
September 9 Meteor Shower: Epsilon Perseids to Dazzle the Night Sky
The night sky is preparing to deliver a spectacular celestial show as the Epsilon Perseids meteor shower reaches its peak on September 9, 2025. This lesser-known but increasingly impressive meteor shower offers stargazers an excellent opportunity to witness nature’s fireworks without the crowded viewing conditions often associated with more famous meteor events like the Perseids or Geminids.
The Epsilon Perseids, also known as the September Perseids, originate from Comet 96P/Machholz and typically produce 5-10 meteors per hour at peak activity. While not as prolific as major meteor showers, this event offers unique advantages including darker skies due to favorable moon phases and optimal viewing times for most Northern Hemisphere locations.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Epsilon Perseids Meteor Shower
Origin and Characteristics
The Epsilon Perseids meteor shower occurs when Earth passes through the debris trail left by Comet 96P/Machholz during its orbital journey around the sun. This comet, discovered in 1986, has a relatively short orbital period of approximately 5.3 years, creating consistent annual meteor activity.
Unlike the more famous August Perseids, the Epsilon Perseids radiate from a different point in the Perseus constellation, specifically near the star Epsilon Persei. This positioning creates distinct viewing angles and meteor trajectories that experienced observers can easily distinguish from other meteor activity.
The meteors themselves typically appear as medium-speed streaks across the sky, burning up at altitudes between 70-100 kilometers above Earth’s surface. Most Epsilon Perseid meteors range from magnitude 2-4 in brightness, making them clearly visible to the naked eye under reasonably dark skies.
Peak Viewing Conditions for September 9, 2025
This year’s Epsilon Perseids peak occurs during particularly favorable conditions. The new moon phase on September 7 ensures minimal lunar interference, creating optimal darkness for meteor observation. Peak activity begins around 10:00 PM local time and continues until dawn, with maximum meteor rates expected between midnight and 3:00 AM.
Weather patterns across most viewing regions show promising clear sky forecasts, though observers should monitor local conditions and have backup viewing dates prepared. The shower maintains elevated activity levels for approximately 3-4 days surrounding the peak, offering multiple viewing opportunities.
Optimal Viewing Locations and Techniques
Site Selection Criteria
Successful meteor observation requires careful location planning to minimize light pollution interference. Rural locations at least 30 miles from major cities provide ideal viewing conditions, though suburban observers can still enjoy the show with proper preparation.
Key location factors include:
- Elevation above 1,000 feet when possible
- Unobstructed northern and eastern horizon views
- Minimal artificial lighting within a 5-mile radius
- Easy access for extended observation periods
Equipment and Setup Requirements
The Epsilon Perseids require minimal specialized equipment, making this an accessible astronomical event for beginners and families. Essential items include comfortable reclining chairs or blankets, red-filtered flashlights to preserve night vision, and warm clothing appropriate for overnight temperatures.
Setup Checklist:
- Arrive at viewing location 30-45 minutes before peak time
- Allow 20-30 minutes for complete dark adaptation
- Position seating facing northeast with 45-degree viewing angle
- Eliminate all white light sources from viewing area
- Prepare snacks and beverages for extended observation
Advanced observers may benefit from binoculars for examining persistent meteor trains, though naked-eye observation remains the primary viewing method for meteor showers.

Photography and Documentation Techniques
Camera Settings for Meteor Photography
Capturing meteor shower photographs requires specific camera configurations and considerable patience. Digital SLR cameras with manual controls provide the best results, though advanced smartphone cameras can produce acceptable images under optimal conditions.
Recommended Camera Settings:
- ISO: 1600-3200 (adjust based on light pollution levels)
- Aperture: f/2.8 or widest available setting
- Focal Length: 14-24mm wide-angle lens
- Exposure Time: 15-30 seconds per frame
- Focus: Manual infinity setting
Mount cameras on sturdy tripods and use intervalometer settings to capture continuous sequences throughout peak activity periods. Plan for 200-300 individual frames during a typical 3-hour viewing session.
Documentation Best Practices
Serious observers contribute valuable scientific data by maintaining accurate meteor count logs and reporting observations to established databases such as the International Meteor Organization. Record meteor magnitude estimates, duration, color variations, and persistent train characteristics.
Digital logging apps designed for meteor observation can streamline data collection while maintaining observation focus. Include environmental factors such as cloud coverage percentages, temperature readings, and visibility conditions in observation records.
Scientific Significance and Research Applications
Comet Debris Analysis
The Epsilon Perseids provide researchers with annual opportunities to study the composition and distribution patterns of Comet 96P/Machholz debris. Spectroscopic analysis of meteor light emissions reveals chemical compositions including sodium, magnesium, and iron content within the original comet material.
Recent studies indicate that Epsilon Perseid meteors exhibit unique spectral signatures compared to other major meteor showers, suggesting distinct formation conditions or evolutionary processes within the parent comet. This data contributes to broader understanding of outer solar system formation and comet composition diversity.
Atmospheric Research Applications
Meteor shower observations contribute to atmospheric science research by providing data on upper atmosphere density variations, seasonal temperature fluctuations, and atmospheric chemistry at altitudes difficult to study through conventional methods.
Professional researchers coordinate with amateur observer networks to collect simultaneous observations from multiple geographic locations, enabling triangulation calculations for precise meteor altitude and velocity measurements.
Safety Considerations and Preparation Guidelines
Weather and Environmental Factors
September meteor viewing typically occurs during pleasant late-summer conditions, though overnight temperatures can drop significantly in many regions. Layer clothing systems allow for temperature adjustments throughout extended viewing sessions without interrupting observations.
Safety Preparation Checklist:
- Check weather forecasts for temperature drops and precipitation
- Inform others of viewing location and expected return times
- Carry emergency communication devices for remote locations
- Prepare backup shelter options for sudden weather changes
- Bring adequate food and water for 4-6 hour sessions
Vehicle and Equipment Safety
Remote viewing locations require additional safety planning including vehicle preparation, emergency supply kits, and navigation backup systems. Ensure vehicles can handle unpaved access roads and maintain sufficient fuel reserves for extended idling periods when warmth becomes necessary.
Red-filtered lighting preserves crucial night vision while providing necessary safety illumination for equipment handling and movement around viewing areas. Standard white flashlights destroy dark adaptation within seconds and require 20-30 minutes for vision recovery.
Maximizing Your Meteor Shower Experience
Timing Optimization Strategies
While peak activity occurs on September 9, the Epsilon Perseids maintain elevated meteor rates from September 5-15, providing multiple viewing opportunities. Monitor weather forecasts throughout this period and select the clearest available night rather than strictly adhering to peak date predictions.
Pre-dawn hours typically offer the highest meteor rates due to Earth’s orbital mechanics and reduced atmospheric interference. Plan viewing sessions from midnight until sunrise for optimal meteor frequency and brightness observations.
Group Viewing Considerations
Family and group meteor watching creates memorable shared experiences while improving overall observation effectiveness. Assign different sky quadrants to individual observers to maximize meteor detection coverage and reduce missed events.
Maintain quiet conversation levels that preserve the peaceful atmosphere while allowing communication about notable meteor sightings. Establish agreed-upon terminology for describing meteor characteristics including brightness levels, color variations, and trajectory directions.
Post-Event Analysis and Future Planning
Observation Data Review
Compile observation logs within 24-48 hours while memories remain fresh and accurate. Compare personal observations with official meteor shower reports and contribute data to citizen science databases when possible.
Digital photograph review often reveals meteors not consciously observed during real-time viewing sessions. Systematic examination of captured images can double or triple documented meteor counts from any given observation period.
Planning Future Meteor Events
The success of Epsilon Perseids observation often motivates interest in additional meteor shower events throughout the year. Major annual showers including the Geminids (December), Quadrantids (January), and Perseids (August) offer increasingly spectacular viewing opportunities for developing observers.
Maintain observation equipment in ready condition and continue monitoring astronomical calendars for unexpected meteor activity including sporadic fireballs and minor shower peaks. Advanced planning enables quick response to special astronomical events and optimal viewing condition windows.
Conclusion
The September 9 Epsilon Perseids meteor shower represents an excellent introduction to serious astronomical observation while offering experienced stargazers a peaceful alternative to major meteor events. The combination of favorable viewing conditions, accessible observation requirements, and genuine scientific value makes this event particularly rewarding for individuals and families interested in connecting with the cosmos.
Success in meteor observation depends more on patience, preparation, and dark sky access than expensive equipment or advanced technical knowledge. The Epsilon Perseids provide an ideal opportunity to develop observation skills, contribute to astronomical research, and experience the wonder of our solar system’s ongoing celestial mechanics.
Plan your September 9 viewing session now, gather friends and family for this shared astronomical adventure, and prepare to witness one of nature’s most reliable and beautiful phenomena. Clear skies and successful observations await those who venture into the darkness to witness the Epsilon Perseids’ celestial display.
News in the same category


