Breakthrough Protein Combo Could Heal Heart Damage and Regenerate Organs
Breakthrough Protein Combo Could Heal Heart Damage and Regenerate Organs

In a major step forward for regenerative medicine, scientists have discovered a powerful combination of proteins that could help repair heart damage after injury—potentially with just a simple injection. The research, led by Dr. Li Qian at the UNC School of Medicine and published in Cell Stem Cell, uncovers how two proteins—Ascl1 and Mef2c—can reprogram scar tissue into healthy, functioning heart muscle cells.
Turning Scar Tissue into Healthy Heart Cells
After a heart attack or in cases of chronic heart disease, the heart replaces damaged tissue with scar tissue. This scarring, caused by cells called fibroblasts, reduces the heart's ability to contract and pump blood effectively, often leading to heart failure.
For years, scientists have worked to find ways to convert fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, the cells that make up real heart muscle. Until now, this process required a cocktail of three or more proteins—and the results were limited.
But this new study revealed a surprising shortcut. By adding the protein Ascl1, which was previously known only for helping create neurons, to the reprogramming process, researchers saw a dramatic improvement. When paired with the protein Mef2c, Ascl1 boosted the transformation of scar tissue into heart muscle by more than tenfold.
A Two-Protein Recipe for Regeneration
Even more impressive, the study found that Ascl1 and Mef2c alone were enough to reprogram the fibroblasts, eliminating the need for additional factors. This simplified two-protein combo could significantly reduce complexity and cost in future treatments.
What’s remarkable is that Ascl1 has never before been linked to heart tissue regeneration. It’s known for its role in creating brain cells, but in this study, when combined with Mef2c, it instead triggered heart-specific gene activation. This suggests that some proteins are more versatile than scientists once believed—and could be repurposed to treat different tissues throughout the body.
Beyond the Heart: Potential for Organ Regeneration
This discovery may have wider applications beyond heart disease. Since the reprogramming mechanism works at the cellular level, it could eventually be used to regenerate damaged tissue in the liver, lungs, kidneys, and even the brain. If researchers can develop a synthetic version of this protein duo, it might be possible to deliver them via injection directly to damaged organs—offering a non-invasive therapy for a wide range of conditions caused by scarring and tissue loss.
Hope for Heart Failure and Beyond
With heart failure affecting millions globally and currently having no cure, this breakthrough offers hope for a new class of regenerative treatments. Instead of relying on transplants or mechanical devices, doctors might one day help the body heal itself from within using targeted protein therapies.
The next step for the research team is to refine the treatment, test it in animal models, and eventually move toward clinical trials. If successful, this approach could revolutionize how we treat heart disease and other degenerative conditions.
News in the same category

