Understanding Liver Damage: Stages, Causes, and How to Prevent It
🟢 New Medical Insight: How Liver Damage Really Progresses — And What Most People Don’t Know
Many individuals believe that liver disease occurs suddenly, as if it just "happens" without warning. However, the reality is far more complex and multifaceted. The liver, one of the most essential organs in our body, is unique in its ability to regenerate itself. Yet, this regenerative capacity is only effective if early damage is identified and reversed in a timely manner. Without early intervention, the liver's healing capabilities become overwhelmed, leading to long-term damage that can have irreversible consequences.
In this article, we will explore the actual stages of liver damage, step by step, highlighting key points that most people don't know about how liver disease progresses and how it can be prevented or even reversed.
1️⃣ Healthy Liver
In a healthy state, the liver is a powerhouse of metabolic functions. It filters blood, removes toxins, stores nutrients, produces bile, and even helps in the regulation of cholesterol levels. The liver is a highly resilient organ, capable of repairing itself after mild damage, which is why it can handle everyday stresses like alcohol consumption and exposure to certain medications. It works tirelessly, without much recognition, to maintain balance within the body.
2️⃣ Fatty Liver (Reversible)
The first stage of liver damage involves the accumulation of fat inside liver cells. This stage is extremely common and is primarily caused by lifestyle factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, rapid weight gain, poor dietary choices (especially diets high in sugar and fats), obesity, and conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol. Fatty liver, known as steatosis, is not necessarily a permanent condition and can be reversible with the right changes.
The good news is that fatty liver can often be reversed within weeks or months by making adjustments to one's lifestyle, such as adopting a balanced diet, reducing alcohol intake, losing weight, and increasing physical activity. Early intervention at this stage can prevent further damage and set the liver back on the path to health.
3️⃣ Inflammation (Steatohepatitis)
If the buildup of fat inside the liver is not addressed, the next stage is inflammation, referred to as steatohepatitis. At this point, the liver cells begin to suffer injury, which leads to swelling and further stress on the organ. The liver becomes irritated, and this chronic inflammation can cause permanent damage to liver tissue.
This stage is the critical turning point in liver disease progression. If steatohepatitis goes unnoticed or untreated, it can lead to the more serious stages of liver damage. Unfortunately, many people do not recognize the symptoms of inflammation until it has already caused significant harm.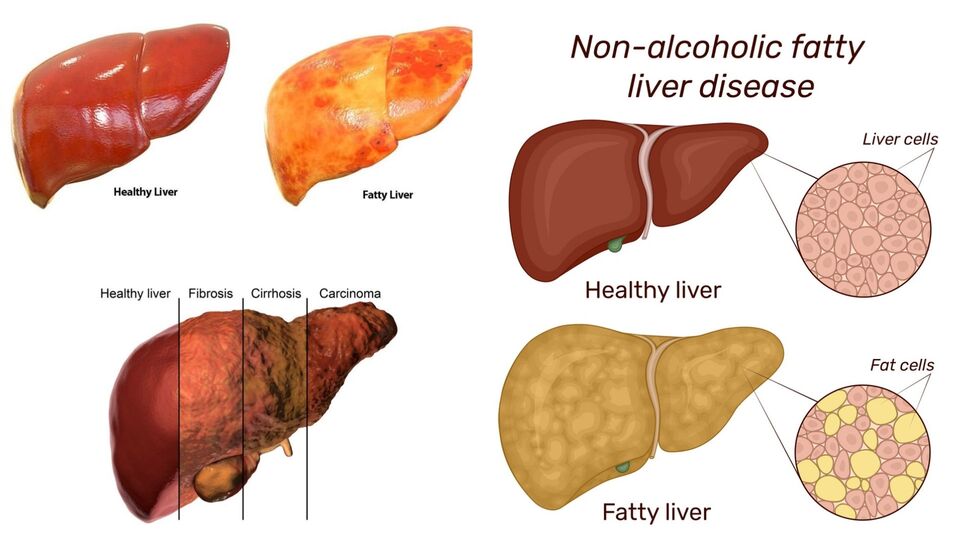
4️⃣ Fibrosis (Scar Tissue)
The liver, attempting to repair itself, produces scar tissue as a result of the chronic injury. This stage is known as fibrosis, where the liver's natural healing process leads to the formation of fibrous scar tissue. Though this stage still offers some opportunity for recovery, it requires medical intervention. With early diagnosis and treatment, fibrosis can be reversed, but if the underlying causes (such as alcohol abuse or obesity) continue unchecked, the fibrosis will progress, and the scar tissue will spread.
At this stage, lifestyle modifications and treatment are critical to halt the disease's progression. The longer fibrosis goes untreated, the greater the risk that the liver will reach a stage of permanent damage.
5️⃣ Cirrhosis (Permanent Damage)
Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of liver disease, characterized by extensive scarring and the loss of normal liver function. The liver becomes stiff and nodular, significantly impairing blood flow and limiting its ability to function properly. As a result, toxins begin to accumulate in the bloodstream, leading to severe complications, including liver failure. Cirrhosis is generally irreversible, and once the liver has reached this stage, the damage is often permanent.
Patients with cirrhosis are at risk for various complications, such as internal bleeding, infections, and liver failure. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary, although not all patients qualify for a transplant due to age, general health, or the underlying causes of their liver disease.
6️⃣ Liver Cancer (Possible Complication)
While not everyone with liver disease will develop liver cancer, the long-term effects of chronic inflammation and cirrhosis significantly increase the risk. The continuous stress on the liver cells over years can trigger abnormal cell growth, leading to liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma. This is one of the most severe consequences of untreated liver disease, and its development underscores the importance of early detection and intervention.
Regular monitoring and early diagnostic imaging are essential in identifying liver cancer before it becomes advanced and difficult to treat. For patients with cirrhosis or chronic liver inflammation, routine screenings for liver cancer are crucial.
⚠️ The Biggest Lesson?
The most important lesson from understanding liver damage is that most liver diseases are preventable — and, in many cases, reversible if caught early. Healthy lifestyle habits, including reducing alcohol intake, staying active, managing body weight, and undergoing routine liver health screenings, can help prevent or mitigate liver damage.
The liver is an incredibly resilient organ that works around the clock to keep us healthy, but it requires our care and attention to continue functioning optimally. Early intervention is the key to ensuring that the liver’s natural healing process can do its job and prevent further damage. Take care of your liver before it’s too late.
Sources:
-
American Liver Foundation – Understanding liver disease and its stages: www.liverfoundation.org
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – Liver diseases and fatty liver: www.niddk.nih.gov
-
Mayo Clinic – Cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer prevention: www.mayoclinic.org
-
World Health Organization (WHO) – Hepatitis and liver disease facts: www.who.int
News in the same category


