5 Warning Signs of Psoriasis You Shouldn’t Ignore
Understanding Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Although it is not contagious, it can significantly impact a person's physical comfort, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. Recognizing the early symptoms, understanding the underlying causes, and seeking proper treatment can make a huge difference in managing the disease effectively.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune response that mistakenly targets healthy skin cells. This leads to accelerated skin cell production, resulting in the buildup of rough, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. The condition can appear at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in adults. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding or going into remission.
Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis manifests in several forms, each with unique symptoms and affected areas. Understanding the type of psoriasis you have is crucial for finding the most effective treatment:
-
Plaque Psoriasis: The most prevalent form, marked by raised, inflamed red patches topped with silvery-white scales. These plaques typically appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
-
Guttate Psoriasis: Characterized by small, drop-like red spots, this form often emerges after bacterial infections like strep throat. It is more common in children and young adults.
-
Pustular Psoriasis: This type appears as painful, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin. It can be localized to certain areas or spread across the body in severe cases.
-
Inverse Psoriasis: Found in skin folds—such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the genitals—this type presents as smooth, shiny, and red lesions without the typical scaling.
-
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare but serious form that causes widespread redness, severe itching or burning, and skin peeling. It can disrupt body temperature regulation and requires immediate medical attention.
What Causes Psoriasis?
The exact cause of psoriasis isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to be a combination of genetics and environmental triggers. Immune system dysfunction causes the skin cells to regenerate much faster than normal, leading to buildup and inflammation. Common triggers include:
-
Infections (e.g., streptococcal throat infections)
-
Cold weather
-
Stress or emotional trauma
-
Smoking
-
Excessive alcohol use
-
Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarial drugs
-
Injury to the skin, like cuts, burns, or sunburn (known as the Koebner phenomenon)
Having a family history of psoriasis increases your risk, and the condition can also be associated with psoriatic arthritis, which affects the joints.
Diagnosing Psoriasis
A dermatologist typically makes a diagnosis through a physical examination of the skin, nails, and scalp. In uncertain cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions such as eczema or fungal infections. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and pave the way for a tailored treatment approach.
Treatment Options
Although there is no definitive cure for psoriasis, several treatment strategies can help manage flare-ups and improve skin appearance and comfort:
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids, salicylic acid, coal tar, or vitamin D analogs like calcipotriol can reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
-
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, particularly UVB, can reduce symptoms in moderate to severe cases. This treatment must be administered under medical supervision.
-
Systemic Medications: For more severe forms of psoriasis, doctors may prescribe oral or injectable medications that affect the whole body. These include biologics (like adalimumab or secukinumab), methotrexate, cyclosporine, and newer drugs that target specific immune pathways.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress, avoiding known triggers, maintaining a healthy diet, and keeping the skin moisturized can all help in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent skin issues such as red patches, flaking, itching, or unusual rashes that don’t go away with over-the-counter treatments, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to preventing complications like skin infections, social discomfort, or the progression to psoriatic arthritis.
Taking Control of Your Skin Health
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but knowledge and proactive care go a long way. By understanding your triggers and staying consistent with treatment, you can take charge of your condition. Don’t ignore the signs—seek professional medical guidance and build a skincare routine that works for you.
News in the same category
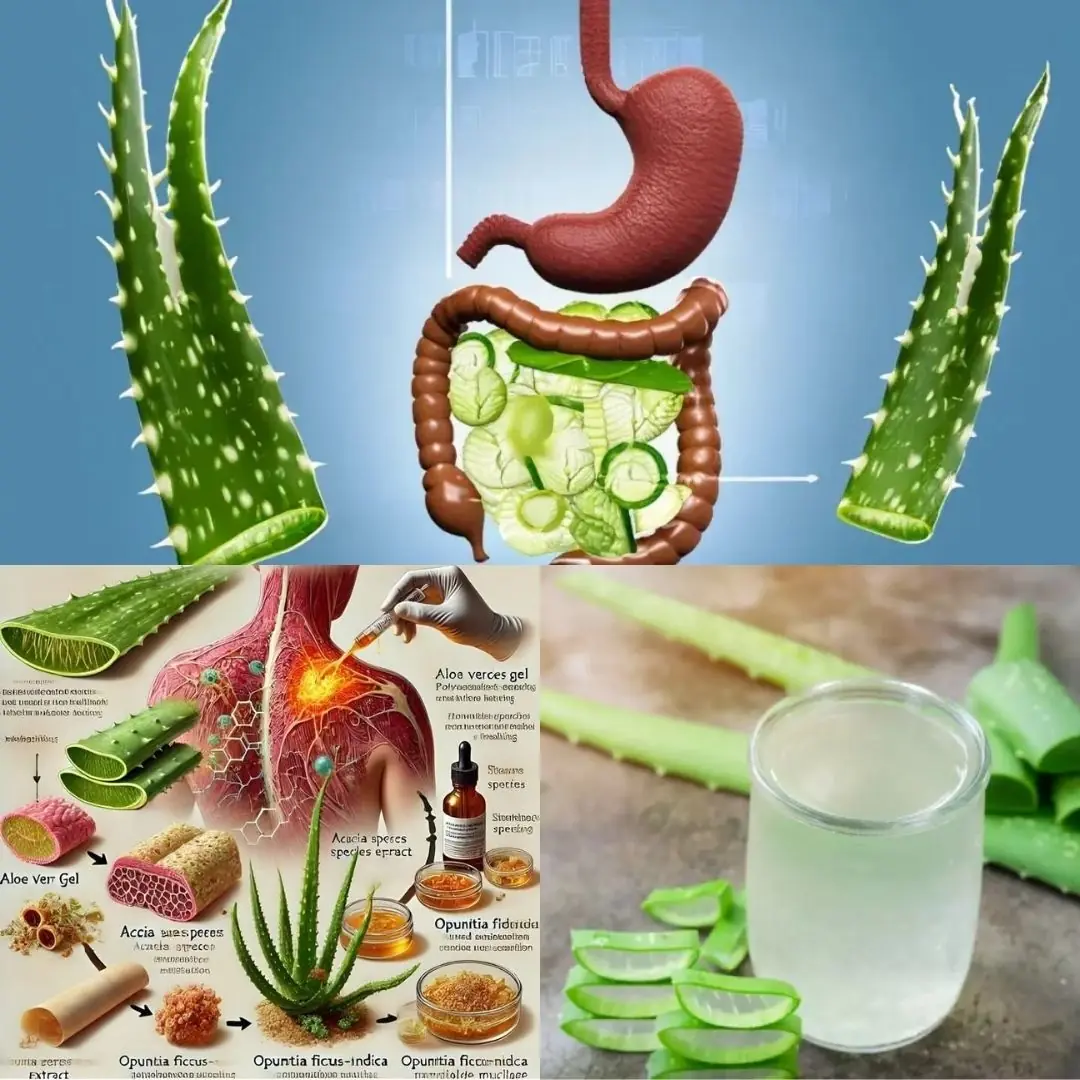


