New Discovery Could Reduce Radiation Side Effects for Cancer Patients
Radiation therapy is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer, but it comes with a major drawback—damage to healthy cells, leading to severe side effects like fatigue, nausea, and an increased risk of secondary cancers. However, a groundbreaking discovery from Harvard Medical School and the University of Iowa could change that, offering a new way to protect healthy cells without reducing the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
How Tardigrades Inspired This Breakthrough
Tardigrades—also known as water bears—are microscopic creatures famous for surviving extreme conditions, including radiation, deep-sea pressures, and even the vacuum of space. Scientists have long studied these tiny organisms to understand how they resist environmental stressors. One of their secrets lies in a special protein called Dsup (Damage Suppressor), which shields their DNA from radiation-induced damage.
By studying this protein, researchers found a way to potentially apply the same protection to human cells—a revolutionary step toward making radiation therapy safer.
How Scientists Are Using mRNA Technology to Reduce Radiation Damage
Instead of permanently altering human DNA, scientists used mRNA technology—the same approach behind COVID-19 vaccines—to temporarily introduce Dsup into healthy cells. Here’s how it works:
- Specialized nanoparticles are used to deliver mRNA instructions to cells.
- Cells read these instructions and begin producing Dsup protein, mimicking the radiation resistance of tardigrades.
- The Dsup protein shields DNA in healthy cells, reducing damage caused by radiation therapy.
Promising Results from Early Trials
In initial studies on mice, this approach reduced radiation-induced DNA damage by up to 50% in some tissues. Importantly, it did not interfere with the effectiveness of cancer treatments, meaning tumors continued to receive full radiation exposure.
While these findings are still in the early stages, they offer hope for safer, less painful cancer treatments in the future.
Beyond Cancer: Other Potential Applications
The impact of this discovery could go beyond cancer therapy. Scientists believe it could help:
- Astronauts survive space radiation during long missions, such as trips to Mars.
- Protect individuals exposed to nuclear radiation in emergencies.
- Reduce the risk of radiation damage in medical imaging procedures like CT scans.
Unlike genetic modification, which can have permanent and unpredictable effects, this mRNA-based solution offers temporary protection, reducing long-term risks.
What’s Next?
Researchers are now exploring ways to refine this technique, test it on humans, and ensure safe, long-lasting protection. If successful, this innovation could revolutionize the way we approach radiation therapy—helping millions of cancer patients receive life-saving treatment with fewer complications.
👉 Read more about this groundbreaking research and what it means for the future: [Insert Link]
News in the same category

Achieve a Brighter Smile Naturally with Rice and Other Powerful Ingredients

Boil Bananas & Drink the Liquid Before Bed – Sleep Like a Baby!

Holy Thistle: Everything You Need to Know About Its Properties, Benefits, and Proper Use

Scent Leaf: The Secret Super Herb You Never Knew!

