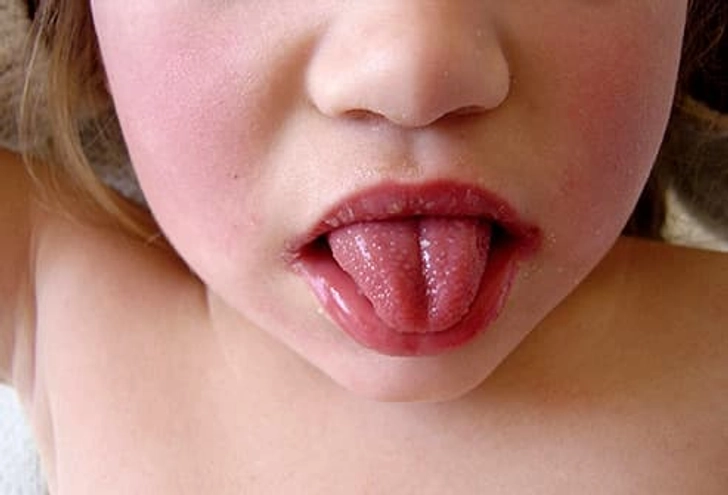
Health 06/05/2025 14:30
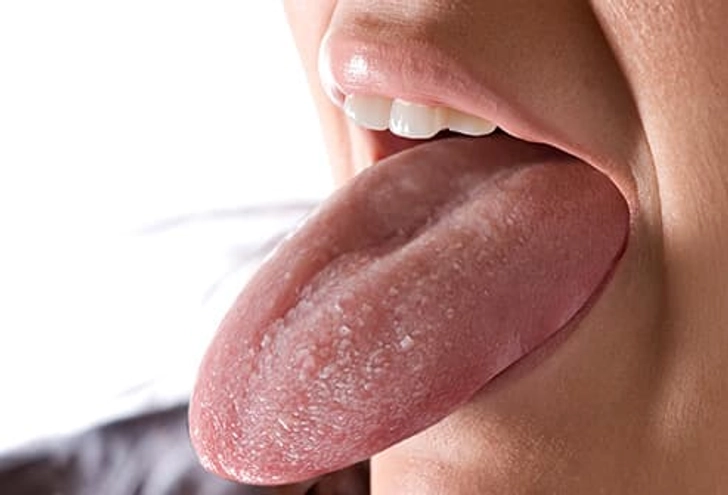
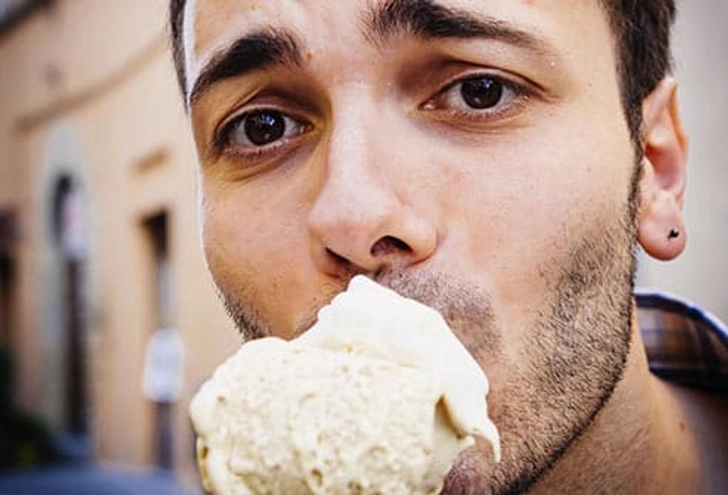
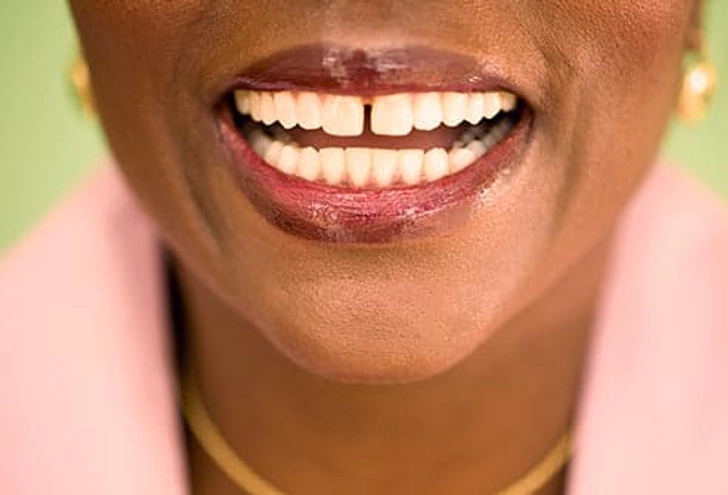