11 Reasons Why You Should Drink Aloe Vera Water Every Day

Shocking findings of new trial on Ozempic alternative pushes it closer to approval

Experts Warn People To Get Rid Of This Common Bedroom Item Over Fears It Might Harm Brain Health

The Side Effects of Ibuprofen You May Not Be Aware Of
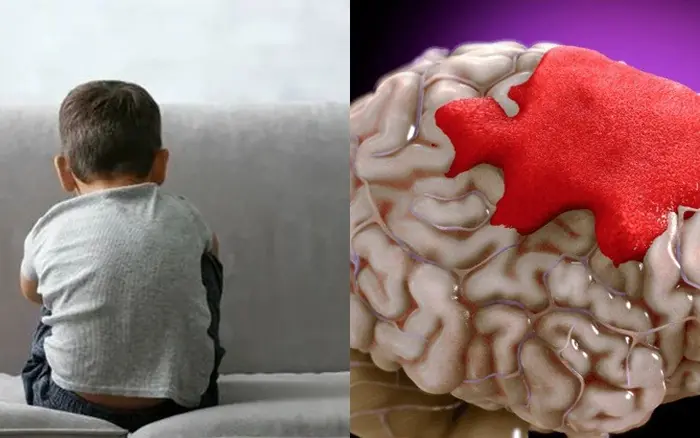

