Surprising Triggers: What May Be Causing Your Hives (Urticaria)
Surprising Triggers: What May Be Causing Your Hives (Urticaria)
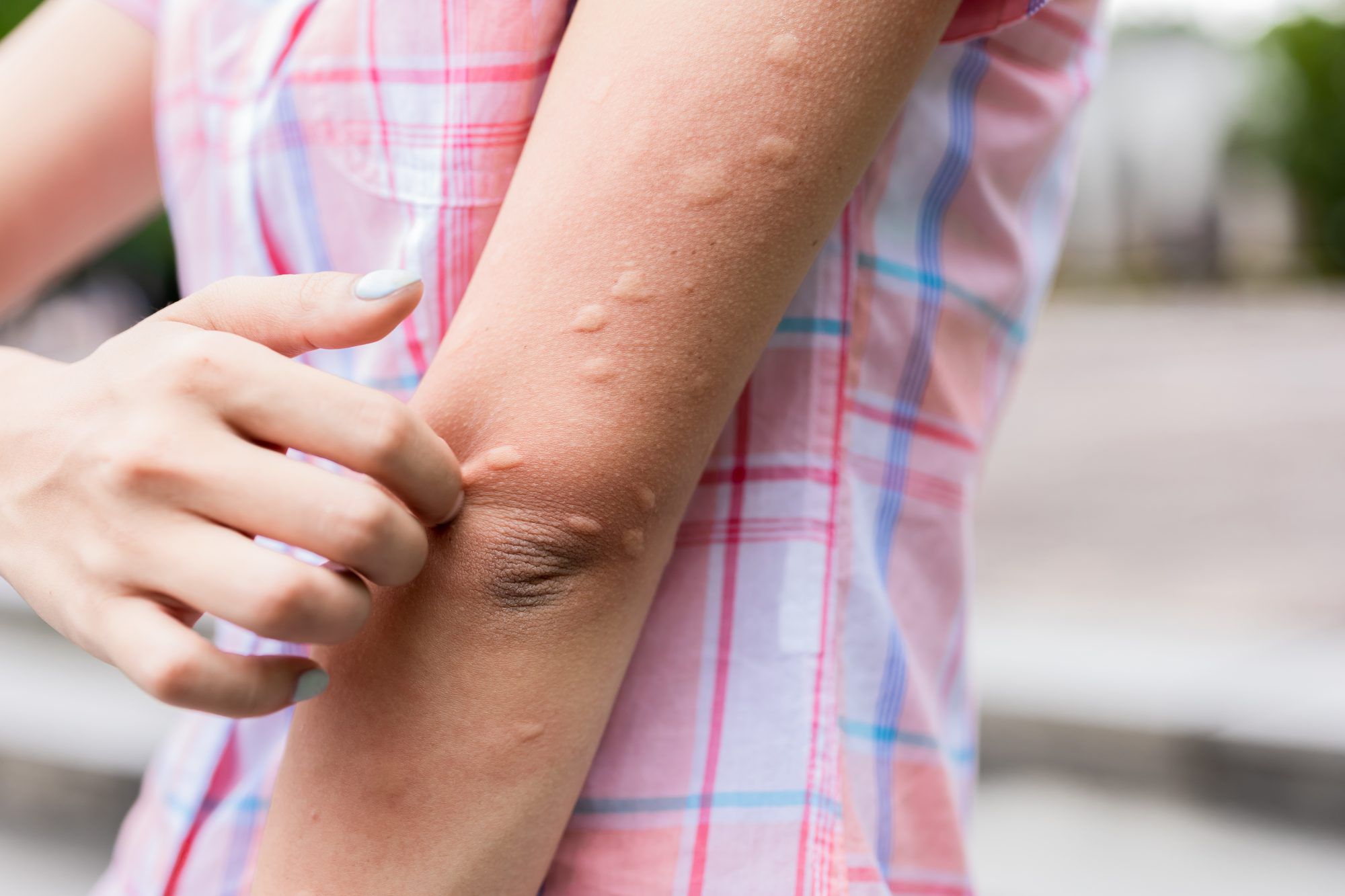
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of raised, red, and intensely itchy welts. These lesions can vary in size, from small patches to large plaques, and may form clusters on various parts of the body, including the face, arms, legs, and torso. While individual welts typically fade on their own within a few hours or days, they can sometimes reoccur, significantly impacting a person's comfort and well-being.
Despite how unsettling they can be, urticaria is usually a harmless and temporary condition. The characteristic oedematous (swollen) welts occur because certain body cells called mast cells release histamine and other chemical mediators into the bloodstream. This causes tiny blood vessels in the skin (capillaries) to leak fluid, leading to the visible swelling.
Key Symptoms of Urticaria
The main symptoms of urticaria include:
-
Hives: These are raised, well-defined lesions that often appear red at the edges and paler in the center.
-
Pruritus: This is characterized by mild to extremely intense itching.
-
Evanescent Character: One of the most distinguishing features is that individual welts typically disappear without leaving a mark in less than 24 hours, though fresh welts may develop elsewhere on the body.
Occasionally, urticaria can be accompanied by angioedema, which is swelling in the deeper layers of the skin. Angioedema frequently affects the hands, feet, lips, eyelids, or genitals and can cause pain or tightness. If angioedema affects the tongue or throat, it is considered a medical emergency because it can make breathing difficult.
Types of Urticaria
Urticaria is primarily categorized by how long the outbreaks last:
-
Acute Urticaria: This is the most common type. Outbreaks typically last less than six weeks, and the cause is often identifiable.
-
Chronic Urticaria: This is diagnosed when breakouts persist for longer than six weeks. Chronic spontaneous urticaria, also known as idiopathic urticaria, is a form where the underlying cause is frequently unclear.
Additionally, there is physical urticaria (also known as inducible urticaria), where hives are triggered by specific external stimuli, such as:
