10+ Foods That Naturally Lower Blood Sugar Levels
11 Best Foods to Naturally Lower Blood Sugar
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and a key factor in preventing conditions like type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and heart disease. While genetics, stress, physical activity, and body weight all play important roles, diet remains one of the most effective tools for blood sugar control. By choosing nutrient-rich foods that support insulin sensitivity and slow digestion, you can help your body maintain stable energy levels throughout the day.
Here are more than ten powerful foods scientifically linked to better blood sugar management.
1. Pumpkin
Pumpkins are more than a festive decoration—they’re packed with nutrients that support healthy blood sugar. Rich in antioxidants, polysaccharides, and fiber, pumpkins have long been used in traditional medicine in countries like Iran and Mexico to manage diabetes. The fiber slows digestion, while the plant compounds help regulate sugar absorption. Pumpkin seeds are also loaded with healthy fats and plant-based protein, making them an excellent addition to a balanced diet.
2. Seafood
Fish and shellfish are excellent sources of lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Protein is especially important for slowing digestion, preventing rapid blood sugar spikes after meals, and promoting satiety. Studies show that regular consumption of fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce post-meal blood sugar levels. Seafood also supports heart health, making it a double win for those managing metabolic health.
3. Broccoli
Broccoli is often called a “superfood” for good reason. It contains sulforaphane, a plant compound released when the vegetable is chopped or chewed. Research has shown that sulforaphane improves insulin sensitivity and reduces oxidative stress. Broccoli sprouts, in particular, are extremely rich in glucosinolates, which enhance the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Adding broccoli to your diet not only helps balance sugar but also provides protection against inflammation and cell damage.
4. Beans and Lentils
Legumes such as beans, chickpeas, and lentils are packed with fiber, resistant starch, magnesium, and plant-based protein. These nutrients slow digestion and improve the body’s ability to manage blood sugar after meals. In fact, studies have found that people who include beans or lentils in their meals experience significantly lower post-meal blood sugar compared to those who eat refined grains. They are also budget-friendly and versatile, making them an easy staple for everyday meals.
5. Chia Seeds
Tiny but mighty, chia seeds are full of fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant-based protein. Research suggests that chia seeds improve insulin sensitivity and stabilize blood sugar. In one study, participants who consumed ground chia seeds alongside a sugar solution saw a 39% reduction in blood sugar levels compared to those who consumed sugar alone. Their gel-like texture when soaked also slows digestion, making them a great addition to smoothies, puddings, or oatmeal.
6. Okra
Okra, often used in traditional remedies, is high in antioxidants, polysaccharides, and flavonoids that support healthy blood sugar regulation. Its seeds, in particular, show promising anti-diabetic properties. While most studies have been conducted in animals, early findings suggest okra may help lower sugar absorption and improve insulin activity. More human research is needed, but it’s a nutritious vegetable worth including in stews, soups, or stir-fries.
7. Avocados
Creamy and nutrient-dense, avocados are a rich source of healthy fats, fiber, potassium, and vitamins. Multiple studies suggest that avocados can lower blood sugar levels and protect against metabolic syndrome, a condition marked by high blood sugar, cholesterol imbalance, and elevated blood pressure. Their high fiber and fat content also promote satiety, helping prevent overeating and sugar cravings.
8. Berries
Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with antioxidants, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Eating berries has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels after meals. The compounds in berries may also help reduce inflammation, making them a smart snack or dessert alternative to sugary treats.
9. Eggs
Eggs are a versatile, high-protein food rich in vitamins B12, D, and minerals such as selenium and choline. Studies show that eating eggs regularly can improve fasting blood sugar and enhance insulin sensitivity. They also promote satiety, which helps control appetite and supports weight management—two crucial factors for stable blood sugar.
10. Oats
Oats are an excellent source of soluble fiber, especially beta-glucan, which slows digestion and prevents rapid blood sugar spikes. Eating oats for breakfast can help you feel fuller for longer while supporting heart health and weight control. Steel-cut or rolled oats are better choices than instant oats, which can contain added sugars and raise blood sugar more quickly.
11. Yogurt and Kefir
Fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir contain probiotics, protein, and beneficial compounds that can help regulate blood sugar. Research shows that kefir consumption reduces HbA1c (a key marker of long-term blood sugar control) and fasting blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. Yogurt has also been linked to a reduced risk of developing diabetes, particularly when consumed without added sugar.
Final Thoughts
Incorporating these foods into your daily meals can significantly improve blood sugar management and overall metabolic health. While no single food is a cure-all, combining them with regular physical activity, stress management, and healthy lifestyle habits can reduce the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
The key is consistency—building a diet that emphasizes fiber, protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants while limiting refined sugars and processed foods. Over time, these small but powerful dietary changes can lead to better blood sugar control, more stable energy, and long-term health benefits.
News in the same category