6-Year-Old Boy Suffers Stroke After Waking Up – Doctor Urges Parents to Know These 4 Warning Signs to Save Their Child
3 Eye Symptoms That Could Warn of a Stroke or Cancer – Don’t Ignore Them

17 Common Foods That May Trigger Kidney Stones – What to Avoid for Healthier Kidneys
12 Strange Signs in Your Feet That Could Be Warning You About Liver Problems
If these happen to you, it’s high time you see a doctor

Man who saw ‘proof’ that ‘death is not the end’ explains the seven levels of afterlife

Over 50 Individuals Die Within Hours Of Symptoms Of An Unknown Illness Alarming Doctors
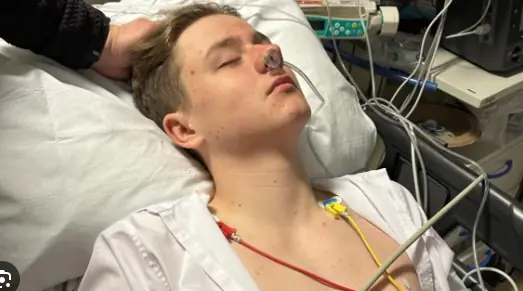
Warning sign of teen’s inoperable cancer that hit hours before diagnosis – now nothing can be done
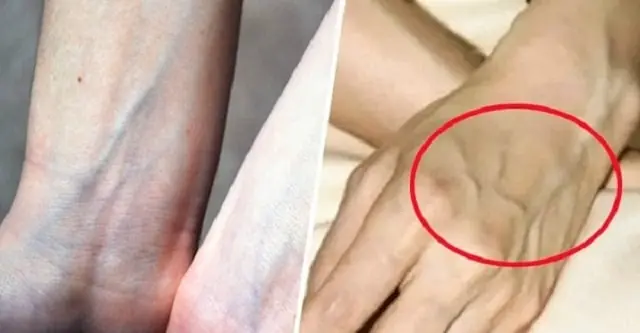
If You See Someone with 'Visible Blue Veins', You Must Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
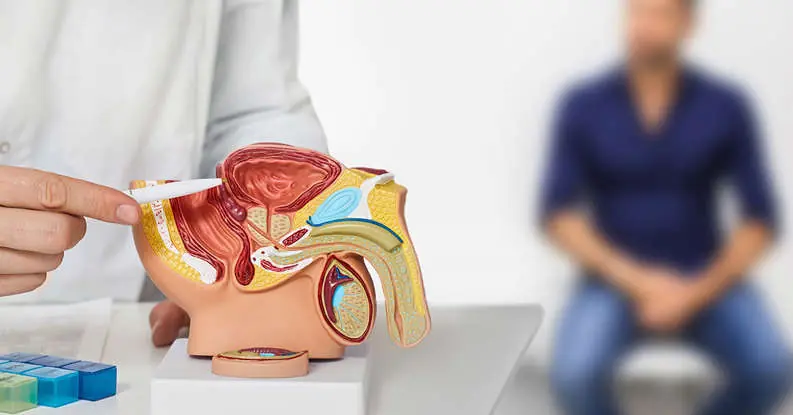
Common Habit Linked to 45% Higher Risk of Prostate Cancer in Men
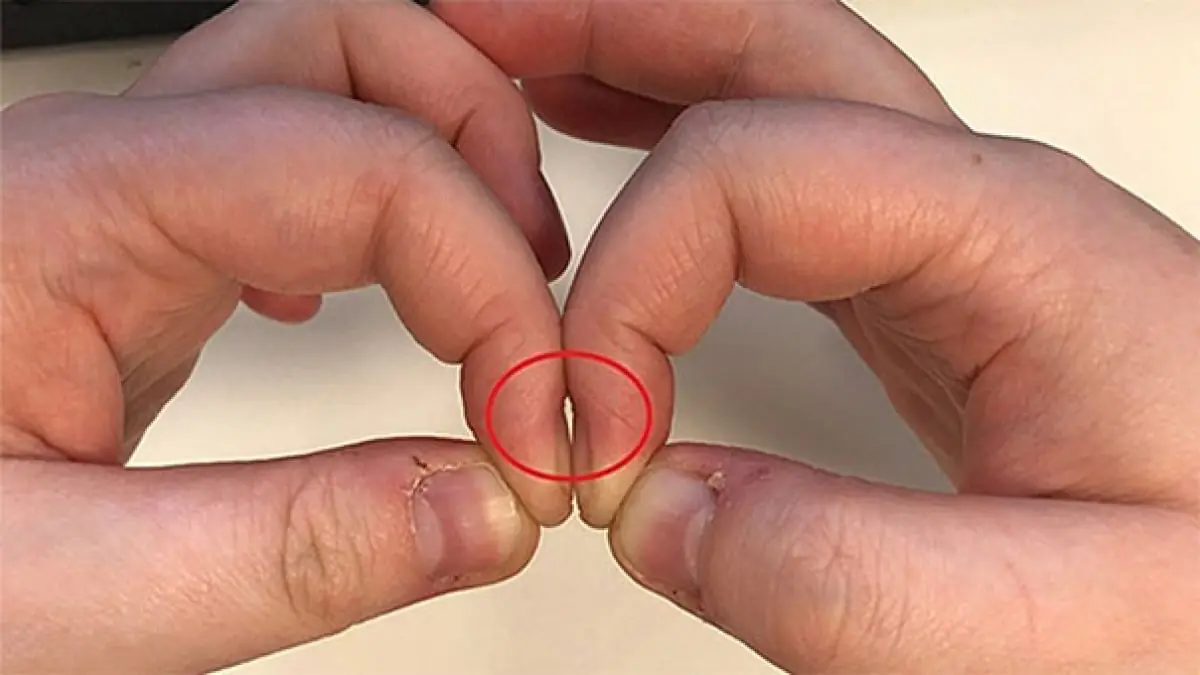
Placing Two Index Fingers Together Can Reveal Lung Cancer: A Quick Test Used by Doctors