Officer Breaks Car Window to Rescue Baby – Then Realizes It Was a Mistake

What Space Actually Smells Like, According to Astronauts and Scientists

Scientist Watches to See If Strange Interstellar Object Releases Any Probes

Prime views of the Andromeda Galaxy and Ceres—October 2

Prime views of the Andromeda Galaxy and Ceres—October 2

Gas Giants of the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus & Neptune
YouTuber destroys new iPhone Air with a blowtorch to test its durability

GameStop issues promising statement following Xbox Game Pass price hike

1st solar eclipse of 2025 puts on stunning show for skywatchers around the world (photos)

10 Safest Countries to Visit in Europe
Majestic Peaks: Top 10 Mountains to Visit in Europe
Explore the Best of Britain: 12 Epic UK Road Trip Ideas

Tomorrow Island (Russia) and Yesterday Isle (USA) Are Just Three Miles Apart But There’s a 21-Hour Time Difference Between Them

The Mighty Moss: Nature’s Unsung Superhero

Demystifying Oxygen Production: Oceans vs. Amazon Rainforest

Bizarre radio signals that defy physics detected under Antarctica: ‘It’s one of these long-standing mysteries’

Do Not Do This On Your Glass Stove
News Post

A simple tip on how to grow ginger using cement bags, never had such a good yield of ginger

Blanching pork in boiling water, you think it's clean but it absorbs more dirt: This is the right way to do it

Married at First Sight UK fans crown 'best match' after two weeks

Selena Gomez’s kidney donor, Francia Raisa, addresses wedding snub and feud rumors

David Ortiz sparks awkward moment on Fox postgame show: ‘Sounds like Hitler’

