Scientists Discover an "Off Switch" for Cholesterol—Could Save Millions of Lives
Scientists Discover an "Off Switch" for Cholesterol—Could Save Millions of Lives

In a discovery that sounds straight out of a science fiction movie, scientists have uncovered a subtle enzyme in our bodies that could be quietly contributing to major health problems. Even more exciting: turning this enzyme off might protect us from some of the deadliest modern diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and even dementia.
This tiny culprit is an enzyme called IDO1. Researchers believe that learning how to "flip the switch" on it could fundamentally reset how our immune system manages cholesterol, potentially saving millions of lives worldwide.
The Cholesterol Conundrum: It's Not Always What You Think
We've all heard the advice: "Avoid high cholesterol." But what's often missed is that cholesterol itself isn't inherently bad; our body actually needs it to build cells and produce hormones. The real danger arises when cholesterol becomes unregulated, particularly when it accumulates in places it shouldn't, like the walls of your arteries.
This is where your immune system, specifically a group of cells called macrophages, comes into play. These cells act as your body's microscopic janitors, patrolling and gobbling up harmful substances like bacteria, dead cells, and yes—excess cholesterol.
The problem starts when your body faces chronic stress or long-term inflammation. These hardworking macrophages get overwhelmed and sluggish, losing their ability to efficiently clear cholesterol. This leads to a dangerous buildup, forming arterial clogs that can cause serious health issues.
Meet IDO1: The Enzyme Hijacking Your Cholesterol Cleanup Crew
Enter the enzyme IDO1 (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1). A groundbreaking study led by Dr. Subhrangsu S. Mandal and his team at the University of Texas at Arlington found that IDO1 becomes active during inflammation and subtly sabotages your macrophages.
How does it do this? IDO1 triggers a chain reaction that produces a molecule called kynurenine, which disrupts how macrophages handle cholesterol. It's like IDO1 gives your cellular janitors a confusing new directive: "Ignore the cholesterol; just keep moving." Naturally, the cleanup process falls behind, and cholesterol starts to accumulate.
But here's the exciting part: when researchers blocked IDO1 in lab tests, the macrophages immediately resumed their normal function, efficiently clearing cholesterol. This seemingly small shift restored the immune system's balance, potentially opening a new frontier in the battle against chronic diseases.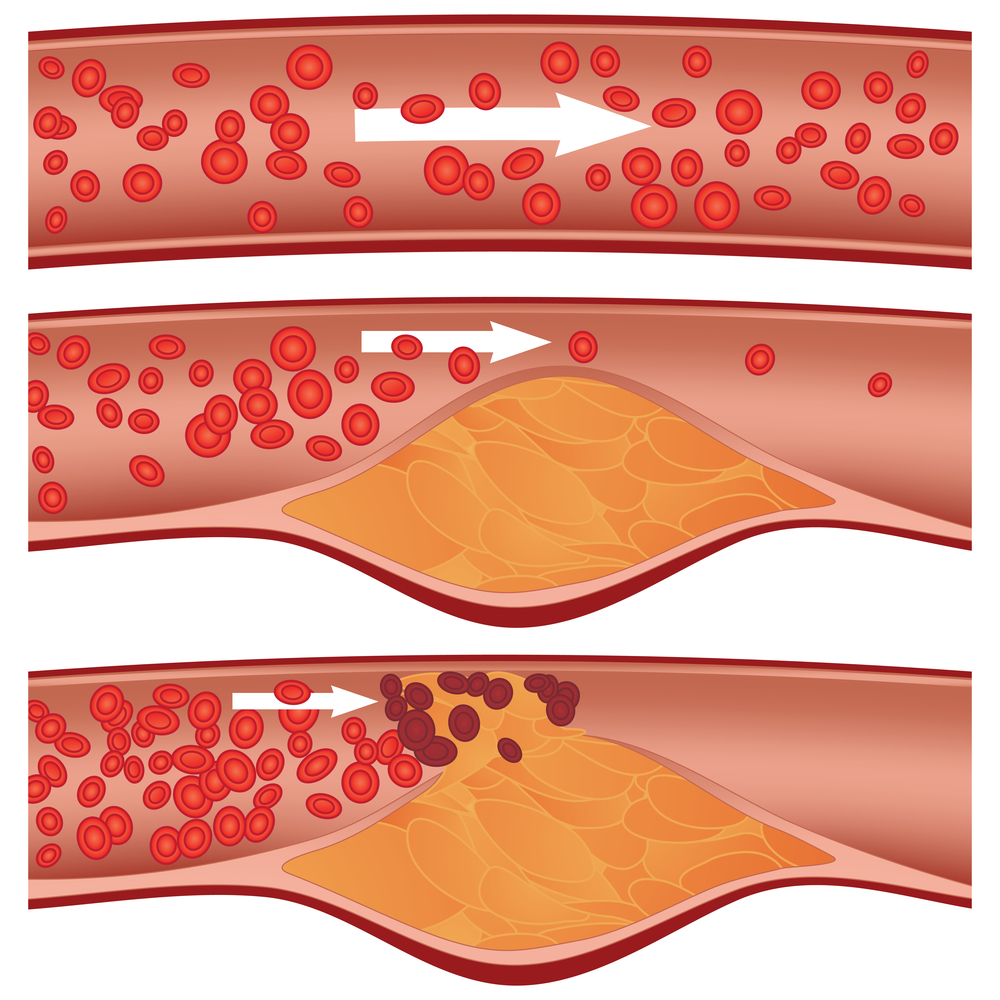
Inflammation: From Friend to Foe
Understanding the role of inflammation is crucial here. Short-term inflammation is beneficial—it's your body's natural response to injury or infection. Think of the redness and swelling around a cut; that's inflammation at work. However, when inflammation persists for too long, it transforms from a protector into a saboteur.
Chronic inflammation is increasingly linked to a wide range of modern illnesses, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's, certain cancers, and autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. It can silently and slowly interfere with normal bodily processes, such as cholesterol management.
