
Linking Digestive Health, Vitamin D, and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Pathway to Cognitive Health
Recent studies have established a significant connection between digestive health, vitamin D levels, and the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Research indicates that individuals suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or those with insufficient vitamin D levels may be at a higher risk of experiencing cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases later in life.
IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that disrupts the gut-brain axis, the communication system between the gut and the brain. This dysfunction affects the way the brain interacts with the digestive system, leading to inflammation in various parts of the body, including the brain. It is well-established that chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the development of many diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders. Studies have shown that individuals with IBS often exhibit higher levels of systemic inflammation, which may accelerate the process of cognitive decline (Source: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH).
On the other hand, vitamin D, a fat-soluble vitamin obtained from sunlight, food sources, and supplements, is crucial for brain health. It plays an essential role in protecting neurons, supporting memory functions, and maintaining overall brain health. Vitamin D receptors are found throughout the brain, and the presence of this vitamin is necessary for the brain to function optimally. Several studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency is linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other cognitive disorders (Source: Alzheimer's Association). Without adequate vitamin D, the brain becomes more vulnerable to damage caused by oxidative stress, inflammation, and age-related degeneration. This connection has been supported by numerous clinical studies suggesting that low levels of vitamin D can contribute to the progression of cognitive impairments and neurodegenerative conditions.
These recent findings underscore the importance of maintaining both gut health and a balanced intake of essential nutrients like vitamin D as preventive measures against neurodegenerative diseases. Experts recommend that individuals, particularly those with IBS or low vitamin D levels, adopt strategies to optimize their gut and brain health. This can include maintaining a healthy, balanced diet rich in fiber and probiotics to promote gut health, managing IBS symptoms effectively, and ensuring adequate vitamin D intake. Vitamin D can be obtained through moderate sunlight exposure, consumption of vitamin D-rich foods such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, or through supplementation. For those with vitamin D deficiencies, supplementation has been shown to improve brain health and cognitive function (Source: Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health).
Early intervention and proactive lifestyle changes are key to enhancing cognitive health and preventing or delaying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases. Managing conditions such as IBS, ensuring adequate intake of vitamin D, and adopting a healthy lifestyle may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline and improve overall quality of life in the long term. Moreover, these changes are not only beneficial for brain health but also contribute to general well-being, as they help reduce inflammation and promote a more resilient immune system.
While research into the precise mechanisms linking gut health, vitamin D, and brain health is still ongoing, these findings provide valuable insights into how the gut-brain connection and nutrient balance play a critical role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases. The growing body of evidence emphasizes that taking proactive measures today, such as addressing gut health and ensuring sufficient vitamin D levels, can have long-lasting benefits for cognitive function and overall health in the future.
In conclusion, the growing recognition of the relationship between digestive health, vitamin D levels, and brain health reinforces the importance of an integrated approach to health that focuses on both the body and the mind. It is crucial for individuals to remain proactive about their health through proper nutrition, lifestyle choices, and managing existing conditions to potentially prevent the onset of devastating cognitive diseases later in life.
News in the same category


Revolutionary Cancer Treatment: Activating Immune Structures Within Tumors to Shrink Cancer and Prevent Relapse

The 400-Year-Old Greenland Shark: A Living Witness to Centuries

The Hidden Dangers of Long-Term Energy Drink Consumption

Frozen Time Capsule: Scientists Reveal Ancient Antarctic Landscape

How Cold-Water Swimming Boosts Mood, Reduces Stress, and Enhances Mental Wellbeing
Snakebite Panic Leads Farmer to Sever Finger, Doctors Confirm No Danger

