
Gas Giants of the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus & Neptune
The outer reaches of our solar system are dominated by four magnificent worlds that dwarf our rocky inner planets. These gas giants—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—represent some of the most fascinating and complex celestial bodies in our cosmic neighborhood. Understanding these massive planets provides crucial insights into planetary formation, atmospheric dynamics, and the evolution of our solar system.
This comprehensive guide explores each gas giant’s unique characteristics, from Jupiter’s Great Red Spot to Neptune’s supersonic winds, helping you understand what makes these distant worlds so extraordinary.
Table of Contents
Understanding Gas Giants: The Basics
Gas giants are massive planets composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with possible rocky cores buried deep beneath thick atmospheric layers. Unlike terrestrial planets such as Earth and Mars, these worlds lack solid surfaces that spacecraft could land on. Instead, their atmospheres gradually increase in density and pressure as you descend toward their centers.
The four gas giants are divided into two categories: the larger Jupiter and Saturn are considered “true” gas giants, while Uranus and Neptune are classified as “ice giants” due to their higher concentrations of water, methane, and ammonia ices.
Formation and Composition
These planets formed in the outer solar system where temperatures were cold enough for volatile compounds to condense into solid particles. This allowed them to grow massive enough to gravitationally capture enormous amounts of hydrogen and helium from the early solar nebula.
The gas giants contain the majority of our solar system’s planetary mass, with Jupiter alone accounting for more than twice the mass of all other planets combined.
Jupiter: The Solar System’s Giant
Jupiter stands as the undisputed king of planets, with a mass greater than all other planets combined. This massive world orbits the Sun every 11.86 Earth years at an average distance of 778 million kilometers.
Physical Characteristics and Atmospheric Features
Jupiter’s most striking feature is its Great Red Spot, a massive anticyclonic storm that has raged for centuries. This storm system is larger than Earth and demonstrates the incredible energy present in Jupiter’s turbulent atmosphere.
The planet’s atmosphere consists of approximately 89% hydrogen and 10% helium, with trace amounts of methane, water vapor, and ammonia. These compounds create the colorful bands and zones that characterize Jupiter’s appearance, with different chemical compositions producing distinct colors at various altitudes.
Jupiter’s rapid rotation period of just 9 hours and 56 minutes creates extreme weather patterns and contributes to the planet’s oblate shape. The differential rotation between equatorial and polar regions generates powerful jet streams that can reach speeds of up to 640 kilometers per hour.
Moon System and Exploration
Jupiter hosts at least 95 confirmed moons, including the four Galilean satellites: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Europa, in particular, has captured scientific attention due to its subsurface ocean, which may harbor conditions suitable for life.
Multiple spacecraft missions have studied Jupiter, including Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, and the ongoing Juno mission, which continues to provide detailed insights into the planet’s interior structure and magnetic field.
Saturn: The Ringed Wonder
Saturn, the second-largest planet in our solar system, is perhaps best known for its spectacular ring system. This gas giant orbits the Sun every 29.5 Earth years at a distance of approximately 1.4 billion kilometers.
Ring System and Structure
Saturn’s rings are composed primarily of countless ice particles ranging in size from tiny grains to house-sized chunks. The ring system spans up to 282,000 kilometers in diameter but is remarkably thin, with a thickness of only about 10 meters in most regions.
The rings are divided into several main sections, designated by letters in order of discovery: the A, B, and C rings are the most prominent and visible from Earth. The fainter D, E, F, and G rings extend the system both inward toward Saturn and outward beyond the main rings.
Atmospheric Composition and Weather
Like Jupiter, Saturn’s atmosphere consists primarily of hydrogen and helium, but with slightly different proportions that affect its overall density. Saturn is actually less dense than water, meaning the entire planet would theoretically float if placed in a sufficiently large ocean.
Saturn experiences seasonal changes due to its 26.7-degree axial tilt, similar to Earth’s seasons but lasting about 7.5 Earth years each. The planet’s hexagonal storm at its north pole represents one of the most unusual atmospheric phenomena in the solar system.
Moons and Satellites
Saturn hosts 146 confirmed moons, with Titan being the largest and most Earth-like. Titan’s thick atmosphere and methane lakes make it a prime target for astrobiology research. Enceladus, another notable moon, spouts water-ice geysers from its south polar region, indicating a subsurface ocean.

