
Study Reveals How Earth’s Orbit Triggers Ice Ages, And There’s One in The Next 11,000 Years
Earth’s climate history has been a dramatic roller-coaster ride of fluctuation, shifting from relatively warm periods to icy epochs of widespread glaciation, only to return again to the more temperate conditions we experience today. These dramatic changes, known as Quaternary ice ages, are part of a larger pattern of long-term climate variability that has shaped the planet for millions of years.
But what actually triggers these massive glacial events? For decades, scientists have suspected that subtle changes in Earth’s orbit around the Sun play a major role. Now, new research has revealed a precise and predictable relationship between these orbital shifts and the timing of ice ages—offering a powerful new tool to forecast Earth's long-term climate future.
“The link between slight changes in axial tilt and orbital geometry and the waxing and waning of continental ice sheets represents one of the oldest mysteries in climate science,” said Earth scientist Stephen Barker of Cardiff University, speaking to ScienceAlert. “It’s a fundamental gap in our understanding of the climate system. Enhancing our knowledge of how Earth’s dynamic climate system functions is crucial if we want to accurately predict future climate shifts.”
The Complex Geometry of Earth’s Orbit
Earth’s orbit around the Sun isn’t a perfect circle—it’s slightly elliptical, a shape known as orbital eccentricity. This means Earth’s distance from the Sun varies throughout the year, influencing the amount of solar energy the planet receives.
In addition to this, the orientation of Earth's orbit in space slowly changes over time, a phenomenon called orbital precession. Meanwhile, the tilt of Earth’s axis—referred to as obliquity—also fluctuates. These three orbital factors influence how solar energy is distributed across the globe and throughout the seasons.
These slow but regular changes, collectively known as Milankovitch cycles, occur on timescales of approximately 20,000, 40,000, 100,000, and even 400,000 years. They have long been associated with periods of warming and cooling, but pinpointing exactly how each cycle contributes to glaciation has proven to be immensely difficult.
“Earth’s climate is an interconnected system of complex processes,” Barker noted. “Modeling these over glacial timescales requires immense computational resources—and even then, it’s difficult to quantify each process independently.”
A New Breakthrough in Climate Understanding
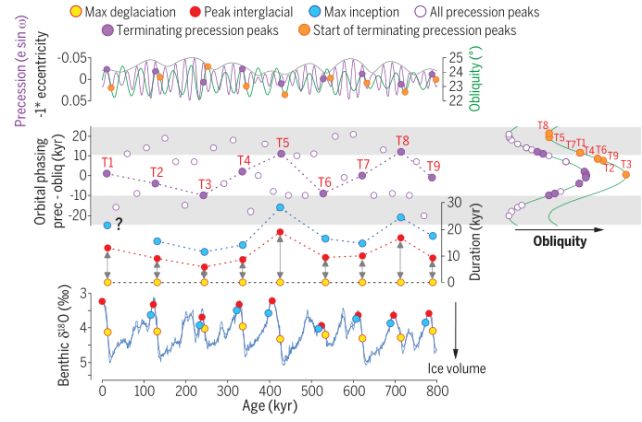
One of the long-standing puzzles is why, over the past 800,000 years, ice ages have ended in a cycle of roughly every 100,000 years. While precession and obliquity are known to drive climate changes, no clear link had been established between these cycles and the precise end—or onset—of glacial periods.
To unravel this, Barker and his colleagues turned to the geological record, specifically by analyzing the ratio of oxygen isotopes in deep-sea sediments. These isotopes, preserved in the fossilized shells of microscopic marine organisms called foraminifera, serve as a reliable proxy for the volume of continental ice sheets over time.
Using this data, the researchers created a high-resolution timeline of glacial and interglacial periods. When they compared this against Earth's orbital precession and obliquity, a striking pattern emerged: the timing of ice age transitions aligned closely with specific interactions between these two orbital factors.
Here’s what they found:
-
Obliquity (axial tilt) is the primary driver for the onset of glaciation.
-
The end of an ice age (deglaciation), however, requires a very specific alignment between precession and obliquity.
This relationship not only explains the mysterious 100,000-year cycle but also confirms that ice ages are deterministic, not random—meaning they follow predictable orbital patterns.
“I was really excited when I saw the relationship between orbital phasing and the shape of the climate curve across these well-known transitions,” Barker said.
“These curves have been around for decades, studied countless times—including by me—but the connection we found had remained hidden until now.”
What This Means for the Future
This discovery has profound implications. For one, it suggests that Earth is currently on a path toward another ice age, due to a gradual decline in axial tilt. According to the team’s calculations, the next ice age could begin within the next 11,000 years—unless something, or someone, interferes.
And that “someone” is humanity.
“According to the latest IPCC reports, human activities—particularly greenhouse gas emissions—have already begun to disrupt the natural trajectory of Earth’s climate,” Barker explained.
This means that while Earth’s orbit might prepare the planet for another glaciation, human influence could override this natural cycle. By comparing predicted future climates to what would have occurred naturally—without anthropogenic interference—we can better understand the full magnitude of our impact.
“At present, projections of future climate change are made relative to modern or pre-industrial conditions,” Barker said.
“But we believe it’s crucial to also consider the natural, orbital-driven climate baseline—what might have happened in a world untouched by industrialization. This comparison will help us quantify humanity’s influence over the coming millennia.”
The research, published in Science, represents a significant step forward in understanding the grand-scale mechanics of Earth’s climate. It gives scientists not just a clearer view of the past, but also a powerful framework for anticipating what lies ahead.
TL;DR
-
Earth’s ice ages are driven by predictable cycles in the planet’s orbit and axial tilt.
-
The onset of ice ages is controlled mainly by obliquity (axial tilt), while their end depends on a precise alignment of precession and obliquity.
-
This explains the long-standing mystery of the 100,000-year glaciation cycle.
-
The next ice age could begin in about 11,000 years—unless human-caused climate change overrides the natural pattern.
-
Understanding these mechanisms is vital for predicting the long-term impact of current climate actions.
News in the same category


