cancer

The Little Run Toward Love: When a Baby Alpaca Taught the World What Affection Looks Like.

Science backs it up: 3 fruits that fight liver fat, regulate sugar and cholesterol

When the World Felt Heavy, He Knocked: The Quiet Friendship of Sandra Bullock and Keanu Reeves.
A Mother’s Unbearable Journey: Little Jimmie’s Fight Against Cancer
Two Battles, One Family: A Firefighter’s Courage and a Premature Baby’s Fight for Life

The Bear Who Rode Beside Her.

People whose mouths feel dry when sleeping at night need to know these 8 reasons
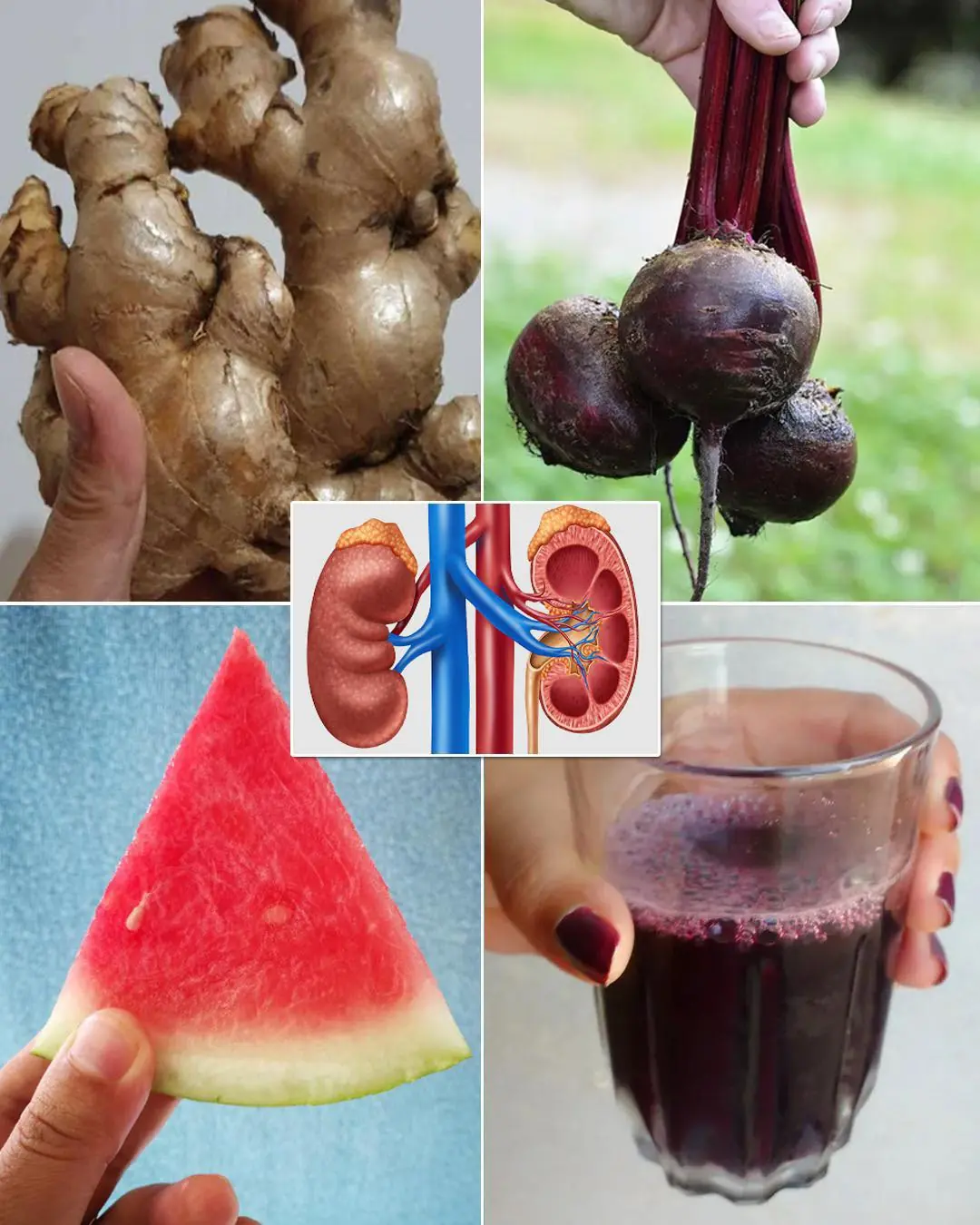

Ginger, Watermelon, and Beetroot Juice: 15-Day Natural Kidney Cleanse