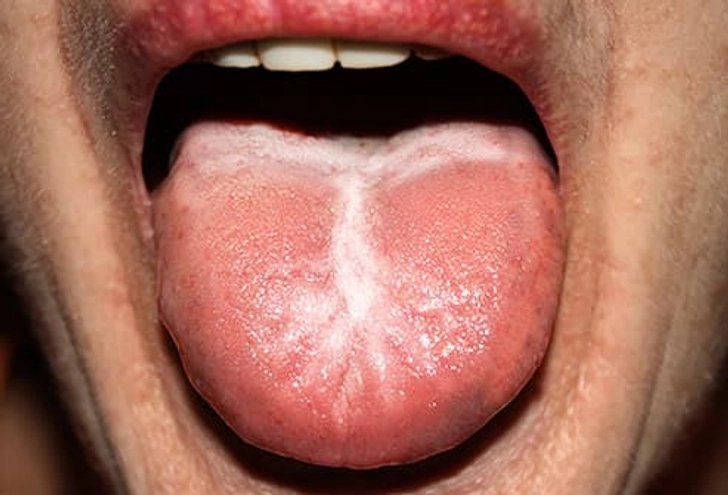
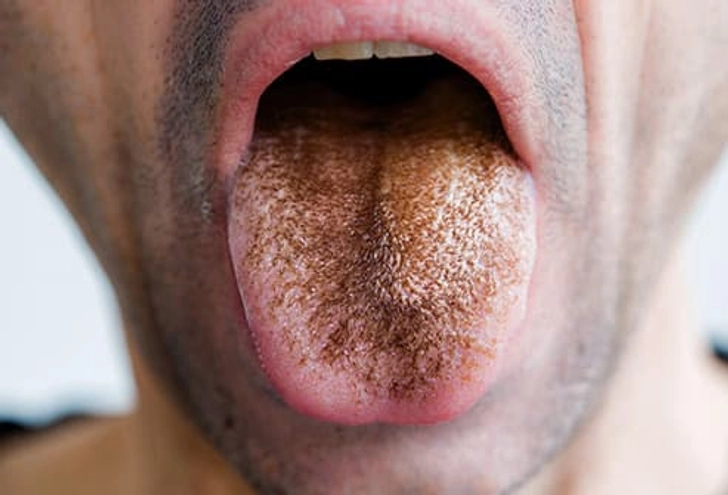
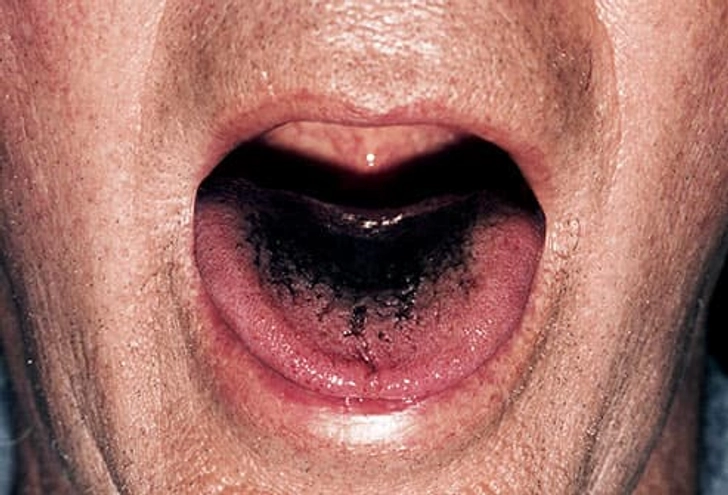
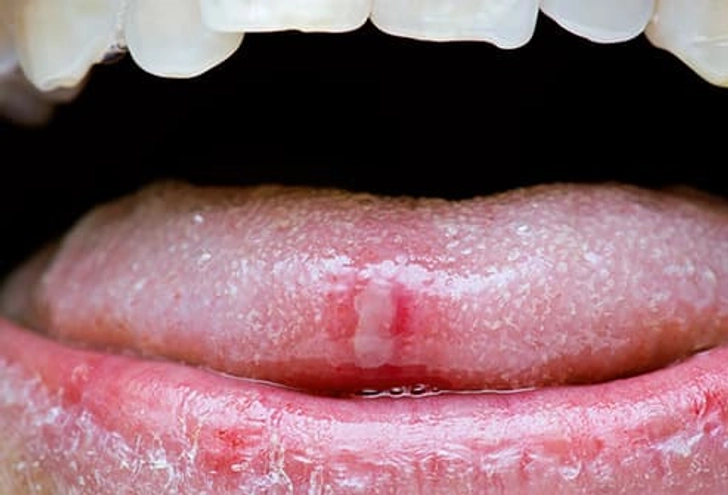
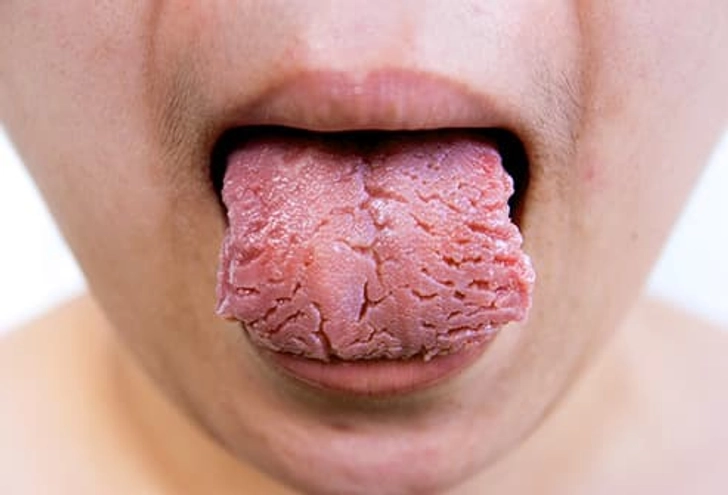
