5 Foods You Should Never Combine with Pumpkin
Pumpkin is a highly nutritious food, naturally rich in vitamin A, fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. These nutrients support healthy eyesight, digestion, immunity, and overall wellness. Despite its benefits, pumpkin may cause digestive discomfort for some people when paired with certain foods—especially those with sensitive stomachs or weaker digestive systems. Understanding these combinations can help you enjoy pumpkin safely and get the most out of its nutrients.
1. Shrimp
Possible Issue:
Pumpkin is considered a warming ingredient in certain traditional food systems, while shrimp is rich in protein, minerals, and can be harder to digest for some individuals. When eaten together, this pairing may increase the likelihood of bloating, gas, or loose stools, particularly among those with sensitive digestion.
Who should be cautious:
-
Individuals with chronic digestive discomfort
-
People prone to bloating, cold stomach sensation, or irritable digestion
Tip:
If you enjoy both foods, try eating them separately or pairing each with milder ingredients.
2. Vinegar
Possible Issue:
Vinegar is highly acidic. In traditional cooking wisdom, strong acids may reduce the stability of nutrients like vitamin A and antioxidants in pumpkin. This doesn’t make the combination harmful, but it may lessen pumpkin’s nutritional benefits.
Recommendation:
Avoid adding vinegar directly to pumpkin soups or stir-fries if your goal is to maximize vitamin retention. Instead, use herbs, spices, or lemon zest as alternative flavor enhancers.
3. Celery
Celery is naturally high in fiber, vitamins A and C, and plant compounds known to support hydration and digestion. However, when cooked with pumpkin, the combination may produce excess gas for some individuals due to the interaction of two high-fiber ingredients.
Possible Effects:
-
Bloating
-
Flatulence
-
Mild stomach discomfort
Tip:
Enjoy celery and pumpkin in separate dishes if you have a sensitive digestive system or are prone to gas.
4. Lamb
Possible Issue:
Both pumpkin and lamb are considered “warming” foods in traditional dietary frameworks. Eating them together may feel too heavy or overly heating for individuals with certain conditions.
Some people report:
-
Overheating sensations
-
Skin dullness or temporary pigmentation changes
-
Liver or gallbladder discomfort (especially in sensitive individuals)
Warning:
People with liver, gallbladder, or chronic inflammatory digestive issues should be cautious and monitor how their body responds to this combination.
Important Notes When Eating Pumpkin
1. Consider Your Body Type
Pumpkin has warming properties, which means people who already feel heat in their stomach, have jaundice, or experience internal “dampness” (in traditional medicine terms) may need to limit intake.
2. Avoid Pumpkin During Fevers or Infections
Because pumpkin is nutrient-dense and warming, some traditional systems advise avoiding it during fever, active infections, or heat-related symptoms, as it may intensify discomfort.
3. Be Careful When Taking Herbal or Traditional Medicines
Pumpkin may interfere with the absorption or effect of certain herbal remedies. If you’re taking traditional medicine, it’s wise to consult a practitioner before consuming pumpkin regularly.
4. Use Freshly Cut Pumpkin Quickly
Once pumpkin is cut, it spoils faster—especially around the core where moisture collects. Try to cook it within a day or two for best quality and safety.
5. Don’t Discard the Skin
Pumpkin skin is rich in carotene, fiber, and antioxidants. If it’s clean and thin-skinned, cook it with the flesh to increase the nutritional value of your dish.
6. Add a Little Oil When Cooking
Beta-carotene, which converts to vitamin A, is fat-soluble. Adding a small amount of healthy oil (such as olive oil or coconut oil) can help your body absorb more of this valuable nutrient.
Final Thoughts
Pumpkin is a wholesome, versatile ingredient that fits beautifully into soups, stews, baked dishes, and even desserts. Understanding how certain food pairings may affect digestion can help you enjoy it more comfortably. By being mindful of combinations and listening to your body, you can enjoy pumpkin’s flavor and nutrition while minimizing unwanted side effects.
News in the same category


