If you notice these signs on your body, consult a doctor immediately
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that causes skin cells to multiply too quickly, leading to red, scaly, itchy patches on the skin.
The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from an
overactive immune system, combined with genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.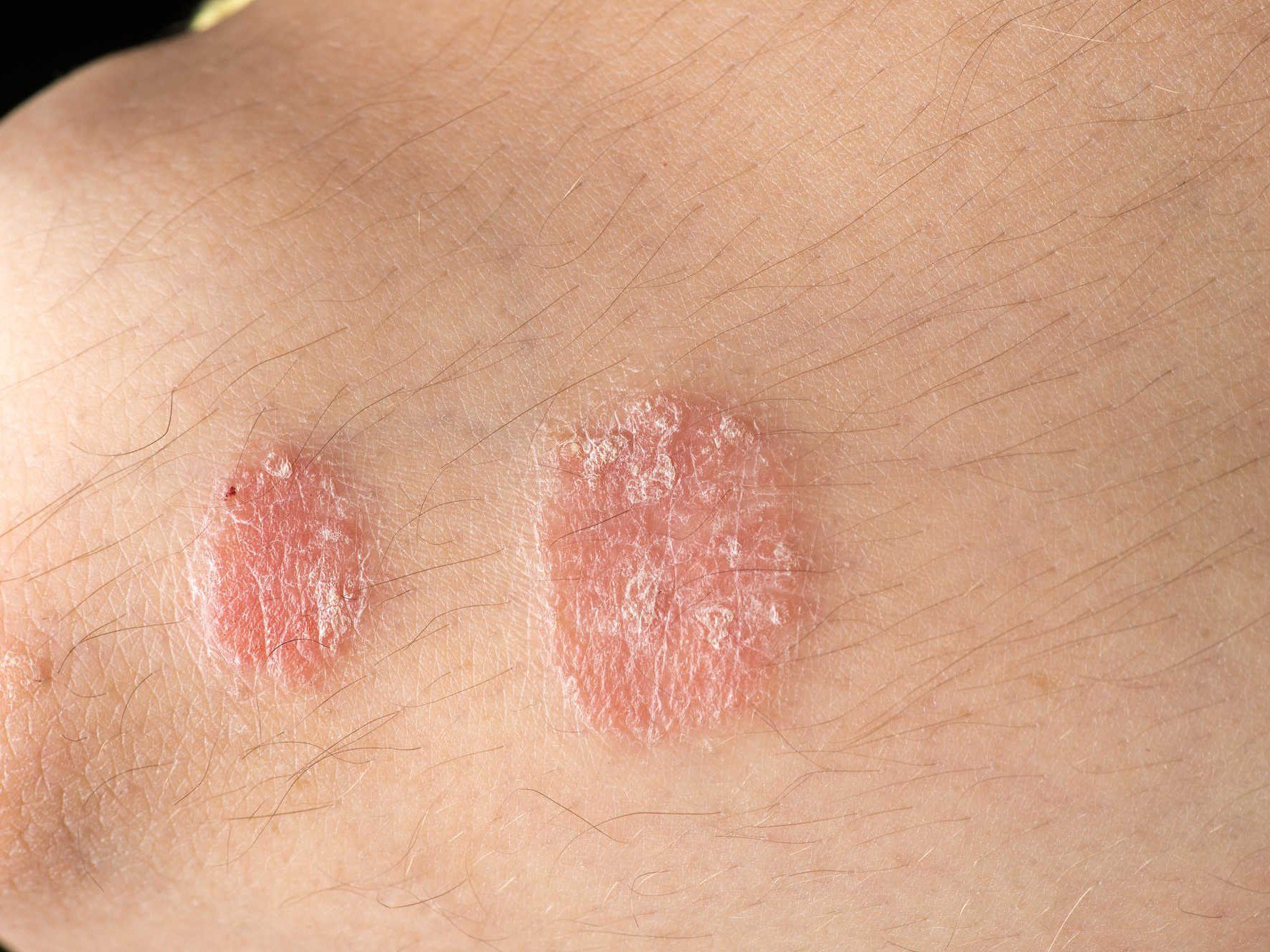
You may develop psoriasis due to:
-
Genetics – If someone in your family has psoriasis, your risk increases.
-
Immune system dysfunction – Your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
-
Triggers – Such as stress, infections, cold weather, certain medications, alcohol, or skin injuries.
Treatment options include:
-
Topical therapies
– Creams, ointments, and medicated shampoos to reduce inflammation and scaling. -
Phototherapy – Controlled exposure to natural or artificial UV light.
-
Systemic medications – Pills or injections that suppress the overactive immune response.
-
Biologic treatments – Advanced therapies targeting specific immune system pathways.
Seasonal patterns: Psoriasis often worsens in winter due to dry air and less sunlight, while many patients notice improvement in summer with increased sun exposure.
Can it come back?
Psoriasis is a chronic condition, meaning there is no permanent cure. Even if symptoms disappear after treatment, flare-ups can return when triggered.
However, with proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments, psoriasis can be managed effectively, and many patients live comfortably with minimal symptoms.
Dietary Recommendations for Psoriasis
✅ Foods that may help:
-
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) – rich in omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation.
-
Fruits and vegetables – especially leafy greens, berries, carrots, and broccoli, which contain antioxidants.
-
Whole grains – oats, brown rice, quinoa for fiber and better digestion.
-
Nuts and seeds – almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds for healthy fats.
-
Olive oil – a healthier fat that reduces inflammation.
-
Green tea – contains polyphenols with anti-inflammatory effects.
-
Turmeric and ginger – natural anti-inflammatory spices.
❌ Foods to avoid (may trigger flare-ups):
-
Processed foods – fast food, packaged snacks, fried foods.
-
Red meat and processed meat – may worsen inflammation.
-
Dairy products – can trigger symptoms in some patients.
-
Refined sugar – cakes, candies, soda, which increase inflammation.
-
Alcohol – a common trigger for flare-ups.
-
Gluten – some people with psoriasis are sensitive to gluten-containing foods (wheat, barley, rye).
👉 Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and staying hydrated are also very important in controlling psoriasis.
News in the same category


