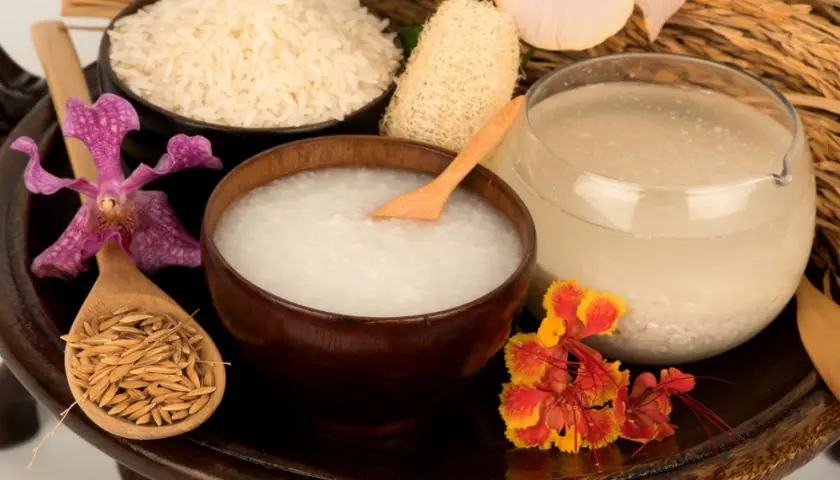

Why Your Legs Cramp at Night (And How to Fix It)
Why Your Legs Cramp at Night (And How to Fix It)
Waking up to a sudden, painful leg cramp can be a jarring and frustrating experience. These involuntary muscle contractions often strike in the middle of the night, disrupting your sleep and leaving your muscles sore.
Understanding why these cramps happen is the first step toward preventing them. This article will explore the most common causes of nocturnal leg cramps and offer simple, effective solutions to help you find relief.
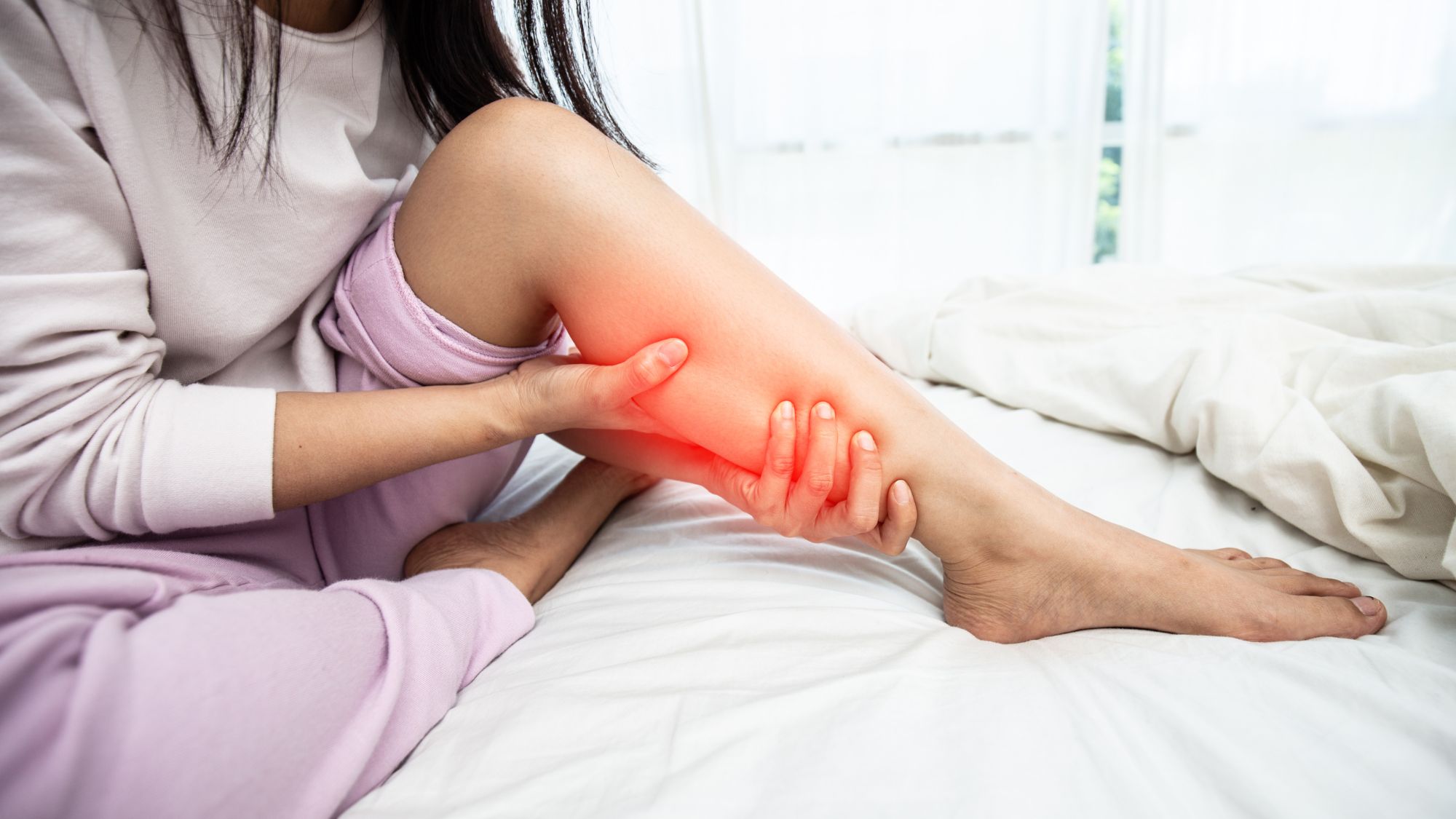
Common Causes of Leg Cramps
1. Magnesium and Calcium Deficiency
Magnesium and calcium are two minerals essential for proper muscle function. Magnesium helps your muscles relax, while calcium signals them to contract. An imbalance in either mineral can lead to muscle spasms and cramps.
-