Uranus: The Tilted Ice Giant
Uranus presents one of the most unusual orientations in the solar system, rotating on its side with an axial tilt of 98 degrees. This ice giant orbits the Sun every 84 Earth years at a distance of approximately 2.9 billion kilometers.
Unique Characteristics and Composition
Unlike Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus contains significantly more water, methane, and ammonia in its composition. The methane in its upper atmosphere absorbs red light, giving Uranus its distinctive blue-green color.
Uranus’s extreme tilt likely resulted from a collision with an Earth-sized object during the early formation of the solar system. This orientation means that each pole experiences 42 years of continuous sunlight followed by 42 years of darkness.
Magnetic Field and Ring System
Uranus possesses a unique magnetic field that is tilted 59 degrees from its rotational axis and offset from the planet’s center. This unusual configuration suggests a different internal structure compared to the other gas giants.
The planet has a faint ring system discovered in 1977, consisting of narrow, dark rings composed of organic compounds altered by radiation. These rings are much darker than Saturn’s bright ice rings.
Moons and Exploration
Uranus has 27 known moons, many named after characters from Shakespeare’s plays. The largest moons—Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel, and Miranda—show diverse geological features despite their small sizes.
Only one spacecraft, Voyager 2, has visited Uranus, flying by the planet in 1986 and providing most of our detailed knowledge about this distant world.
Neptune: The Windiest Planet
Neptune, the outermost gas giant, experiences the most extreme weather in the solar system despite receiving only one-thousandth of the sunlight that Earth receives. This ice giant completes one orbit around the Sun every 165 Earth years at a distance of about 4.5 billion kilometers.
Extreme Weather and Atmospheric Dynamics
Neptune’s atmosphere contains the fastest winds in the solar system, with speeds reaching up to 2,100 kilometers per hour. These supersonic winds blow in the opposite direction of the planet’s rotation, a phenomenon that still puzzles scientists.
The planet’s deep blue color results from methane in its atmosphere, which absorbs red light more effectively than Uranus’s atmosphere, creating a more vivid blue appearance.
Neptune’s most famous atmospheric feature was the Great Dark Spot, a storm system similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot but much more transient. When the Hubble Space Telescope observed Neptune in the 1990s, this storm had disappeared, demonstrating the dynamic nature of Neptune’s atmosphere.
Internal Heat and Magnetic Field
Neptune radiates 2.6 times more energy than it receives from the Sun, indicating a significant internal heat source. This internal energy likely drives the planet’s extreme weather patterns and helps maintain its dynamic atmosphere.
Like Uranus, Neptune’s magnetic field is tilted significantly from its rotational axis and offset from the planet’s center, suggesting similarities in their internal structures.
Triton and Other Moons
Neptune’s largest moon, Triton, is unique among large moons because it orbits retrograde (backward) relative to Neptune’s rotation. This massive moon likely represents a captured Kuiper Belt object and shows evidence of geological activity despite the extreme cold.
Triton’s thin atmosphere and nitrogen geysers make it one of the most interesting moons in the outer solar system. The moon is gradually spiraling inward toward Neptune and will eventually be torn apart by tidal forces.
Comparative Analysis and Future Exploration
The gas giants showcase the diversity possible in planetary formation and evolution. Jupiter and Saturn, forming closer to the Sun, captured more hydrogen and helium, while Uranus and Neptune incorporated more heavy elements and water ice.
These planets play crucial roles in shaping our solar system’s architecture. Jupiter, in particular, acts as a “vacuum cleaner,” protecting inner planets from comet and asteroid impacts while also influencing the orbits of other celestial bodies.
Future missions to these distant worlds will continue expanding our understanding. Proposed missions include atmospheric probes for Uranus and Neptune, detailed studies of their moon systems, and continued monitoring of their dynamic atmospheres.
Significance for Planetary Science
Study of gas giants provides insights into planetary formation processes, atmospheric dynamics under extreme conditions, and the potential for life in subsurface oceans of their moons. These worlds serve as natural laboratories for understanding physics and chemistry under conditions impossible to replicate on Earth.
Conclusion
The gas giants of our solar system represent some of the most magnificent and scientifically valuable objects within our cosmic neighborhood. From Jupiter’s massive influence on solar system dynamics to Neptune’s supersonic winds, each world offers unique insights into planetary science and the formation of our solar system.
Understanding these distant giants not only satisfies our curiosity about the cosmos but also helps us better comprehend planetary processes that shape worlds throughout the universe. As technology advances and new missions launch, our knowledge of these remarkable planets will continue to grow, revealing new mysteries and deepening our appreciation for the complexity and beauty of our solar system.
For the latest discoveries about gas giants and other astronomical phenomena, consider following space agencies’ research updates and peer-reviewed astronomical publications.
News in the same category


Elon Musk Calls on 226 Million Followers to Cancel Netflix Amid Surging Boycott Movement

Officer Breaks Car Window to Rescue Baby – Then Realizes It Was a Mistake

Scientist Watches to See If Strange Interstellar Object Releases Any Probes

Prime views of the Andromeda Galaxy and Ceres—October 2

Prime views of the Andromeda Galaxy and Ceres—October 2

September 9 Meteor Shower: Epsilon Perseids to Dazzle the Night Sky
YouTuber destroys new iPhone Air with a blowtorch to test its durability

GameStop issues promising statement following Xbox Game Pass price hike

1st solar eclipse of 2025 puts on stunning show for skywatchers around the world (photos)

10 Safest Countries to Visit in Europe
Majestic Peaks: Top 10 Mountains to Visit in Europe
Explore the Best of Britain: 12 Epic UK Road Trip Ideas

Tomorrow Island (Russia) and Yesterday Isle (USA) Are Just Three Miles Apart But There’s a 21-Hour Time Difference Between Them

The Mighty Moss: Nature’s Unsung Superhero

Demystifying Oxygen Production: Oceans vs. Amazon Rainforest

Bizarre radio signals that defy physics detected under Antarctica: ‘It’s one of these long-standing mysteries’

Do Not Do This On Your Glass Stove
News Post

A simple tip on how to grow ginger using cement bags, never had such a good yield of ginger

Blanching pork in boiling water, you think it's clean but it absorbs more dirt: This is the right way to do it

Married at First Sight UK fans crown 'best match' after two weeks

Selena Gomez’s kidney donor, Francia Raisa, addresses wedding snub and feud rumors