-
Dermographism: Hives form when the skin is scratched or rubbed.
-
Cold Urticaria: Hives appear after exposure to cold temperatures.
-
Pressure Urticaria: Constant pressure on the skin (e.g., from tight clothing) can result in hives.
-
Solar Urticaria: Hives are triggered by sunlight exposure.
-
Cholinergic Urticaria: This type is linked to a rise in body temperature, for example, during exercise or a hot bath.
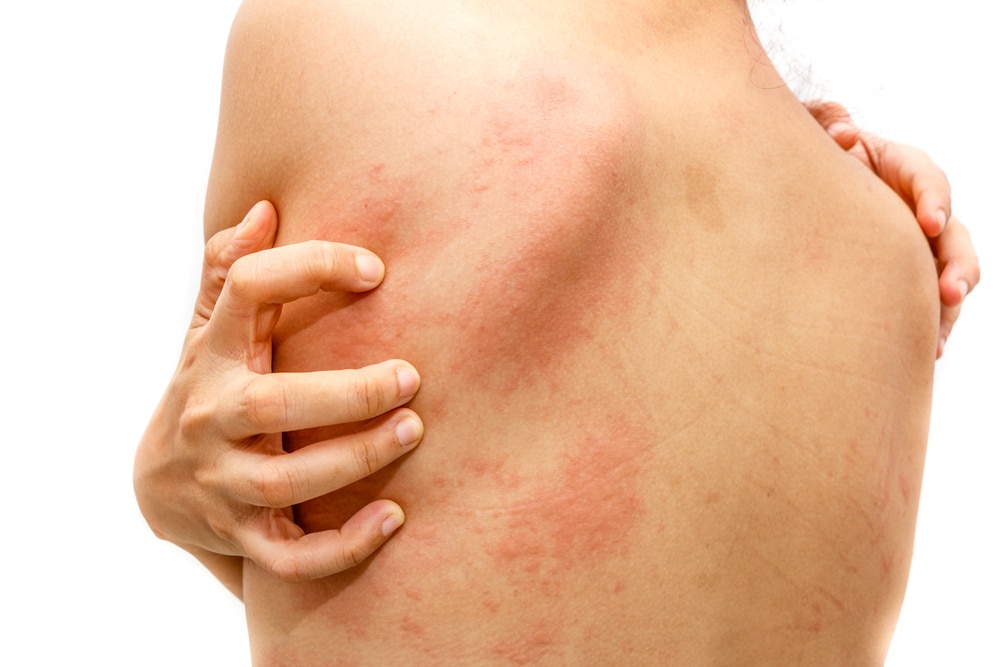
Common Causes of Urticaria
There are many potential causes of acute urticaria, including:
-
Allergic Reactions: Common culprits include certain foods (like shellfish, nuts, eggs, and milk), drugs (such as antibiotics, painkillers like aspirin or ibuprofen), insect bites, or latex.
-
Infections: Both bacterial infections (e.g., strep throat) and viral infections (like the common cold or hepatitis) can trigger hives.
-
Physical Factors: As seen in inducible urticaria types mentioned above (e.g., cold, pressure, sunlight).
-
Emotional Stress: While not a direct cause, emotional stress can exacerbate outbreaks in susceptible individuals.
For persistent (chronic) urticaria, it's often impossible to identify a specific external cause. A significant portion of these cases are thought to be linked to autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets its own mast cells.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing urticaria primarily involves a review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. The physician will aim to determine the duration of the outbreaks and explore potential triggers.
The main goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms and, whenever possible, avoid known triggers:
-
Antihistamines: These are the cornerstone of treatment. They work by blocking histamine's activity, thereby lessening itching and hive formation. Both prescription and over-the-counter antihistamines are used.
-
Corticosteroids: In more severe or chronic situations, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for a brief period to reduce inflammation.
-
Avoid Triggers: The most crucial step, if a specific trigger (like a food or medicine) has been identified, is to consistently avoid it.
Have you ever experienced hives, and if so, did you identify a specific trigger?
News in the same category


