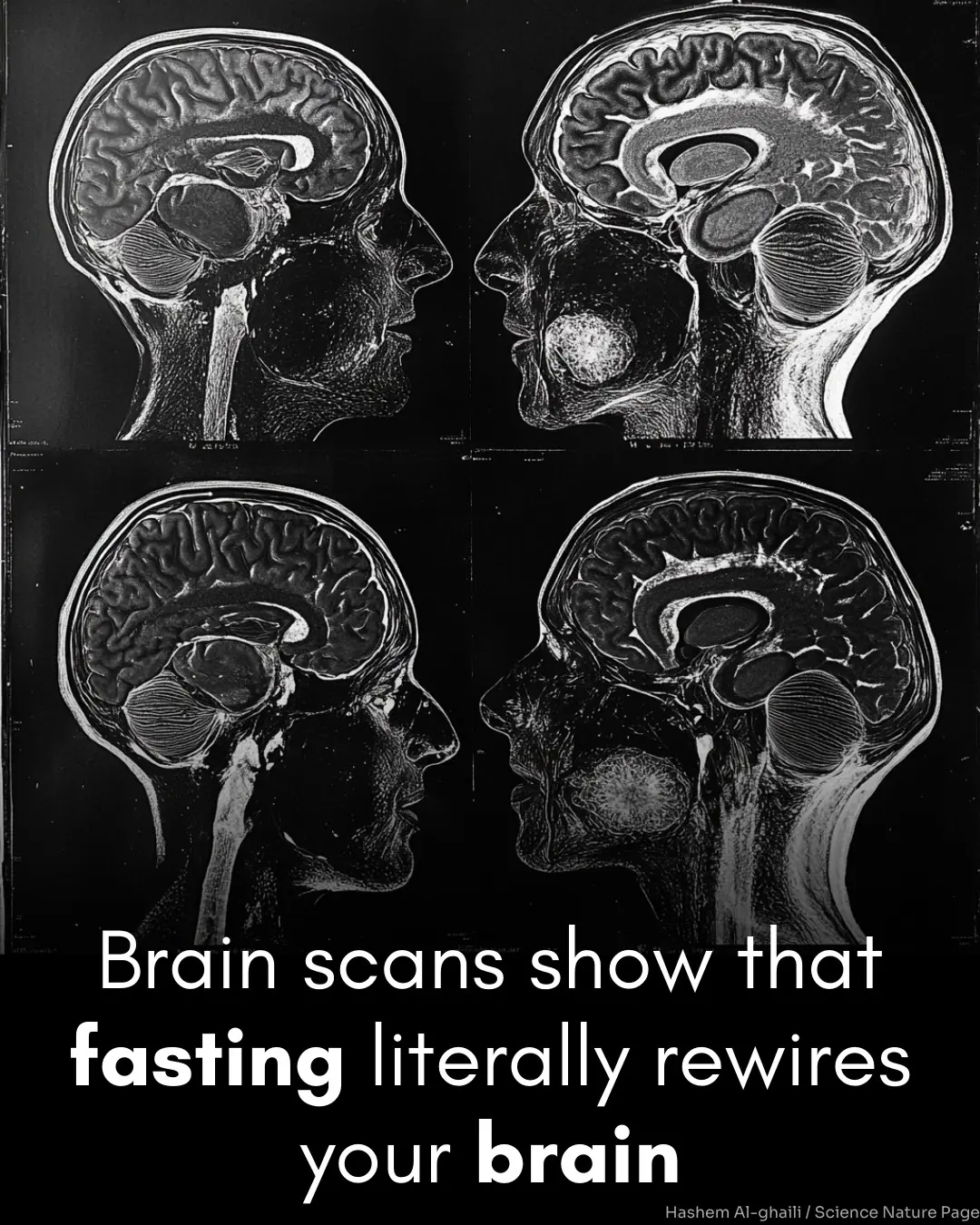
Effects of smartphone restriction on cue-related neural activity
With the increasing popularity of smartphones in the past decades, the physical, social, and psychological consequences of excessive smartphone use (ESU) have been increasingly debated. Cue-reactivity (CR) has been discussed as a core mechanism driving this behavior, and previous studies have highlighted distinct neural mechanisms underlying CR in individuals with ESU. Understanding the neural basis of ESU is crucial for developing effective interventions and prevention strategies to mitigate its negative impact on mental health and daily functioning.
Here, we used a functional MRI (fMRI) CR-paradigm to investigate the effects of smartphone restriction over 72 hours in 25 young adult smartphone users. The CR-task used contrasts of images showing smartphones vs. neutral stimuli and active vs. inactive smartphones. By analyzing these contrasts, we aimed to determine how brain activity patterns change in response to smartphone-related cues and whether these changes reflect alterations in craving, reward processing, and self-control mechanisms.
Region-of-interest-based correlations with psychometric scores were performed, and activity changes after 72 hours were investigated on a neurochemical level using neurotransmitter probability maps. Our findings revealed that CR-related brain activity changes over time were most prominent in the nucleus accumbens and anterior cingulate cortex (p < 0.001), two regions heavily implicated in reward processing and habit formation. Such changes were significantly associated with dopamine- and serotonin-receptor probabilities (pFDR < 0.05), suggesting a potential neurochemical basis for ESU-related compulsive behaviors.
Furthermore, significant associations between parietal cortex activity and craving were detected (p < 0.05), emphasizing the role of attentional control and sensory processing in smartphone addiction. The observed neural adaptations indicate that even short-term smartphone restriction can lead to measurable changes in brain function, potentially altering reward sensitivity and self-regulatory processes.
This study provides evidence for CR-related modulation of neural activity in key regions of salience, motor-inhibition, and reward processing after 72 hours of smartphone restriction. These findings suggest that prolonged smartphone abstinence may trigger neural plasticity in circuits linked to craving and impulse control, shedding light on the underlying neurobiological mechanisms that contribute to excessive smartphone use. The identified neural mechanisms may substantially promote addictive behavior in people at risk for ESU, highlighting the need for further research into targeted interventions that address both behavioral and neurochemical aspects of smartphone addiction.
News in the same category