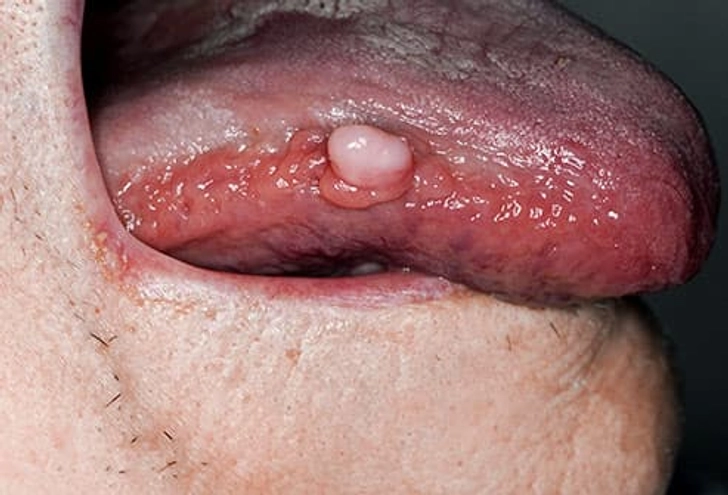
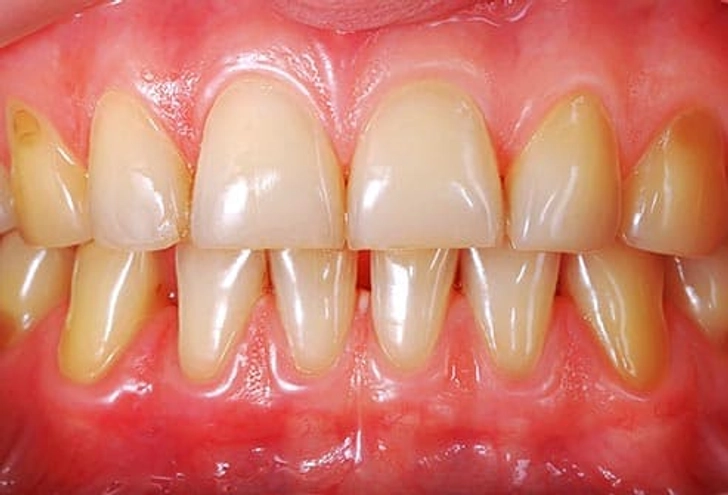
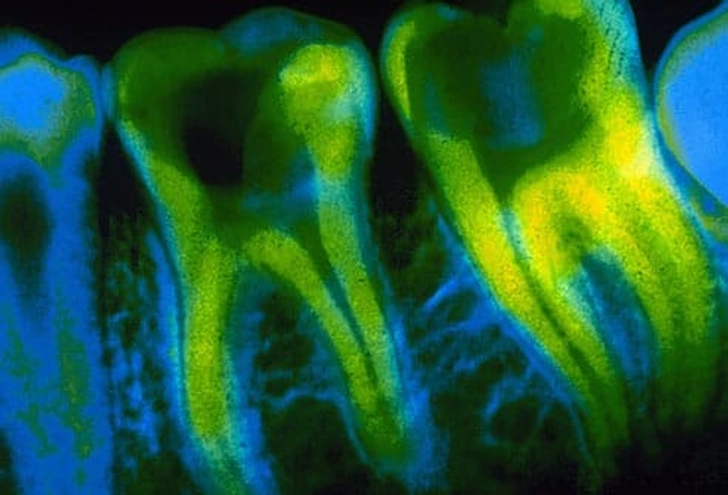
What Your Tongue Says About Your Health
News in the same category

