
Children Who Are Hugged Often Have Stronger Immune Systems, Studies Show
In recent years, scientific studies have increasingly confirmed what many parents and caregivers have instinctively believed for generations: physical affection, especially hugging, has profound health benefits for children. Among the most surprising findings is the link between frequent hugging and a stronger immune system. Research now supports the idea that children who are hugged often are not only emotionally healthier, but also physically more resilient.
Hugging plays a critical role in a child’s development. From birth, human touch is essential. It’s one of the first ways that infants experience the world and connect with their caregivers. Numerous studies have shown that physical touch, including hugs, stimulates the release of oxytocin—a hormone often referred to as the “love hormone.” Oxytocin promotes bonding and reduces stress. When children are hugged, their brains produce more oxytocin, which in turn helps to regulate mood, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of safety.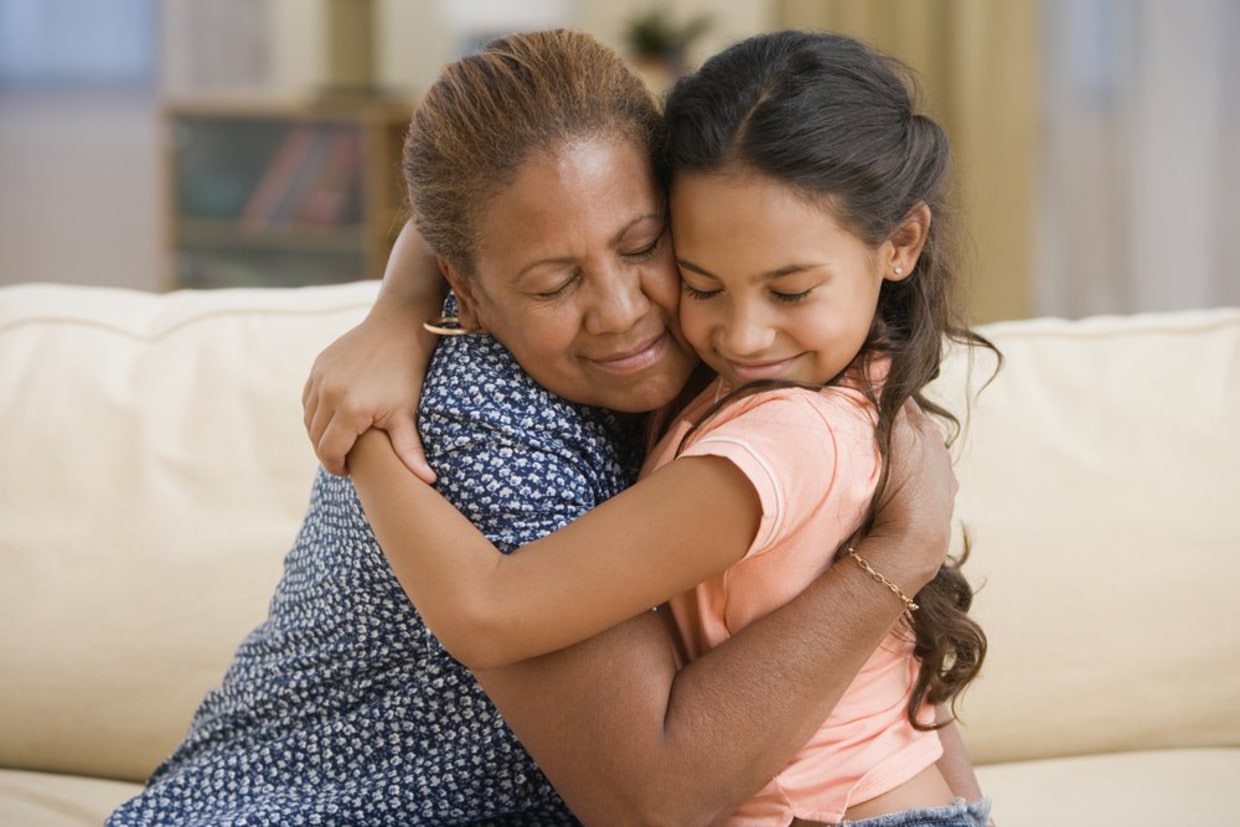
However, the effects of hugging go beyond emotional comfort. Stress and anxiety are well-known factors that weaken the immune system. When children are under chronic stress—perhaps due to neglect, isolation, or fear—their bodies produce high levels of cortisol, a stress hormone that can suppress immune function. On the other hand, when children feel loved and secure through physical touch like hugging, their cortisol levels decrease. This allows their immune systems to function more effectively, helping them fight off infections and recover faster from illnesses.
One well-known study conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University found that individuals who received more hugs were less likely to catch a cold after being exposed to a virus. Though the study was conducted on adults, the implications for children are significant. If regular physical affection can provide a buffer against illness in adults, its impact on developing immune systems in children may be even more powerful.
Moreover, hugging encourages the development of positive social behaviors and mental health, which are closely linked to physical health. Children who are regularly hugged often grow up feeling secure, confident, and emotionally balanced. They are less likely to suffer from anxiety, depression, or behavioral issues, all of which can contribute to a weakened immune system if left unchecked.
Unfortunately, in modern society, physical affection is sometimes overlooked or undervalued, especially as children grow older. With busy schedules, screen distractions, and cultural norms that sometimes discourage physical closeness, many families may unintentionally limit this essential form of connection. Yet, even brief, daily hugs can make a substantial difference.
It's important to remember that hugs don’t have to be long or dramatic to be effective. A simple, warm hug in the morning before school, a quick embrace after a long day, or a cuddle while reading a bedtime story can all contribute to a child’s emotional and physical well-being. These small moments of connection are what help build the foundation for strong immune health and resilience.
In conclusion, science supports what love has always taught: hugging is healing. Children who are hugged often are not only happier and more secure, but also physically healthier. Their immune systems benefit from the emotional safety that physical affection provides. As simple as it may seem, a daily hug may be one of the most powerful tools we have to support our children’s long-term health. In a world that often feels fast-paced and disconnected, taking the time to hug our children is a small act that can have lasting, measurable impact.
News in the same category