Why Even Small Amounts of Light at Night Can Harm Your Sleep and Mental Health
Apple Extract: A Natural Alternative to Chemotherapy for Treating Colon Cancer
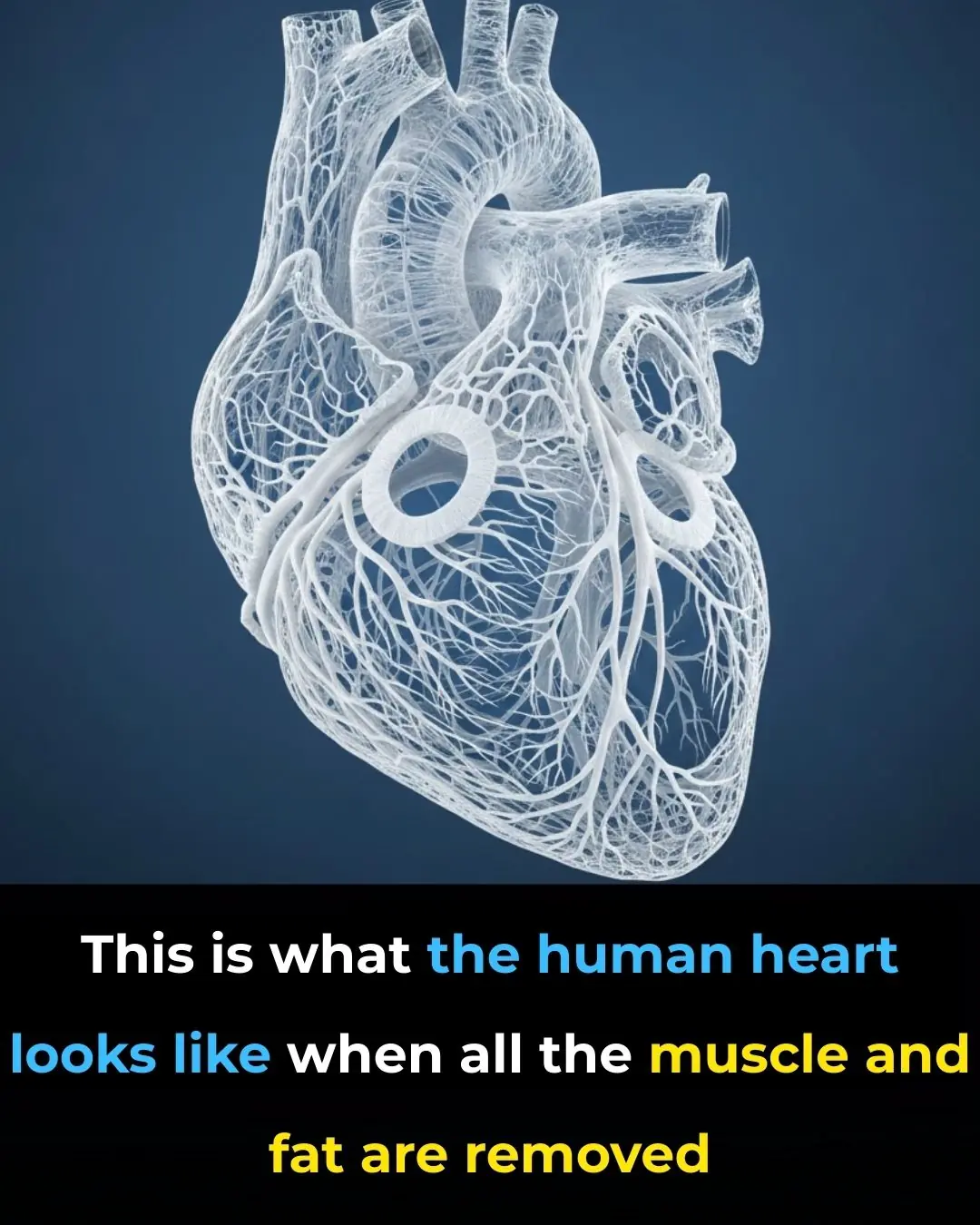
Revealing the Human Heart: A Stunning Look at Its Circulatory System Without Muscle or Fat

Why the Brain Remembers Negative Experiences More Than Positive Ones: Implications for Mental Health and Well-Being

