What Is an ESR Test? Understanding the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and Its Role in Detecting Inflammation
What Is an ESR Test? Understanding the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and Its Role in Detecting Inflammation

The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test is a common blood test that measures how quickly red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle at the bottom of a test tube over a specified period—usually one hour. While red blood cells normally settle slowly, the presence of inflammation causes them to clump together and settle more rapidly. This makes the ESR test a useful tool in detecting inflammatory activity in the body.
Why Is the ESR Test Done?
Healthcare providers often order an ESR test when patients show signs or symptoms that suggest inflammation. These can include:
-
Persistent headaches
-
Joint pain or stiffness
-
Fever of unknown origin
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
General signs of chronic illness
Although the ESR test doesn’t pinpoint the exact cause of inflammation, it helps doctors determine whether further testing is needed for conditions such as autoimmune disorders, infections, or blood diseases.
How Is the ESR Test Performed?
The ESR test is simple and minimally invasive:
-
A healthcare professional draws a small amount of blood from a vein in your arm.
-
The blood sample is placed in a tall, thin test tube.
-
The rate at which the red blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/hr).
What Are Normal ESR Levels?
Normal ESR values can vary depending on age, sex, and individual health. General reference ranges include:
-
Men under 50: less than 15 mm/hr
-
Women under 50: less than 20 mm/hr
-
Older adults: slightly higher values may be considered normal
Higher ESR levels may indicate:
-
Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
-
Chronic infections
-
Kidney disease
-
Anemia
-
Inflammatory heart conditions
Extremely high ESR readings can signal more severe conditions such as multiple myeloma or giant cell arteritis.
What Does a High ESR Mean?
A high ESR level is not a diagnosis on its own—it simply signals that inflammation is present in the body. Your doctor may recommend additional tests such as C-reactive protein (CRP), complete blood count (CBC), or imaging scans to identify the underlying cause.
Conclusion: Should You Be Concerned About Your ESR Level?
If your doctor orders an ESR test, it’s typically part of a larger diagnostic process. While a high ESR can point to potential health issues, it must be interpreted in the context of your overall symptoms and medical history.
If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms or have concerns about chronic inflammation, consult your healthcare provider. Early detection is key to managing conditions that affect your long-term health.
News in the same category

Sudden Sharp Chest Pain? The Mystery May Finally Be Solved

8 Warning Signs Your Oxygen Levels May Be Too Low — And How to Improve Them Naturally

Man Loses 400 Pounds Naturally and Raises Funds to Remove Excess Skin
47-Year-Old Man Dies of Liver Cancer: ‘2 Pains and 2 Itches’ Could Be Warning Signs of Liver Disease

Losing 93 Kilograms by Eating Only Meat and Eggs for Half a Year — Even the Doctor Was Shocked
How Dangerous Are Brain Tumors? If You Have These Symptoms, Get Checked Before It's Too Late

Dangers of 36-hour fasting revealed in shocking simulation
2 Types of Fruits That Cancer Cells “Love” – What You Need to Know
7 Warning Signs of Cancer: Don’t Ignore the SOS Signals Your Body Is Sending You!
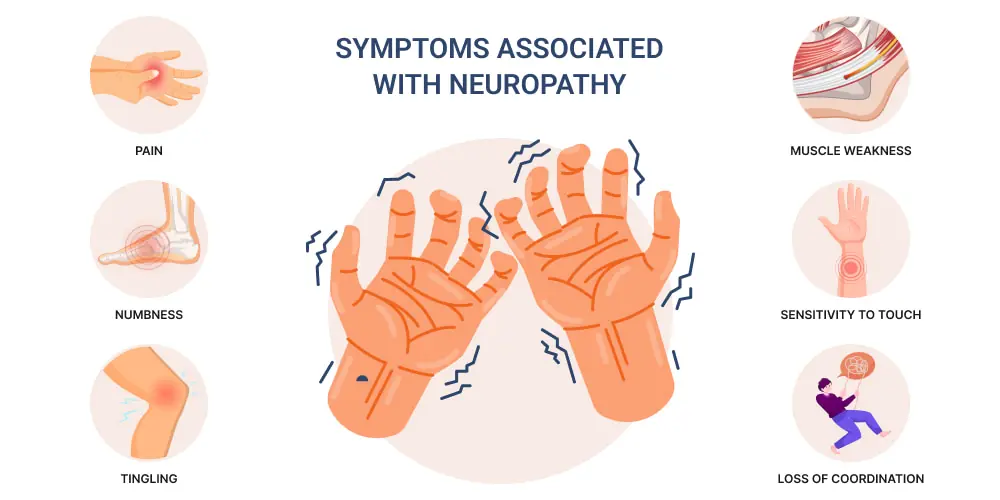
Peripheral Neuropathy in Hands: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
‘Ghost Boy’ Martin Pistorius Regains Awareness After 12 Years—Reveals He Was Conscious All Along

Hospice chef reveals the one comfort food most people ask for before they die

Parents Who Feared COVID Allegedly Confined Children at Home for Years

Common Symptoms of the New Covid-19 Variant
The Power of Gyan Mudra: Benefits and How to Practice It
How Can You Tell If Someone Has a Blood Clot? Doctor Says People With Blood Clots Often Show 4 Symptoms During Sleep
Shocking Discovery: 95 Gallstones Removed From a 40-Year-Old Woman – Doctors Urge “Stop This Eating and Sleeping Habit Immediately”
News Post