If your private parts smell fishy, it’s something you should be aware of
#1 Best Way to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally and Fast

Neurologists urge: stop this daily habit now—it’s linked to strokes!
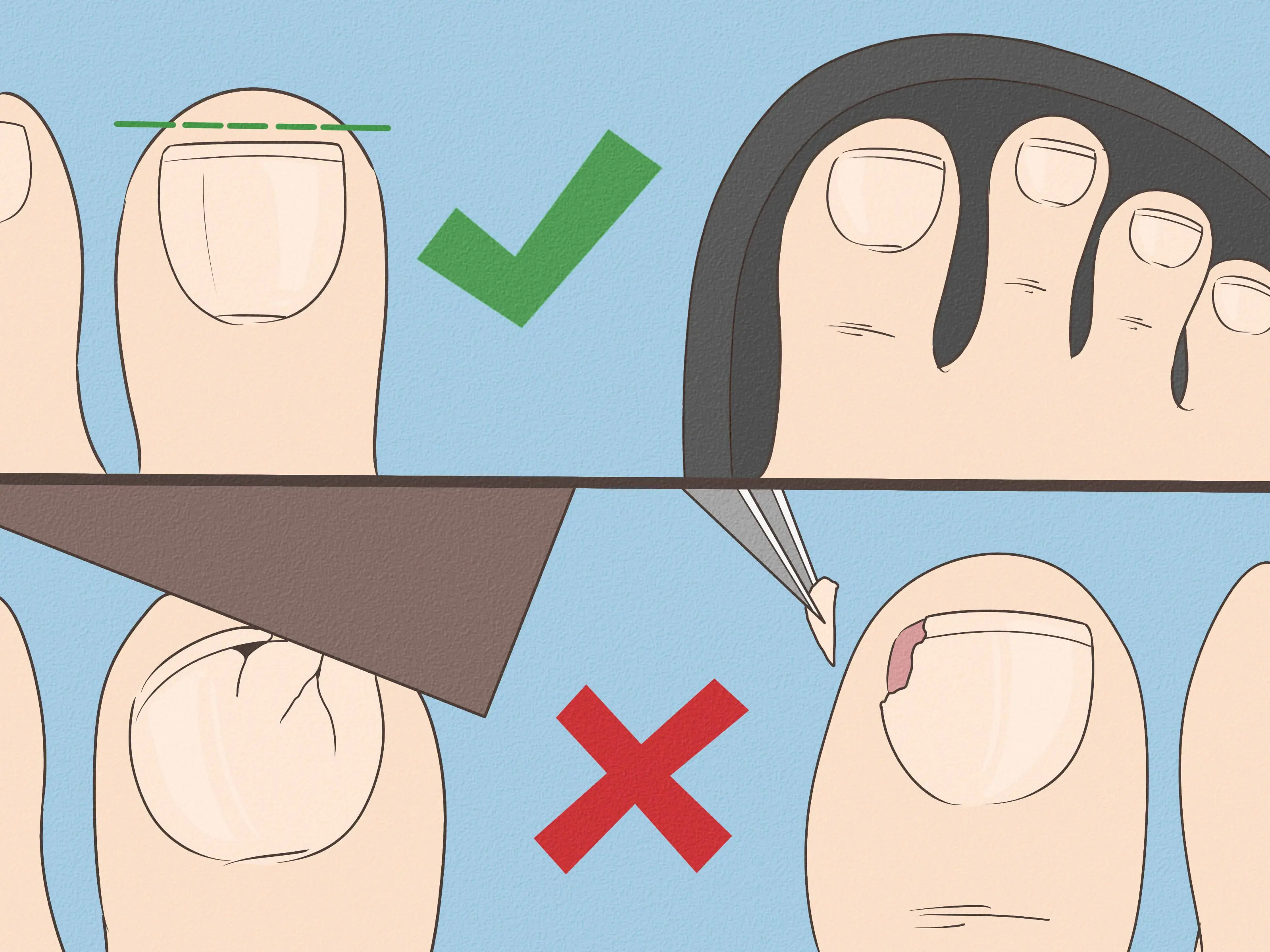
Natural Home Remedies for Ingrown Toenails That Bring Quick Relief
This Is What Happens to Your Body When You Start Eating Raw Garlic
What Those Red Spots on Your Skin Are Warning You About and How to Remove Them Naturally
Small Morning Habits That Many Overlook but Boost Blood Flow and Energy
Woman Urged to See Doctor After Spotting Concerning Line