Health 06/05/2025 20:06
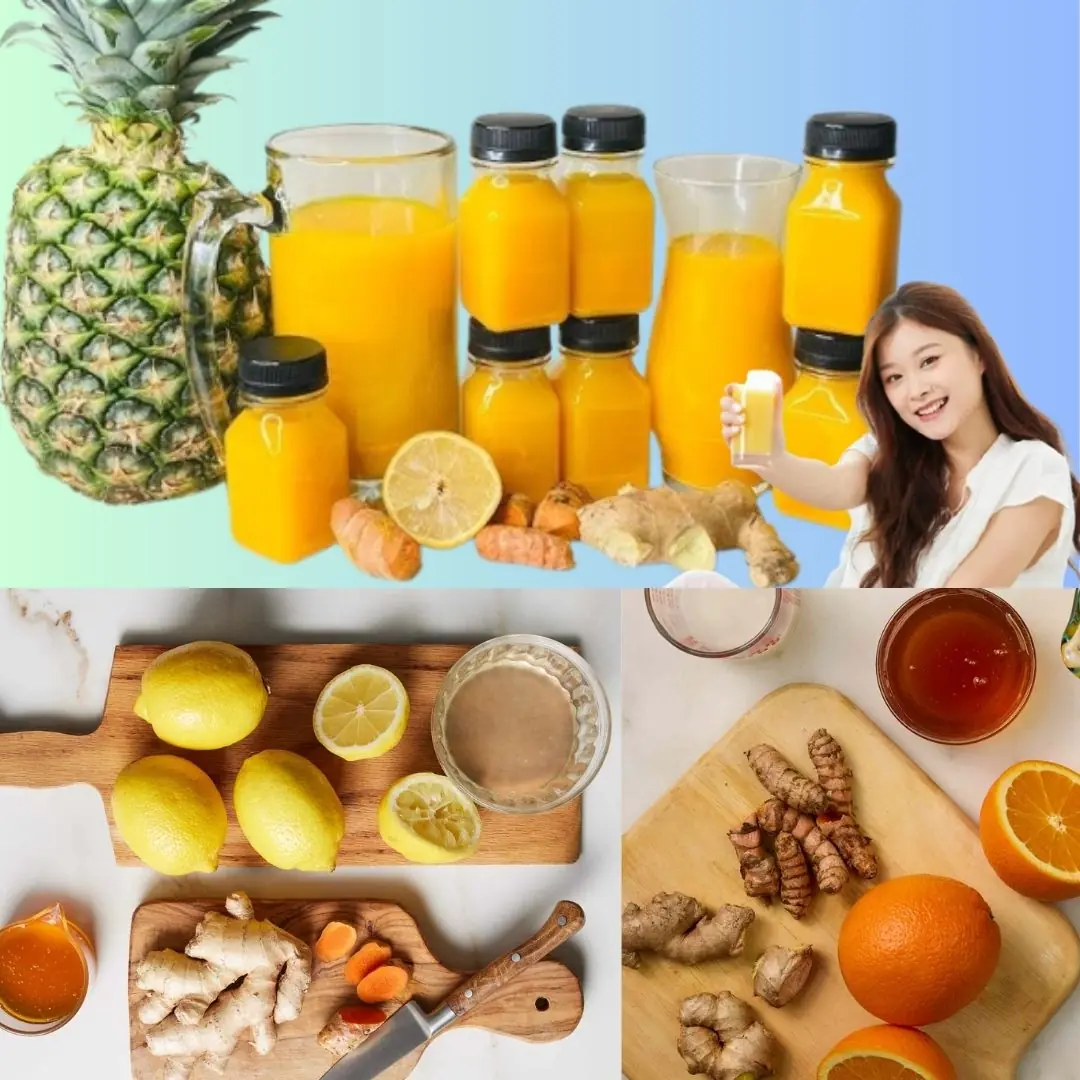

DIY Lemon Ginger Turmeric Power Shots: Boost Your Health Naturally
Health 06/05/2025 19:57
7 Early Warning Signs of Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Even One Symptom Is a Reason to See a Doctor
Health 06/05/2025 16:08
Breakthrough: Scientists Discover How to Revert Cancer Cells Back to Normal
Health 06/05/2025 16:00
9 Early Signs of Lung Cancer You Should Not Ignore
Health 06/05/2025 15:56
Professors blame one childhood eating habit for surge in colon cancer among Gen Z and Millennials
Health 06/05/2025 14:47