Crabgrass for Hair Loss: Natural Remedies and Uses
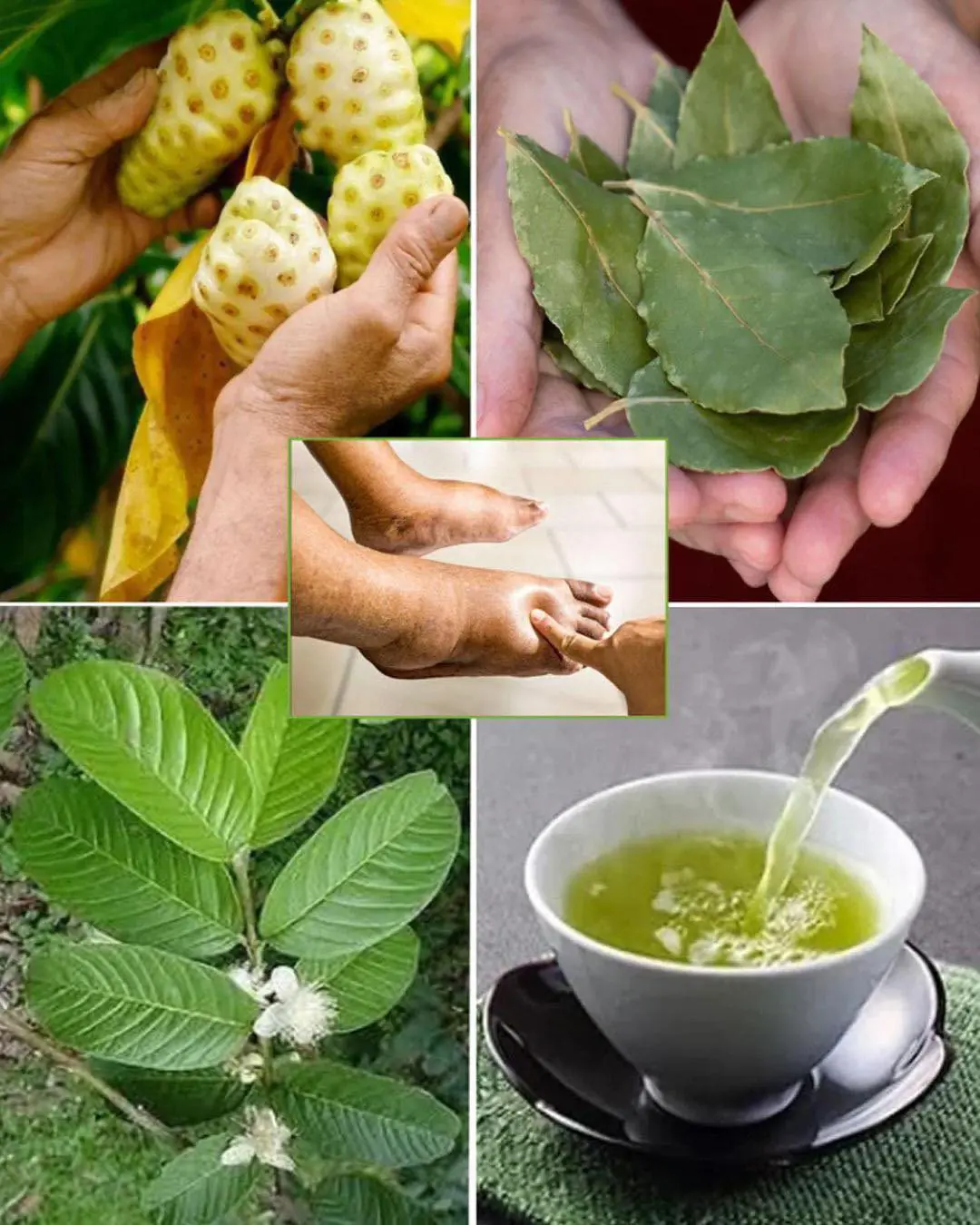

The Ultimate Healing Tonic: A Powerful Drink to Combat Swollen Feet, Diabetes and Poor Circulation
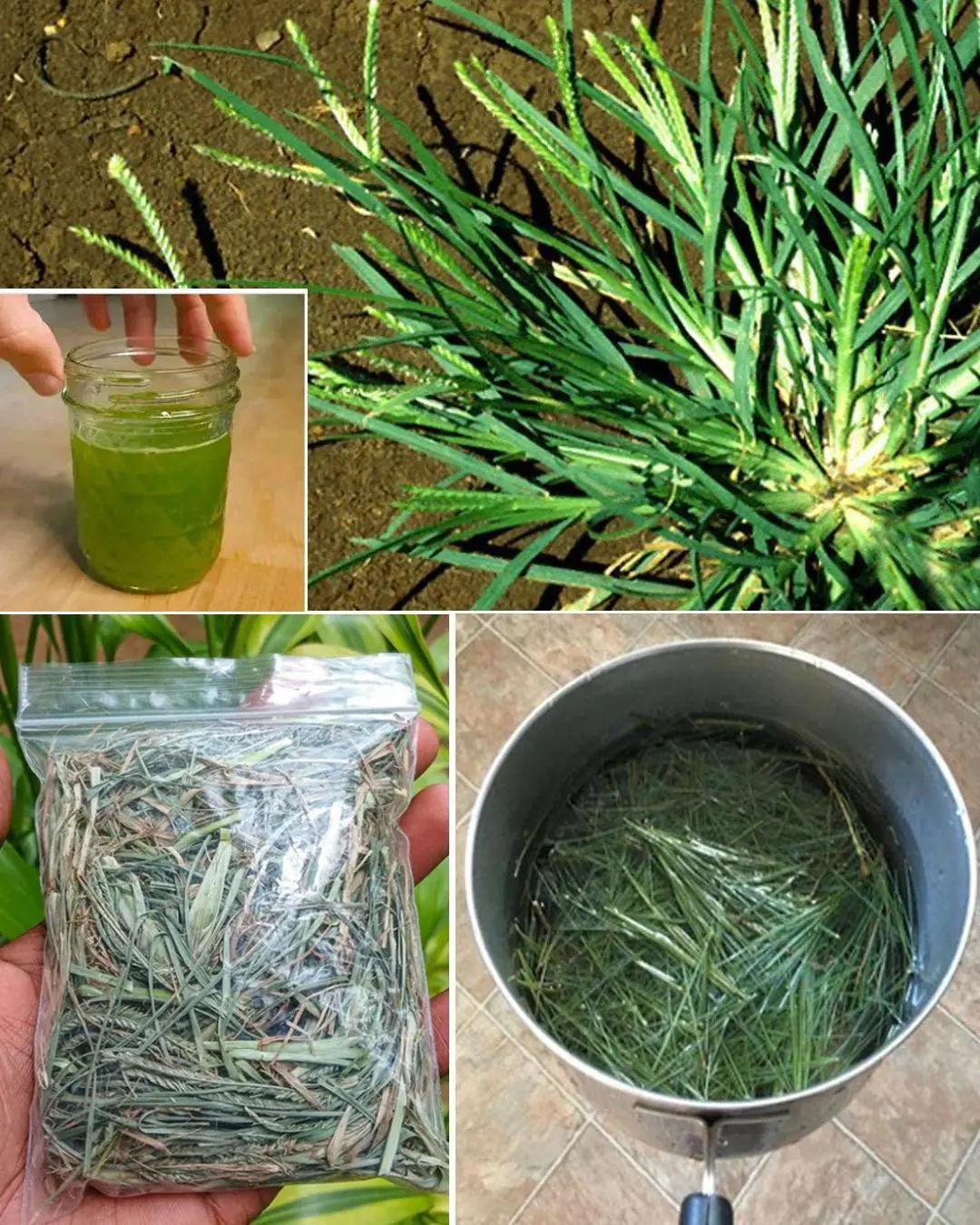