How to help naturally relieve gout and joint pain

Sudden Sharp Chest Pain? The Mystery May Finally Be Solved

8 Warning Signs Your Oxygen Levels May Be Too Low — And How to Improve Them Naturally

Man Loses 400 Pounds Naturally and Raises Funds to Remove Excess Skin

47-Year-Old Man Dies of Liver Cancer: ‘2 Pains and 2 Itches’ Could Be Warning Signs of Liver Disease

Losing 93 Kilograms by Eating Only Meat and Eggs for Half a Year — Even the Doctor Was Shocked

How Dangerous Are Brain Tumors? If You Have These Symptoms, Get Checked Before It's Too Late

Man Spends Life Savings On Abandoned Ghost Town Once Worth $500 Million
Detox Naturally with Tangerine, Walnuts, and Ginger: A Gentle Reset for Energy, Digestion & Vitality

🌿 10 Amazing Health Benefits of Okra

Clove Benefits: The Tiny Spice with Powerful Healing Properties You Need to Know

Clear Mucus from Your Lungs in Just 3 Days and Support Your Thyroid with Just One Orange – See the Recipe!

My Stepdaughter Was Locked up in a Closet During My Wedding Ceremony – We Were Shocked to Discover Who Did That to Her and Why

My Parents Chose My Sister Over My Wedding — So My Best Man Put Them on Blast

Flight Attendant Woke Me Up & Told Me to Check My Husband's Bag While He Was Away — I Never Expected What I Found

My Husband Brought an Xbox to the Delivery Room and Invited His Friend Because He 'Didn't Want to Be Bored While I Was in Labor'

I Found Tickets in My Husband's Old Jacket and Filed for Divorce the Next Day

Scientists Baffled By Perfect Sphere Emitting Radio Signals From Deep Space
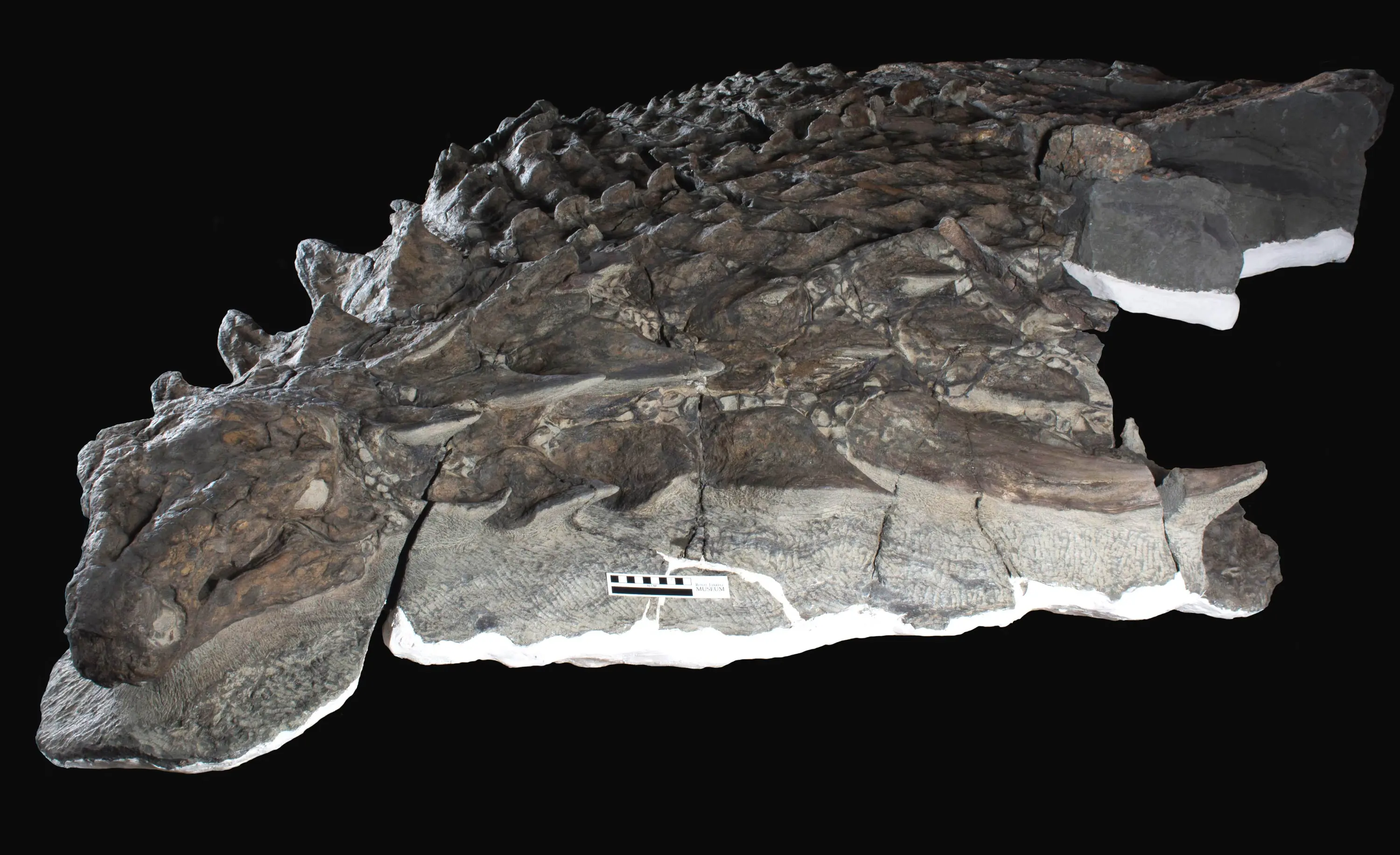

Meet Borealopelta markmitchelli: The Best-Preserved Dinosaur Fossil Ever Discovered