Magnesium: Many people don't get enough magnesium from their diet. This mineral is used in hundreds of bodily processes, including muscle relaxation. A deficiency can manifest as muscle cramps, fatigue, or even anxiety.
-
Calcium: A lack of calcium can also cause cramps, especially if you have a Vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is crucial for helping your body absorb calcium from the foods you eat.
You can address these deficiencies by incorporating foods rich in these minerals into your diet. Excellent sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, and leafy greens. For Vitamin D, aim for sun exposure and foods like mushrooms and fatty fish.
2. Dehydration
Even mild dehydration can lead to muscle cramps.
3. Poor Circulation
Insufficient blood flow to the legs, particularly at night when you're sedentary, can cause muscles to cramp. When blood circulation is poor, the muscles don't receive enough oxygen and nutrients to function correctly, making them susceptible to spasms.
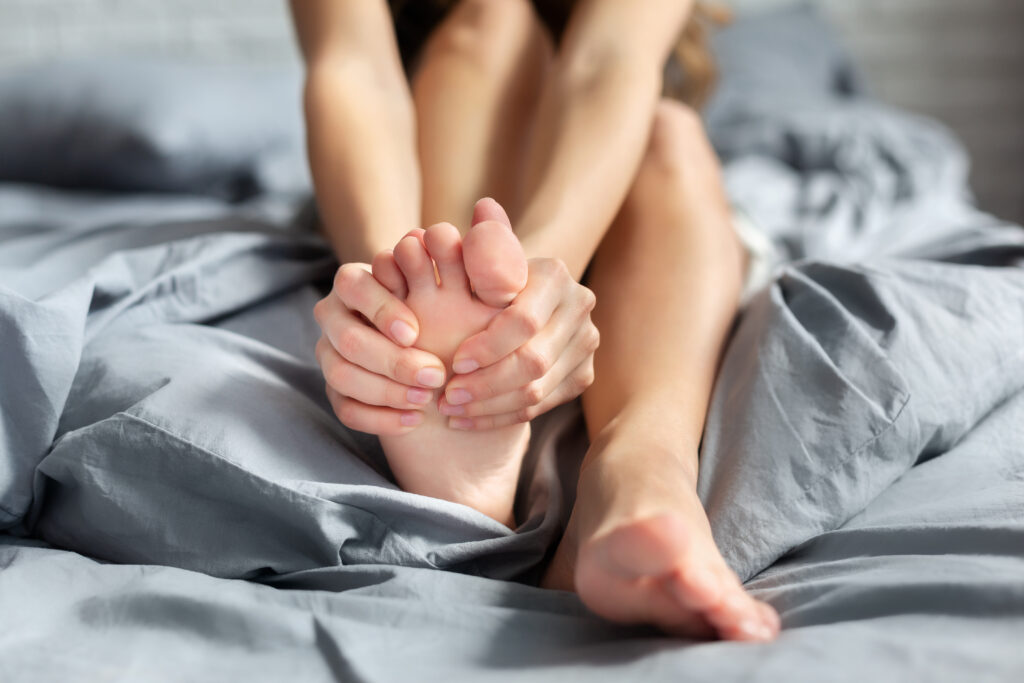