David Ortiz sparks awkward moment on Fox postgame show: ‘Sounds like Hitler’

Crabgrass for Hair Loss: Natural Remedies and Uses
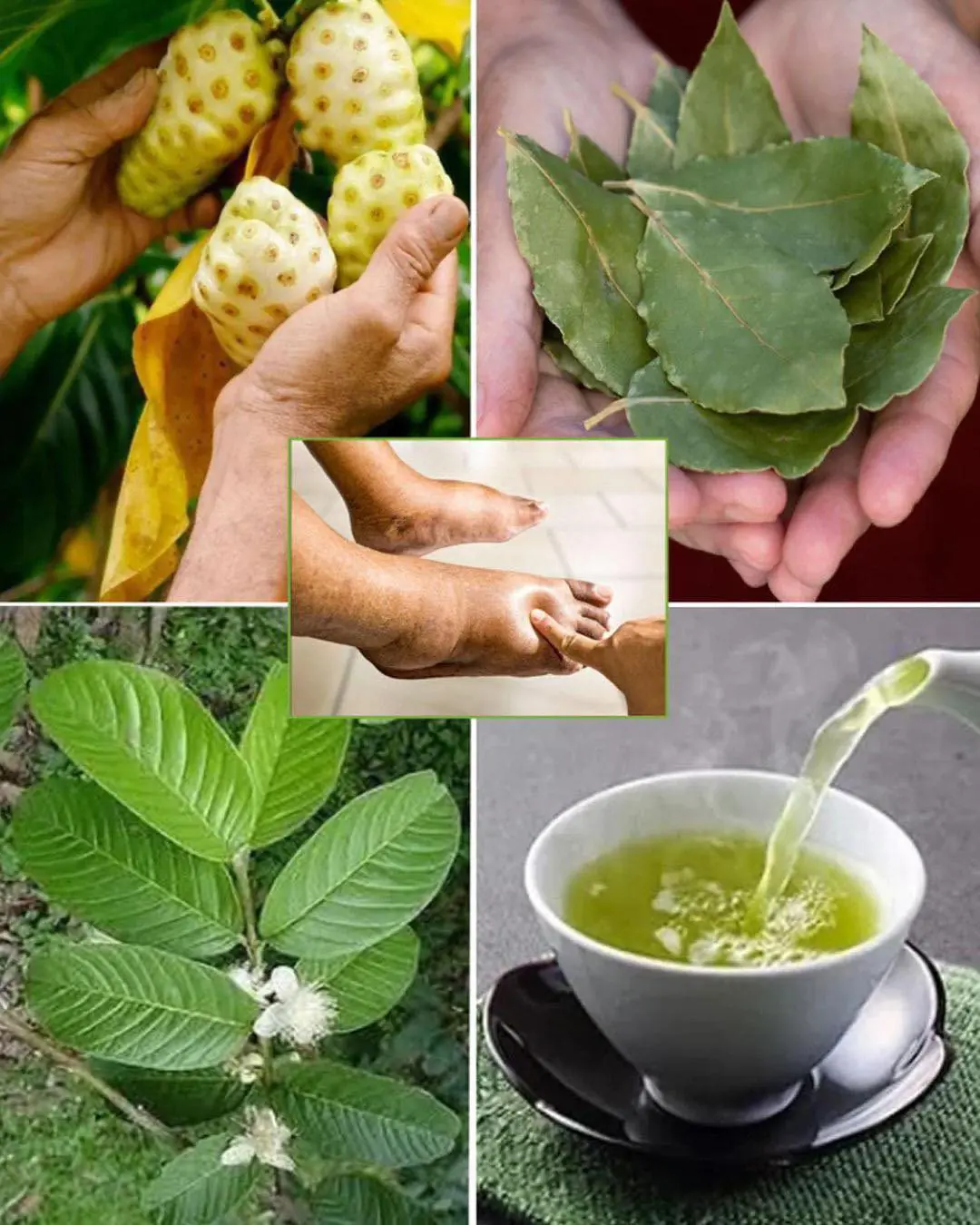