The Right Way to Boil Chicken: This Method Keeps the Meat Firm, Juicy, and Delicious

No Need for Air Fresheners: Keep This in Your Bathroom to Eliminate Odors and Save Hundreds Every Year

Why You Should Keep a Small Bottle of Medicinal Oil in Your Bathroom: Special Benefits Everyone Should Know

4 Simple Ways to Remove the Bitter Taste from Bitter Melon: Stir-Fry for a Delicious and Nutritious Dish

One Person Washes the Dishes, the Whole Family Gets Sick? 4 Dishwashing Mistakes Everyone Should Stop Immediately
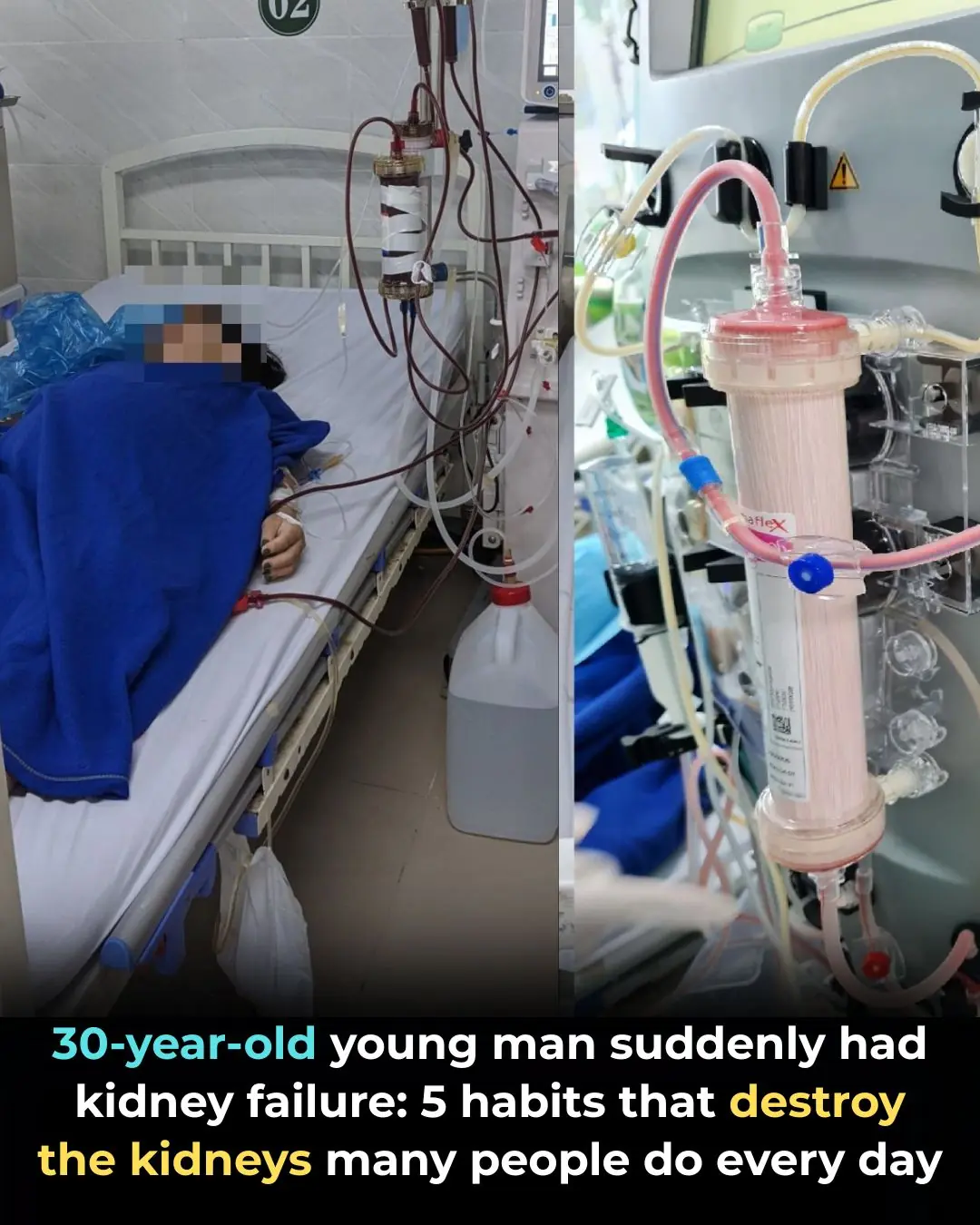
A 30-Year-Old Man Suddenly Developed Kidney Failure: 5 Daily Habits Destroying Your Kidneys Without You Realizing