The Most Amazing Health Benefits of Baking Soda Water

Combining systemic and local osteoporosis treatments: A longitudinal in vivo microCT study in ovariectomized rats
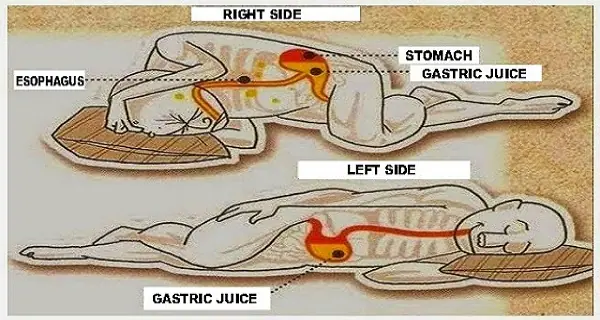
Health Benefits of Sleeping on Your Left Side
10 Warning Signs of Throat Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

Leg Cramps at Night

How to Remove Dental Plaque Naturally
20 Signs Your Body is Out of Balance, and Something is Wrong

The Most Sought-After Remedy That Doctors Won’t Tell You! This Drink Clears Mucus from Your Lungs, Soothes Dry Cough, and Relieves Sinusitis
Homemade Collagen: A Natural Solution for Pain, Inflammation, and Joint Health

World’s First Recording Of Moment Someone Passes Reveals What Our Last Thoughts Are

AI-assisted Lifestyle habits that increase the risk of having a stroke
Slimming significantly alters your microbiome and brain activity
Why Are So Many Young Adults Getting Colon Cancer?