The Ultimate Healing Tonic: A Powerful Drink to Combat Swollen Feet, Diabetes and Poor Circulation
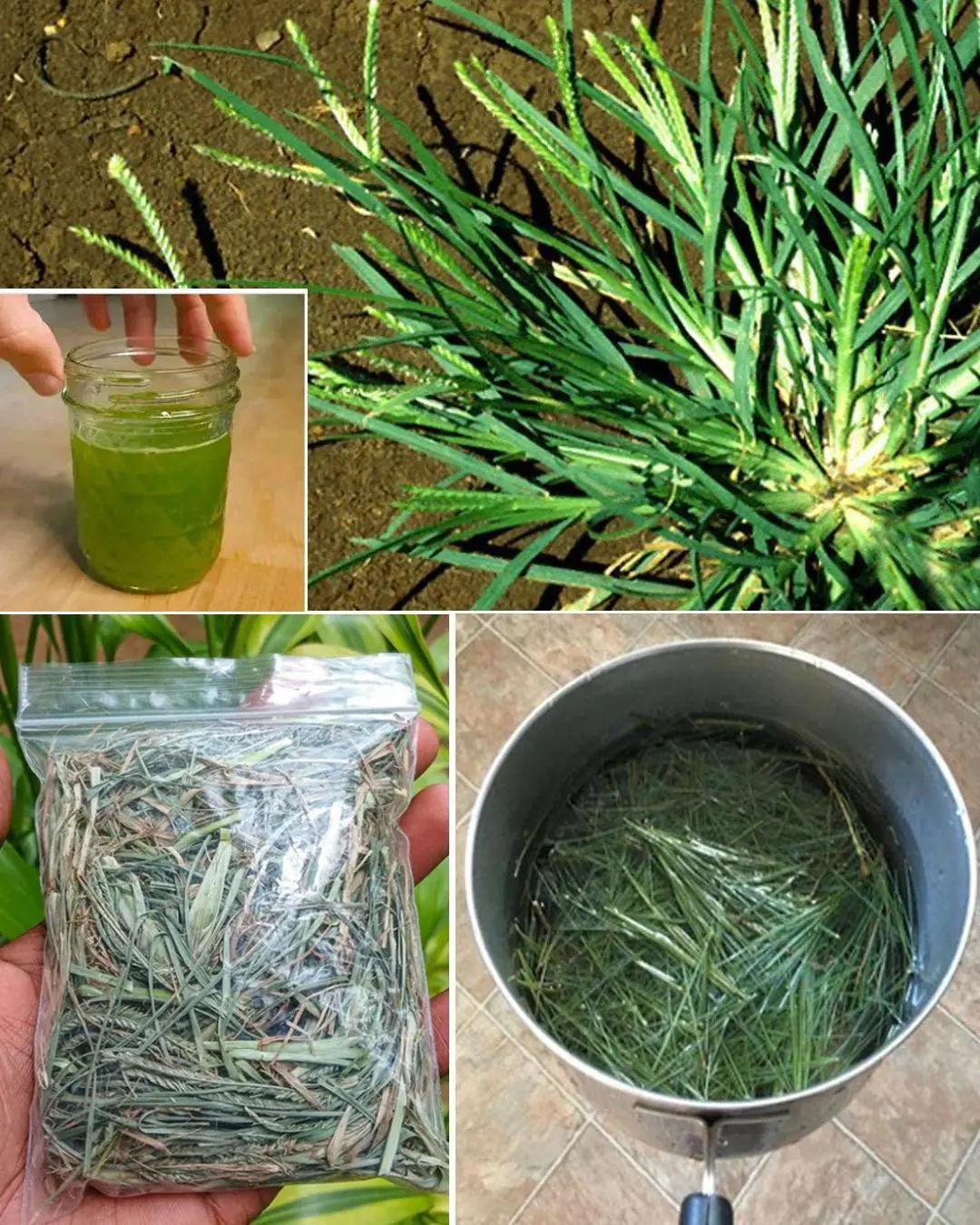

