If you don't know, read more
In the advanced stages, diabetes often manifests with the following symptoms:
-
Chronic Non-Healing Wounds (Diabetic Ulcers):
- High blood sugar damages blood vessels and nerves, impairing circulation and the body's ability to heal wounds.
- Symptoms include open sores, especially on the feet (diabetic foot ulcers), which can lead to infections and even amputations if untreated.
-
Severe Fatigue:
- Persistent high blood sugar levels disrupt energy metabolism, leaving patients feeling weak and fatigued.
- Fatigue may also result from complications such as anemia, kidney dysfunction, or cardiovascular issues.
-
Kidney Failure (Diabetic Nephropathy):
- Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease. In advanced stages, the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste, resulting in swelling (edema), high blood pressure, and reduced urine output.
- Symptoms include foamy urine, fluid retention, and a general feeling of unwellness.
-
Vision Loss (Diabetic Retinopathy):
- Prolonged high blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems such as blurriness, dark spots, or even blindness.
- Advanced stages of retinopathy can involve retinal detachment or glaucoma.
-
Severe Neuropathy (Nerve Damage):
- Nerve damage caused by diabetes can result in severe pain, numbness, or tingling in the extremities (hands and feet).
- Autonomic neuropathy may also affect organs, causing digestive issues, sexual dysfunction, and irregular heartbeats.
These symptoms indicate that diabetes has caused widespread damage to multiple organ systems, requiring immediate medical attention.
2. Why Do These Symptoms Develop?
Advanced diabetes symptoms result from prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels, which lead to:
- Blood Vessel Damage: Hyperglycemia damages small and large blood vessels, reducing blood flow to critical organs and tissues.
- Nerve Damage: Persistently high blood sugar interferes with nerve function, leading to pain, numbness, or organ dysfunction.
- Weakened Immunity: Diabetes impairs the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections.
- Chronic Inflammation: Systemic inflammation exacerbates tissue damage and accelerates disease progression.
3. Risks Associated with Advanced Diabetes
The final stage of diabetes carries significant risks, including:
- Amputations: Non-healing wounds and severe infections can necessitate limb amputations, reducing mobility and quality of life.
- End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD): Without treatment, kidney failure may require dialysis or transplantation.
- Blindness: Vision loss can be irreversible if diabetic retinopathy is not treated early.
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Advanced diabetes increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes due to vascular damage.
- Premature Death: Untreated complications can lead to multi-organ failure, significantly reducing life expectancy.
4. Preventing the Progression to Advanced Diabetes
Preventing the onset of advanced diabetes involves proactive management and lifestyle changes:
-
Blood Sugar Control:
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and follow your doctor’s recommendations for medication, diet, and exercise.
- Aim for an HbA1c level below 7% (or as advised by your healthcare provider).
-
Regular Medical Checkups:
- Schedule routine screenings for complications such as kidney function tests, eye exams, and foot checks.
- Early detection of complications can prevent irreversible damage.
-
Healthy Diet:
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Limit sugar, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods.
-
Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or strength training, to improve blood sugar control and cardiovascular health.
-
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol:
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption worsen diabetes complications and should be avoided.
-
Mental Health Support:
- Living with diabetes can be stressful. Seek support from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups to manage emotional well-being.

5. When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you or someone you know experiences the symptoms of advanced diabetes, seek medical help immediately. Delayed intervention increases the risk of severe complications and decreases the chances of recovery.
Signs that require urgent attention include:
- Persistent wounds that do not heal.
- Sudden vision changes or blindness.
- Severe swelling or reduced urine output.
- Unexplained, debilitating fatigue.
- Uncontrolled pain or numbness in the extremities.
News in the same category


How to Treat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally to Combat Hair Loss, Brittle Nails and Lack of Sleep
5 signs on the nose warn of diseases

Soak 5 cloves of garlic in a jar full of water: because many people do it

Put this for 1 hour in your house, you will never see flies, mosquitoes or cockroaches again.