Goosegrass: Health Benefits and Uses
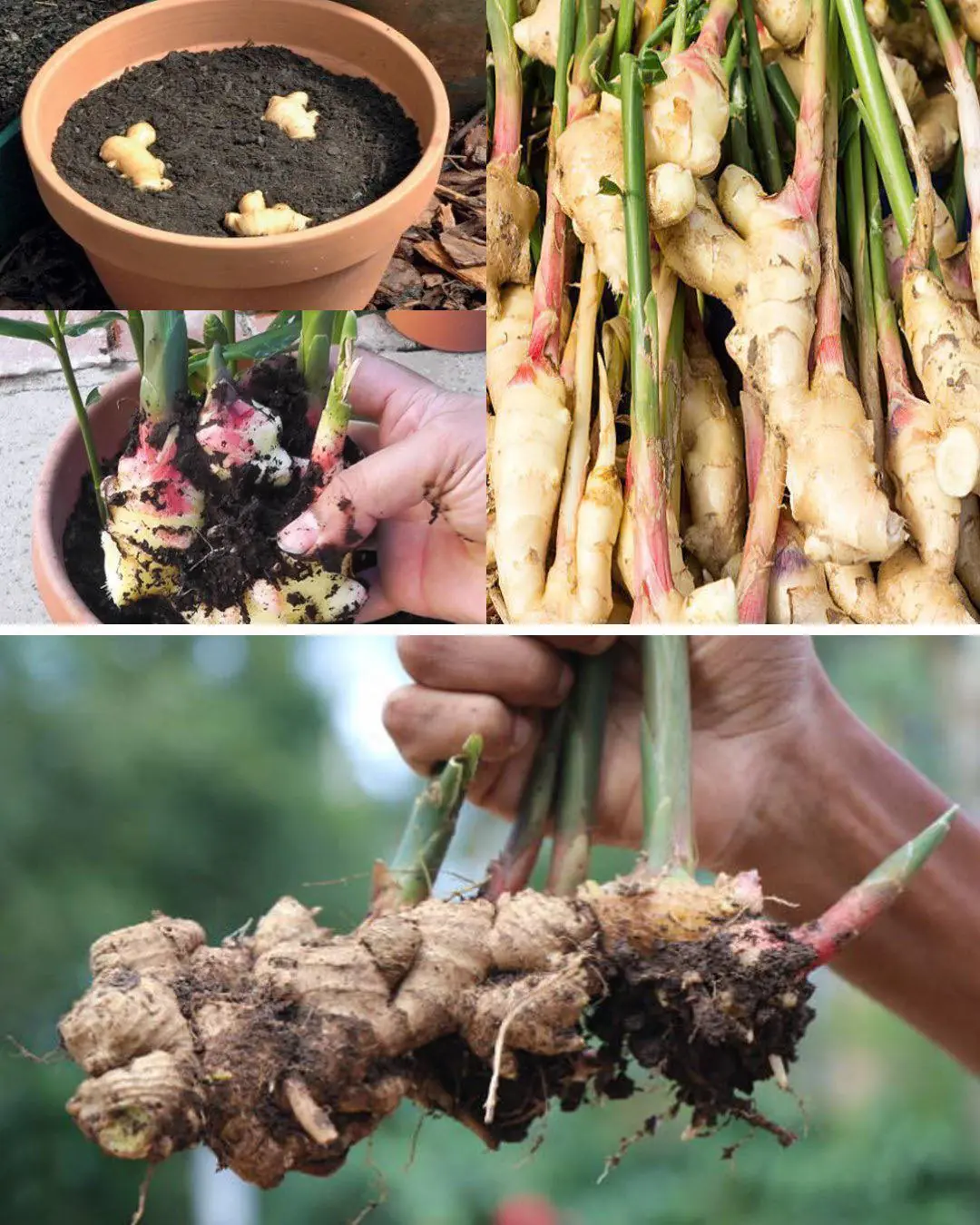

How to grow ginger at home to have an endless supply (and make it flower)
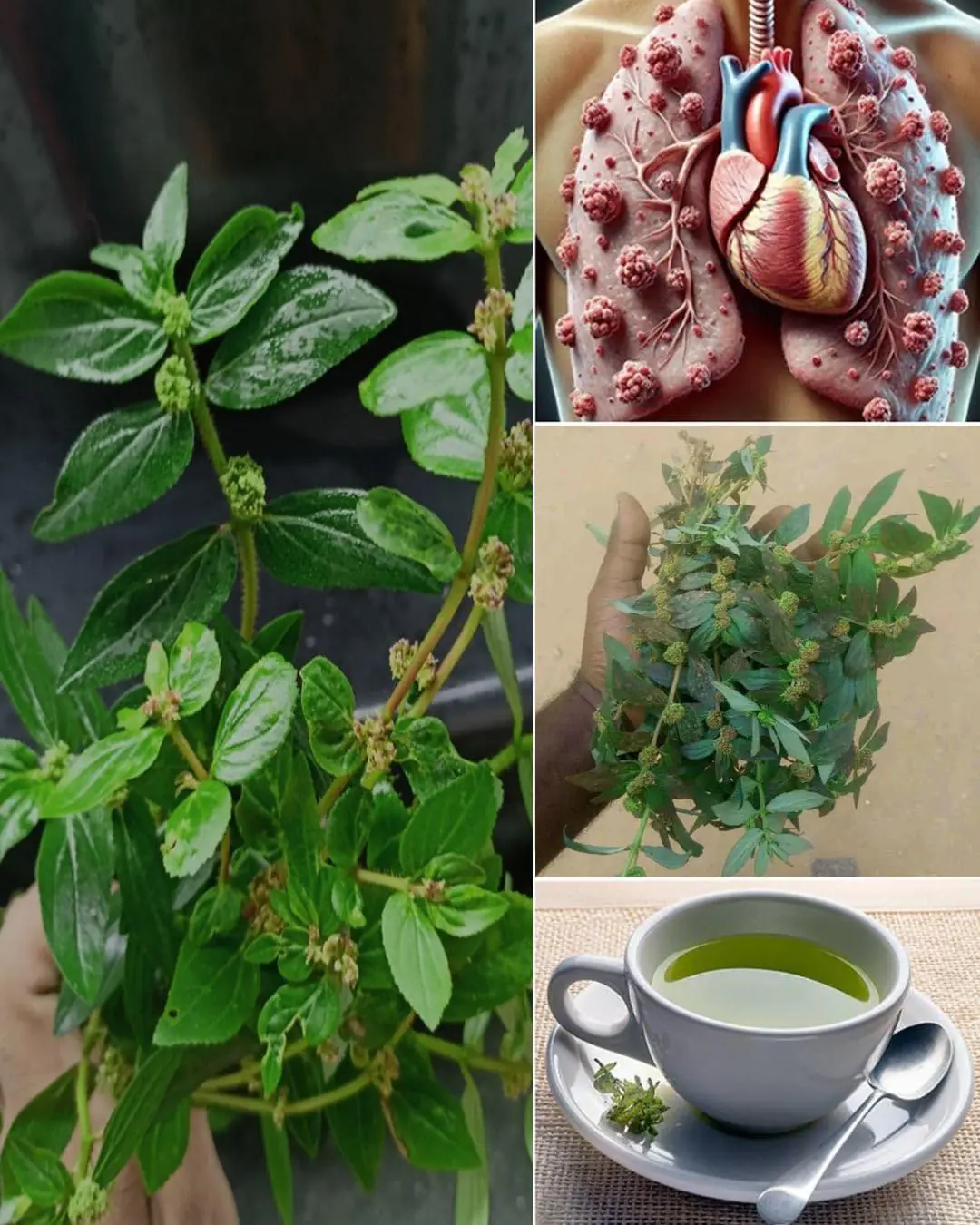