Goosegrass: Health Benefits and Uses
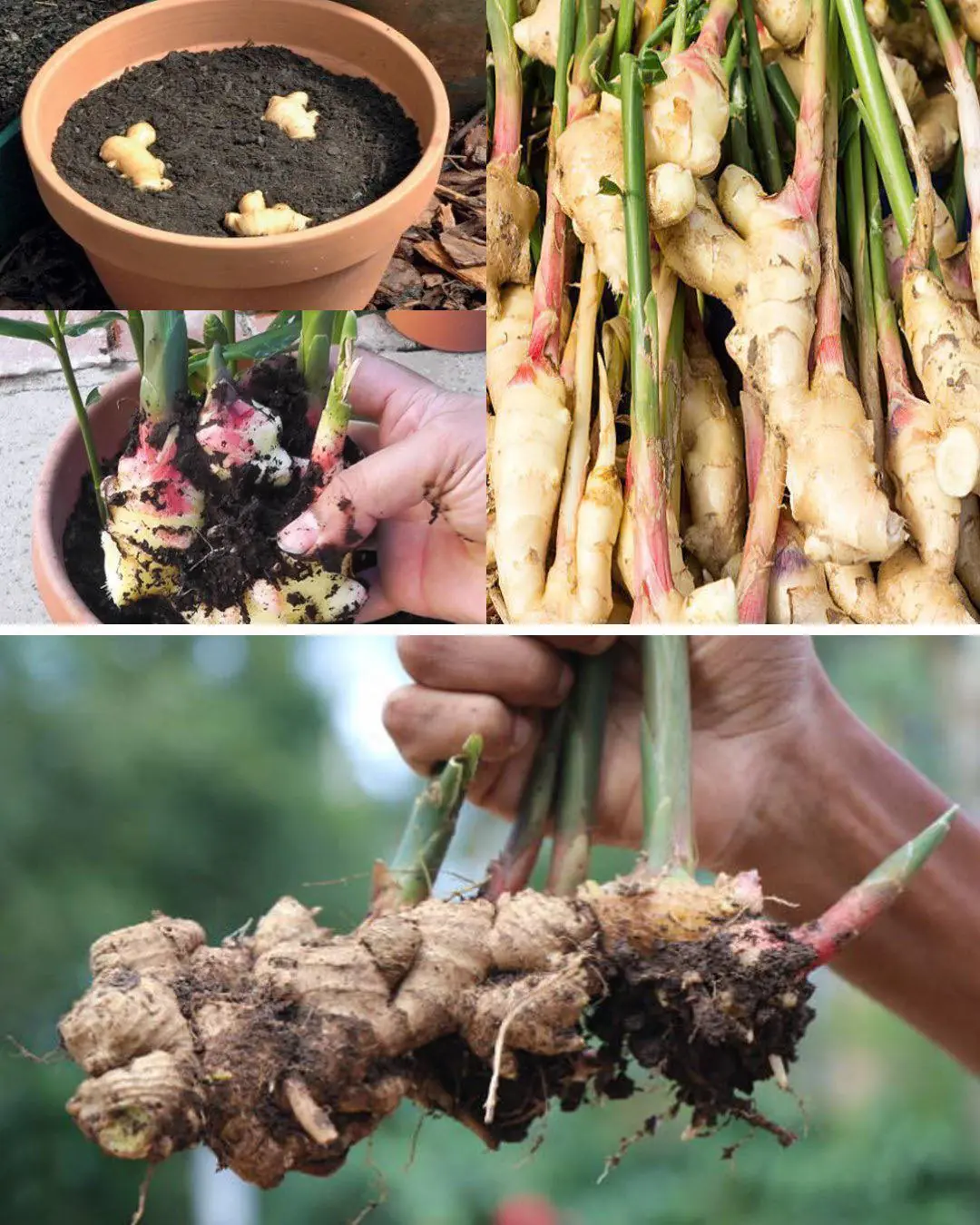

How to grow ginger at home to have an endless supply (and make it flower)
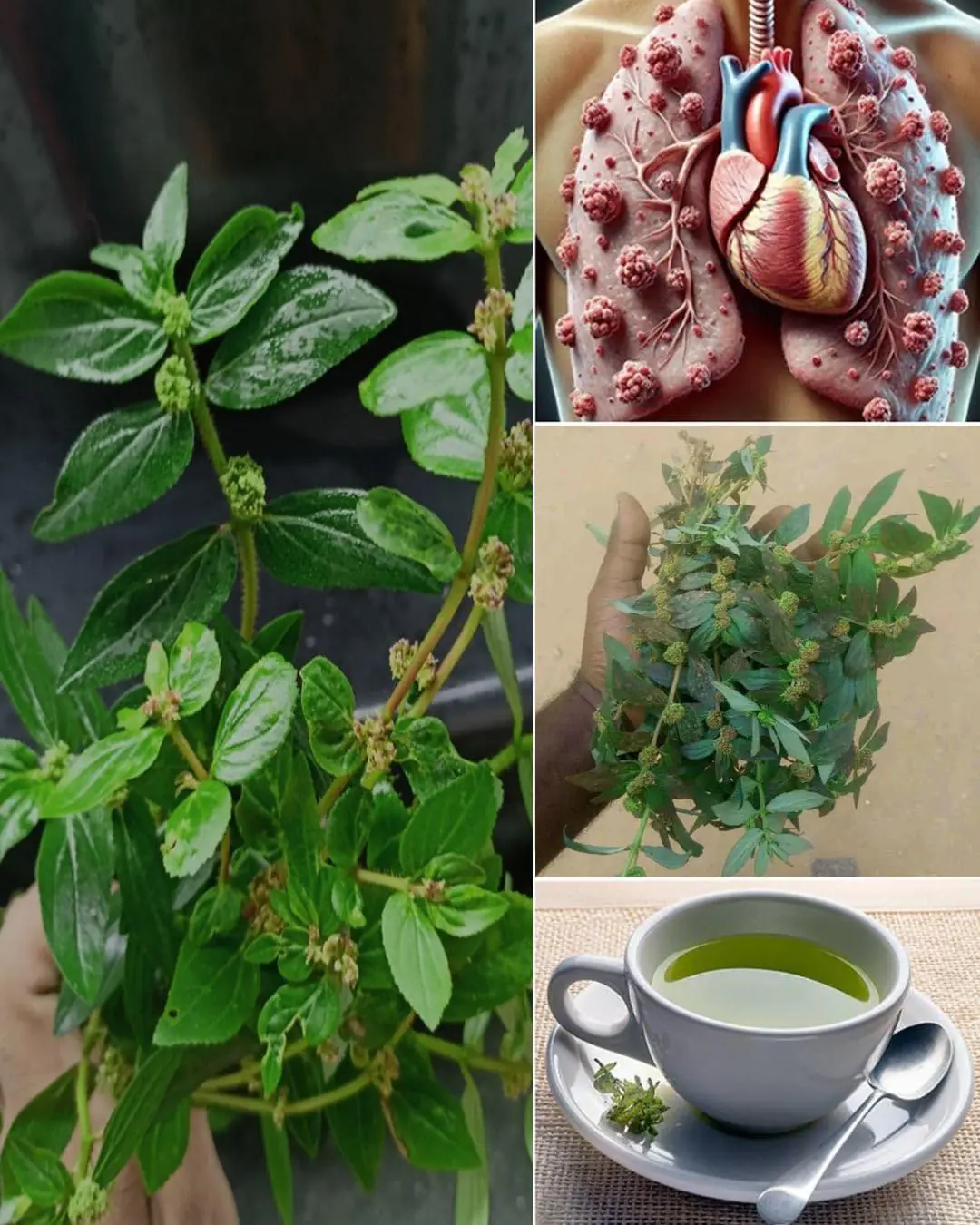