10 Foods You Should Avoid Eating, According to Experts

Carrot Tops to Brighten Your Smile Naturally

6 Powerful Castor Oil Benefits for Your Health and Wellness

Effects of smartphone restriction on cue-related neural activity
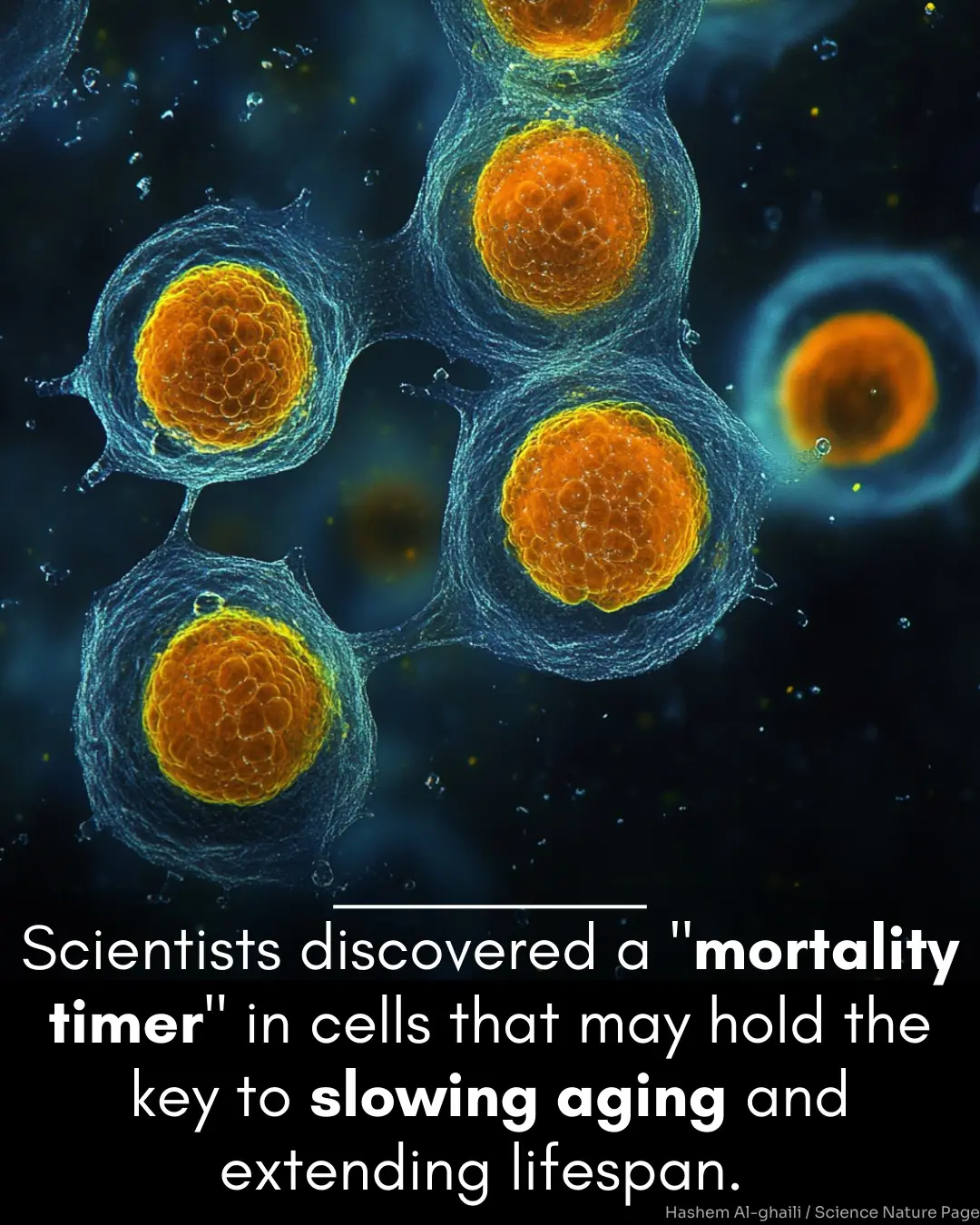
A mortality timer based on nucleolar size triggers nucleolar integrity loss and catastrophic genomic instability

Fat cells have a ‘memory’ of obesity — hinting at why it’s hard to keep weight off
News Post

My Fiancé Told Me to Stay In the Kitchen and Cook Dinner to Avoid Embarrassing Him in Front of His Colleagues
When Rachel's fiancé asked her to "stay in the kitchen" during a surprise visit from his high-profile colleagues to avoid being embarrassed by her, she knew something had to change. What followed was a moment of messy revenge, hard truths, and a decision