Are you sleeping on hidden toxins?
Health 06/05/2025 14:37

Tapeworms in Humans: Symptoms and Treatments (Pictures Included)
Health 05/05/2025 15:34

11 Health Warnings Your Fingernails May Be Sending
Health 05/05/2025 15:27

Lemon + Cucumber: The Underrated Power Duo That Will Transform Your Health
Health 05/05/2025 14:45

Refresh Your Health: Benefits of Cucumber, Ginger, Mint, Lemon, and Water
Health 05/05/2025 14:40

If Cancer Is Lurking in the Body, These 3 Signs Often Appear at Night — But Many People Ignore Them
Health 05/05/2025 11:14

Cancer Is Painless at First, But If You Notice These 8 Signs While Using the Toilet, See a Doctor Early: Don’t Ignore Them
Health 05/05/2025 11:06

9 Indications of lack of magnesium You Ought to Be aware
Health 05/05/2025 11:03
17-Year-Old Girl Hospitalized Due to Kidney Failure, Requires Lifelong Dialysis: Doctors Warn of 3 Common Habits Among Young People
Health 05/05/2025 11:02

Boy, 6, dies after experiencing common symptom which affects almost every child

The 7 Covid symptoms that shouldn't be mistaken for hay fever this summer
Warning: 9 Silent but Dangerous Signs of Cancer – Listen to Your Body
7 Early Signs of Blood Cancer Everyone Should Know
News Post

The Miracle Remedy That Has People Abandoning Hospitals: Cures Cancer, Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, and Poor Circulation!
Health 06/05/2025 20:06

DIY Lemon Ginger Turmeric Power Shots: Boost Your Health Naturally
Health 06/05/2025 19:57

7 Early Warning Signs of Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Even One Symptom Is a Reason to See a Doctor
Health 06/05/2025 16:08

Breakthrough: Scientists Discover How to Revert Cancer Cells Back to Normal
Health 06/05/2025 16:00