Asthma Plant Tea – Benefits and Uses of Euphorbia hirta
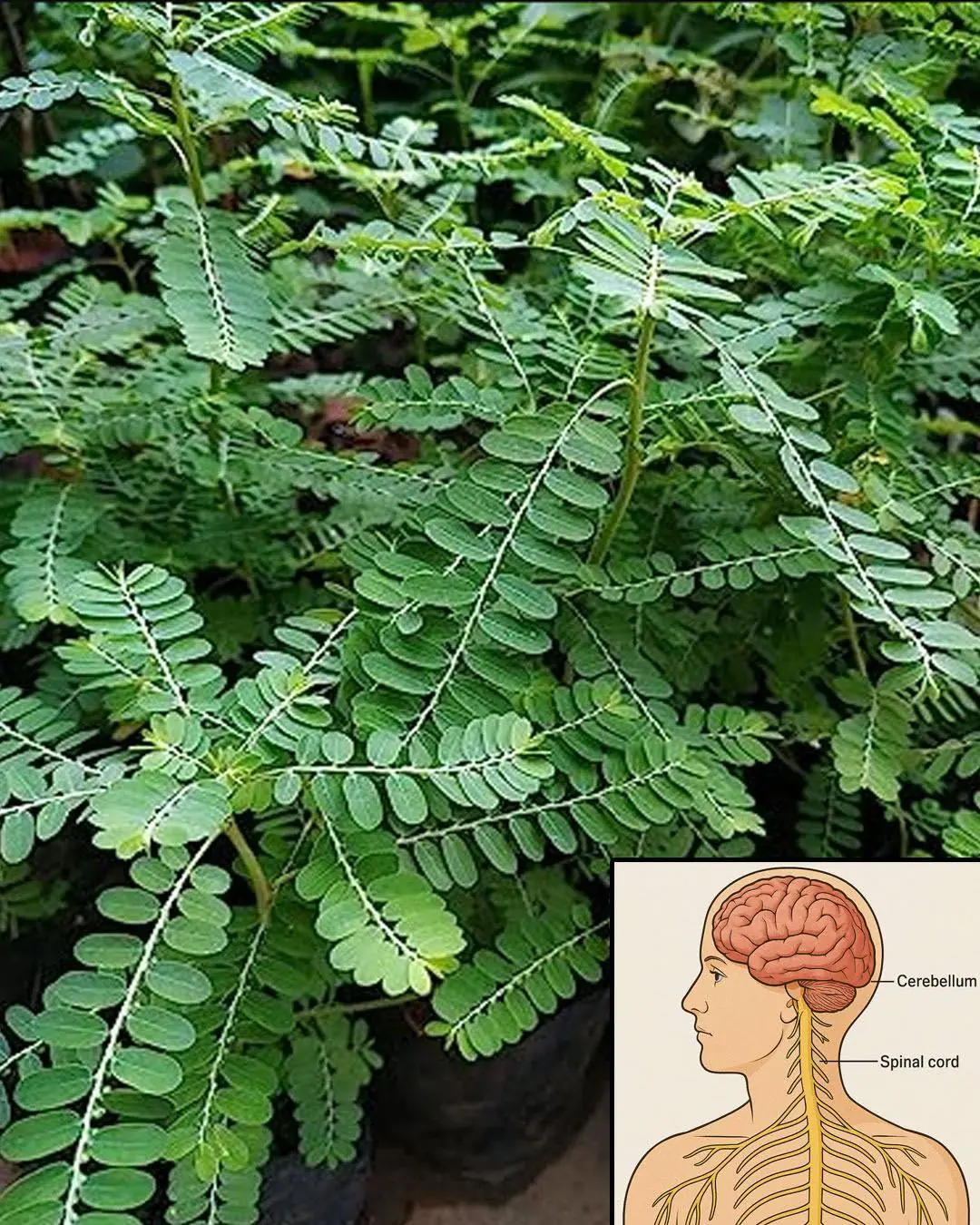