This is where IDO1 becomes particularly dangerous: it's activated by inflammation, and in turn, it exacerbates the problem—including cholesterol buildup—by disabling macrophages. It's a vicious cycle, and scientists believe that breaking this loop could be key to achieving better health.
Not One, But Two Culprits Identified
As if IDO1 wasn't enough, the researchers also identified a second enzyme that worsens the problem: nitric oxide synthase, or NOS. While NOS typically helps produce nitric oxide, which is vital for relaxing blood vessels and maintaining healthy circulation, it forms a problematic partnership with IDO1 in this context.
Together, these two enzymes intensify inflammation's negative effects. When both are active, the body’s cholesterol regulation system becomes even more severely disrupted. This dual discovery has led scientists to consider a dual-blocking approach, where medications could be designed to shut down both enzymes simultaneously. Imagine it as cutting the power to two faulty switches instead of just one.
What This Could Mean for Millions
According to Dr. Mandal, the implications of this research extend far beyond mere laboratory curiosity. "This could change how we treat diseases tied to inflammation and cholesterol," he explains. "Instead of only focusing on lowering cholesterol with drugs like statins, we may now have the option to prevent that buildup in the first place by targeting the inflammation that causes it."
This innovative approach could be a major leap in how we manage diseases affecting millions globally. Envision treatments that not only keep cholesterol in check but also reduce inflammation, lower the risk of heart attacks, and potentially slow the progression of other chronic conditions like Alzheimer's and even certain cancers.
Furthermore, because IDO1 is present in various parts of the body, including the brain, this discovery could also help researchers unlock clues to conditions like dementia or depression, both of which have been linked to inflammation and immune dysfunction.
What Happens Next?
This groundbreaking discovery is just the beginning. The researchers are now investigating how IDO1 interacts with other bodily systems and whether other enzymes or molecules play supporting roles in this complex cholesterol-inflammation dynamic.
The ultimate goal is to develop safe, effective medications that can block both IDO1 and NOS without interfering with other critical bodily functions. If successful, this could lead to a new generation of "smart" anti-inflammatory drugs—medications that target the root causes of chronic disease rather than merely treating symptoms.
These potential new medications could complement existing treatments like statins or insulin, or even reduce the need for them in some individuals. They could also offer new hope for patients who don't respond well to current therapies, providing doctors with more options in the ongoing fight against chronic illness.
Final Thoughts: The Power of Small Discoveries
It’s easy to overlook enzymes like IDO1, which are invisible to the naked eye and operate silently within our cells. However, discoveries like this powerfully remind us that sometimes, solving monumental problems begins with understanding the tiniest components.
A single molecular switch, flipped at the right moment, could be the crucial difference between widespread disease and enduring health. Thanks to a dedicated team of researchers in Texas—including seasoned scientists, students, and postgrads who contributed to this breakthrough—we may be closer than ever to flipping that switch in our favor.
News in the same category