Asthma Plant Tea – Benefits and Uses of Euphorbia hirta
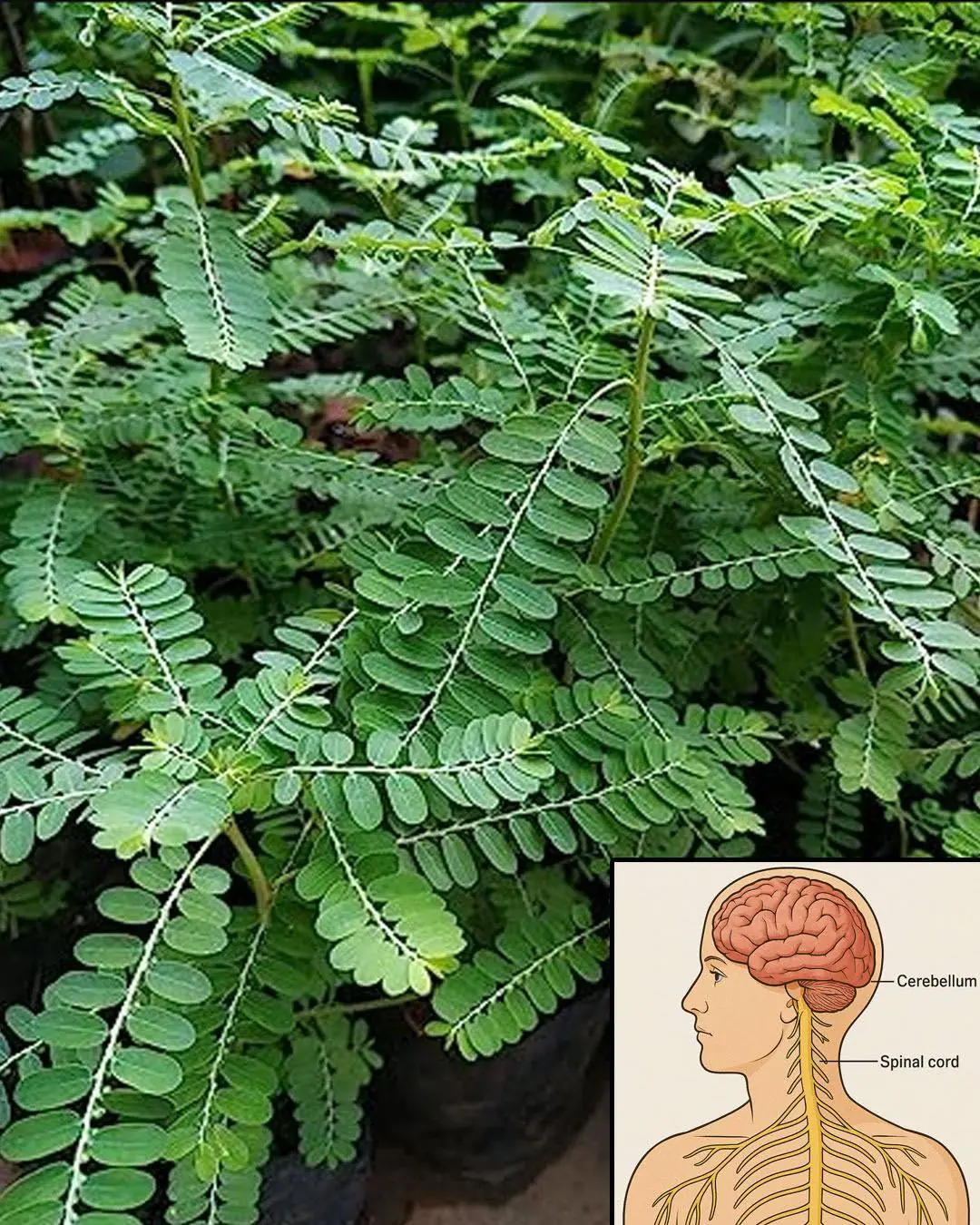