Chanca Piedra (Stonebreaker): Benefits and Uses
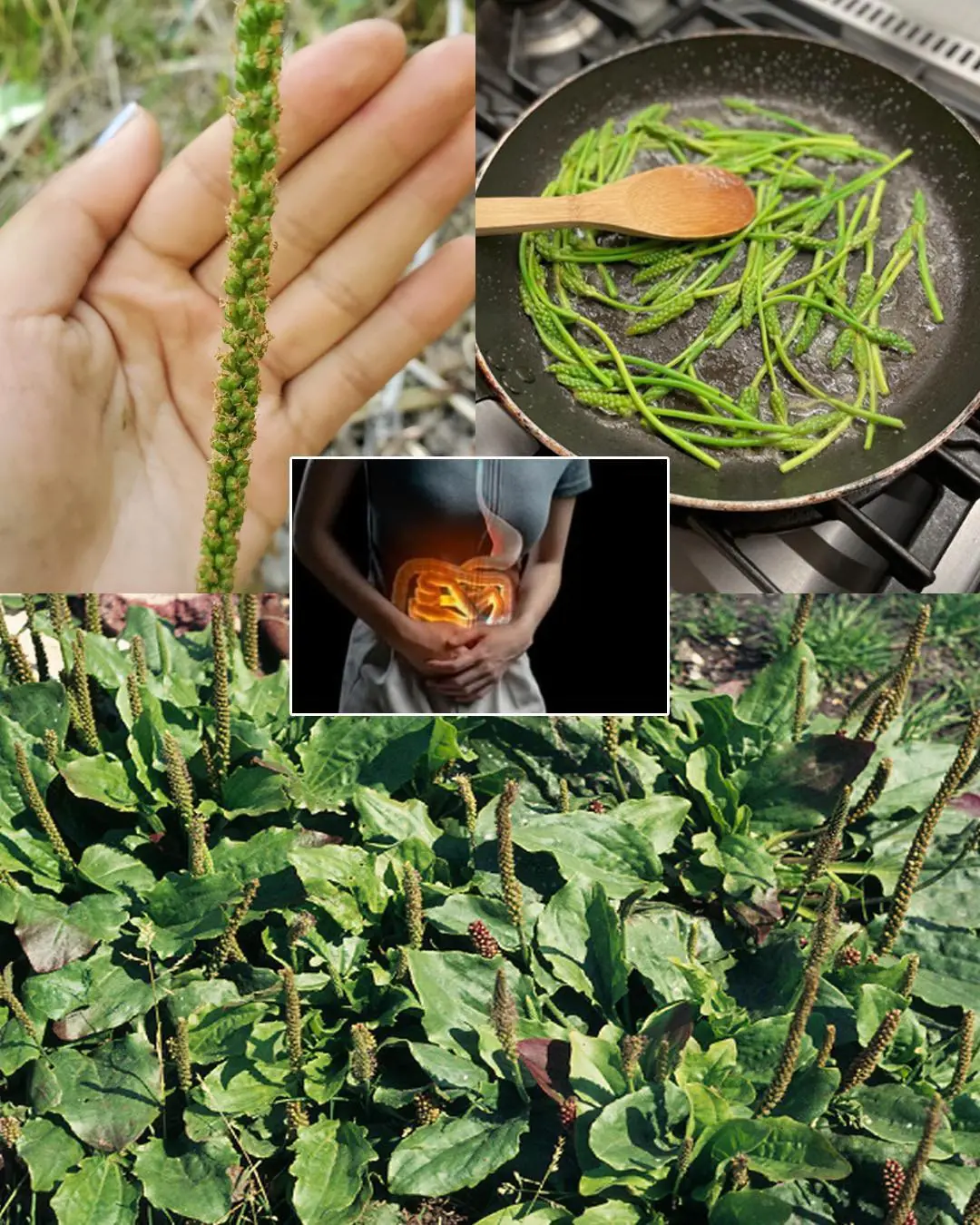