Groups of People Who Need to Avoid Eating Bread
What those strange skin patterns might really mean

Should You Eat Rice for Breakfast

Preventing Stroke At Any Age: 3 “Don’ts” After Meals—And 4 “Don’ts” Before Bed
Why You Should Stop Using Petroleum Jelly On Your Skin (It’s a Byproduct of the Petroleum Manufacturing Process)
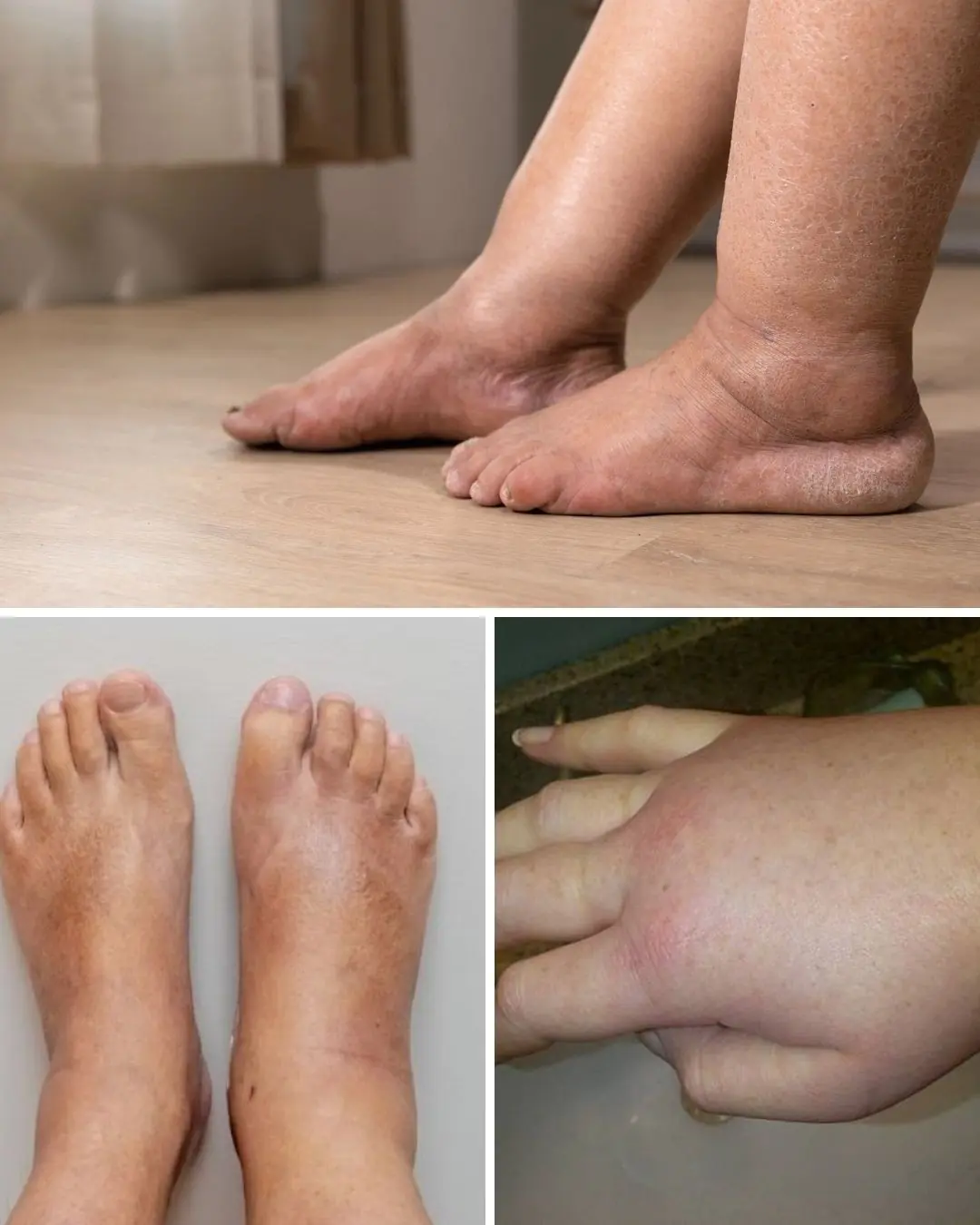
Foods that can ease swelling in hands and feet
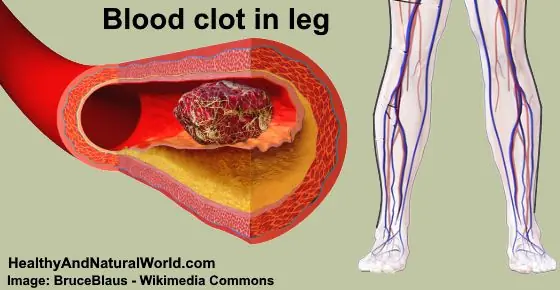
Blood Clot in Leg: Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore (Pictures Included)
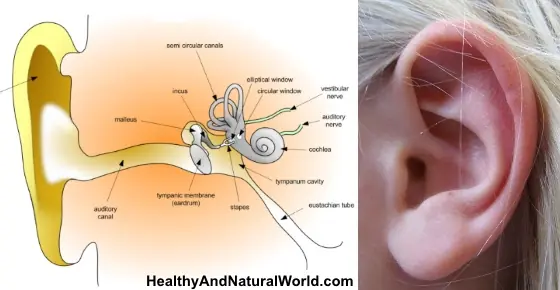
The Most Effective Ways to Naturally Get Rid of Clogged Ears