Scientific Breakthroughs in Women's Health: How Research is Finally Addressing Gender Gaps

Monkeys, Money, and Unexpected Behavior: Insights from a 2005 Yale Study on Capuchin Monkeys and Economic Decision-Making

Bamboo and Hemp: Sustainable Solutions for a Greener, Plastic-Free Future

The Myth of “Safe” Smoking Debunked: How Minimal Tobacco Use Still Damages the Body

Boost Your Memory Naturally: How Rosemary's Scent Enhances Cognitive Function by 75%

The Regal Cat on the Beer Box: A Quiet Reminder of the Power of Stillness and Simplicity

Johan Eliasch's Impact on Amazon Conservation: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Empowering Indigenous Communities

The Science Behind Cats’ Calming Influence on Stress and Heart Health

12 Phrases That Reveal Someone Is Struggling More Than They Want To Admit

For the first time in 40 years, Panama’s Ocean lifeline has vanished

The Meaning Behind the WC Toilet Sign

Why Zohran Mamdani may not be sworn in as New York's 111th

'Living Nostradamus' makes truly terrifying prediction for 2026 - here's what he said

Cosmic Double Feature Tonight: Taurid Fireball Meteor Shower & Strong Solar Storm

How Sugar Affects Mood and Mental Health: What Recent Research Reveals

Mark Your Calendars: The Final Supermoon of 2025 is Coming on December 4!

California Reaches New Economic Heights, Becomes 4th-Largest Economy in the World
News Post

Kaaba’s Radiant Glow Seen from Space: A Celestial Spotlight on Islam’s Holiest Site

Scientific Breakthroughs in Women's Health: How Research is Finally Addressing Gender Gaps

Monkeys, Money, and Unexpected Behavior: Insights from a 2005 Yale Study on Capuchin Monkeys and Economic Decision-Making

How Europe's Skin Pigmentation Evolved: Dark to Light Over Millennia

Bamboo and Hemp: Sustainable Solutions for a Greener, Plastic-Free Future

People with heart problems should avoid these 4 things to reduce stimulation to the heart
12 Bizarre Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency You Need to Know
Natural Remedies and Prevention Strategies for Bunions: What Really Works
Natural Scar Remedies: How Scars Form and the Most Effective Evidence-Based Treatments to Help Them Fade
Eight Digestive Red Flags You Should Never Ignore: Causes, Risks, and When to Seek Medical Care

How Microscopic Glass Flaws Can Lead to Oven Door Breakage—and How to Prevent It
A Complete Guide to Bulging Veins: Causes, Complications, and Care

The Myth of “Safe” Smoking Debunked: How Minimal Tobacco Use Still Damages the Body

Boost Your Memory Naturally: How Rosemary's Scent Enhances Cognitive Function by 75%

The Regal Cat on the Beer Box: A Quiet Reminder of the Power of Stillness and Simplicity

Johan Eliasch's Impact on Amazon Conservation: A Commitment to Sustainable Practices and Empowering Indigenous Communities
Woman reveals 5 colon cancer symptoms that shouldn’t be ignored

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...