Think Bottled Water Is Safer Think Again

5 Early Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer That 90% of Women Overlook
Cervical cancer is not a silent killer—it sends out warnings. The challenge is whether women notice and act on them in time.

8 Shocking Toilet Clues That Could Signal Cancer: Don’t Ignore These Early Warnings
Many people dismiss subtle changes in bathroom habits as minor or temporary issues. However, certain unusual signs when you go to the toilet could be early red flags of serious health problems. Recognizing them in time can make the difference between earl

This 3,200-Year-Old Tree Is So Big, It’s Never Been Captured In A Single Photograph…

Travel Coast-to-Coast by Train and See America’s Greatest Sites For Just Over $200

Descend Into the Heavenly Pit: Exploring Xiaozhai Tiankeng, the World’s Deepest Sinkhole

The Walking Trees of Ecuador: They Reportedly Move Up to 20 Meters Per Year

How to See Halos, Sun Dogs and Other Delights of the Daytime Sky

When someone in the family passes away, you should know that you should not keep these 4 relics for your children and grandchildren.

Student dies by suicide after undergoing a beard transplant in Turkey from an ‘estate agent posing as a surgeon’

The Sun Begins Killing off Elon Musk’s Starlink Satellites as Scientists Sound Alarm

Never Leave a Charger in Outlet Without Phone. Here Are the Top 6 Reasons Why

3 Coffee Types That Can Add Years to Your Life and Shield You from Heart Disease and Stroke
Enjoying two to three cups of ground, instant, or decaf coffee daily can be a powerful step toward a longer and healthier life.

Bananas Are Packed With Nutrients, But These 4 Groups Should Avoid Eating Too Many
Bananas are undeniably one of the most versatile and beneficial fruits. From boosting digestion to supporting heart health, they offer a wide range of nutrients. However, they are not suitable for everyone.

9 Early Warning Signs of Stomach Cancer You Should Never Ignore
. Paying attention to subtle but persistent warning signs, combined with regular health screenings, offers the best chance for timely intervention.

MAHA Chief Medical Advisor Dr. Aseem Malhotra Just Declared That No One Should Have Ever Taken the COVID mRNA Vaccines.

New mRNA Shot Turns Immune Cells Into Cancer-Killers Directly Inside the Body, Study Finds
News Post

Remove these 7 everyday foods from your fridge—they could raise cancer risk

The Anti-Cancer Diet: Cancer Fighting Foods to Help Prevent Cancer (Evidence Based)

Drinking guava leaf water, the body receives these 6 great benefits

With just one lemon: You can get rid of all the ants in your house in no time, never to return.

Used Coffee Grounds: Don’t Throw Away Money – Amazing Everyday Uses You Should Know

I Put 3 Ice Cubes in the Washing Machine Like My Neighbor Did—What Happened Surprised Me

Another US doctors’ group breaks with federal policy, recommends COVID-19 vaccines for all adults

5 Best Drinks for Kidney Health — Especially #1, Free and Longevity-Boosting

10 Best Potato Face Packs for Glowing, Clear, and Youthful Skin
From acne and pigmentation to dryness and aging, potatoes address nearly every skin issue without side effects or hefty price tags. With consistent use, these DIY packs can reveal skin that’s clearer, smoother, and radiant.

Reverse Premature Grey Naturally with This Easy Homemade Hair Oil
While it is natural for hair to turn grey as we age, there are many natural remedies, dietary changes, and cosmetic treatments available that can help slow down or reverse the process.

Donald Trump Says There Could Be People in Epstein Files Who ‘Don’t Deserve to Be’ There in Shocking Statement
Clean Your Kidneys and Urinary Tract Naturally: One Teaspoon a Day

Think Bottled Water Is Safer Think Again

A Surprising Drink That May Help Prevent Cancer – And It's Not Tea or Coffee
How To Get Rid of Phlegm And Mucus

5 Early Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer That 90% of Women Overlook
Cervical cancer is not a silent killer—it sends out warnings. The challenge is whether women notice and act on them in time.

8 Shocking Toilet Clues That Could Signal Cancer: Don’t Ignore These Early Warnings
Many people dismiss subtle changes in bathroom habits as minor or temporary issues. However, certain unusual signs when you go to the toilet could be early red flags of serious health problems. Recognizing them in time can make the difference between earl

3 Powerful Ways to Keep Snakes Out of Your Home and Protect Your Family
By combining natural repellents, careful use of traditional methods, and the protective instincts of pets, households can greatly reduce the likelihood of encountering these stealthy reptiles.