🌿 17 Health Conditions That May Benefit from Guava Leaf Tea + Easy Homemade Recipe

A Scientific Look at Oregano’s Role in Supporting Wellness
Scientists discover ‘stealth bacteria’ from your mouth are hiding in your arteries and triggering heart at:tacks
Cold, numb legs or feet? Eat this one food to restore circulation naturally

Tomato Extract: Better And Safer B::lood Thinner Than Aspirin
Top 10 foods that improve blood circulation in legs
Foods to Stimulate the Liver to Remove Toxins Fast

Why Some People’s Skin Turns Red When Drinking Alcohol
Things That No Longer Appeal to People With High IQs as They Age

10 Strange Habits of Highly Intelligent People That Others Just Don’t Understand, According to Psychology
Laser-Free Eye Surgery Could Correct Vision With Electrical Currents

Why Charging Your Phone Overnight Might Be a Bad Habit

Blurred Vision in One Eye and a Headache: Don't Ignore These Warning Signs

Why a Hard-Boiled Egg Before Bed Could Be a Game-Changer for Sleep and Metabolism

Proven Health Benefits of Black Seed and Black Seed Oil

1 cup that instantly wakes your kidneys up and strengthens them naturally

This Is What Happens To Your Body When You Get Aspartame Poisoning From Diet Sodas
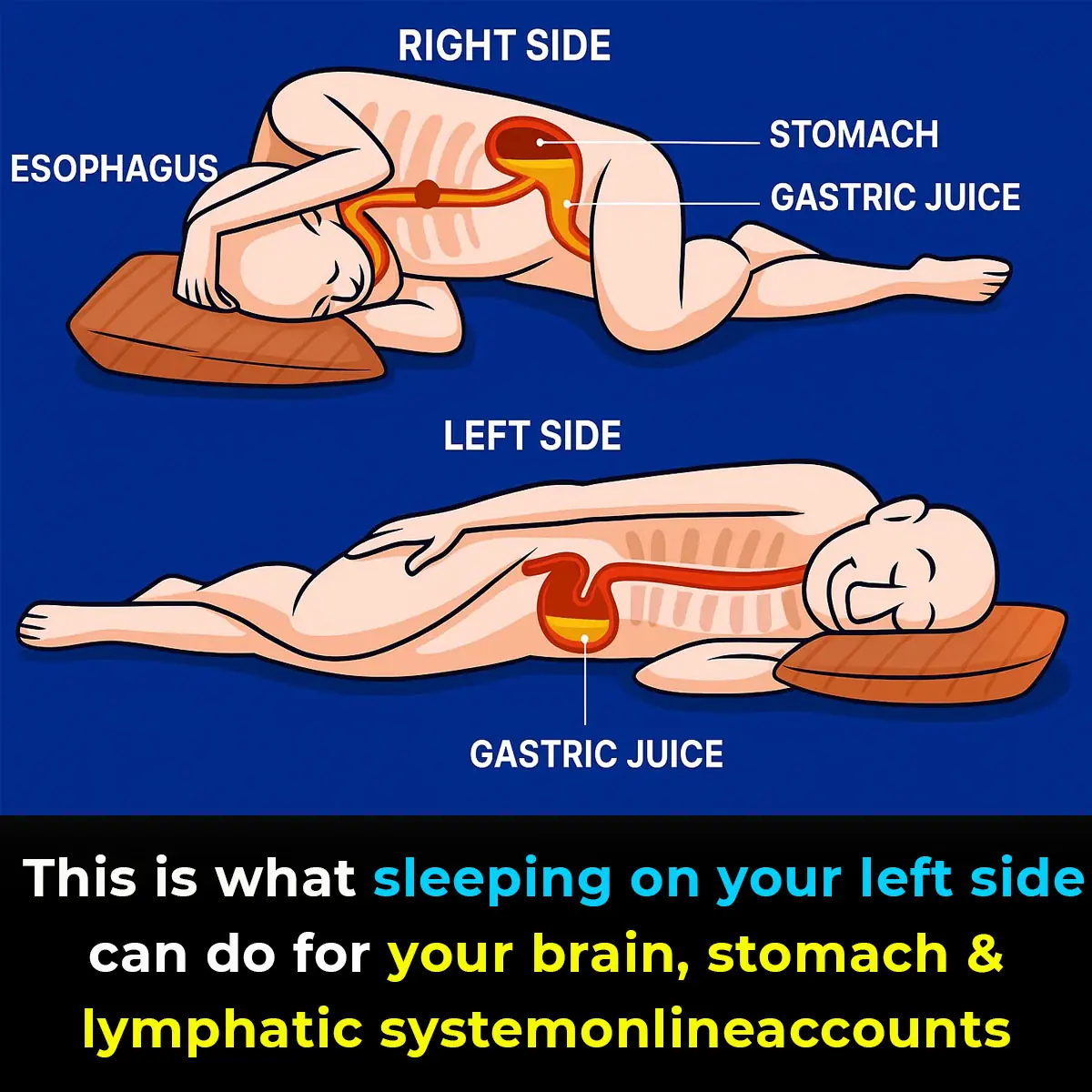
This is what sleeping on your left side can do for your brain, stomach and lymphatic system
News Post