Your Eyes: Windows to Your Health – Uncovering Diabetes and Cancer Through Vision
5 Early Warning Signs of Cancer in Children: Parents Must Know to Save Their Child
If Your Body Has a Bad Odor in These 3 Areas, It Could Mean Poor Liver Detox and Declining Function – Get Checked Before It’s Too Late!
Warning: If You Notice This Symptom in Your Body, Go to the Hospital Immediately – It Could Be Late-Stage Nasopharyngeal Cancer

Astonishing Cancer-Fighting Power of One Juice — Even Doctors Are Surprised
5 Types of Cancer with Over 90% Cure Rate: Early Signs Everyone Should Pay Attention To

Doctor's Advice: Whether You're Rich or Poor, Never Eat These 3 Foods for Breakfast – They Can Lead to Aggressive Cancer

Scientists Use CRISPR to Eliminate HIV from Human Immune Cells
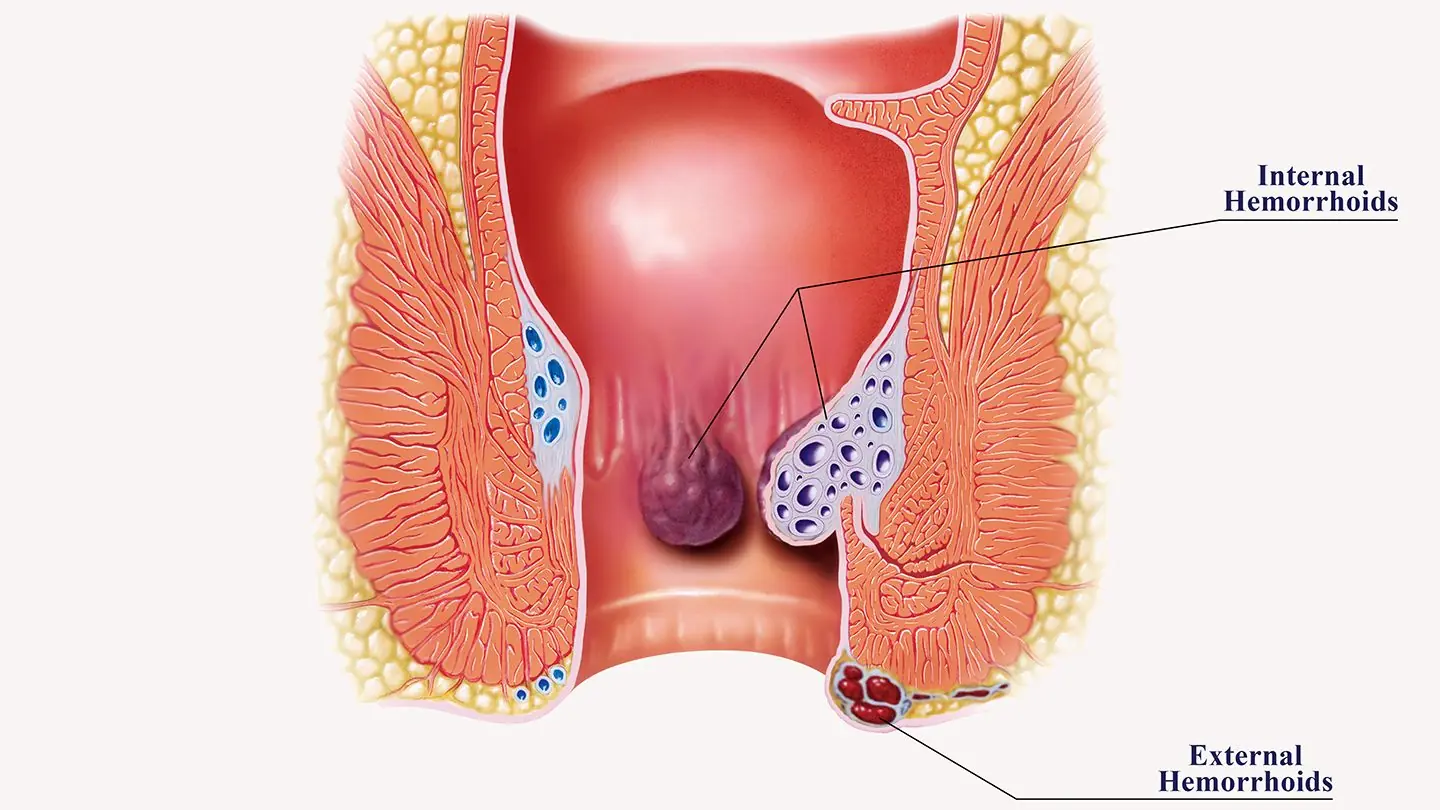
Hemorrhoids: Fast, Effective, Science-Backed Ways to Find Relief
Ovarian Cancer: 8 Early Signs You Need to Know