7 Health Benefits of Bledo Blanco: A Nutritional Powerhouse You Can’t Miss

Culantro: The Underrated Super Herb That Packs a Nutritional Punch

Unlocking the Secrets of Morel Mushrooms: Benefits You Need to Know

The Surprising Benefits of Rosemary Tea: A Sip Toward Better Health and Happiness

How Goose Grass Can Heal You: A Natural Remedy For Dozens Of Diseases

7 Incredible Ways Crowfootgrass Can Improve Your Health

Can Lemon Leaves Improve Sleep? Discover the Calming Benefits of This Natural Remedy

Waking Up with Numb or Tingling Hands: What It Really Means
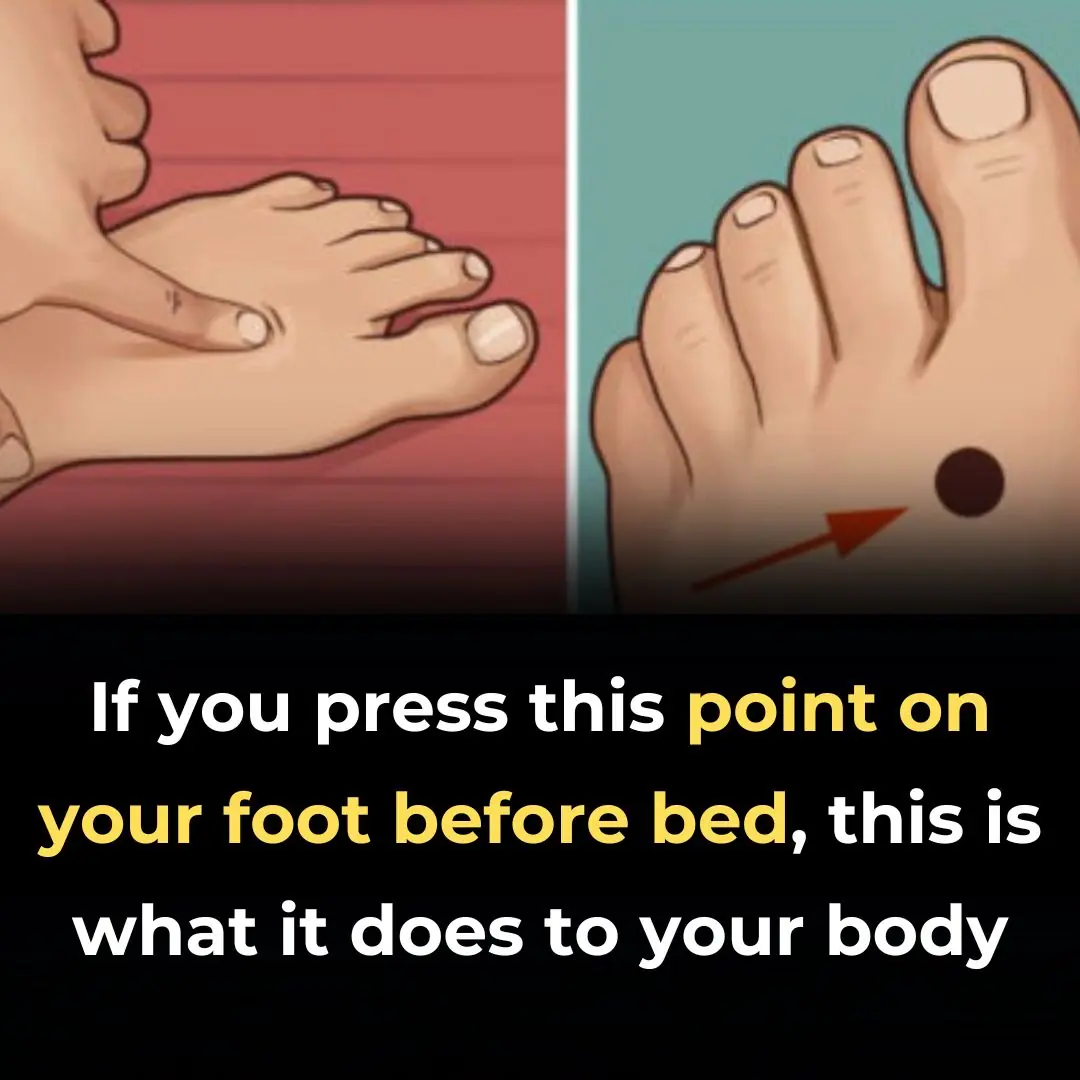
Press These Points for Wherever You Have Pain – Every Body Part is Linked to Your Palm and Foot

