Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
A blood clot in your leg is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention. While some blood clots are harmless, a clot that forms deep within a vein, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can have life-threatening consequences. DVT can lead to a pulmonary embolism (PE), where a piece of the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, blocking a pulmonary artery.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of DVT is crucial for early detection and treatment. This article will help you identify the common warning signs of a blood clot in the leg and explain what to do if you suspect you have one.

What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot (or thrombus) is a gel-like mass formed by platelets and proteins in the blood. Clotting is a natural and necessary process that helps stop bleeding after an injury. However, when a clot forms unnecessarily inside a blood vessel, it can become a problem. DVT most commonly occurs in the deep veins of the lower leg or thigh.
Risk Factors for DVT
Blood clots in the legs are typically caused by conditions that disrupt normal blood flow. Several factors can increase your risk:
-
Prolonged Immobility: Sitting for long periods, such as on a long-haul flight or during a long car ride, can cause blood to pool in your lower legs. Similarly, being bedridden after surgery or illness is a major risk factor.
-
Injury to the Veins: Damage to the lining of a vein from surgery, trauma, or a broken bone can trigger a clot.
-
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, and the use of hormonal birth control or hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of clotting.
-
Medical Conditions: Obesity, cancer, heart disease, and inherited clotting disorders can all increase the likelihood of DVT.
Signs and Symptoms of a Blood Clot in the Leg
The signs of DVT often appear in one leg and can be subtle at first. It’s important to be aware of the following symptoms:
1. Swelling
Swelling in the affected leg, ankle, or foot is one of the most common signs of DVT. The clot can block blood from flowing back to the heart, causing fluid to build up in the tissues. The swelling may feel tender and warm to the touch.
2. Pain or Tenderness
The pain from a DVT can feel like a persistent ache, a dull throbbing, or a sharp cramp. It may worsen with movement or when you bend your foot toward your knee. The pain can be localized to the calf or can be felt throughout the leg and thigh.
3. Redness or Discoloration
The skin over the clot may become reddish or bluish. This is caused by blood pooling in the area and is often accompanied by a feeling of warmth.
4. Warmth
The skin around the affected area may feel noticeably warmer than the surrounding skin. This is due to the inflammation and blood pooling around the clot.
Warning Signs of a Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
A pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening complication of DVT. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms, as they may indicate a clot has traveled to your lungs:
-
Sudden Shortness of Breath: This is the most common symptom of a PE.
-
Chest Pain: Sharp, stabbing chest pain that may worsen with a deep breath or a cough.
-
Rapid Heart Rate: An unusually fast or irregular heartbeat.
-
Coughing: May produce blood or pinkish, frothy sputum.
-
Lightheadedness or Dizziness: A feeling of faintness.
Prevention and Treatment
Prevention
The best way to avoid DVT is to stay active.
-
Move Around: If you have to sit for long periods, get up and walk every hour or two. While seated, you can do leg exercises like ankle rotations and calf raises.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps prevent your blood from becoming too thick.
-
Wear Compression Stockings: These can help improve blood flow in your legs, especially during long periods of sitting or travel.
Treatment
If you are diagnosed with DVT, your doctor will likely prescribe blood-thinning medication (anticoagulants) to prevent the clot from growing and to allow your body to dissolve it over time. In some severe cases, more aggressive treatments may be needed.
When to See a Doctor
Because the consequences of DVT can be fatal, you should never ignore the warning signs. If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, especially if they are unexplained and occur in only one leg, contact your doctor or seek emergency medical care right away. Early diagnosis is critical to a full recovery.
News in the same category


Most US Neurologists Who Prescribe MS Drugs Take Industry Money

Cognitive Benefit From Ginkgo biloba Monotherapy in MCI

Keeping Up on HS Management When Guidelines Are Outdated

How Your Body Changes in Your Forties and What It Means for Your Health

17 Foods That Increase Magnesium And Prevent High Blood Pressure, Blood Clots And Muscle Fatigue

New Blood Test Shows Over 90% Accuracy for Lyme Disease

Is AI Use Causing Endoscopists to Lose Their Skills?
7 silent signs of high blood sugar most people miss

If you didn’t drink more water, why are you peeing so often?

