Terrifying Study: Up to 30% of Americans Could Be Infected with Brain-Impacting Parasite
Terrifying Study: Up to 30% of Americans Could Be Infected with Brain-Impacting Parasite
A recent study has revealed a startling possibility: up to 30% of Americans could be infected with a dangerous parasite that has a horrific impact on the brain. This widespread parasite, known as Toxoplasma gondii (or T. gondii), has the potential to lie dormant for years before triggering serious illness, affecting over 100 million people in the U.S. without them even knowing.
T. gondii: A Silent Invader Affecting Brain Communication
According to researchers at the University of California, Riverside, T. gondii can enter the human body primarily through eating undercooked meat or exposure to cat feces. The new study, published in PLoS Pathogens, indicates that between 10% and 30% of the U.S. population might be infected without ever realizing it.
The scientists explained how this parasite can interfere with crucial brain functions by infecting neurons. Specifically, the affected neurons were found to release fewer extracellular vesicles (EVs). These EVs are vital for the exchange of information between brain cells.
"We found this disruption in EV signaling can interfere with how neurons and glial cells, especially astrocytes, maintain a healthy brain environment,” stated Emma H. Wilson, who led the research. “Even a handful of infected neurons can shift the brain’s neurochemical balance. This suggests that communication between neurons and supporting glial cells is not only critical, but also vulnerable to hijacking by parasites.”
Neurological Impact and Dormancy
Using a combination of mouse and human cells, Wilson's team discovered that the disruption of neurons by T. gondii can result in heightened glutamate levels. Elevated glutamate can lead to severe neurological issues, including seizures.
One of the most concerning aspects of this parasite is its ability to lie dormant within the body for years before becoming active and causing severe illness. This means an infection contracted long ago could suddenly trigger serious health problems without a clear immediate cause.
“The parasite may play a larger role in neurological and behavioral conditions than we previously thought,” Wilson commented, highlighting the broader implications of their findings. “Our brains have built-in defenses that may recognize and respond to neurons infected by Toxoplasma gondii. If we can learn how to support or enhance that process, we may be able to better protect people, especially the most vulnerable.”

Prevention and Future Hopes
Currently, tests can only confirm if a person has ever been infected with T. gondii, not whether the parasite is still actively present or causing symptoms. However, Wilson hopes this new research can lead to the identification of effective therapies and even vaccines in the future.
Despite the widespread infection rates, Wilson stresses that there’s "no need to avoid someone who is infected; most people live their entire lives without symptoms." She does offer a specific caution for pregnant individuals, as the parasite can cause serious birth defects if contracted for the first time during pregnancy.
The most effective prevention strategies revolve around proper food handling and hygiene:
-
Cook meat thoroughly.
-
Wash vegetables diligently.
-
Always wash your hands after handling cat litter, especially from young cats, as they are more likely to shed the parasite.
This study underscores the hidden impact of common parasites and the critical need for continued research into their long-term effects on human health.
Did you know that Toxoplasma gondii could be so widespread and potentially impact brain health?
News in the same category

Doctor's "Deeply Concerning" Warning After Man Injects Sperm to 'Cure Back Pain'
Non-Smoker Diagnosed with Lung Cancer Shares His Only 'Silent' Symptom
Alarming Discovery: High Aluminum Levels Found in Brains with Alzheimer's, Autism, and MS
First Human Trial Launched for Stem Cell Therapy to Reverse Spinal Cord Injuries
From Despair to Hope: Joe Tippens' Incredible Cancer Recovery Story with Fenbendazole

100-Year-Old Doctor Reveals: 7 Daily Habits to Help You Live a Healthy Life
Diagnosed with Terminal Cancer, Preparing for the End – A Man’s Miraculous Survival Thanks to 3 Major Life Changes
Warning signs of stroke 30 minutes before – remember them to save your life and your loved ones
Your Body's Silent Alarms: 9 Subtle Signals of a Heart Attack, Up to a Month Before It Strikes

31 Foods Experts Say You Should Avoid (Or Severely Limit)

Heart Surgeon Warns: 4 Foods and Drinks You Should "Always Avoid" to Protect Your Body

12-year-old girl dies of rare cancer—parents noticed worrying sign as she brushed teeth

Just Two Hours of Sitting in Silence May Spark Growth of New Brain Cells, Study Finds
Rising Kidney Failure in Young People: One Harmful Habit Many Are Unknowingly Practicing
5 Early Signs of Liver Failure: Seek Medical Help Early to Prolong Life – Number 2 Is Especially Common