The Surprising Reason to Keep a Glass of Water by Your Bedside at Night
Scientists Have Identified Specific Cognitive Skill Linked To Longer Life In Older Adults

21-Year-Old Woman With Terminal Colon Cancer Warns Of The Early Symptoms That Are Simple To Ignore

Understanding the Causes of a Fishy Vaginal Odor
News Post

Here’s What The Lines On Bath Towels Actually Mean

Fake Honey is Flooding The Market — Here’s How To Spot The Real Thing

Here’s What It Really Means When A Man Turns His Back In Bed

Stop Shaving! Discover Natural Ways to Permanently Remove Facial, Body, and Pubic Hair

11 Reasons Why You Should Drink Aloe Vera Water Every Day

Shocking findings of new trial on Ozempic alternative pushes it closer to approval

Experts Warn People To Get Rid Of This Common Bedroom Item Over Fears It Might Harm Brain Health

The Side Effects of Ibuprofen You May Not Be Aware Of

6-Year-Old Boy Suffers Stroke After Waking Up – Doctor Urges Parents to Know These 4 Warning Signs to Save Their Child

3 Eye Symptoms That Could Warn of a Stroke or Cancer – Don’t Ignore Them

My MIL Ruined Our Wedding Three Times – But She Was the Only One Who Lost in the End

Child Made a New Friend at School, but Mom Is Shocked to Learn Who the Girl's Mother Is

I Became a Surrogate for My BIL and His Wife – When He Saw the Baby, He Yelled, 'This Must Be a Mistake!'

My Ex-husband Gifted Our Kid a Rocking Horse – When I Saw What Was Inside, I Called My Lawyer

My Husband and His Mistress Accidentally Got Into My Taxi So I Gave the Cheater an Anniversary He’ll Never Forget

Man Mocks Wife for Gaining Weight after Giving Birth, Finds Her Diary after She’s Hospitalized

My Stepdaughter Betrayed Me and Kicked Me Out After I Raised Her Like My Own – So I Used My Experience to Turn My Life Back Around

17 Common Foods That May Trigger Kidney Stones – What to Avoid for Healthier Kidneys

12 Strange Signs in Your Feet That Could Be Warning You About Liver Problems
