Voyager Spacecraft: A 40-Year-Old Marvel of Engineering Exploring Interstellar Space
The Voyager program, consisting of the twin spacecraft Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, stands as one of the most successful and enduring efforts in the history of space exploration. Launched by NASA in 1977, these probes were intended to undertake a grand tour of the outer planets of our solar system, including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Although Voyager 1 focused primarily on Jupiter and Saturn, it was later directed on a trajectory that took it out of our solar system, while Voyager 2 conducted flybys of all four outer planets, providing invaluable scientific data.
As of today, both spacecraft have crossed the heliopause, the boundary that marks the end of the solar wind’s influence, and are now exploring interstellar space. They are the most distant human-made objects ever created, continuing to send data back to Earth from beyond the realm of the solar system. Despite being more than 40 years old, the Voyager probes remain operational, transmitting valuable scientific information about the environment of interstellar space, offering a snapshot of conditions far beyond what was ever imagined at the time of their launch.
The technology that drives the Voyager spacecraft serves as a remarkable testament to the engineering capabilities of the 1970s. These probes were designed to endure the harsh conditions of space for decades, relying on a set of three redundant computers to manage guidance and control systems. These include the Flight Data System (FDS) and two Computer Command Systems (CCS). These systems were groundbreaking at the time, but by today’s standards, they are extremely limited. Together, the spacecraft’s total computer memory and data storage amount to just around 69 kilobytes—a minuscule fraction of what modern devices contain.
For data storage, when the probes are unable to transmit information directly to Earth due to their distance or alignment, they use a digital tape recorder (DTR). This system is essential for storing scientific data during periods when communication with Earth is impossible. The DTR allows the spacecraft to gather valuable measurements and information, which are then sent back to Earth once communication can be re-established.
Despite the technological advancements made in the field of space exploration, the software used to operate the Voyager probes is still based largely on original programming written using FORTRAN, a high-level programming language that was widely used for scientific and engineering applications in the 1970s. This reliance on the original software is a testament to the foresight of the engineers who designed the spacecraft, ensuring that it could function long after the technology that created it had been surpassed.
One of the most remarkable aspects of maintaining the Voyager missions today is that NASA’s engineers and operators still rely on the 50-year-old schematics and blueprints that were originally created to guide the spacecraft. These vintage documents are consulted to accurately understand the hardware and ensure that system adjustments or software patches are implemented correctly. This process underscores the mission’s age and highlights the extraordinary effort required to continue operating two spacecraft that are now over 14 billion miles away from Earth.
This reliance on aged technology and documentation is a critical part of maintaining communication and functionality with the Voyager probes, yet it also demonstrates the remarkable endurance of the original design. The ability to keep the spacecraft operational for over four decades is a true marvel of long-term engineering, proving the lasting value of well-built, thoughtfully designed systems that were made to stand the test of time.
As the Voyagers continue their journey through the vastness of space, their success is not only a testament to the ingenuity and perseverance of the engineers and scientists who built and continue to maintain them, but also to the incredible legacy of human space exploration. The Voyager program has fundamentally expanded our understanding of the cosmos, providing us with invaluable data about the outer planets, the interstellar medium, and beyond.
In conclusion, the Voyager spacecraft remain operational, sending data from the furthest reaches of space, and the story of their survival and continued functionality serves as an inspiring example of the effectiveness of thoughtful engineering and the profound dedication required to keep such an ambitious mission alive. These spacecraft, with their 69 KB of memory and reliance on decades-old technology, symbolize a truly remarkable achievement in the history of space exploration, offering a window into a future where such missions can continue to push the boundaries of what humanity can achieve in space.
Sources:
-
"Voyager Mission: A Legacy of Exploration" – NASA. https://www.nasa.gov
-
"The Voyagers: 40 Years of Space Exploration" – Smithsonian Institution. https://www.si.edu
-
"FORTRAN and Its Role in Space Exploration" – IEEE Spectrum. https://spectrum.ieee.org
-
"Voyager’s Journey Into Interstellar Space" – European Space Agency. https://www.esa.int
News in the same category


Gray Wolves: The Remarkable Lifelong Bond Between Mates and Their Role in Pack Survival

Sebastian Errazuriz’s Robotic Dogs: A Satirical Commentary on Tech Billionaires and the NFT Market

How the U.S. Escaped Hurricane Landfalls in 2025

Ancient Shark Fossils Unearthed in Mammoth Cave Rewrite 325 Million Years of Evolutionary History