7 early warning signs that cancer is growing inside your kidneys
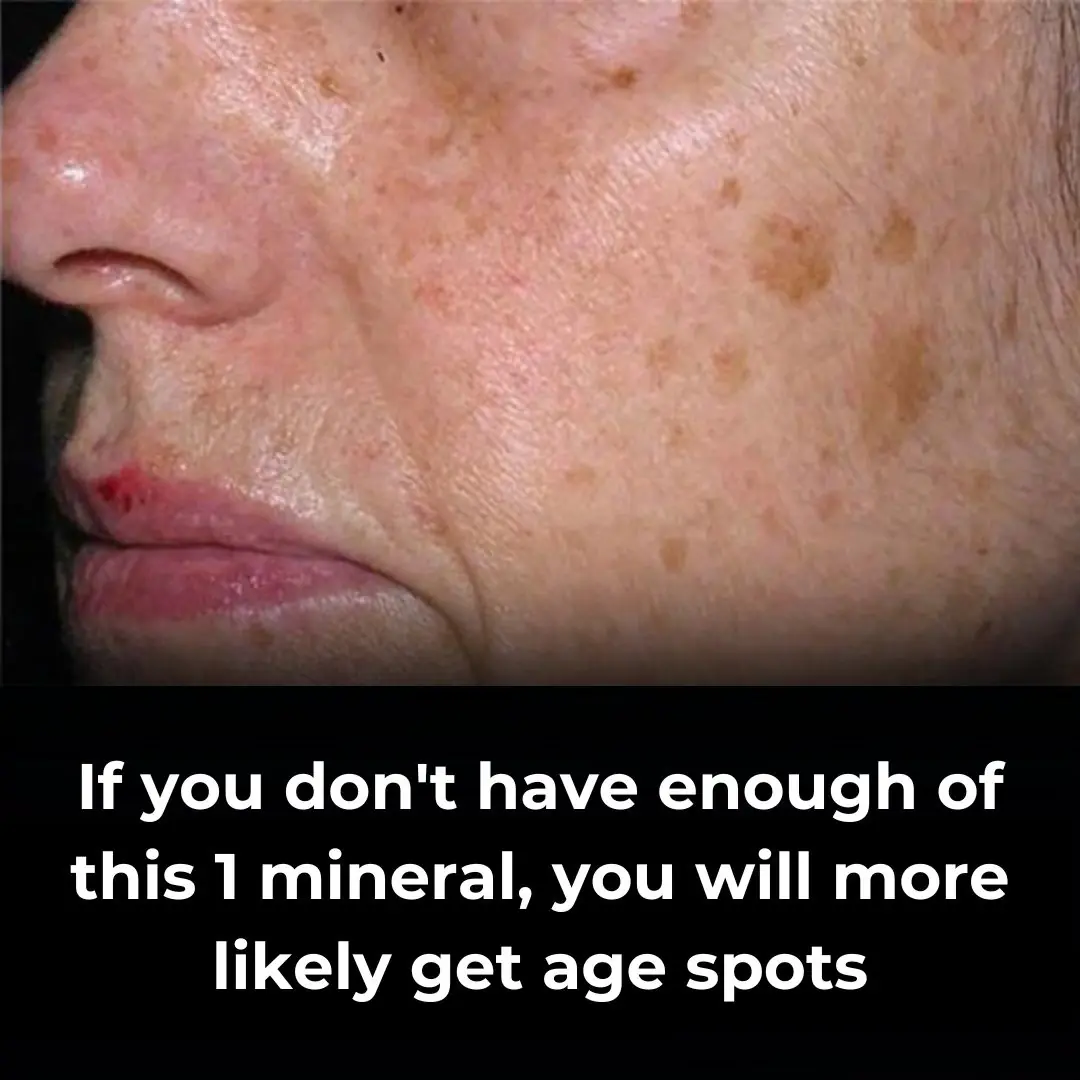
How To Reduce Age Spots: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Fatty Liver: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Home Remedies