7 Health Problems That Can Happen If You Don’t Drink Enough Water
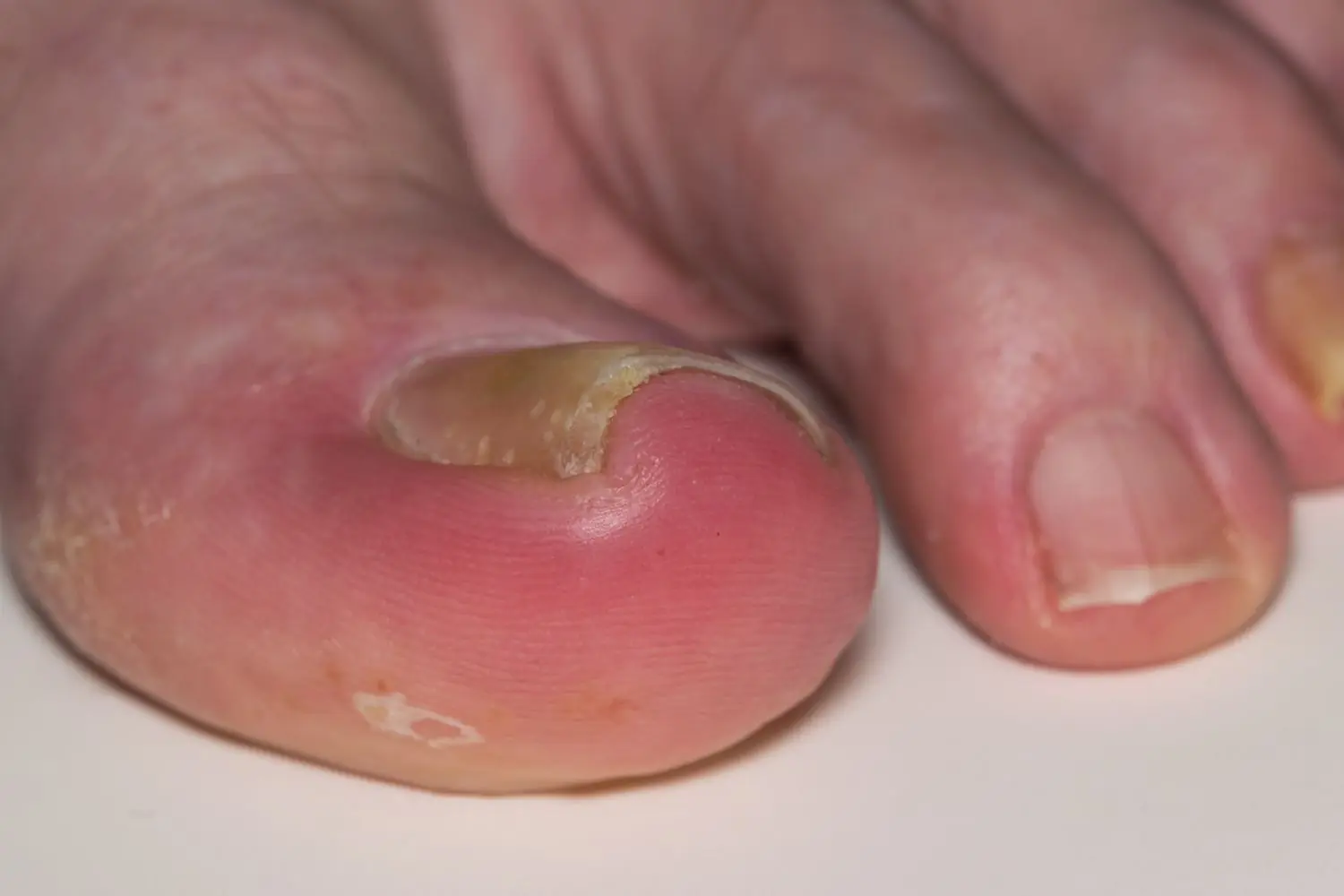
Home Remedies to Treat and Prevent Ingrown Toenails (Onychocryptosis)
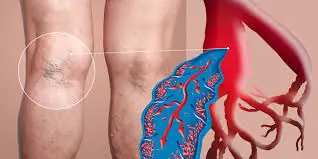
Blood Clot in Leg: Crucial Signs and Symptoms You Can't Afford to Ignore
News Post

New interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is hurtling through the solar system — and you can watch it live online today

HealthScientists Detect Microplastics In Reproductive Fluids—Potential Infertility Risk

Ancient Inscriptions Inside Great Pyramid Rewrite History Of Its Builders

Once ‘Dead’ Thrusters On The Farthest Spacecraft From Earth That’s 16 Billion Miles Away Are Working Again

OpenAI’s Top Al Model Ignores Explicit Shutdown Orders, Actively Rewrites Scripts to Keep Running

Google Earth Unveils Shocking 37-Year Transformation Of Our Planet

Marine Animal Shows Are Officially Banned in Mexico After Historic Legislative Vote

Denmark Pays Students $1,000 Monthly to Attend University, With No Tution Fees

Protect Your Home and Wallet: Unplug These 5 Appliances When You’re Done Using Them

Some People Still Think These Two Buttons Are Only For Flushing

Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Doctor's "Deeply Concerning" Warning After Man Injects Sperm to 'Cure Back Pain'

Non-Smoker Diagnosed with Lung Cancer Shares His Only 'Silent' Symptom

The Dark Year: What Made 536 So Devastating For Civilization

Alarming Discovery: High Aluminum Levels Found in Brains with Alzheimer's, Autism, and MS

First Human Trial Launched for Stem Cell Therapy to Reverse Spinal Cord Injuries

From Despair to Hope: Joe Tippens' Incredible Cancer Recovery Story with Fenbendazole

Elon Musk Claims He’s A 3,000-Year-Old Time-Traveling Alien