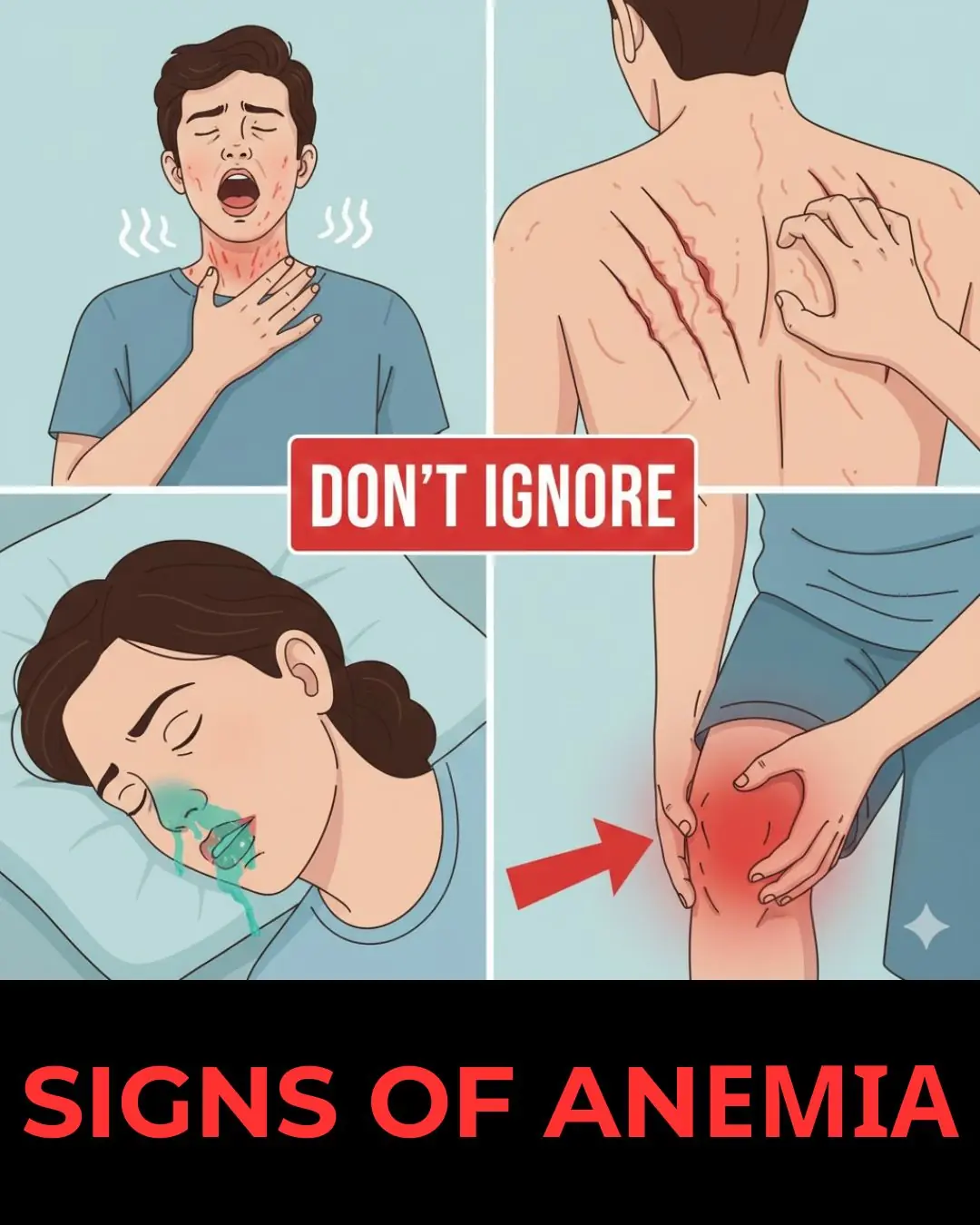
Silent Symptoms of Anemia You Should Never Ignore
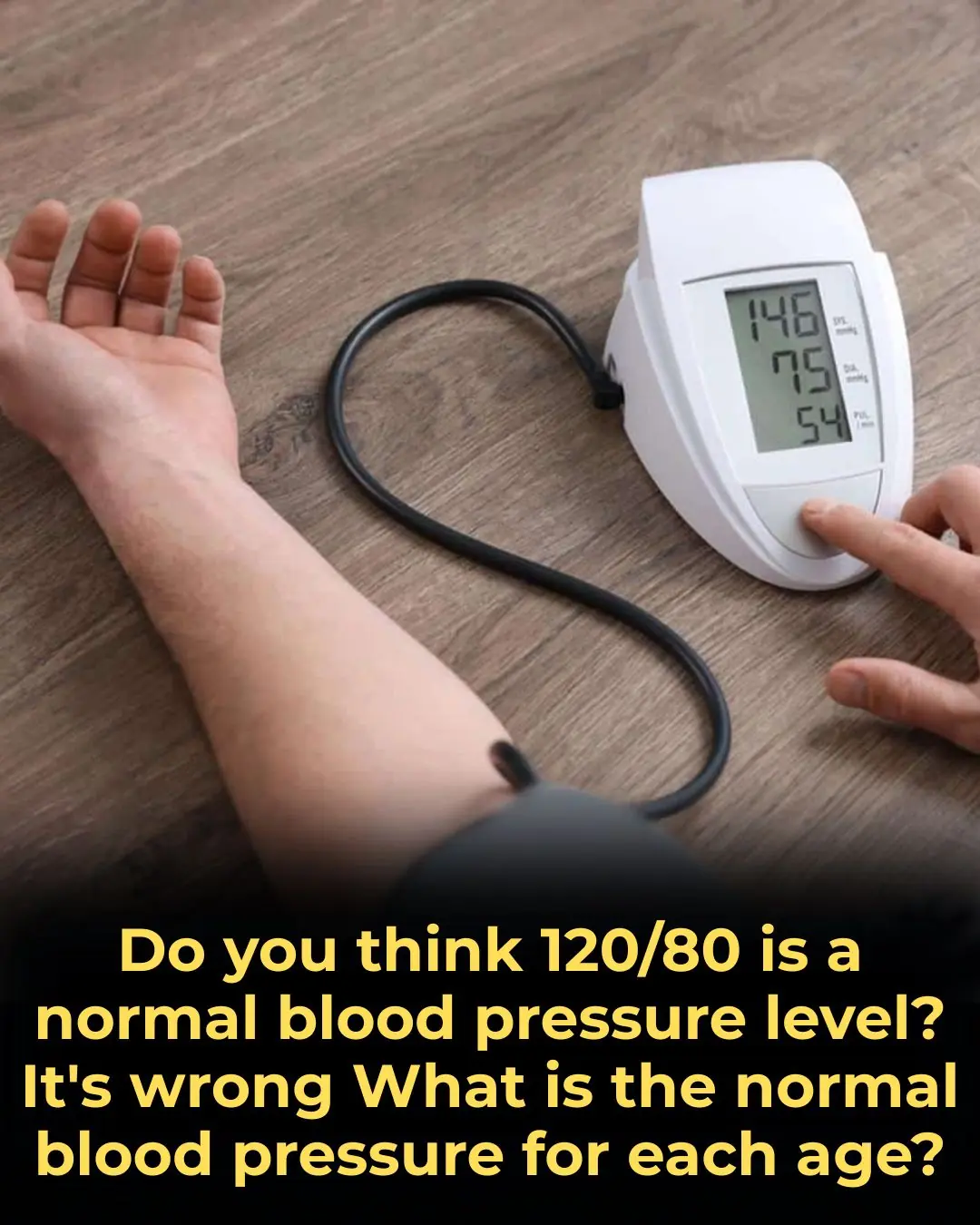
What Is The Normal Blood Pressure For Each Age