Women Who Age Faster and Live Shorter Often Do These 4 Things at Night — How Many Apply to You?

Doctors Warn: 3 Common Beauty Habits That Many Don’t Realize May Increase Cancer Risks

The dirty fan needs to be disassembled, do this for just a few minutes to clean it, clean the dirty fan. over

4 Signs It’s Time to Replace Your Water Filter Cartridge Immediately

Burn a few garlic bulbs and keep them in the middle of the house. It has great benefits that every family wants to do

If You See a Hole in a Pen Cap, This Is What It Means

So clever

Clothes worn for a long time turn yellow, use this method to make them white again like new

How to remove fishy smell in the refrigerator with simple ingredients

It only takes 5 minutes to plant green onions in the core of toilet paper, saving you money all year round.

Whatever you fry, just add 1 spoon of this powder to the pan, no oil will splatter, the food will be golden brown and crispy.
News Post

When Wild Hearts Trust Us — The Unspoken Bond Between Humans, Lions, and Tigers.

The Lion Who Loved Back: Jupiter’s Final Goodbye.

Don’t Rush to Refrigerate Lemons: This Method Keeps Them Fresh and Juicy for a Whole Year

The Right Way to Boil Chicken: This Method Keeps the Meat Firm, Juicy, and Delicious

No Need for Air Fresheners: Keep This in Your Bathroom to Eliminate Odors and Save Hundreds Every Year

Why You Should Keep a Small Bottle of Medicinal Oil in Your Bathroom: Special Benefits Everyone Should Know

Six Prisoners, One Fallen Officer, and a Choice That Revealed Their True Hearts.

4 Simple Ways to Remove the Bitter Taste from Bitter Melon: Stir-Fry for a Delicious and Nutritious Dish

One Person Washes the Dishes, the Whole Family Gets Sick? 4 Dishwashing Mistakes Everyone Should Stop Immediately

A 30-Year-Old Man Suddenly Developed Kidney Failure: 5 Daily Habits Destroying Your Kidneys Without You Realizing

“The Cry That Saved Us”: The Night Two Fort Worth Officers Refused to Give Up.

Women Who Age Faster and Live Shorter Often Do These 4 Things at Night — How Many Apply to You?

A Prom Night 76 Years in the Making.

My Husband Left Me and the Kids at Home on Christmas Eve to Celebrate at His Office Party So We Decided to Pay Him a Visit

A 42-Year-Old Man Died of a Stroke Despite Not Smoking or Drinking — Doctors Shocked to Find the Real Daily “Killer” in His Diet

Doctors Warn: 3 Common Beauty Habits That Many Don’t Realize May Increase Cancer Risks

How to Remove Water Stains from Wood with Mayonnaise

I PAID FOR A STRANGER’S GROCERIES TWO YEARS AGO—AND TODAY, I GOT THIS IN THE MAIL
MY MOTHER-IN-LAW DESTROYED MY DAUGHTER’S GARDEN – I MADE HER PAY THE PRICE SHE NEVER EXPECTED