With just two cloves a day, you can prevent many diseases...👇 Write me a hello to let me know you're reading... I'll give you a health tip!

The Hidden Power of Guava Leaves: Why More People Are Drinking Them Daily 🍃
Doctors Are Impressed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain
10 Warning Signs of Breast Cancer You Should Never Ignore

Freeze a Lemon, Grate It, and Add It to Your Food

Blending Cucumber and Pineapple May Support Digestive Health — But “Colon Detox” Claims Need Context

Breakthrough against osteoporosis: a mechanism identified that could reverse and regenerate damaged bones
This is how stomach cancer is detected: symptoms and warning signs that appear when eating and that you shouldn't ignore

Natural Drink That Can Transform Your Health: Cinnamon, Bay Leaves, Ginger, and Cloves

Discover Chayote: The Humble Squash That Naturally Transforms Your Health

The Surprising Power of Banana, Onion, and Turmeric for Joint and Bone Pain Relief

Wormwood: Benefits, Contraindications and How to Take It

DID YOU KNOW? If hair grows on your ears, it’s because your body is responding to changes — not because something is “wrong.”

Common Mistakes That Affect Balance in Older Adults
Autophagy: The Body's Power to Heal Itself

Do you have a lump on your wrist? Pay close attention to these symptoms, don't ignore them

These Fruits Help Lower Glucose Levels!
Cilantro Seed Water: The Mexican Wellness Ritual Revolutionizing Natural Health
News Post

Just 1 Cup Before Bedtime: Sleep Deeper and Support Visceral Fat Loss Naturally

With just two cloves a day, you can prevent many diseases...👇 Write me a hello to let me know you're reading... I'll give you a health tip!

The Hidden Power of Guava Leaves: Why More People Are Drinking Them Daily 🍃

Doctors Are Impressed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain

10 Warning Signs of Breast Cancer You Should Never Ignore

Avoid Infections with Your Partner by Adopting This Simple Habit

Freeze a Lemon, Grate It, and Add It to Your Food

Blending Cucumber and Pineapple May Support Digestive Health — But “Colon Detox” Claims Need Context

Breakthrough against osteoporosis: a mechanism identified that could reverse and regenerate damaged bones

This is how stomach cancer is detected: symptoms and warning signs that appear when eating and that you shouldn't ignore

4 surprising uses of egg boiling water.

Karen Tried to Sneak Into Business Class — Flight Attendant Made Her Walk Back in Front of Everyone.

Natural Drink That Can Transform Your Health: Cinnamon, Bay Leaves, Ginger, and Cloves

Discover Chayote: The Humble Squash That Naturally Transforms Your Health

Christmas Nightmare: Racist Flight Attendant Tries to Frame a Pilot, Ends Up in Handcuffs After One Secret Call!

His Final Wish Was to See His Dog—What the German Shepherd Did Stunned Everyone in the Yard

She Collapsed in the Ballroom—And the Duke’s Kindness Changed Her Fate Forever

The Photograph That Haunts the Internet: A Mystery Science Still Cannot Fully Explain

Abandoned to Die in the Snow: How a Lone Lumberjack Saved the Woman a Town Condemned