Symptoms That Can Be Caused by Stress
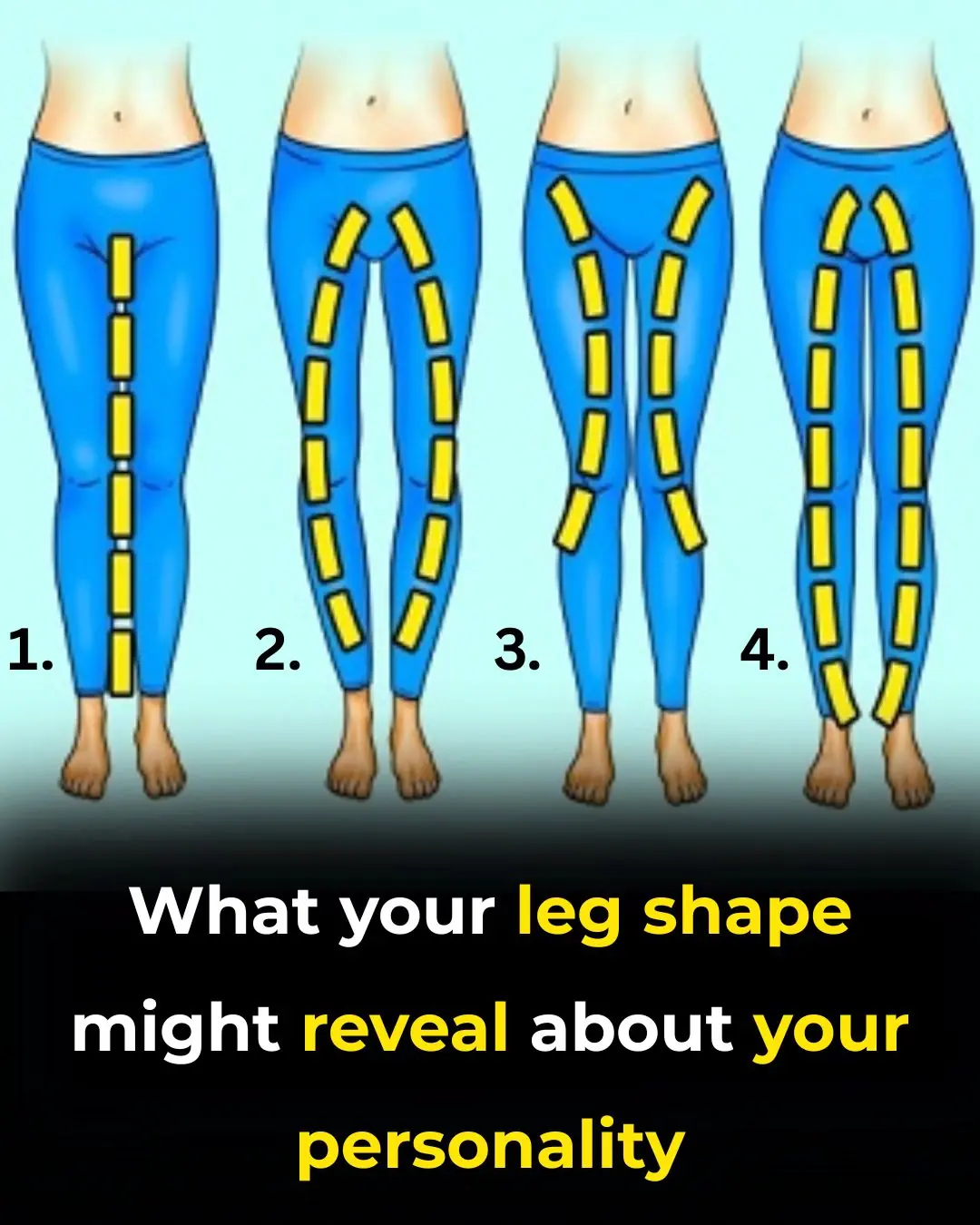
What the Shape of Your Legs Might Say About Your Personality

How surgeon who amputated his own legs was caught as he's sentenced to 32 months in prison

PlayStation handing out rare refunds to gamers over popular new game

🌿 17 Health Conditions That May Benefit from Guava Leaf Tea + Easy Homemade Recipe

If your non-stick pan has lost its coating, don't rush to throw it away: Just do this, and you can fry and cook without it sticking or falling apart.

The golden 4-hour window for drinking coffee helps your body gain maximum benefits: detoxifying the li:ver and promoting smooth digestion.

Eating boiled bananas at this time, after just 1 week, your body will experience 7 changes

Add potato to coffee to get rid of wrinkles in just 1 week

Homemade Rice water & Methi Dana Toner for Glowing Skin

The DIY anti-ageing cream that is very effective to get rid of wrinkles and fine lines on your face