9 Early Signs of Lung Cancer You Should Not Ignore
Health 06/05/2025 15:56
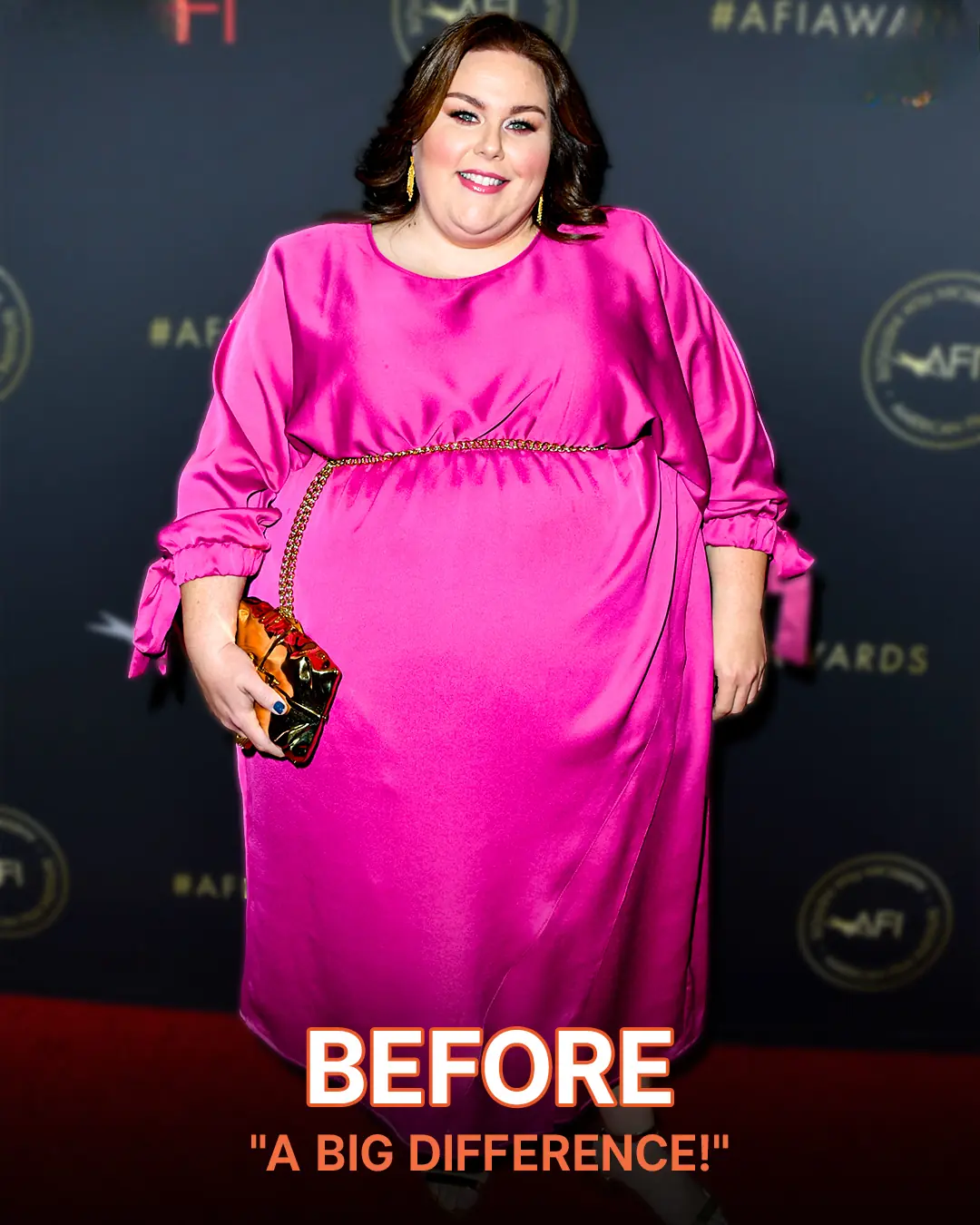

'This Is Us' Star Chrissy Metz Stuns in Multicolored Ruffled Dress at the Variety Power of Women Nashville Event – Photos
News 06/05/2025 15:26

Reba McEntire Is a Proud Mom of One Son – She Shared a Heartwarming Dance with Him at His Fairytale Wedding
News 06/05/2025 15:06
Top 10 Spices & Herbs to Support Arterial Health
News 06/05/2025 15:04
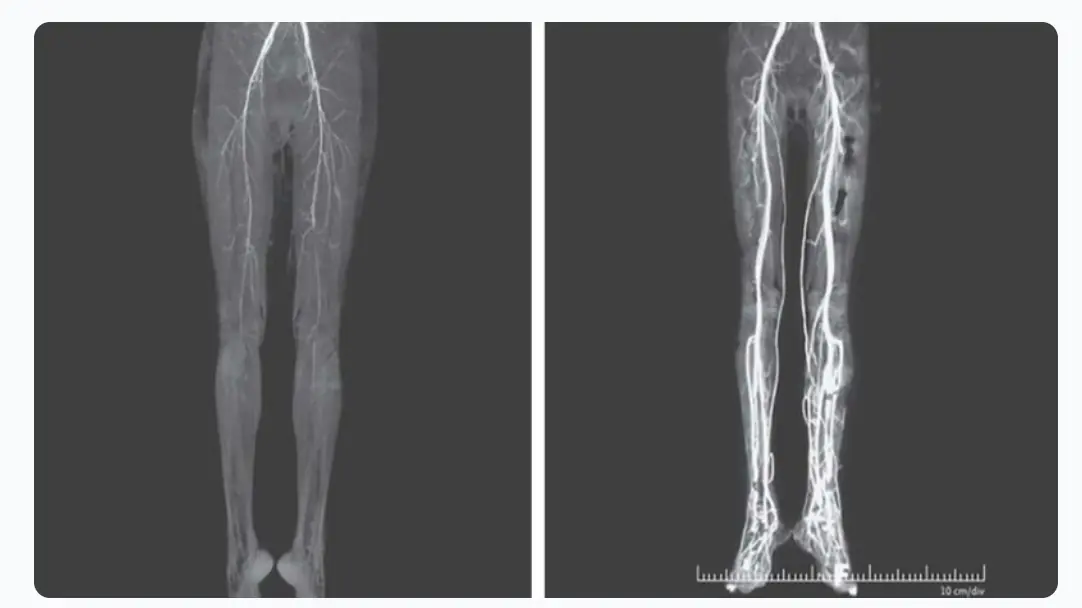
Woman Experiencing Burning Pains Turns Out To Have Medieval ‘Holy Fire’ Disease
News 06/05/2025 15:03

The Truth Behind ‘Durex’: What Its Name Actually Stands For Has Left People Stunned
News 06/05/2025 15:01
The New Leading Infectious Disease: COVID-19 No Longer Top of the List
News 06/05/2025 14:59

