Top 10 Foods to Heal Knee Pain and Rebuild Cartilage Naturally
Keeping your knees strong and pain-free is essential for long-term mobility and quality of life. Knee joints depend heavily on cartilage — a smooth, flexible, shock-absorbing tissue that prevents bones from grinding against each other. Unfortunately, age, injury, chronic inflammation, and poor nutrition can gradually wear cartilage down, leading to stiffness, swelling, and conditions like osteoarthritis.
The good news? While cartilage doesn’t regenerate easily, the right foods can slow deterioration, reduce inflammation, and support your body’s natural repair processes. Below are the top nutrient-rich foods and habits that help restore joint comfort and strengthen knee cartilage — plus some additional insights to help you build a long-term joint-healthy lifestyle.
Why Cartilage Breaks Down
Cartilage is made of collagen fibers, water, and proteoglycans — compounds that help it stay firm yet cushioned. When these components degrade, the joint loses lubrication and shock absorption, leading to:
-
Grinding or clicking sounds
-
Sharp pain during movement
-
Morning stiffness
-
Reduced range of motion
Left untreated, this deterioration progresses into chronic inflammation and even bone-on-bone contact.
But your diet can dramatically influence how quickly this damage happens.
10 Superfoods That Support Knee Cartilage & Reduce Pain
1. Omega-3 Rich Fish

Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, tuna, and mackerel deliver powerful EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids known to:
-
Reduce swelling and inflammation
-
Protect cartilage cells
-
Improve joint mobility
Plant omega-3s (ALA) in walnuts, chia, and flaxseeds are helpful, but your body converts only a small portion into EPA/DHA—meaning fish sources remain the most effective.
2. Glucosamine-Rich Broths & Shellfish
Shrimp, lobster, crab, beef trachea, chicken feet, and oxtail are natural sources of glucosamine, a compound your body uses to rebuild cartilage and lubricate joints.
Bone broth provides a powerful combination of:
-
Collagen
-
Gelatin
-
Glucosamine
-
Chondroitin
-
Hyaluronic acid
Taken regularly, it can noticeably reduce knee stiffness and support cartilage flexibility.
3. Antioxidant-Rich Fruits & Greens
Oxidative stress is a major driver of cartilage breakdown. Foods like:
-
Blueberries
-
Strawberries
-
Spinach
-
Arugula
-
Red cabbage
provide vitamins C, E, and polyphenols that protect cartilage cells and fight inflammation inside the joint.
4. Vitamin C Foods
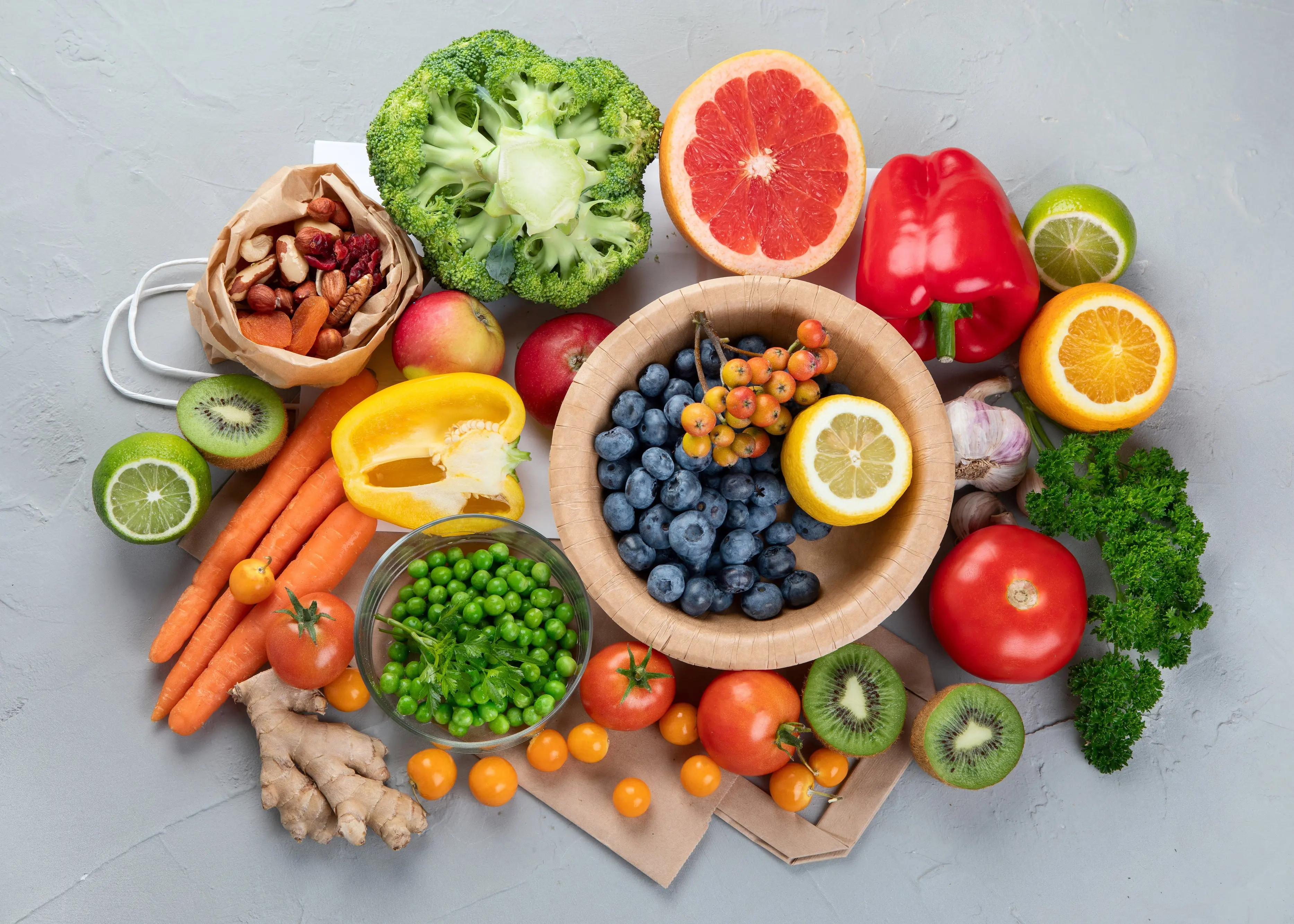