Herbal Remedies for Strong, Lush Hair: Easy Recipe Everyone Can Make At Home

Flaxseed Gel for Wrinkles: The Natural DIY Solution for Smoother, Youthful Skin

10 Tomato Slice Skincare Remedies for Wrinkles, Pores, and Glowing Skin: Natural DIY Treatments

Super Effective DIYs to Achieve Soft, Pink, and Perfect Lips

A Scientific Look at Oregano’s Role in Supporting Wellness

Reverse Hair Greying Naturally: Effective Treatments and Remedies for Restoring Hair Color
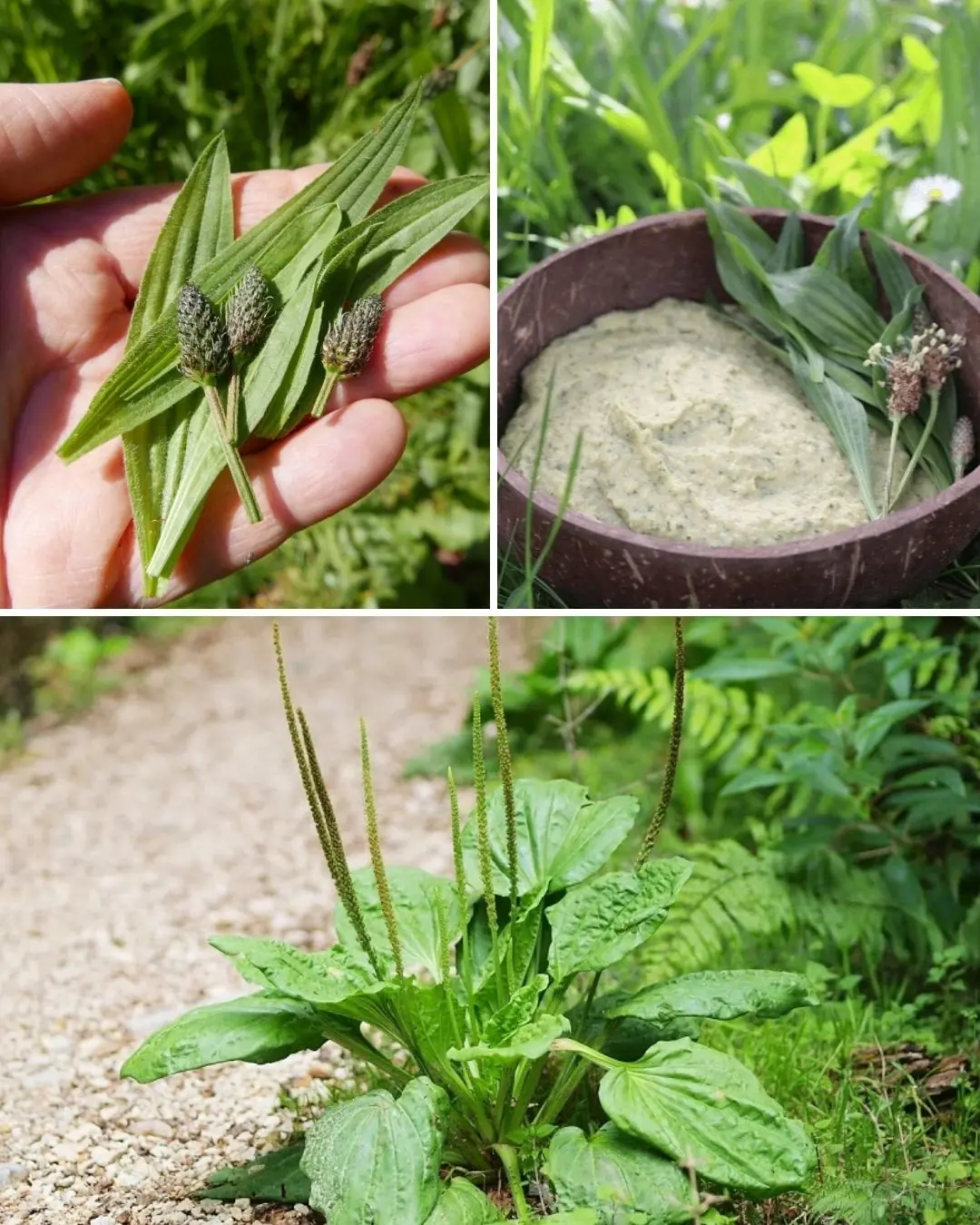

The Incredible Benefits of Plantago lanceolata and How to Use It

CCF Detox Drink For Glowing Flawless Skin