Having the letter M on the Palm of your hand means that

5 Unique Things You Only Experience When Loving an Older Woman

Doggy School on Wheels: How Canada Reinvented Pet Daycare
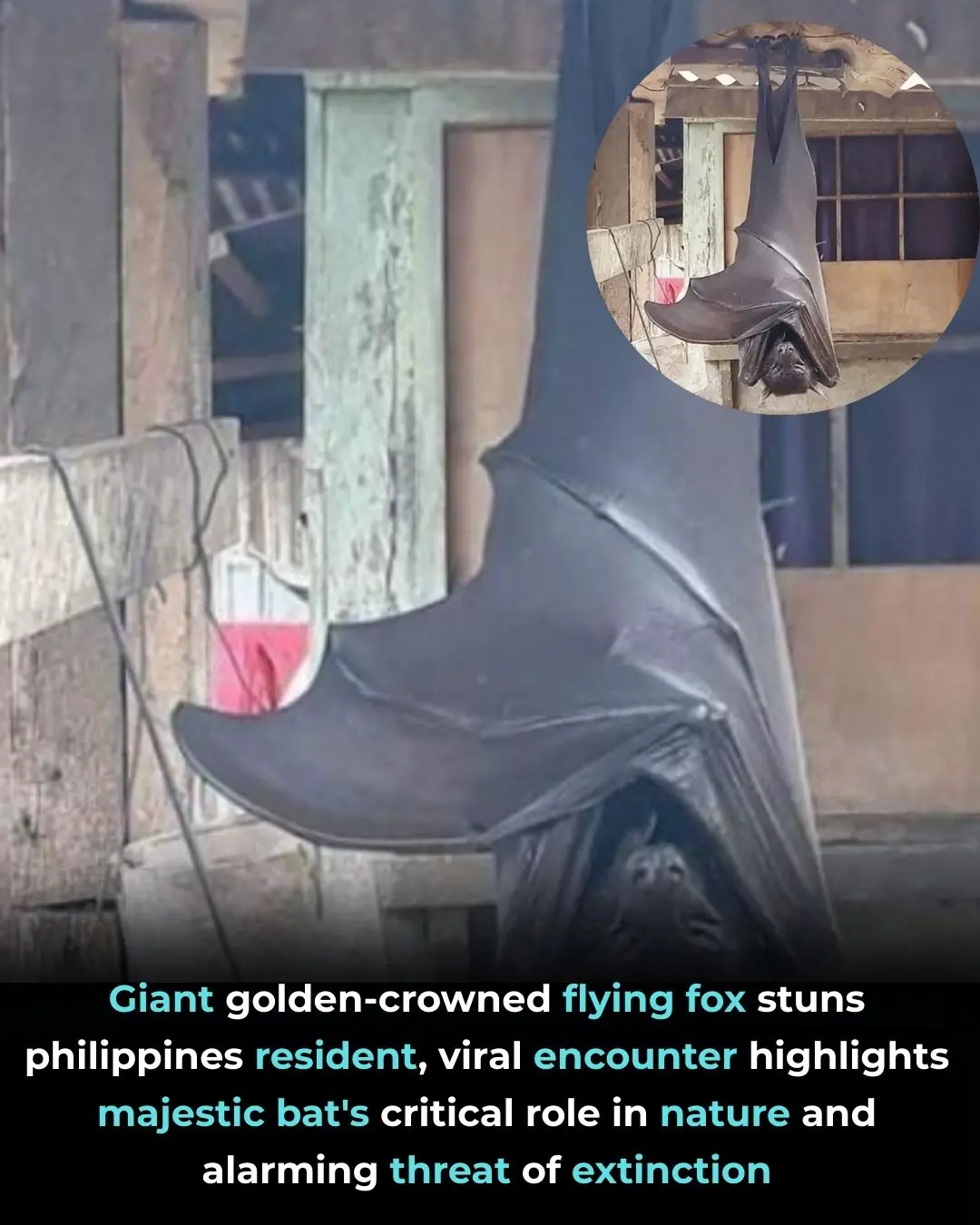

The Giant Golden-Crowned Flying Fox: A Viral Encounter With a Critically Endangered Giant

Dolphins and Pufferfish: The Stunning Discovery Behind Their Trance-Like Behaviour
Revolutionary MRI Technology Offers Non-Invasive Tumour Treatment in Sydney

Recreating a Legacy: Ruben Flowers Joins His Father as Co-Pilot on Captain Flowers’ Final Southwest Airlines Flight

Wood vs. Diamonds: The Cosmic Rarity of Life's Fingerprint
News Post

Belgian Prodigy Laurent Simons Earns PhD in Quantum Physics at Just 15 Years Old

Revolutionary Cancer Treatment: Activating Immune Structures Within Tumors to Shrink Cancer and Prevent Relapse

Flaxseeds Gel For Faster Hair Growth

The 400-Year-Old Greenland Shark: A Living Witness to Centuries

The Hidden Dangers of Long-Term Energy Drink Consumption

Frozen Time Capsule: Scientists Reveal Ancient Antarctic Landscape

How Cold-Water Swimming Boosts Mood, Reduces Stress, and Enhances Mental Wellbeing

Snakebite Panic Leads Farmer to Sever Finger, Doctors Confirm No Danger

Why Even Small Amounts of Light at Night Can Harm Your Sleep and Mental Health

Apple Extract: A Natural Alternative to Chemotherapy for Treating Colon Cancer

Revealing the Human Heart: A Stunning Look at Its Circulatory System Without Muscle or Fat

Why the Brain Remembers Negative Experiences More Than Positive Ones: Implications for Mental Health and Well-Being

You're doing it all wrong. Here’s the right way to clean humidifiers

Nurse Promises Not to Laugh at This Man’s Problem

What Your “Odd Animal Out” Choice Says About You

As he nears 100, Dick Van Dyke, 99, makes a touching confession about his life

Two Golden Elixirs for Energy, Glow & Balance

The Power of Hawthorn (Genus Crataegus): A Natural Ally for Heart and Cholesterol Health