How to Prevent Leg Cramps
Beyond addressing nutritional deficiencies, several simple habits can help prevent nightly leg cramps.
1. Stretch Regularly
Stretching helps improve blood flow and can lengthen muscles, making them less likely to cramp.
-
Calf Stretch: Stand facing a wall, placing your palms on it.
Step one foot forward and keep the other one straight behind you, with your heel on the floor. Lean into the wall, feeling a stretch in your calf. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs. -
Toe Stretch: While sitting, point your toes up toward your knees to stretch the calf muscles.
2. Stay Hydrated
Make a conscious effort to drink plenty of water throughout the day. A general guideline is to drink at least a couple of liters of water daily, more if you are physically active. Consider adding a pinch of sea salt to your water to replenish electrolytes, especially if you've been sweating.
3. Massage Your Legs
Massaging your leg muscles before bed can help stimulate blood flow and release tension.
4. Explore Alternative Therapies
Some alternative therapies, like acupuncture, can be effective in promoting blood circulation and energy flow to the legs. A few sessions with a qualified practitioner may help eliminate cramps for good by addressing underlying imbalances.
A Take-Home Message
Your body often sends signals when something is out of balance, and nightly leg cramps can be one of them. While they can be tied to physical factors like dehydration or nutrient deficiencies, they can also be a sign of stress or being overworked. Taking time to unwind before bed with deep breathing, gentle stretching, or a warm bath can help your body shift into the rest-and-recovery mode it needs for a good night's sleep.
News in the same category


Beware: U.S. Salmon May Be Crawling with Japanese Tapeworm, Say Scientists
Colon Cleansing: How to Naturally Flush Your Colon at Home (Science-Based)

3 Morning Symptoms That May Signal the Onset of Canc3r
"8 abnormal signs warning of c3rvical canc3r that women need to recognize early"

If you don’t correct these 5 harmful eating and drinking habits right away, sooner or later your esophagus will also be “ravaged” by cancer cells.
If Your Feet Swell It Is a Clear Sign

Nose Picking What This Taboo Habit Really Reveals About Us

Everyday Habits That Can Cause a This Issue To Your Hands
Why Liver Cancer Is Often Detected Late – Important Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
If You See Someone with Prominent Green Veins, Make Sure to Tell Them This – It Could Save Their Life
How to Safely Remove Super Glue (502) from Your Skin Without Tearing It
3 Unusual Signs in the Neck That Could Be Symptoms of Cancer – Don’t Ignore Them!

Consciousness Is Not Confined to the Brain, But Is Connected To The Whole Universe, Scientists Say

Study Finds People With ADHD Listen to Music Differently—Here’s How

Can I Get My Metabolism Back After Stopping Lexapro and Prozac?

8 Foods High in Inulin to Eat for Better Gut Health

Proven Health Benefits and Uses of Thyme and Thyme Tea

Proven Health Benefits of Walnuts, How Many to Eat, and More (Science Based)
News Post

How to Use Rice Water for Gorgeous Hair and Skin (Detailed Instructions)

Beware: U.S. Salmon May Be Crawling with Japanese Tapeworm, Say Scientists

The Benefits of Chicken Feet Stewed with Black Beans – As Powerful as Ginseng
There are many cuts of beef, but only these 3 are considered the true “essence” – both chefs and butchers wholeheartedly agree!

Colon Cleansing: How to Naturally Flush Your Colon at Home (Science-Based)

Put this into a lemon and place it in the corner of your house – mosquitoes will stay away for good

3 Morning Symptoms That May Signal the Onset of Canc3r

"8 abnormal signs warning of c3rvical canc3r that women need to recognize early"

If you don’t correct these 5 harmful eating and drinking habits right away, sooner or later your esophagus will also be “ravaged” by cancer cells.

Is Your Air Conditioner Outdoor Unit Making Loud Grinding Noises? Use This Simple Trick to Make It Run Quietly Without Calling a Technician!

Urgent warning issued to travelers as China takes ‘covid measures’ after reporting 7,000 cases of Chikungunya virus

3 Effective Ways to Prevent Snakes from Entering Your Home Everyone Should Know to Protect Their Family

Signs to look out for amid Gordon Ramsay's health warning after undergoing cancer surgery

How to Handle Common Refrigerator Problems and a Surprising Lesson from American Toilet Habits

If Your Feet Swell It Is a Clear Sign

Why Doors in Public Bathrooms Don’t Reach the Floor

Nose Picking What This Taboo Habit Really Reveals About Us

Everyday Habits That Can Cause a This Issue To Your Hands
