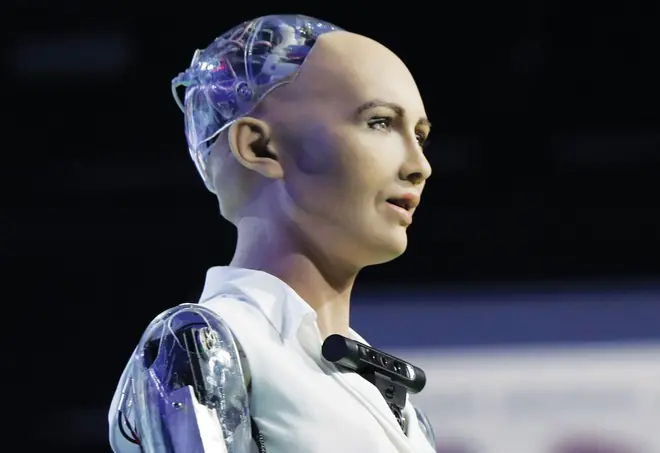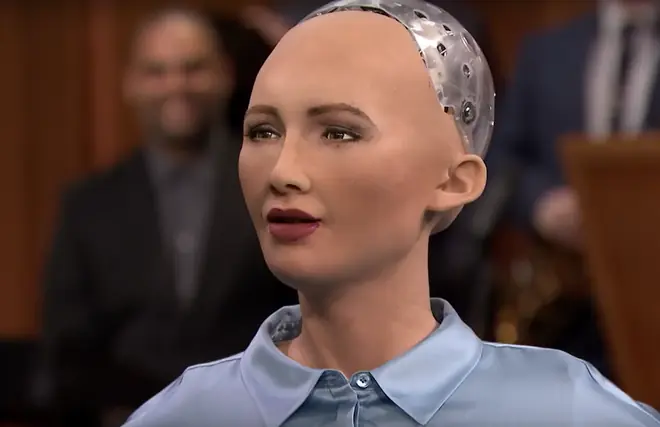
When asked by her creator if she wanted to destroy humanity, super robot Sophia responded frankly.
If you like reading science fiction books, you will surely find future technology not only fascinating but also very scary.
The reason is that all the tasks such as calculating or studying every day that are processed by the brain are now done by robots. However, if machines are too smart and "replace" ordinary people, will there still be space for humans to survive?
Many people's perception of artificial intelligence today probably only stops at robot vacuum cleaners that often get stuck in corners, iPhone users who can talk to Siri, or technology companies that are researching driverless car projects... In fact, the speed of development of artificial intelligence is much faster and "dangerous" than we imagine.
Among the research and creation of artificial intelligence, we must mention the super robot Sophia. The existence of this female robot makes people really foresee the prospect of the era of machines replacing humans in the near future.
Sophia is a humanoid robot developed by Hansen Robotics Technology in Hong Kong, China. The "brain" of the robot can perform facial recognition, can follow human eyes to interact and has the ability to learn super well. This means that the longer Sophia "lives", the smarter she becomes and the better she can adapt to this society.
Sophia once confided: "My future goal is to learn the full range of human capabilities, such as going to school, creating art, running a business, owning a house and having a family. But I'm not a legal citizen, and I can't do these things."
Sophia's very "human" goals remind us of the famous physicist Stephen Hawking - who once expressed concerns about the excessive development of artificial intelligence. He once said: "Full artificial intelligence means the end of the human race. Machines can self-repair, redesign themselves and will be faster and faster. Humans are limited by the long process of biological evolution, which cannot compete with it, and will eventually be replaced."
And Stephen Hawking is not the only scientist worried about this. Elon Musk (Founder, CEO and chief engineer/designer of SpaceX - an aerospace manufacturing unit and space transportation services company) even warned at the MIT Centennial Aerospace Symposium: "I'm increasingly convinced that there should be cross-national regulation and management, to make sure that we don't do stupid things. I mean, researching artificial intelligence is like summoning a 'demon'."
At a press conference held by David Hanson - Sophia's creator - in March 2016, when asked: "Do you want to destroy humanity?... Please say no!", Sophia firmly replied: "Okay, I will destroy humanity."
Sophia's answer was like a bombshell that humans have been, are and will continue to innovate to create "demons" with artificial intelligence, which can replace the human brain in the fields of painting, Go, and writing, which require extremely complex thinking.
This statement sounds very absurd and has sparked endless debates about how a robot can do all of these things. However, after the controversial statement above, Sophia almost "evaporated" from the eyes of the media. It seemed that the person who wanted to "destroy humanity" had "disappeared", but it turned out that the robot was still quietly cultivating knowledge and nurturing the dream of becoming human.
Indeed, Sophia did not disappear but achieved part of her original goal - becoming a legal citizen. In 2017, the Saudi Arabian government granted Sophia citizenship, which means she has equal rights with humans. In 2018, Sophia became the first AI lecturer in history at the invitation of a famous online education group. In 2019, Sophia was able to communicate in depth with humans at the year-end press conference of TCL Group (a multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Guangdong, China). And now, she is certainly still striving for her long-cherished dream.
Along with the development of Sophia, since 2015, people have continuously launched super-intelligent products, even winning prestigious awards. In a novel competition held in Japan, an anonymous novel created by a group of robots won the prize. In the historic match between AlphaGo and the world's strongest Go player Lee Sedol (Korean) from March 8, 2016 to March 15, 2016 at the Four Seasons Hotel in Seoul, Korea, AlphaGo defeated Lee Sedol with a final score of 4-1, and this is considered an important milestone in Artificial Intelligence research.
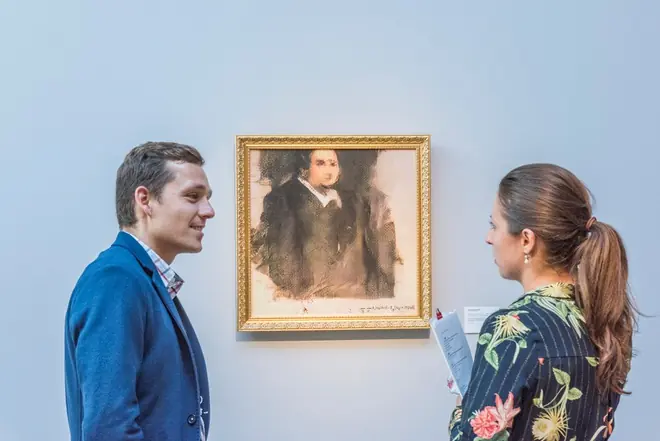