How an Italian Police Lamborghini Huracán Helped Save Lives by Delivering Kidneys Across Italy
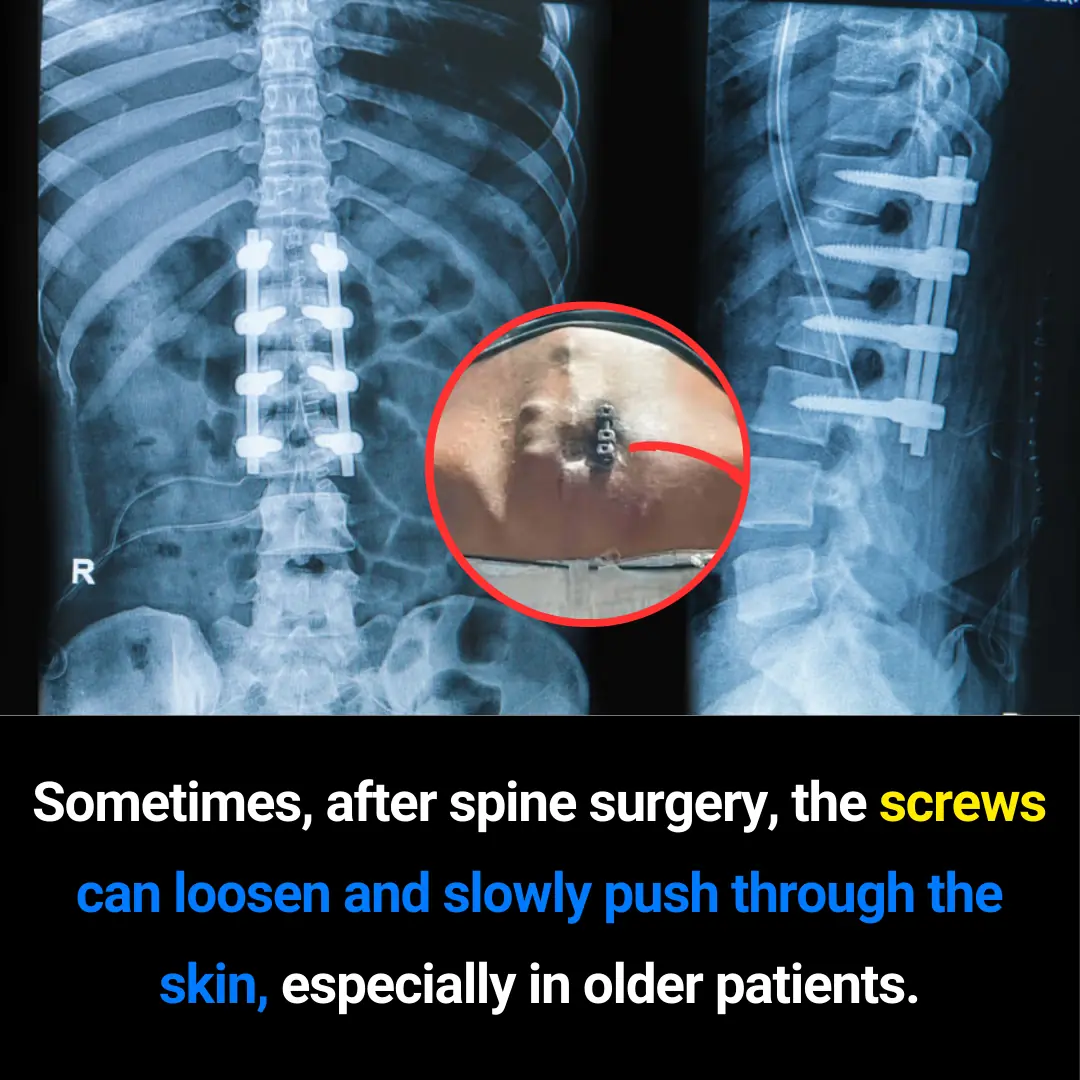
Can Spinal Screws Push Through the Skin? Understanding a Rare but Serious Post-Surgery Complication
Why the Tongue Is One of the Most Important Organs in the Human Body

What You Do First in This Scenario

Small Steps, Big Impact: How 4,000 Steps a Day Can Transform Your Health

Rising Concerns Over Excessive Headlight Brightness: A Growing Challenge for Nighttime Driving Safety in the UK

Unwavering Loyalty: The Stray Dog's Final Journey of Love and Devotion

Revolutionary MRI-Guided Cryoablation Offers Non-Invasive Cancer and Pain Treatment in Sydney