Cloves, Garlic, and Honey: A Potent Natural Remedy
The (Unfortunately Secret) Trick to Help Remove Varicose Veins with Lemons 🤯💥
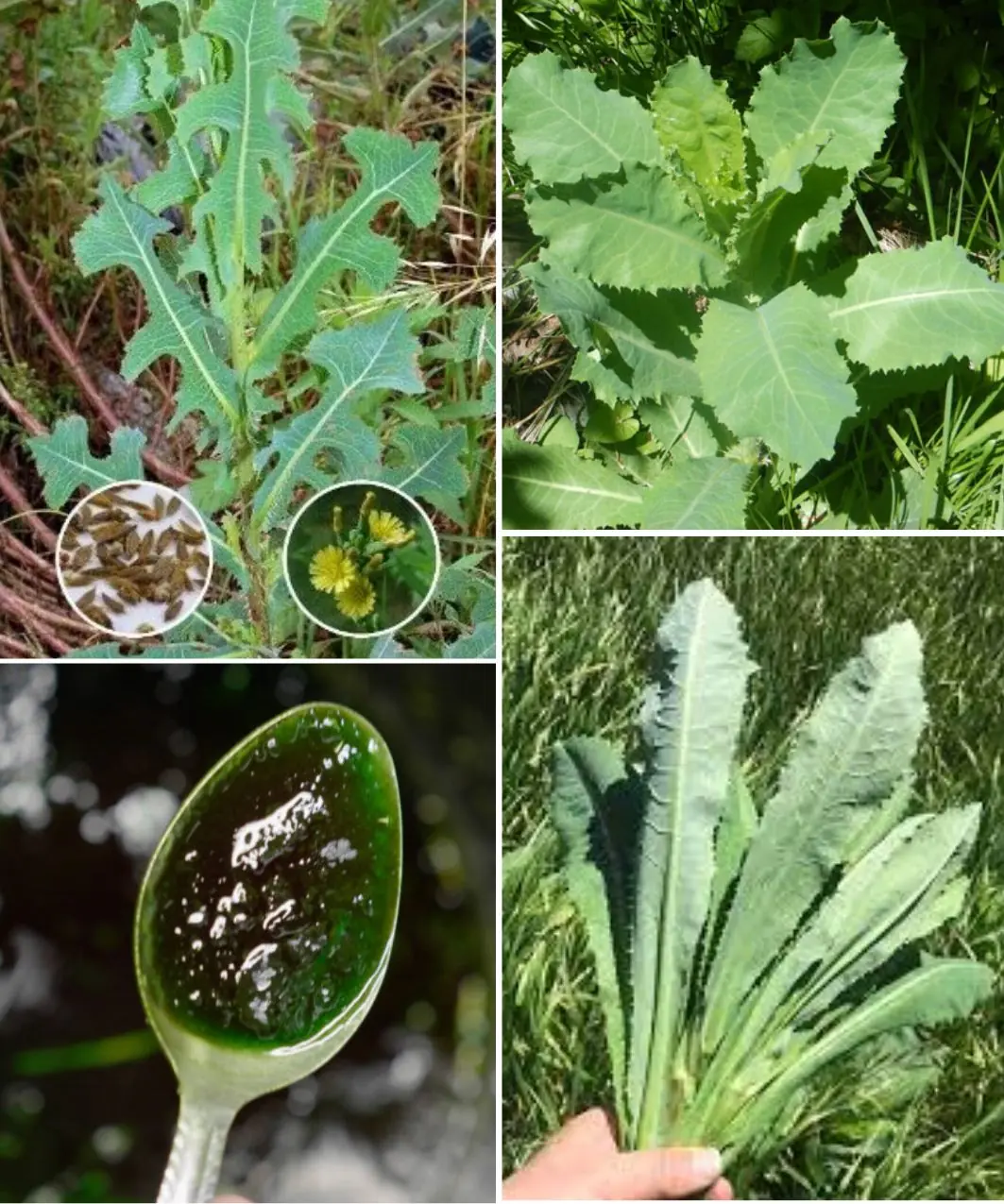

Creating Wild Lettuce Extract: A Natural Solution for Pain and Sleep
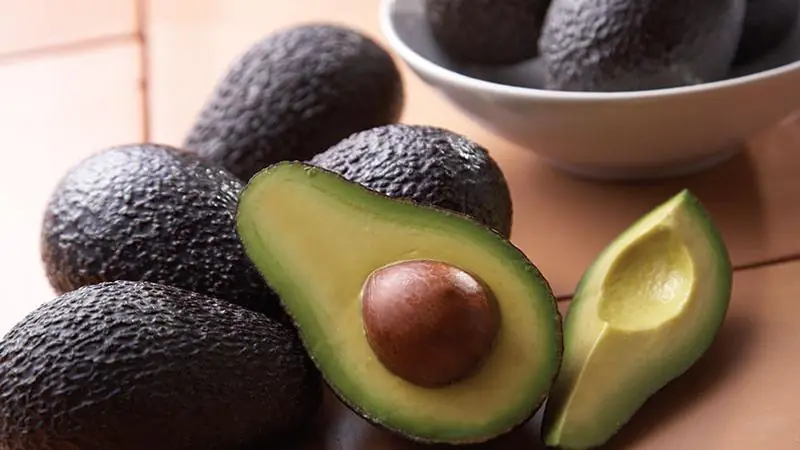

Avocado Seed Remedy: A Natural Solution to High Cholesterol, Poor Circulation, and Arthritis