Most US Neurologists Who Prescribe MS Drugs Take Industry Money

Cognitive Benefit From Ginkgo biloba Monotherapy in MCI
News Post

🌿 Can Papaya Leaves Turn Gray Hair Black Naturally? Unlock Nature’s Secret to Vibrant Hair

Japanese airport has never lost luggage in over 30 years – This is why

The Ultimate DIY Clove Skincare Routine

A Company in Kenya Builds Houses From Recycled Shipping Containers – Solar-Powered and Ready in Days

5 Types of Drinks You Shouldn’t Store in a Thermos

Smart Tips for Boiling Eggs: Prevent Cracks, Easy to Peel, and How to Time Them Perfectly

🥕 3-Day Carrot-Based Detox: Cleanse Your Liver and Intestines Naturally

Coconut Oil for Hair Growth – Add this in your Hair Oil

What Terrible Things Happen When Women Lack Intimacy? A Painful Yet True Reality

Why You Should Never Place Your Bed Like This

Sink Trick You Should Always Do Before Vacation

Elon Musk Issues Serious Warning on Japan’s Population Decline

A Fruit Growing Abundantly in Gardens That Few People Eat Turns Out to Be an Autumn ‘Miracle’ Better Than Ginseng and Bird’s Nest

Why Should You Drop a Clove of Garlic into the Toilet Bowl at Night? Knowing Its Benefits, Every Household Wants to Try It

Revealed: How to Make Ceramic Tiles Sparkle at Home – Without Spending a Dime

If your private parts smell fishy, it’s something you should be aware of

Soak the vermicelli in a bowl of fish sauce, after 2 minutes you will know if the vermicelli is clean or contains borax.

The refrigerator seal has black mold, use this to wipe it, and it will be completely clean in just 5 minutes.