12 Best Foods To Support Digestive and Gut Health
News 06/05/2025 14:55

Professors blame one childhood eating habit for surge in colon cancer among Gen Z and Millennials
Health 06/05/2025 14:47

Are you sleeping on hidden toxins?
Health 06/05/2025 14:37

Sabrina Carpenter Shows Up at the 2025 Met Gala Pantsless, Igniting Online Buzz
News 06/05/2025 11:52

'Hope It's a Girl': Fans Are Convinced Rihanna Is Pregnant Following Her 2025 Met Gala Appearance — Photos
News 06/05/2025 11:29

Halley’s Comet Is Back, But This Time, It’s Raining Fire
News 06/05/2025 10:00
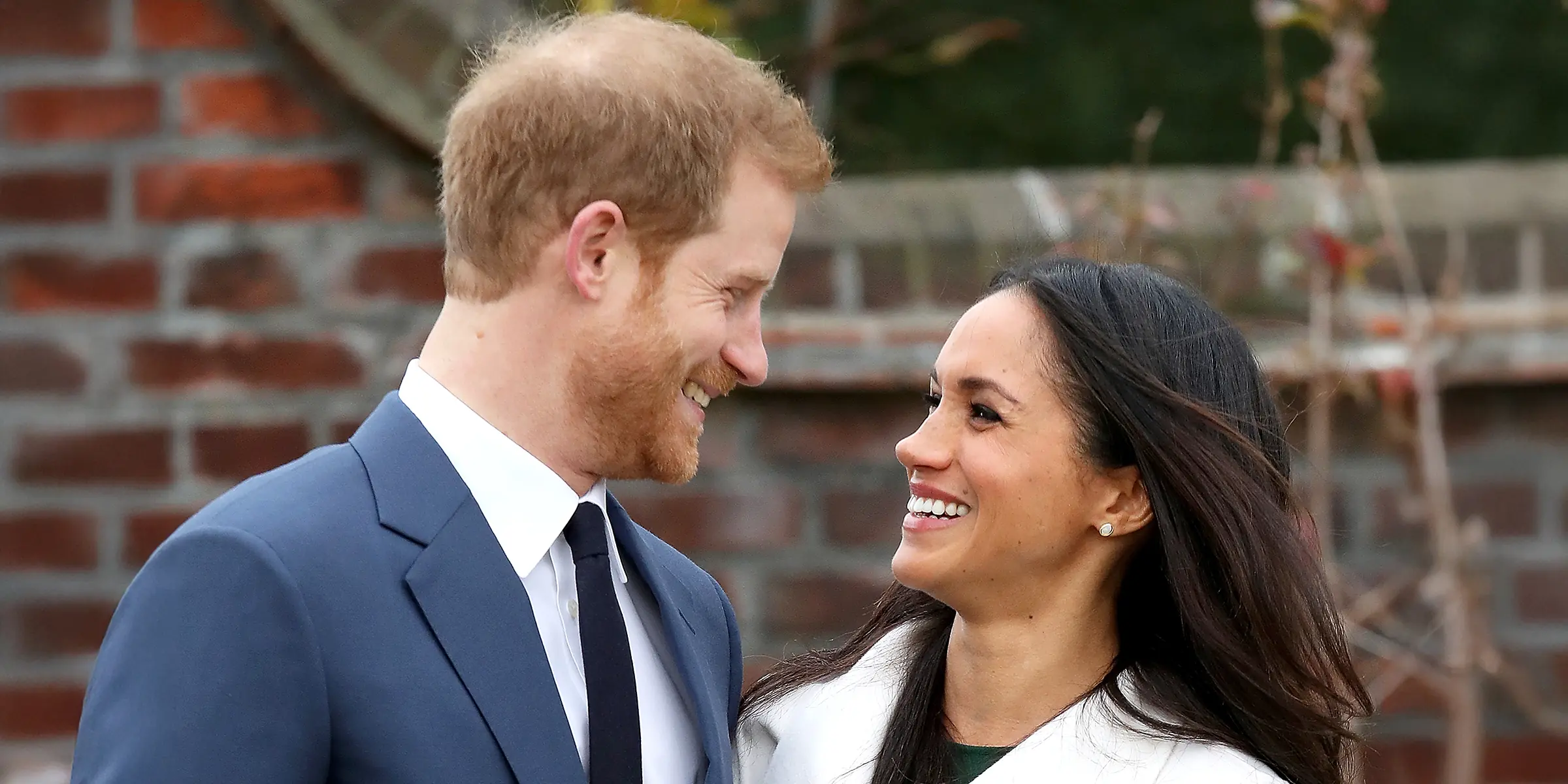