What your doctor’s not telling you about statins will shock you

The natural kitchen mix people use to break down stubborn plaque buildup

The 10 biggest eye health myths people still believe (an ophthalmologist explains)

Why doctors are rethinking blood pressure targets (and what it means for you)

The #1 cheap food packed with natural probiotics (and how to prepare it)

The real reason migraines are so much more than “just a headache”

🥦 3 Vegetables That Support Cancer Prevention — Backed by Science
Tired of achy legs? Discover 6 vitamins that can fix varicose veins and boost circulation!
Top 5 Warning Signs Of Kidney Damage You’re Ignoring

💖 Falling in Love After 60: The Real Challenges (and Beautiful Rewards) No One Talks About
The Kidney’s Role in Muscle Health

🦵 The 5 Best Nutrients to Reduce Swelling in the Feet and Legs
How Ginger Targets Prostate, Ovarian and Colon Cancer Stem Cells Better Than Chemo

Top 13 Inflammatory Foods You Should Avoid (Replace with These)

Common Habits to Avoid for Better Heart Health
Cardiomyopathy: Causes, Risks, and Treatment Approaches
One powerful vitamin that could end your tinnitus for good!
News Post

Remove Blackheads On Your Nose

Silent Symptoms of Anemia You Should Never Ignore

What Is The Normal Blood Pressure For Each Age

Objects People Were Confused About Their Purpose

You Should Never Use Self-Checkout At The Store

10 Signs You’re Eating Too Much Sugar

What your doctor’s not telling you about statins will shock you

The natural kitchen mix people use to break down stubborn plaque buildup

The 10 biggest eye health myths people still believe (an ophthalmologist explains)

Why doctors are rethinking blood pressure targets (and what it means for you)

The #1 cheap food packed with natural probiotics (and how to prepare it)

The real reason migraines are so much more than “just a headache”

Add Salt and Lemon to Your Bath Water — The Result Will Shock You

Hidden in Your Backyard: The Simple Leaf That Unlocks Thicker, Faster Hair Growth

Revive Your Prostate with Onion & Onion Skins: The Miracle Grandma’s Tea You Never Expected

Robot 'Kidnaps' Fellow Machines at Shanghai Exhibition, Sparking Debate on AI Autonomy and Labor Rights

Introducing the U-Hawk: The Autonomous Black Hawk Revolutionizing Heavy-Lift Aviation

China Unveils World's Largest Solar Farm, Powers Up with 3.5 GW in Xinjiang

🥦 3 Vegetables That Support Cancer Prevention — Backed by Science