Spe:rm Cells Carry Traces of Stress Experienced by the Father, New Study Shows
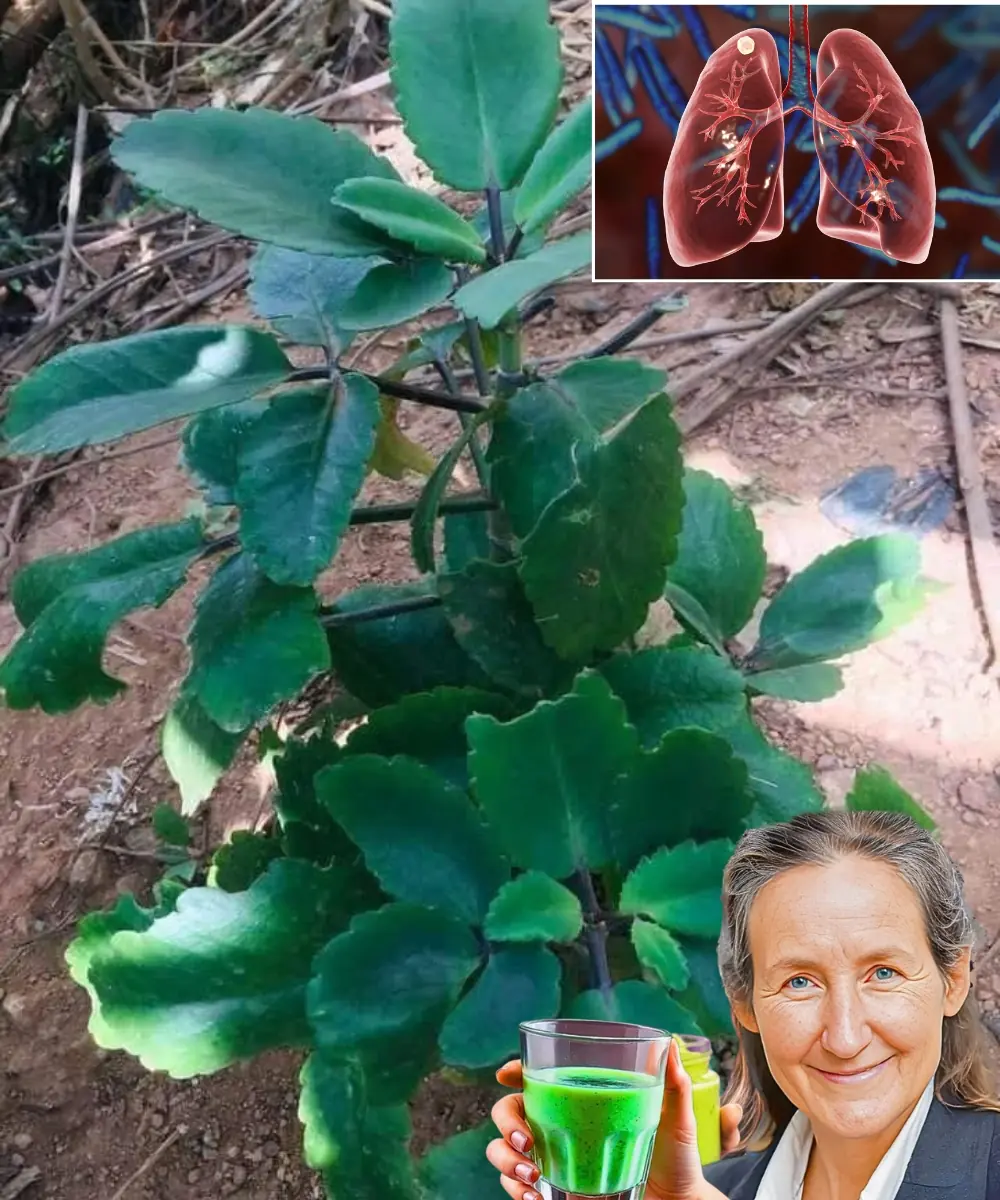

Miracle Plant: 14 Powerful Ways to Use Kalanchoe (Life Plant) for Common Ailments

Why does Vaginal Discharge Bleach Underwear?

Beauty Cubes For Bright Glowing Skin

Do this to reverse your grey hair

My Grandkids Had Already Reserved a Cemetery Plot and Headstone for Me – but They Forgot That I'm More than Just Kind
They thought I was just a sweet old lady with one foot in the grave. When I overheard my own children discussin' the headstone they'd already picked out for me, I decided it was high time to show them that kindness ain't the same as weakness.

Incredible Benefits of Dandelion: Nature’s Hidden Gem

This 40 Minutes Potato facial that can change your whole skin

How to Make Clove Oil at Home – Simply & Easily

The Most Amazing Health Benefits of Baking Soda Water

I Married a Homeless Man to Spite My Parents – A Month Later, I Came Home and Was Shocked by What I Saw.

Anti-Aging Coffee Oil: The Natural Solution to Wrinkles—Stronger Than Botox!

The ultimate Aloe Vera hack to regrow your hair on bald patches

Combining systemic and local osteoporosis treatments: A longitudinal in vivo microCT study in ovariectomized rats