7 benefits and uses of Plantago Major
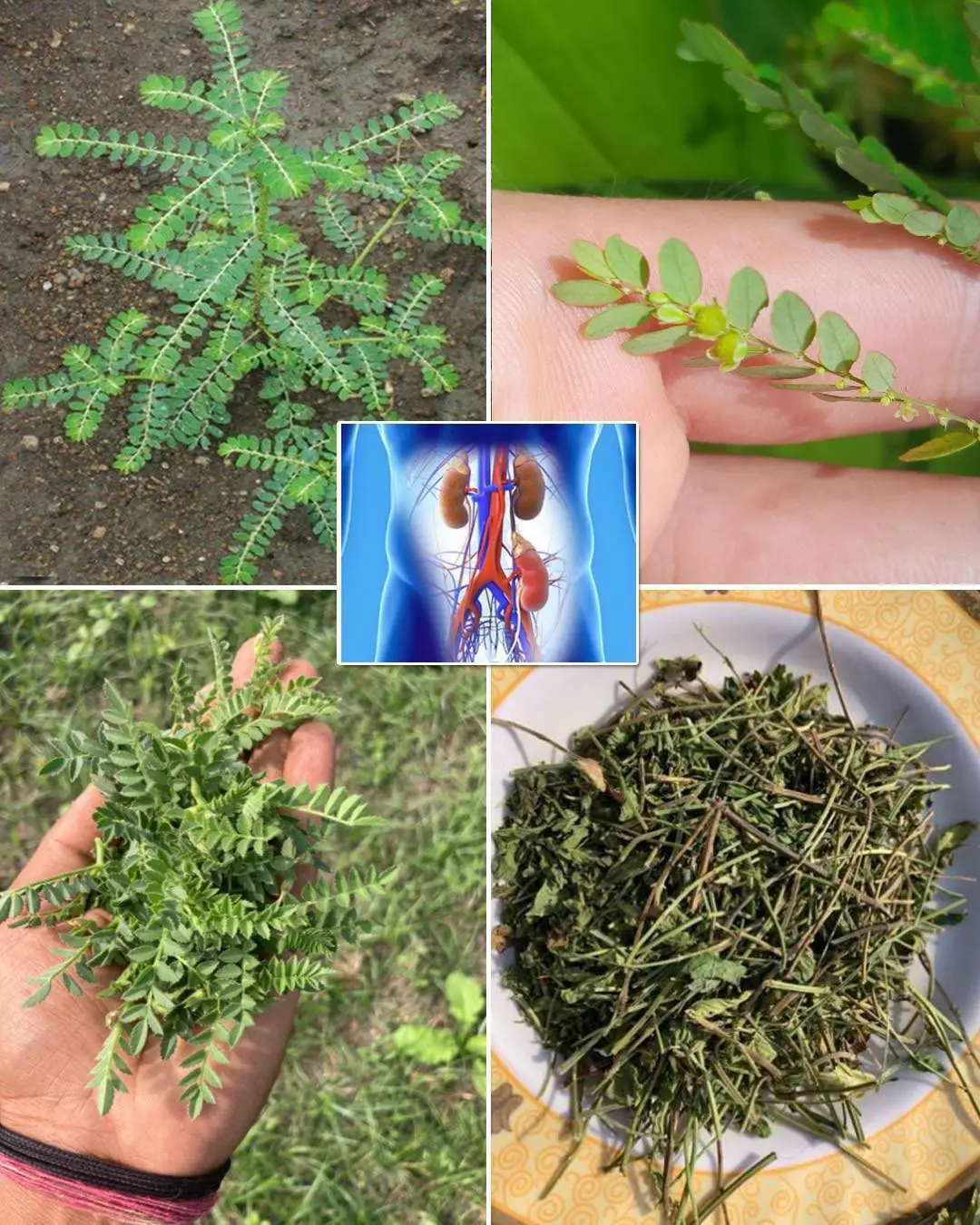

Chanca Piedra (Stonebreaker): Benefits and Uses
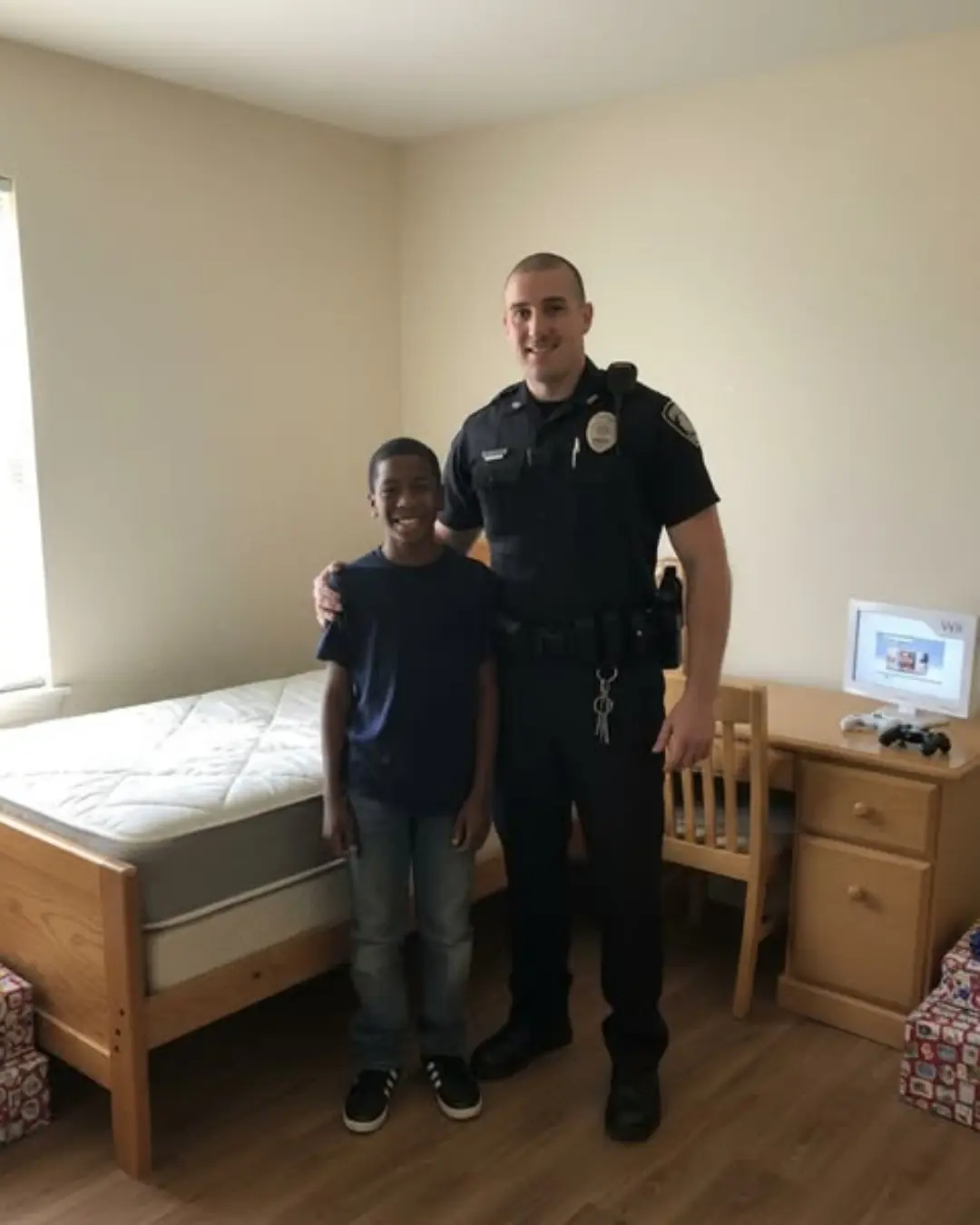

A Call for Help at 2 AM: How One Officer Changed a Boy’s Life with Compassion

Ten Minutes From Tragedy—A Dog’s Warning Changed Everything!

Teen Builds $500 Dialysis Machine That Works Faster Than Hospital Models
A Split-Second Decision: Mother’s Quick Thinking Saves a Child

A Letter from My Doggy Heart

The Honey Heist: Bear Cub Breaks Into Store and Naps After Feast