Meghan Markle Shares a Picture of Prince Harry with Their Children Archie and Lilibet Enjoying a Walk in the Garden
Following Prince Harry's BBC interview, where he shared his hopes for reconciliation with his family, Meghan Markle posted an endearing black and white photo of her husband and their kids on Instagram.
News 06/05/2025 06:39
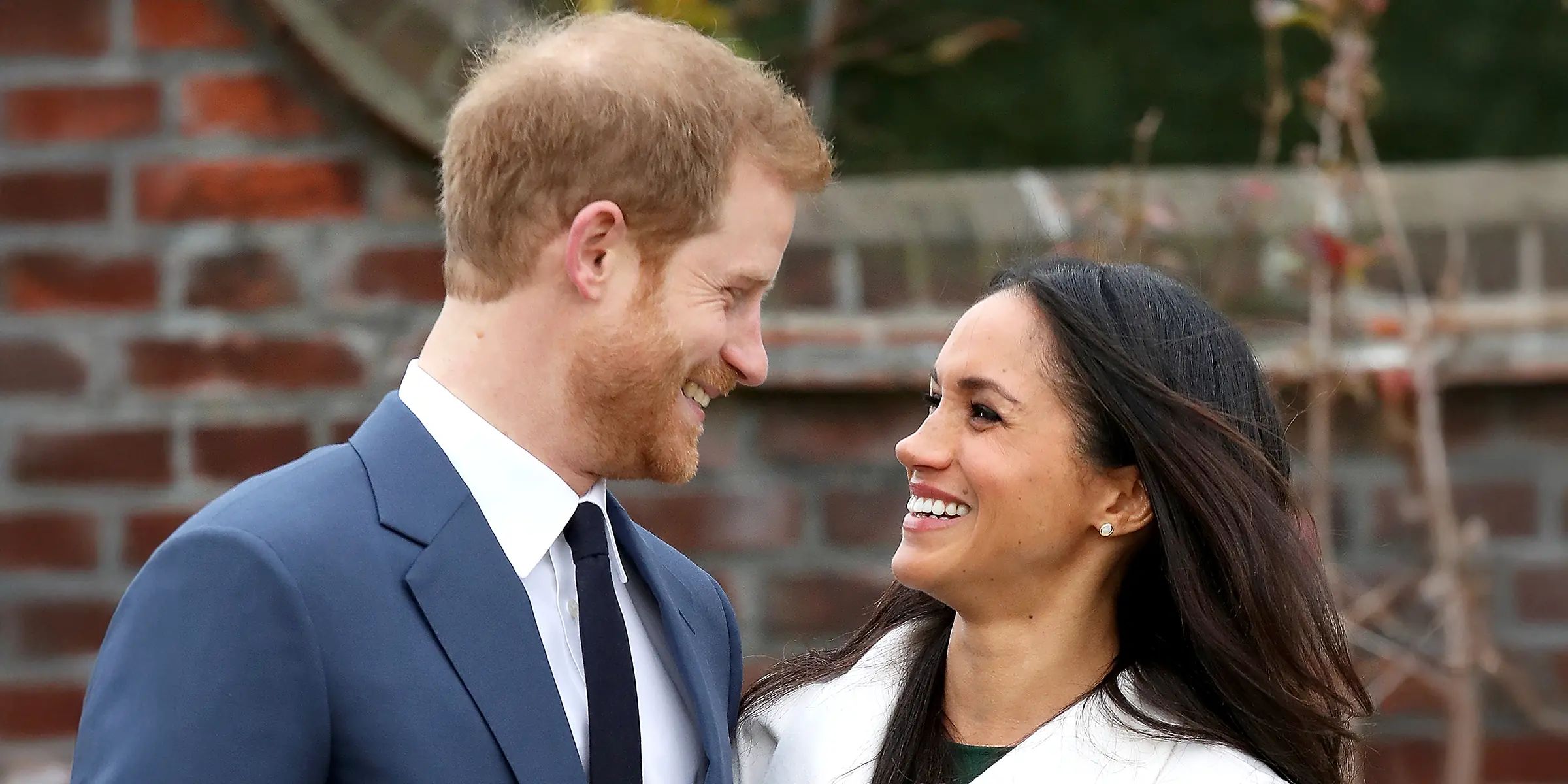

Meghan Markle Shares a Picture of Prince Harry with Their Children Archie and Lilibet Enjoying a Walk in the Garden
Following Prince Harry's BBC interview, where he shared his hopes for reconciliation with his family, Meghan Markle posted an endearing black and white photo of her husband and their kids on Instagram.
News 06/05/2025 06:32