Chanca Piedra (Stonebreaker): Benefits and Uses
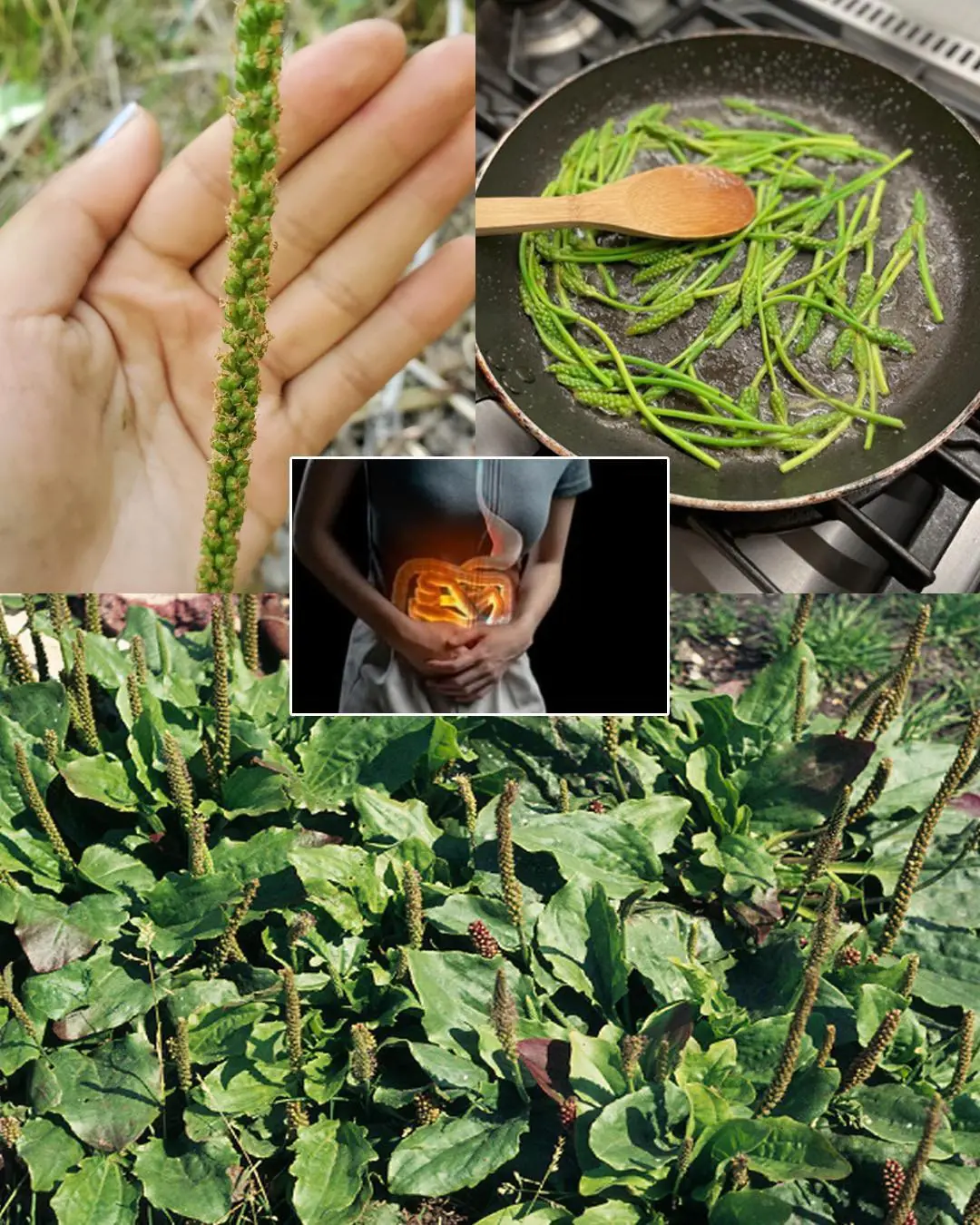