9 Foods to Eat Regularly to Maintain a Sharp Brain and Prevent Memory Loss as You Age
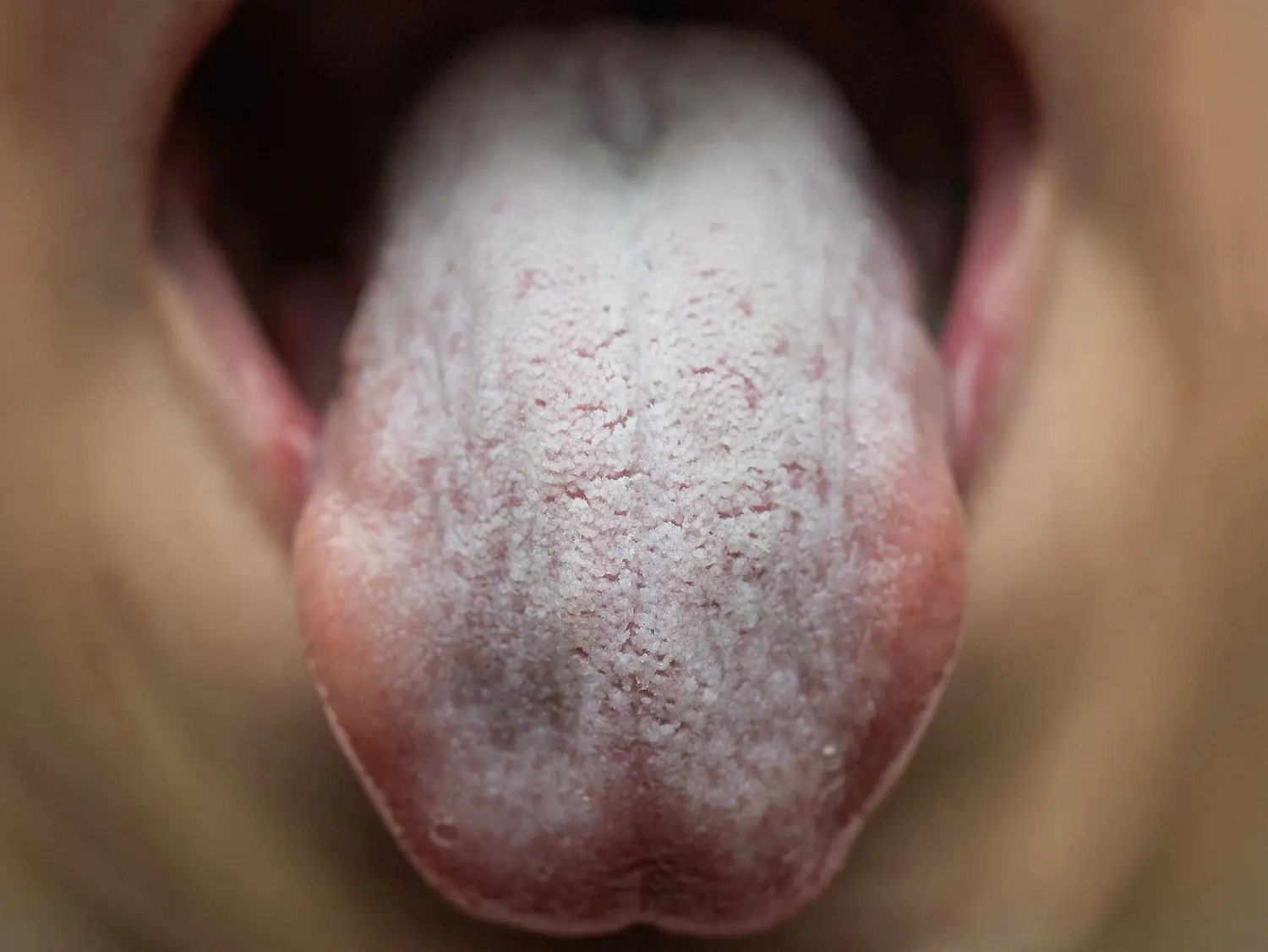
Top Signs That You Have Candida Infection and What to Do About It
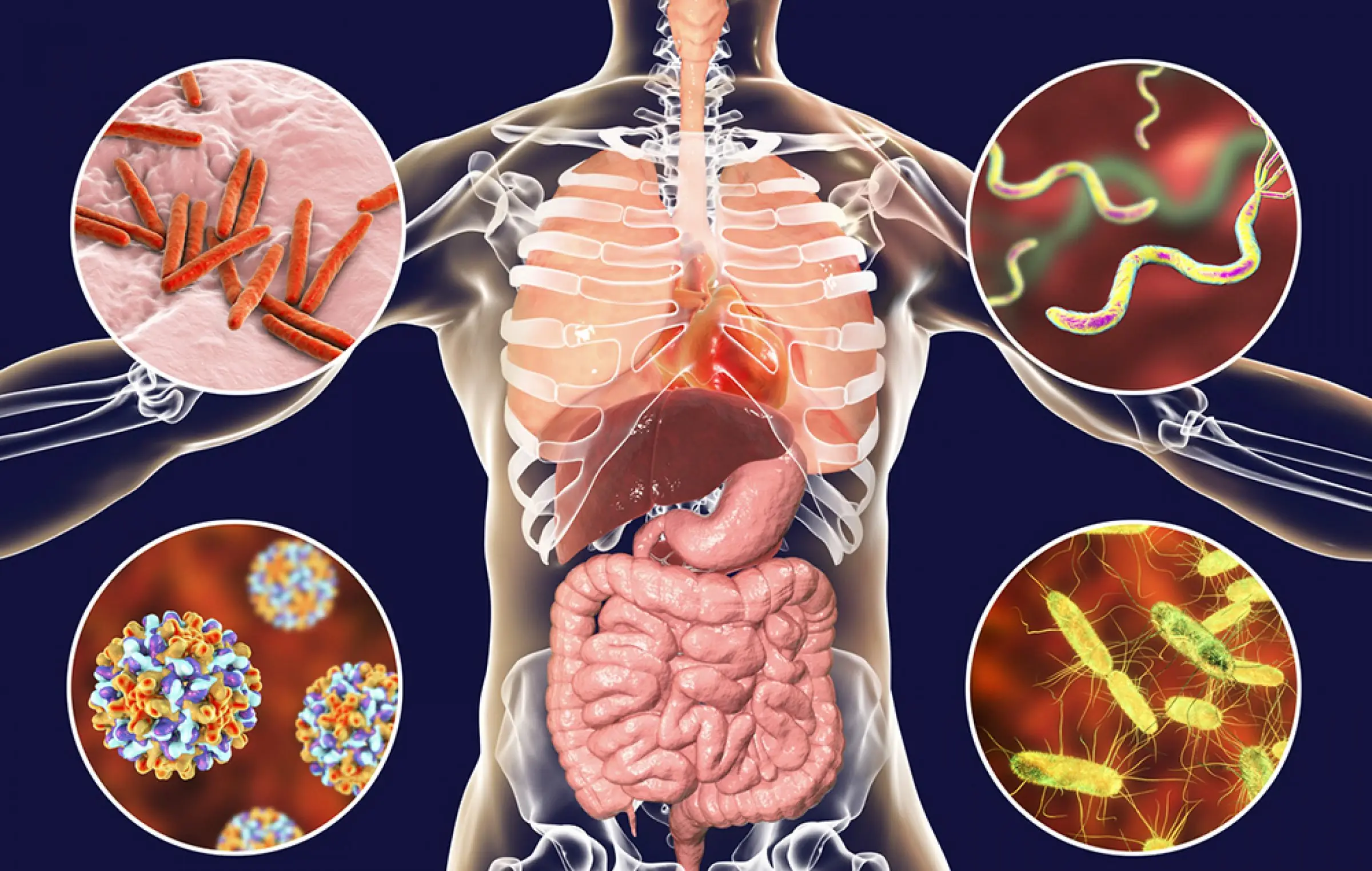
How to Get Rid of Worms in Humans (Including Parasite Cleanse Diet)