Vitamin C is essential for collagen production—the primary protein in cartilage.
Top sources:
-
Citrus fruits
-
Kiwi
-
Berries
-
Bell peppers
-
Parsley
Low vitamin C levels are directly linked to faster cartilage degeneration.
5. Vitamin D Foods
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and plays a major role in bone and joint integrity.
Sources:
-
Sunlight
-
Salmon
-
Egg yolks
-
Fortified foods
Many adults are deficient, unknowingly worsening joint pain.
6. Calcium-Rich Foods
Calcium strengthens the bones that support your cartilage. It is found in:
-
Dairy products
-
Kale
-
Broccoli
-
Sardines
Weak bone structure increases pressure on cartilage, accelerating wear.
7. Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium is required for:
-
Healthy bone density
-
Regulating calcium
-
Producing hyaluronic acid (which lubricates joints)
Great sources include:
-
Pumpkin seeds
-
Avocados
-
Spinach
-
Almonds
-
Dark chocolate
A deficiency can worsen stiffness and inflammation.
8. Probiotic & Fermented Foods
Gut health strongly influences inflammation throughout the body. Probiotics help lower systemic inflammation, benefiting joint pain.
Eat more:
-
Yogurt
-
Kefir
-
Sauerkraut
-
Kimchi
-
Fermented pickles
Better digestion also means better nutrient absorption—critical for joint repair.
9. Whole Grains
Brown rice, quinoa, barley, and oats support joint health thanks to their:
-
High fiber
-
Anti-inflammatory phytonutrients
-
Long-lasting energy
However, people with joint problems often react poorly to wheat or gluten, so reducing wheat-based products may help decrease inflammation.
10. Turmeric & Ginger
Both plants contain potent anti-inflammatory compounds:
-
Curcumin (turmeric)
-
Gingerol (ginger)
They help soothe chronic joint pain, reduce swelling, and protect cartilage from oxidative damage. Drinking ginger-turmeric tea daily can improve flexibility in as little as a few weeks.
Foods to Avoid for Joint Health
To prevent further cartilage damage, limit:
-
Processed foods
-
Sugary snacks
-
Refined carbohydrates
-
Trans fats and hydrogenated oils
-
Additives like aspartame, sucralose, nitrites
These ingredients spike inflammation and accelerate joint deterioration.
Lifestyle Add-Ons That Boost Results
Low-Impact Exercise
Combining diet with movement gives the best long-term results. Activities like:
-
Swimming
-
Yoga
-
Pilates
-
Cycling
-
Walking on soft surfaces
strengthen muscles around the joint, improve circulation, and enhance cartilage nutrition.
Healthy Weight Management
Extra body weight increases pressure on your knees by up to 4x per pound gained. Even a small reduction in weight can drastically decrease pain and inflammation.
Hydration for Joint Lubrication
Cartilage is nearly 70% water. Dehydration stiffens the joint, reduces shock absorption, and speeds up deterioration. Aim for:
-
6–8 glasses per day
-
More if active or living in hot climates
Anti-Inflammatory Meal Routine
A joint-friendly daily meal could look like:
-
Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and chia
-
Lunch: Salmon salad with spinach, avocado, and lemon
-
Snack: Walnuts or pumpkin seeds
-
Dinner: Bone broth soup with quinoa and vegetables
This eating pattern reduces inflammation throughout the body and provides all the building blocks needed for cartilage repair.
Conclusion
You have far more control over your joint health than you may realize. By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, nutrient-dense meals, bone broth, fatty fish, fermented foods, and magnesium-rich ingredients, you can:
-
Reduce knee pain
-
Support cartilage repair
-
Lower inflammation
-
Improve mobility
-
Prevent long-term degeneration
Pair these foods with low-impact exercise, proper hydration, and reduced processed food intake, and you can dramatically improve how your knees feel—starting within just a few weeks.
News in the same category