Alarming Rise: Liver Damage Linked to Supplement Use Sparks Scientific Concern
This Is How Long It Takes Your Liver to Return to Normal From Drinking

Can Your Eyes Reveal Diabetes or Cancer? Don’t Miss the Signs
Clear Signs of Kidney Failure Everyone Should Pay Attention To
5 Typical Early Symptoms of Childhood Cancer: When to Take Your Child to the Hospital Immediately
Doctor’s Warning: Early-Stage Lung Cancer Doesn’t Always Include a Cough – Watch for These 4 Unusual Signs

5 Early Signs of Diabetes That Many People Often Overlook
To Prevent Stroke, Remember the ‘3 Don'ts’ After Meals and the ‘4 Don'ts’ Before Bed — Stay Safe at Any Age

Scientists Warn: Most Infectious Covid Strain Yet Is Now Dominating
Bloated Stomach: 8 Common Reasons and How to Treat Them (Evidence-Based)

Foamy Urine: Why You Have Bubbles in Your Pee and When to Worry
What Causes Belly Fat: Foods to Avoid and Other Key Factors

Notice These 4 Unusual Signs Before Sleep? Be Careful – They May Signal a Risk of Stroke
5-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed With Terminal Cancer: A Wake-Up Call for All Parents
Good News: Successful Trial of Method That Destroys 99% of Cancer Cells

Terrifying Study: Up to 30% of Americans Could Be Infected with Brain-Impacting Parasite
Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common
Doctor's "Deeply Concerning" Warning After Man Injects Sperm to 'Cure Back Pain'
News Post

Breakthrough Blood Test Detects Cancer Years Before Symptoms Appear

Alarming Rise: Liver Damage Linked to Supplement Use Sparks Scientific Concern

A Missing Little Girl Who Was Featured On “Unsolved Mysteries” Has Finally Been Found

This Is How Long It Takes Your Liver to Return to Normal From Drinking

Biohacker Claims 90 Days Of Oxygen Therapy Reversed His Biological Age To That Of A 10-Year-Old

Tomato, Turmeric, and Sugar: The DIY Glow-Up Trick for Radiant Skin
7 Early Warning Signs of a Stroke – Recognize Stroke Symptoms FAST: THIS Could Save Your Life

🍃 People Love Papaya – But Most Don’t Know How Powerful Its Leaves Are! Here’s How to Use Them
18 Lifestyle and Dietary Habits to Improve Gut Health and Digestive Issues

The Trans-Canadian Rail Route: An Iconic Journey Across Canada

Vocal Speech Observed in Wild Chimpanzees. Are Apes Evolving Into Humans?

Photograper Captures A Once-In-A-Lifetime Shot Of A ‘Horizontal Rainbow’ That Filled The Whole Sky

Scientists Discover Massive Underground Reservoir Holding 3x More Water Than All Our Oceans Combined

If You Kill One Dragonfly, You Are Responsible For Over 100 Mosquito Bites

Tesla Dreamed It—Now Wireless Electricity Is Closer To Reality Than Ever

Can Your Eyes Reveal Diabetes or Cancer? Don’t Miss the Signs

Discover The Miraculous Benefits of Moringa

Clear Signs of Kidney Failure Everyone Should Pay Attention To