Kidney Stones: Why Do They Form and How to Prevent Them?
Scientists discover 'k.i.ll switch' that triggers de.a.th of can.cer cell in breakthrough
News Post

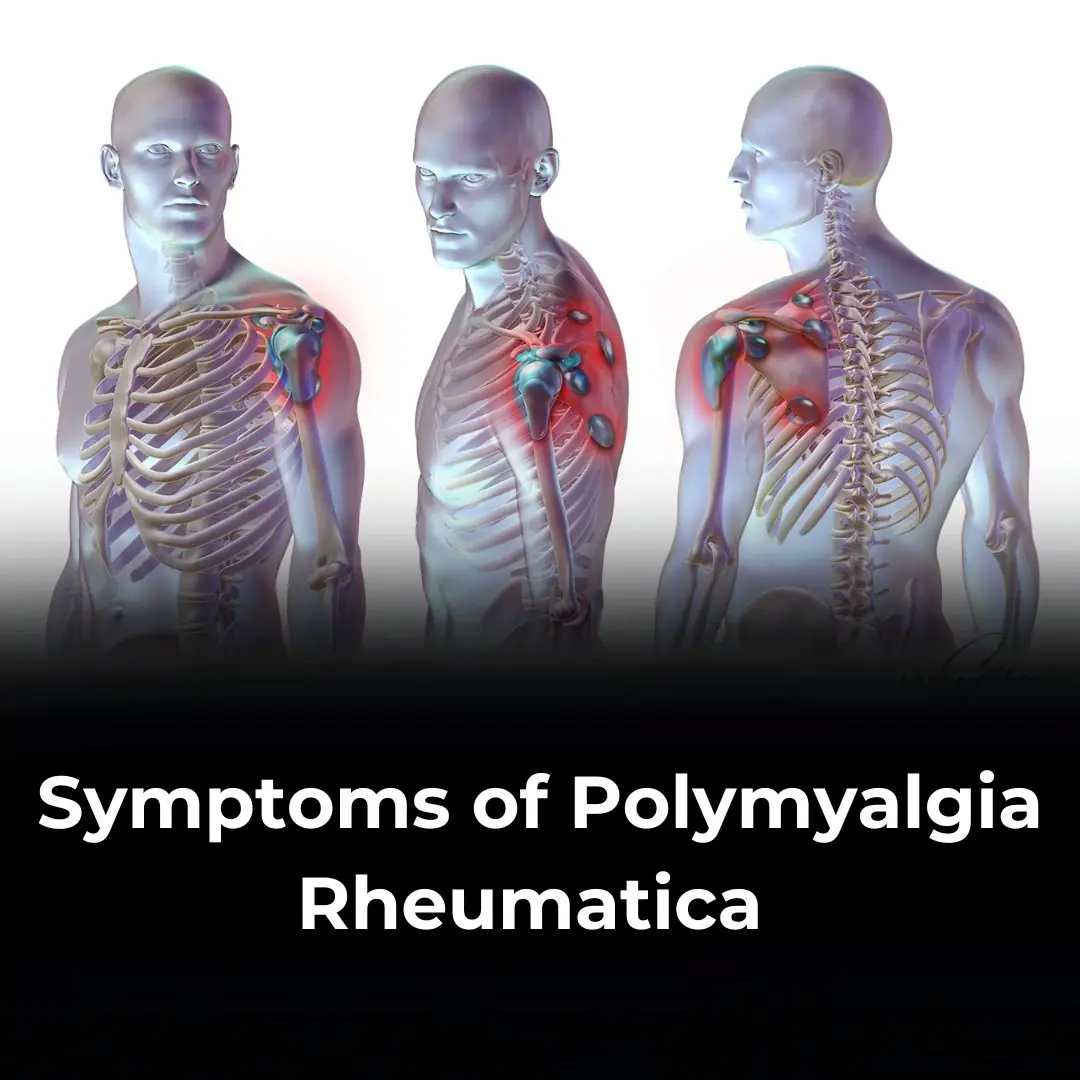
Important Signs To Look For That Could Suggest You Have Polymyalgia Rheumatica