5 Miracle House Plants That Heal Your Body Inside Out!

Long-Term Study of Heart Rate Variability Responses to Changes in the Solar and Geomagnetic Environment
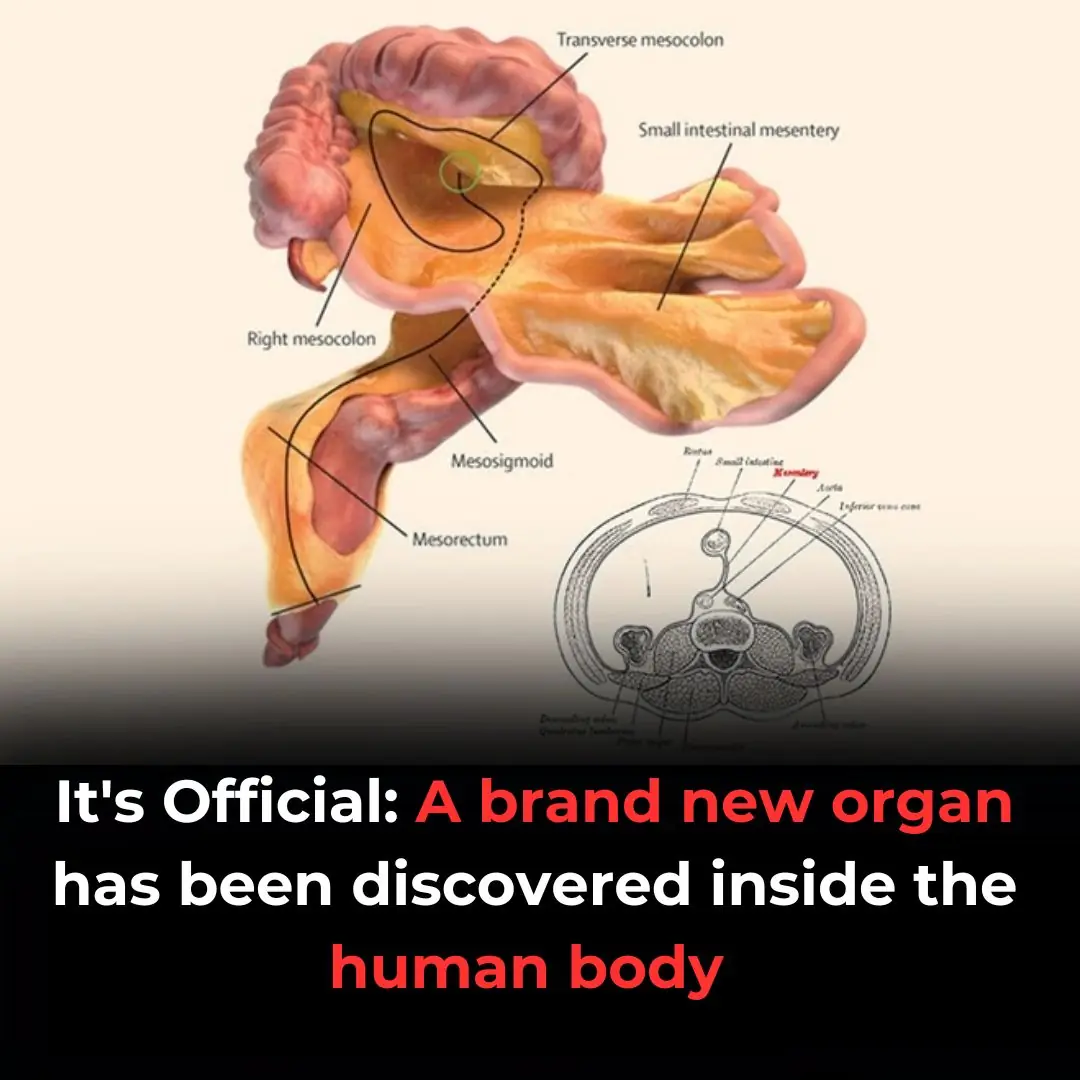
The mesentery: structure, function, and role in disease

Exposure to childhood maltreatment is associated with specific epigenetic patterns in sperm

Team builds first living robots—that can reproduce

A Simple Homemade Remedy to Relieve Cough Naturally

Struggling with Kidney Inflammation? Detox and Refresh with Just Two Simple Ingredients

How to Make Pomelo Flowers Soaked in Honey – A Natural Remedy for Many Ailments

If You Spot These 20+ Signs Cancer May Be Growing In Your Body

Hibiscus Leaves and Flowers: Benefits and Homemade Uses

Drink This Before Bed & Sleep Peacefully! – Perfect for Milk Lovers!

Powerful Natural Blend for Men Over 40: Regain Your Strength and Vitality

10 Signs of Pancreatic Cancer You Should Never Ignore

What Does It Mean When You Dream About Someone Close Who’s Died?
News Post

Dr. Barbara O'Neill Reveals the DANGEROUS Habit That’s Silently Damaging Your Health

Achieve a Brighter Smile Naturally with Rice and Other Powerful Ingredients

Boil Bananas & Drink the Liquid Before Bed – Sleep Like a Baby!

Holy Thistle: Everything You Need to Know About Its Properties, Benefits, and Proper Use

Scent Leaf: The Secret Super Herb You Never Knew!

5 Miracle House Plants That Heal Your Body Inside Out!

Long-Term Study of Heart Rate Variability Responses to Changes in the Solar and Geomagnetic Environment

The mesentery: structure, function, and role in disease

Exposure to childhood maltreatment is associated with specific epigenetic patterns in sperm

Team builds first living robots—that can reproduce

A Simple Homemade Remedy to Relieve Cough Naturally

Struggling with Kidney Inflammation? Detox and Refresh with Just Two Simple Ingredients

How to Make Pomelo Flowers Soaked in Honey – A Natural Remedy for Many Ailments

If You Spot These 20+ Signs Cancer May Be Growing In Your Body

Hibiscus Leaves and Flowers: Benefits and Homemade Uses

X My Ex-Husband Asked Me to Be a Surrogate for Him and His New Wife - It Ended Not as He Expected

Drink This Before Bed & Sleep Peacefully! – Perfect for Milk Lovers!

Powerful Natural Blend for Men Over 40: Regain Your Strength and Vitality

10 Signs of Pancreatic Cancer You Should Never Ignore