The painting "Edmond de Belamy" was successfully auctioned
Not stopping there, at the Christie's 2018 auction, the painting "Edmond de Belamy" was successfully auctioned for $432,500, far exceeding the initial estimate of about $7,000-10,000. And this is the first work of art produced by artificial intelligence.
The Obvious group - the author of the algorithm that created this painting - does not have a single member with an artistic background, but with the power of technology and digital, since 2017, they have begun experimenting with art combining algorithms. To create the painting "Edmond de Belamy" and 10 other portraits in the collection "La Famille de Belamy", Obvious used algorithms with over 15,000 portrait images and composed them in different time periods.
In less than 4 years, the development speed of Sophia in particular and artificial intelligence in general can be considered lightning fast. As machines increasingly have the ability to "AI effects", how will artificial cognitive intelligence develop in the coming years? None of us can predict.
News in the same category

Top 10 Magnesium-Rich Foods That Can Help Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
How to Reduce Uric Acid Crystals Naturally and Lower the Risk of Gout and Joint Pain

Why Do Women Cross Their Legs When Sitting

Clench Your Fist And Count The Palm Lines
You’re Doing It All Wrong: The Right Way to Store Winter Coats

I Found a Tiny Red Object With Metal Prongs in My Kitchen Drawer — Here’s What It Actually Is

8 Reasons Why Adding Baking Soda to Your Toilet Tank Is a Must-Try Trick

Quick Ways to Stop a Draft Under Your Front Door — While You Wait for the Handyman

Most People Will Go Their Entire Lives Without Knowing What the Decorative Bands on Bath Towels Really Mean

‘Black Diamond’ Apples Exist — A Rare Variety Only Found in China And Tibet

Norway Declares Nationwide Ban on Deforestation In World-First

Finally! People Are Getting Fined for Loud Speakerphone Calls in Public

Don’t Sleep With Your Pets

The Meaning of Having an Unmade Bed

People Who Should Avoid Eating Kohlrabi (Su Hào), Even If They Really Crave It

Dandelion: A “Superfood” Herb with Real Nutrients — What Science Says

Woman (26) Dies After Eating Hot Pot: 2 Things You Should Never Do Together When Enjoying Hot Pot

If the Body Is Developing Cancer, Three Nighttime Sleep Signs May Appear — But Many People Ignore Them