How to Treat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally to Combat Hair Loss, Brittle Nails and Lack of Sleep

5 signs on the nose warn of diseases
My Dad Had an Affair While My Mom Was Dying in a Hospital – He Thought He Got Away with It Until I Taught Him a Lesson He'll Never Forget
When Blair loses her mother to cancer, grief isn't the only thing she's forced to carry. Beneath the silence lies betrayal... and a promise she intends to keep. In a story of quiet rage, slow revenge, and poetic justice, Blair proves that some daughters d

My MIL 'Gifted' Me a Refrigerator and Then Made Me Pay for It Myself – She Tried to Trick the Wrong Person
When my mother-in-law handed me the "gift receipt" for my new refrigerator, something in me snapped. Three thousand dollars of debt wasn't a birthday present. It was a trap. But Denise didn't know who she was messing with.

My Husband Came to Take Me and Our Newborn Triplets Home – When He Saw Them, He Told Me to Leave Them at the Hospital
After years of longing, Emily's dream finally came true: she gave birth to beautiful triplet daughters. But just one day later, her husband abandoned them, claiming the babies were cursed.

After Our Mom’s Death, My Sister Claimed I Had No Right to Inheritance and Brought Out Old Documents—But in the End, She Deeply Regretted It
When Charlotte's mother dies, her sister Barbara wastes no time trying to cut her out of the inheritance. Armed with an old document, Barbara smugly tries to throw a spanner in the works. But when the truth comes out, it's Barbara who faces the ultimate b

My Friend Dropped Me Three Days Before Her Wedding over My Haircut – The Other Bridesmaids Got Payback on My Behalf
My best friend wanted a picture-perfect, "magazine-worthy" wedding. She controlled every detail, down to the bridesmaids' eyelashes. But three days before the big day, she dropped me, claiming my new haircut didn't "fit" her vision. I was shattered, but n

Soak 5 cloves of garlic in a jar full of water: because many people do it

Put this for 1 hour in your house, you will never see flies, mosquitoes or cockroaches again.

7 Health Benefits of Bledo Blanco: A Nutritional Powerhouse You Can’t Miss

Culantro: The Underrated Super Herb That Packs a Nutritional Punch

Unlocking the Secrets of Morel Mushrooms: Benefits You Need to Know

The Surprising Benefits of Rosemary Tea: A Sip Toward Better Health and Happiness

How Goose Grass Can Heal You: A Natural Remedy For Dozens Of Diseases

7 Incredible Ways Crowfootgrass Can Improve Your Health

Can Lemon Leaves Improve Sleep? Discover the Calming Benefits of This Natural Remedy

Lady Gets Call from Hospital, Finds Out She Lost Her Loathed Sister and Got Two Newborn Nephews – Story of the Day
At a young age, Linda's older sister abandoned her in a group home. Years later, she is left to care for her young nephews, who face the same fate.

At Our Housewarming, My Husband and MIL Demanded We Give Our Apartment to His Sister – My Mom's Response Shut Them Down

Five Years After My Wife's Death, I Took My Child to My Best Friend's Wedding – When I Saw the Bride, My Daughter Asked, 'Daddy, Why Are You Crying?'
Five years after losing my wife, my daughter and I attended my best friend's wedding. But my world shattered when he lifted the bride's veil. As my daughter whispered, "Daddy, why are you crying?" the bride locked eyes with me — and in that instant, eve