So this is what it does, here is the answer
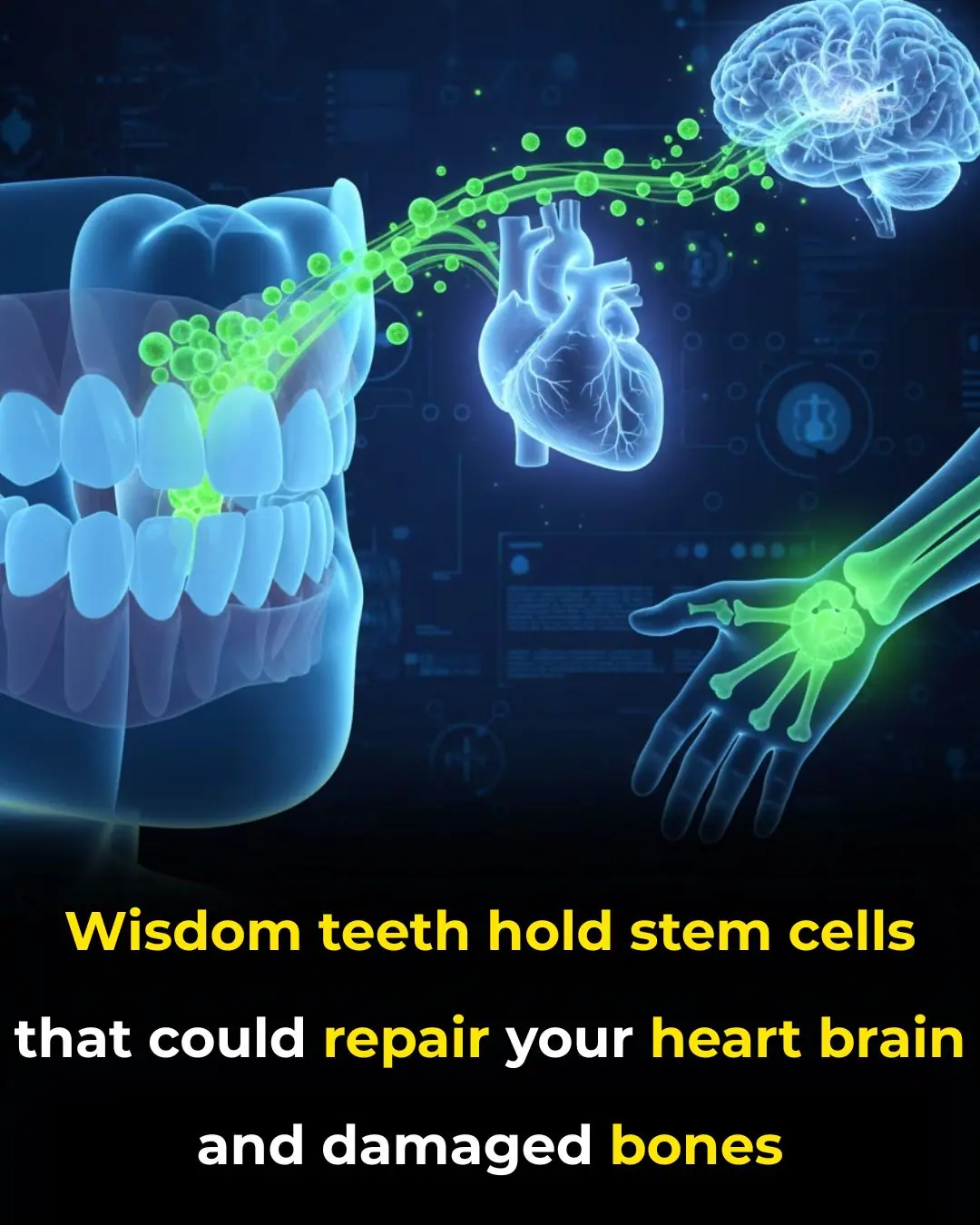
Scientists Unlock Healing Potential of Wisdom Teeth: Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine

1054 Supernova: The Cosmic Explosion That Shaped the Crab Nebula

The zodiac signs with a supernatural sixth sense… See now

Acts of Kindness Amid the Flames: A Firefighter's Reminder of His Purpose
The surprising power of 4 seeds to repair your nerves naturally
News Post

Revolutionary Nanobodies Offer New Hope for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Treatment

Gray Wolves: The Remarkable Lifelong Bond Between Mates and Their Role in Pack Survival

Sebastian Errazuriz’s Robotic Dogs: A Satirical Commentary on Tech Billionaires and the NFT Market
High-Dose Nifedipine Linked to Increased Risk of Sudden Cardiac Arrest, New Study Suggests

How the U.S. Escaped Hurricane Landfalls in 2025

Ancient Shark Fossils Unearthed in Mammoth Cave Rewrite 325 Million Years of Evolutionary History

Powerful Health Benefits of Pineapple You Should Know

How an Italian Police Lamborghini Huracán Helped Save Lives by Delivering Kidneys Across Italy

Can Spinal Screws Push Through the Skin? Understanding a Rare but Serious Post-Surgery Complication

Why the Tongue Is One of the Most Important Organs in the Human Body

What You Do First in This Scenario

The Surprising Health Benefits of Sleeping in a Cold Room

A 4-Minute, Zero-Effort Hack to Clean Grill Gunk – The Simple Trick My Nana Taught Me
High Blood Sugar Warning Signs

🥚 A Look at How Certain Boiled Egg Habits May Affect Your Heart Health

Small Steps, Big Impact: How 4,000 Steps a Day Can Transform Your Health

🌿 Clove Water Sitz Baths for Women: A Gentle Guide to Hygiene and Comfort

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Canned Tuna Every Day