7 benefits and uses of Plantago Major
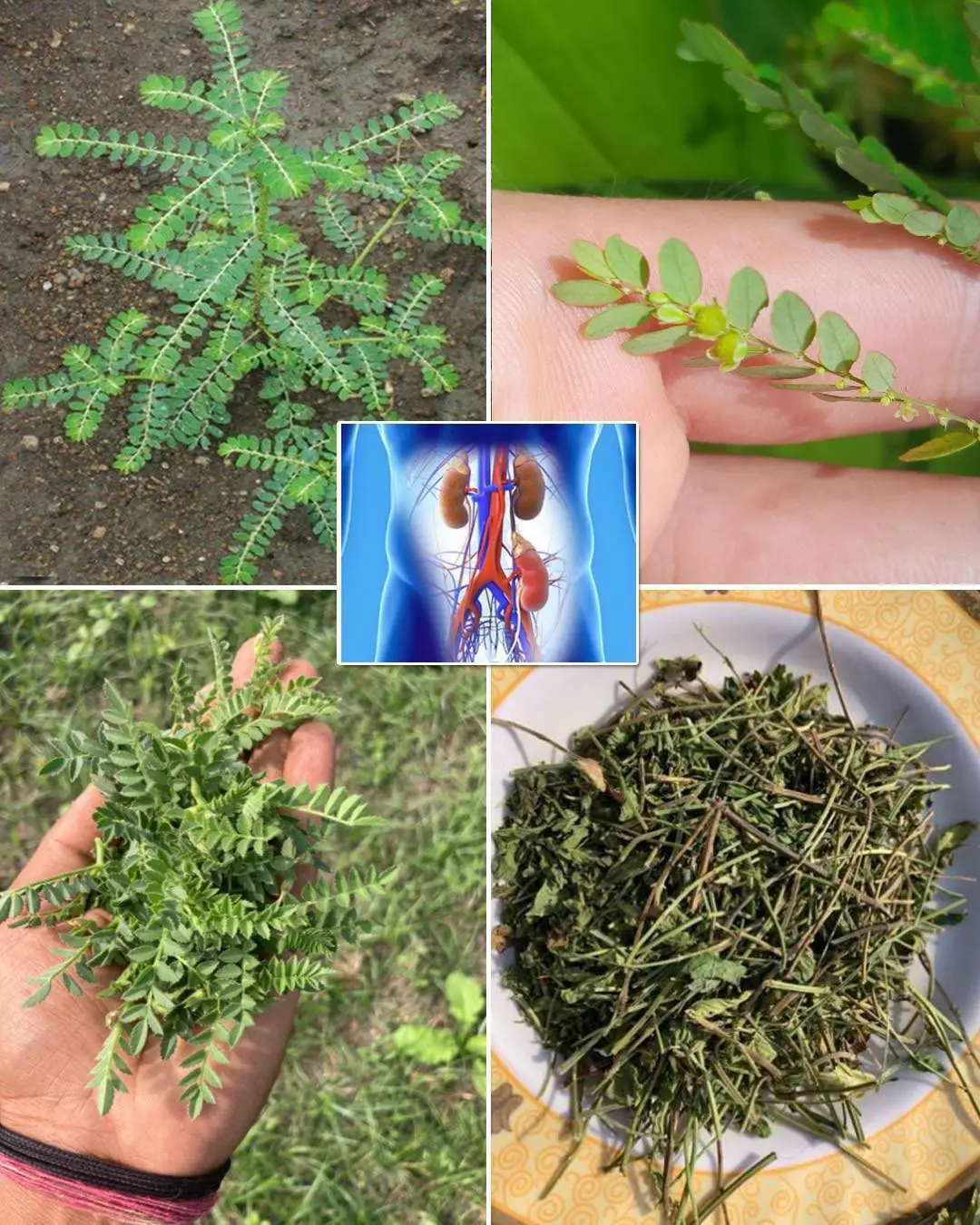

Chanca Piedra (Stonebreaker): Benefits and Uses
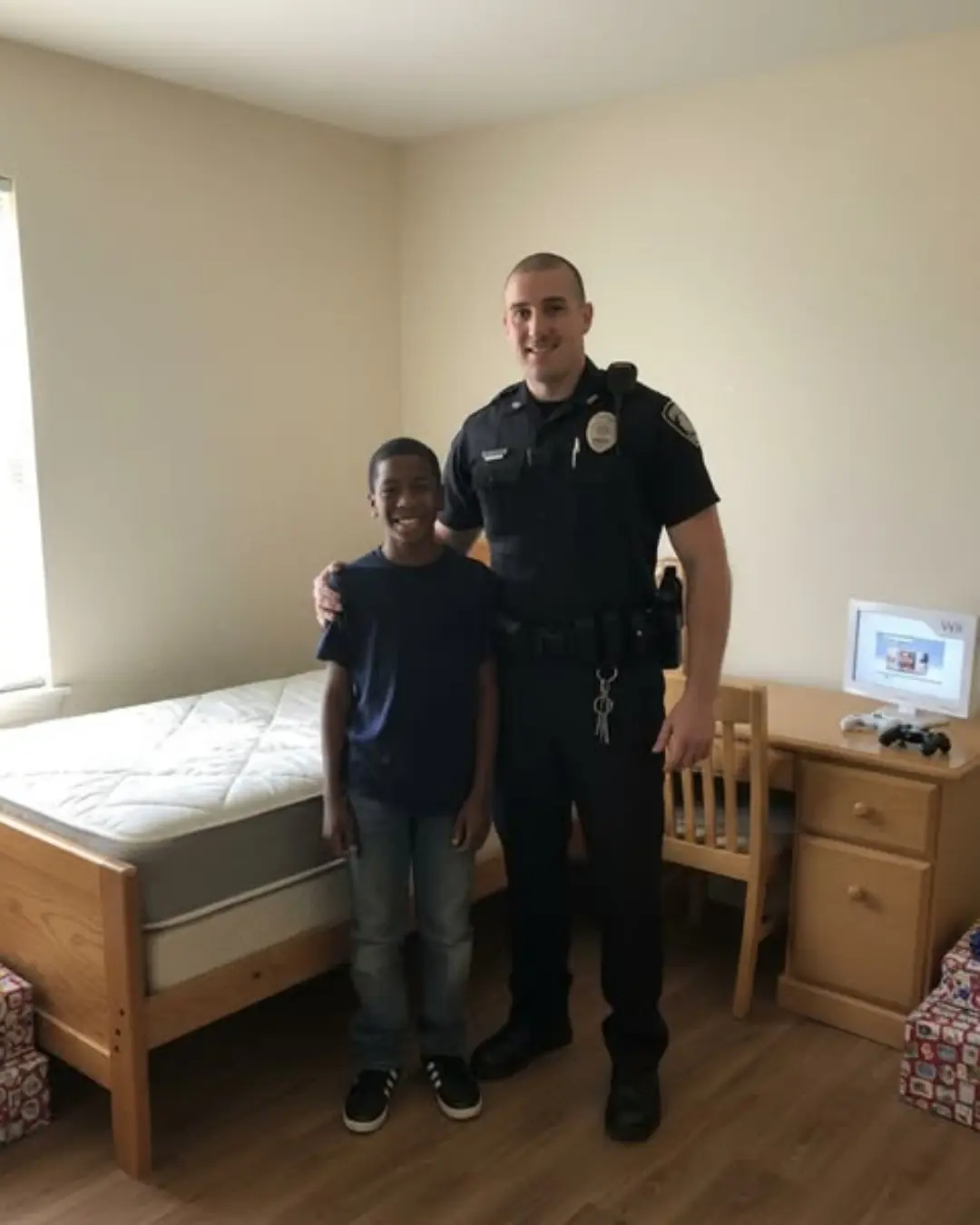