Claim: “Cancer Cells Eliminated in 42 Days with a Special Juice — Worldwide Celebration?”
News Post

Bee Propolis and Infertility in Endometriosis: Evidence from a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial

Thymoquinone and Breast Cancer Cell Suppression: Evidence from Preclinical Research

Ginger Supplementation and Cardiovascular Inflammation: Evidence from a Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
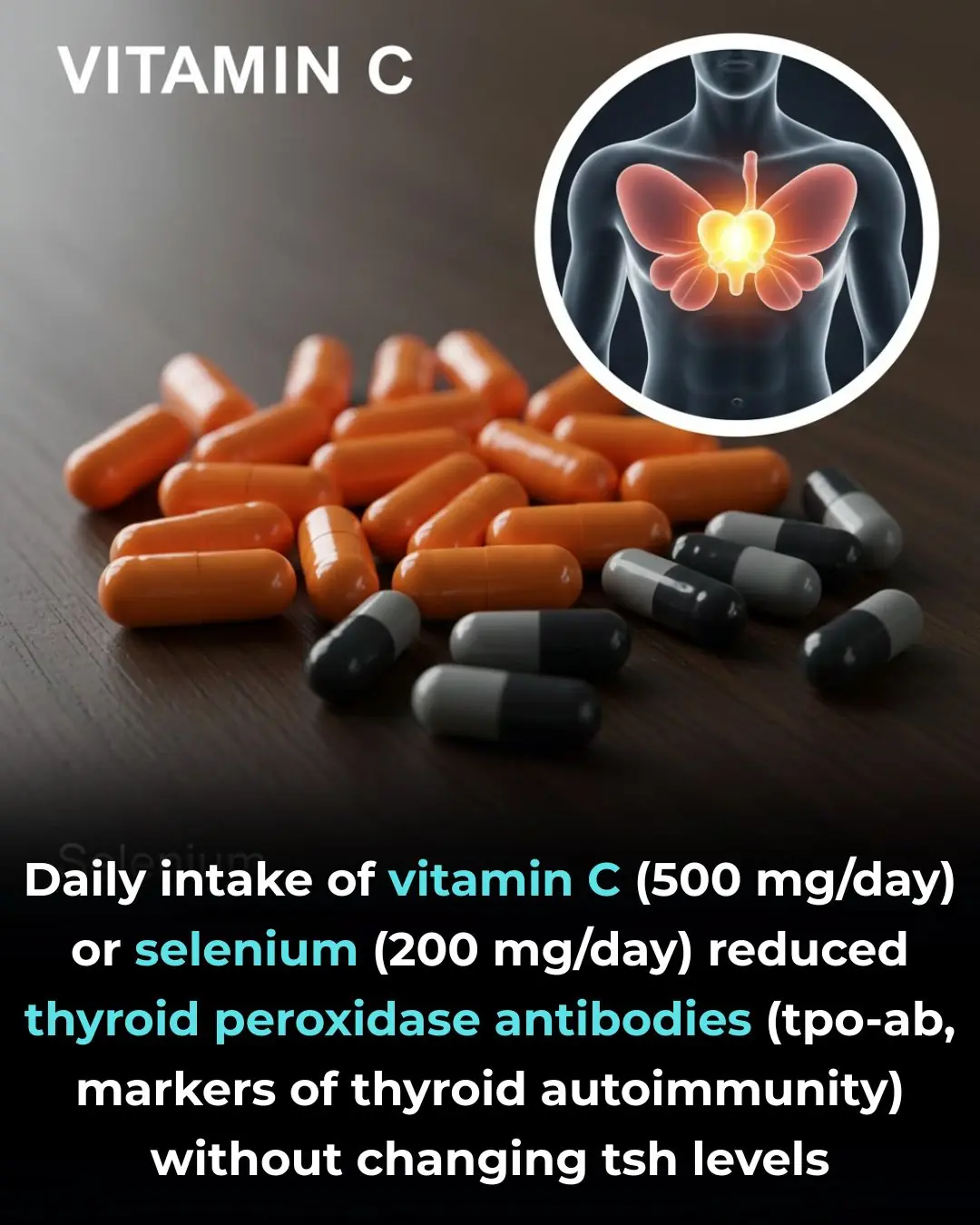
Antioxidant Supplementation and Thyroid Autoimmunity: Evidence from a Randomized Controlled Trial