Never Toss Banana Peels Again: The 2,000-Year-Old “Trash” Trick That Erases Wrinkles, Heals Scars, Whitens Teeth & Drops Blood Pressure Overnight

The $5 Kitchen Secret: Why You Should Be Brushing Your Teeth with Turmeric and Baking Soda

This carb is more damaging to your blood sugar than pure sugar
A neurosurgeon says your legs could predict dementia years before memory loss

Avoid Ginger If You Have THESE Health Problems

The step-by-step plan to drop 30 pounds quickly in 2025

Got High Blood Pressure? Try This 2-Ingredient Tea!
The Best Natural Remedies to Treat and Prevent Varicose Veins Effectively

People Who Do This Every Morning Have Better Circulation and More Energy
12 warning signs of poor circulation in your legs.

Treating Nail Fungus Naturally

7 ways to protect your heart during the winter months
Unexplained Bruising on Your Body: Causes and Treatments

Coconut water: Is It Good for You, Nutrition, Benefits, Side Effects (Science Based)

Lose just 1 gram of fat in your pancreas – and your diabetes may reverse, study finds

Doctors warn about 7 overlooked prostate cancer signs you should never ignore
The best way to lower blood pressure fast!
News Post

When a Woman Bites Her Lip While Staring at You, It Means She Is ...

Have you noticed small white spots on your arms or legs… and you don't know what they are?

4 Best Clove Toners for Beautiful Skin

How Europe Says "Street": A Multilingual Journey Through Language and Culture

Never Toss Banana Peels Again: The 2,000-Year-Old “Trash” Trick That Erases Wrinkles, Heals Scars, Whitens Teeth & Drops Blood Pressure Overnight

A New Dawn for Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment: From Management to Possible Remission

A Butterfly, A Flute, and Unshakable Composure: The Legendary Performance of Yukie Ota

The $5 Kitchen Secret: Why You Should Be Brushing Your Teeth with Turmeric and Baking Soda

Felix Baumgartner's Record-Breaking Jump: Breaking the Sound Barrier from Space
A Pacemaker the Size of a Grain of Rice: Revolutionizing Heart Care

Denmark’s Ground‑Breaking Proposal: Granting Citizens Copyright Over Their Face, Voice and Body to Combat Deepfakes

10 DIY Beauty Ice Cubes for Radiant, Glowing Skin

This carb is more damaging to your blood sugar than pure sugar

A neurosurgeon says your legs could predict dementia years before memory loss

Science vs. Disney: What Finding Nemo Didn’t Tell You About Clownfish

U.S. Grocery Costs Hit Record High: Families Now Spending Over $1,000 a Month

When Mating Turns Dangerous: The Fierce Behavior of the Sydney Octopus

Welcome to the Monkey Madness: Thailand’s Unforgettable Lopburi Buffet

Why Height Matters So Much in Online Dating — And What the Numbers Reveal