It’s Not Just Tooth Decay: 2 Common Signs in Your Mouth That Are SOS Signals From Your Body — Don’t Ignore Them

3 Early Signs of Lung Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore — It Could Become Life-Threatening
Is Cancer Hereditary? Useful Tips to Prevent Cancer from Developing
Health Experts Suggest 7 Ways to Detox Your Liver and Cleanse Your Body Daily
The Back of Your Hand Reveals Longevity Secrets: 4 Signs Everyone Should Check

13cm of Intestine Fell Out After 2 Hours on the Phone in the Toilet: 5 Dangers of Using Your Phone in the Bathroom

Don't Drink Water Right After Waking Up — Doctors Recommend Doing These 5 Things First

A 40-Year-Old Man Suffers a Stroke After Dinner: Doctor Points Out 3 Critical Mistakes
News Post

The Truth Behind ‘Durex’: What Its Name Actually Stands For Has Stunned Many

Your Eyes: Windows to Your Health – Uncovering Diabetes and Cancer Through Vision

Psychology: People Who Talk To Their Pets Like They Are Humans Display Certain Emotional Traits

It’s Official! Mexico City Has Banned Bullfighting, Ending A 500-Year-Old Tradition

Disconnect WiFi at Night Sleep With the Phone on Airplane Mode in Another Room

The Hidden Dangers of Cooking with Aluminum Foil: Health Implications and Safer Alternatives

Japan Has Created a New Plastic That Dissolves in the Sea Within Hours and Enhances Soil Health
Scientists Reveal Simple Blood Test Can Detect Cancer Years Before Symptoms Appear

Bill Gates Says Only 3 Jobs Are Safe From AI — Are You In One Of Them?

5 Early Warning Signs of Cancer in Children: Parents Must Know to Save Their Child

People Unvaccinated Against COVID Are 48 Percent More Likely To Get Into Traffic Accidents

If Your Body Has a Bad Odor in These 3 Areas, It Could Mean Poor Liver Detox and Declining Function – Get Checked Before It’s Too Late!

Warning: If You Notice This Symptom in Your Body, Go to the Hospital Immediately – It Could Be Late-Stage Nasopharyngeal Cancer

A ‘Zombie’ NASA Satellite Woke Up After 60 Years—And It Sent Out A Powerful Radio Pulse

Scientists Claim That If Humans Go Extinct, Octopuses Have The Best Chance Of Building The Next Civilization

23-Year-Old Ukranian Discovers Way To Make Paper From Fallen Leaves Without Cutting Down Trees

Rare ‘Doomsday’ Oarfish Washes Ashore In Tasmania, Igniting Superstitions Of Impending Disaster
Sore Throat Relief: How Ginger Can Soothe Your Throat Naturally