The Music That You Listen To Literally Causes Changes In Your Brain

Scientists: 3 Days of Silence Is Enough to Rewire Your Brain

8 Common Hygiene Myths You Shouldn’t Believe
Early Signs of Liver Damage & How to Strengthen Your Liver
The Best Natural Gout Treatments: Remove Uric Acid Crystallization To Prevent Gout And Joint Pain
News Post
Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore (Pictures Included)

Weak Toilet Flush with No Suction Power? A Simple DIY Hack from the Pros

Don’t Throw Away Rotten Tomatoes – The More Rotten, the More “Valuable”! Few People Know This, So Share It with Your Family

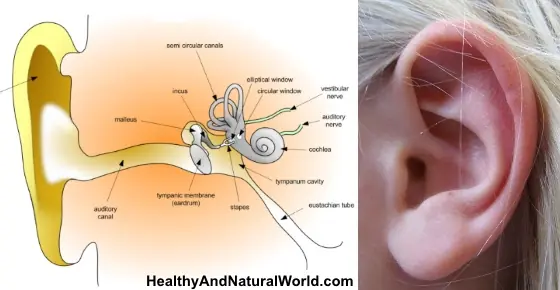
The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears

30 Powerful Reasons You Should Stop Ignoring Purslane

DIY Aloe Vera and Clove Toner: A Natural Remedy for Aging Signs

Treat Premature Gray Hair with a Natural Dye Using Tamarind and Potato – Cheap and Effective!

Here are 3 coffee drinking habits of many young people that can accelerate aging and cause various health problems

It's not a snake, this is the "a:ss@ssin" that can crawl out of your air conditioner at home.

Most US Neurologists Who Prescribe MS Drugs Take Industry Money

Cognitive Benefit From Ginkgo biloba Monotherapy in MCI

Keeping Up on HS Management When Guidelines Are Outdated

Orlando Bloom explains ‘horrible’ side effects his weight-loss transformation caused

A:dult star reveals the clause written into her contract that helps keep her safe

How Your Body Changes in Your Forties and What It Means for Your Health
Why Should We Not Open the Bedroom Door at Night?

8 Body Language Tips to Help You Appear More Confident

Why Should You Not Close the Door When Using the Air Conditioner?

Flight Attendants Reveal Surprising Truth About Coffee Cups on Airplanes