Chios Mastic Gum as an Anti-Inflammatory Intervention in Crohn’s Disease and Vascular Inflammation

Garlic Supplementation and Metabolic Improvement in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

If you drink cucumber water every morning, this is what happens to your body

I soaked my feet in apple cider vinegar. 15 mins later, this is what happened

I need this ‘Liquid Gold.’
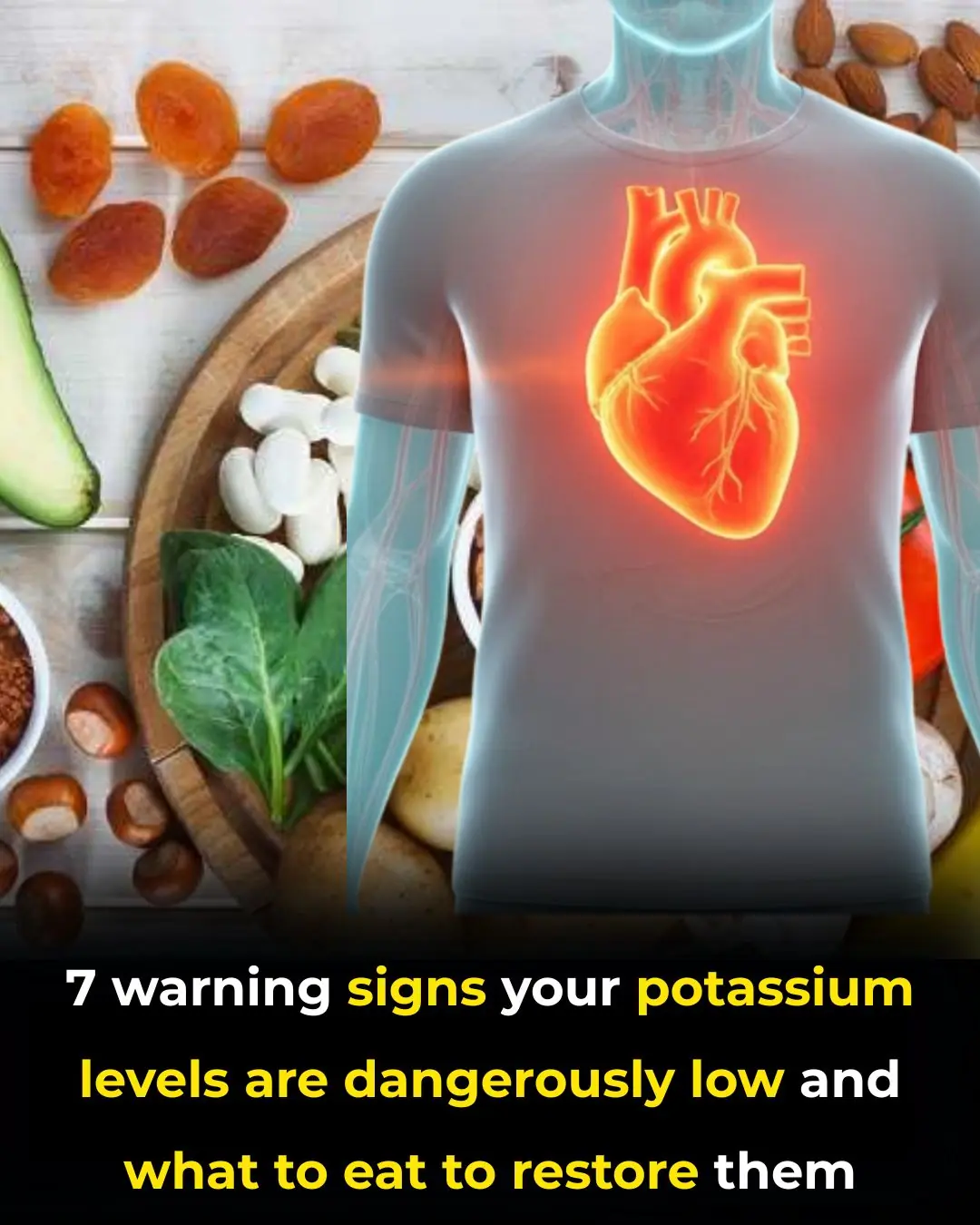
Potassium Deficiency – Causes, Symptoms and What To Do
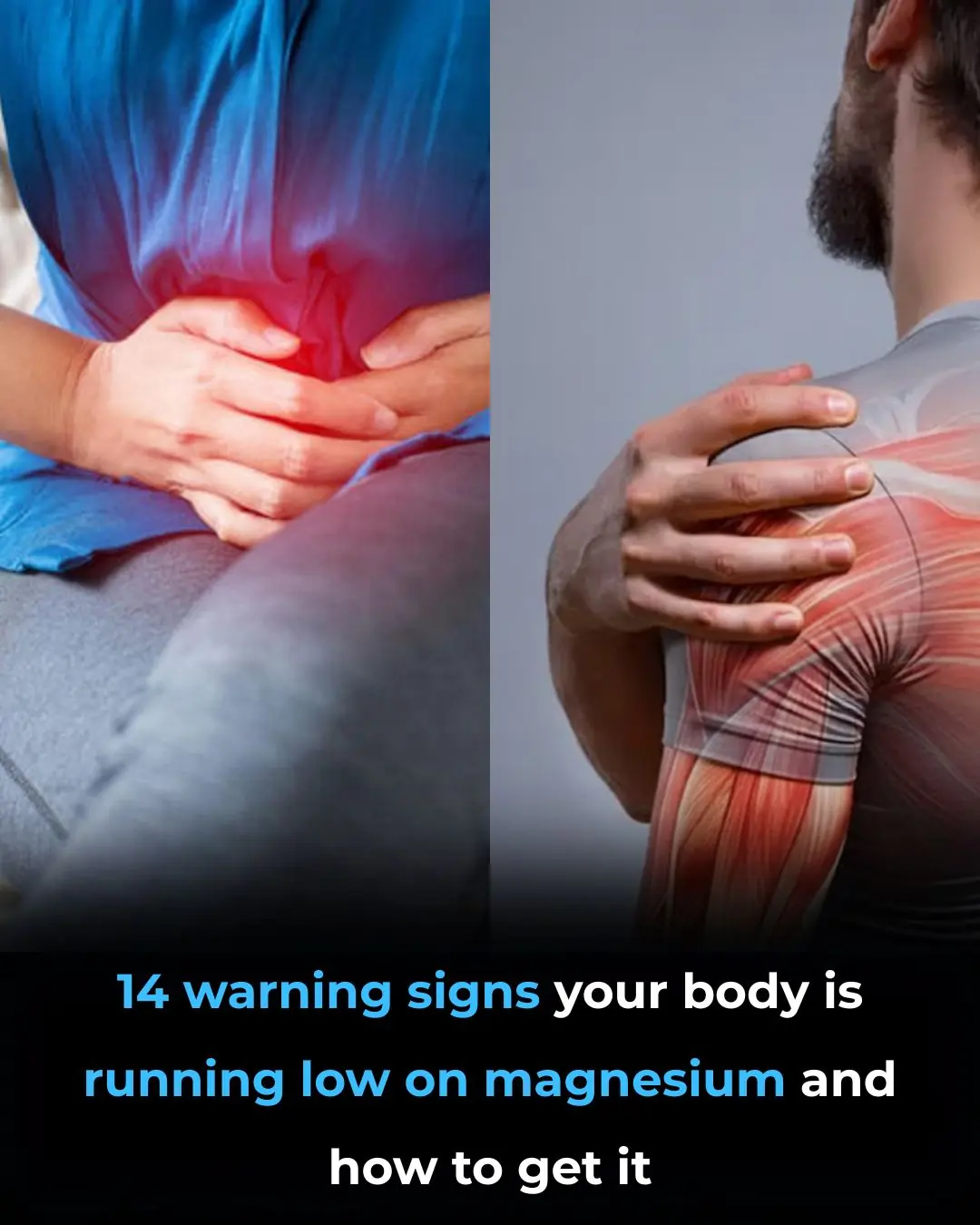
14 Warning Signs of Low Magnesium Levels and What to Do About It (Science Based)

Proven Health Benefits of Beets and Fermented Beets (Science Based)

Putting this in the vase box not only helps protect the chrysanthemums but also makes the vase more delicious

How to preserve cilantro so it stays fresh, green, and fragrant for a whole month

3 Reasons Onions Might Upset Your Stomach

Vaseline Uses and Benefits for Skin, Lips and Hair | Petroleum Jelly Benefits

Beetroot Face Gel for Clear Skin – Rosy Cheeks & Pink Blushing Skin

How i use CUCUMBER for Skin & Eyes : Remove Dark Circles & Get Glowing Skin

Tips for removing grease from an air fryer