A Call for Help at 2 AM: How One Officer Changed a Boy’s Life with Compassion
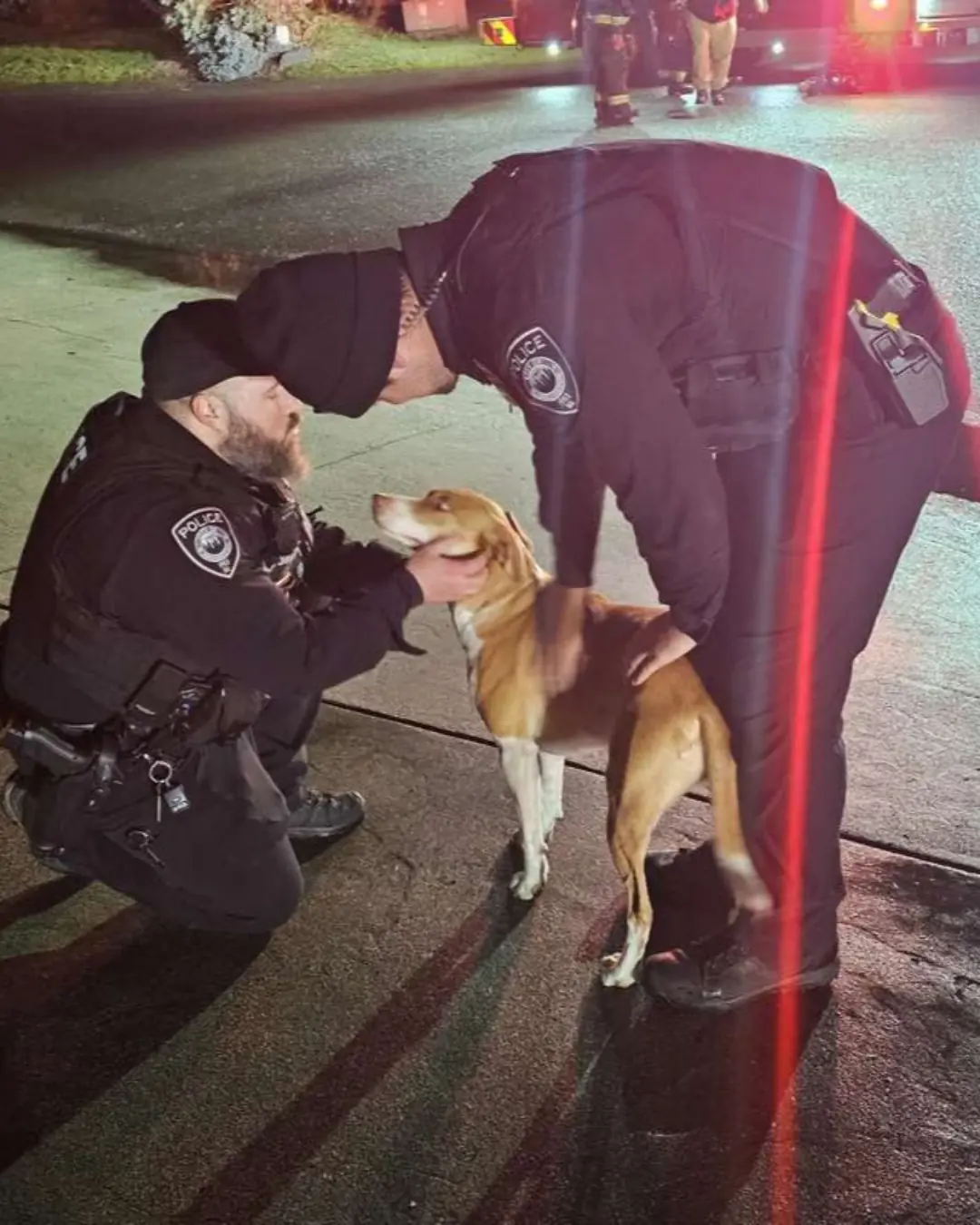

Ten Minutes From Tragedy—A Dog’s Warning Changed Everything!

Teen Builds $500 Dialysis Machine That Works Faster Than Hospital Models
A Split-Second Decision: Mother’s Quick Thinking Saves a Child
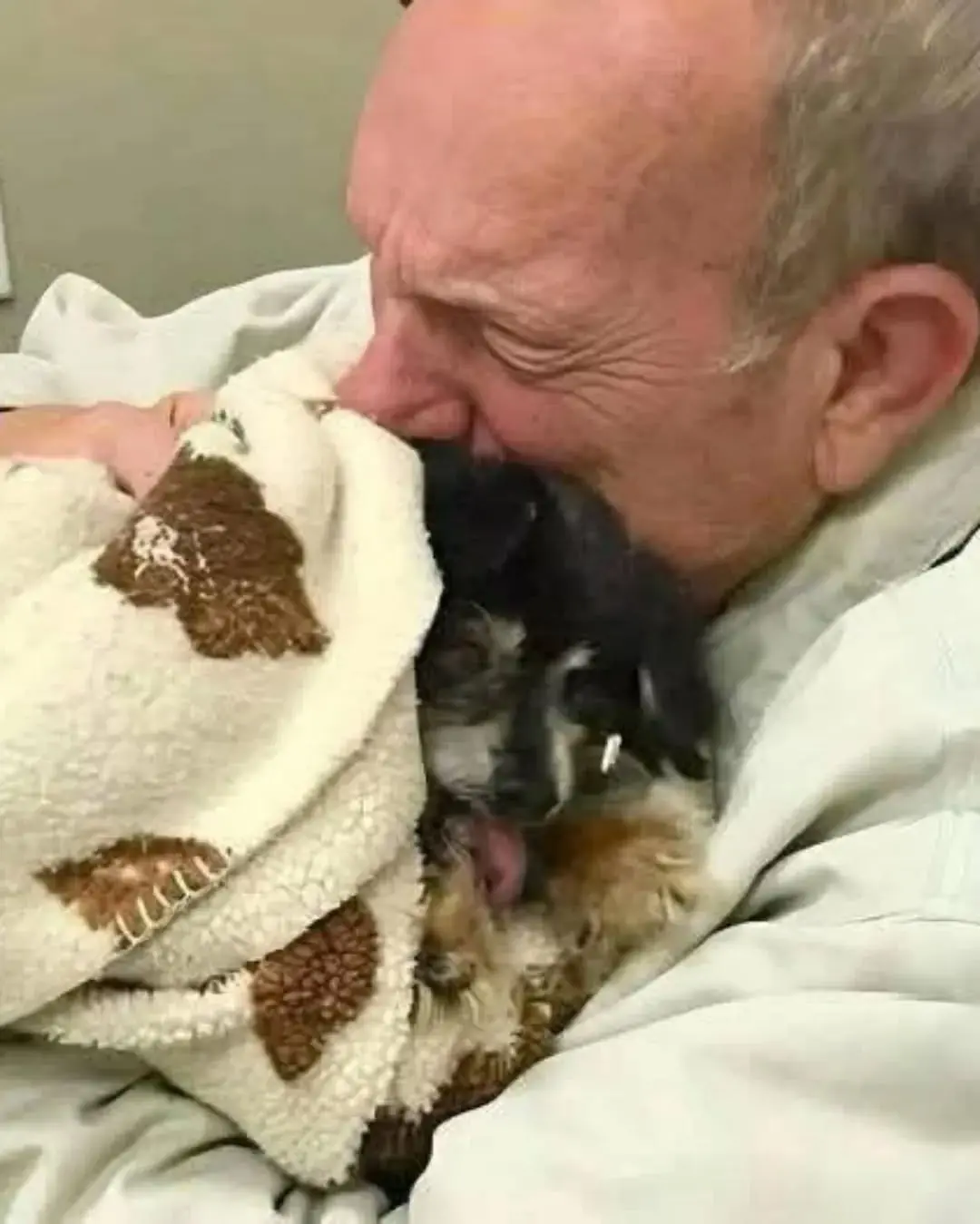

A Letter from My Doggy Heart
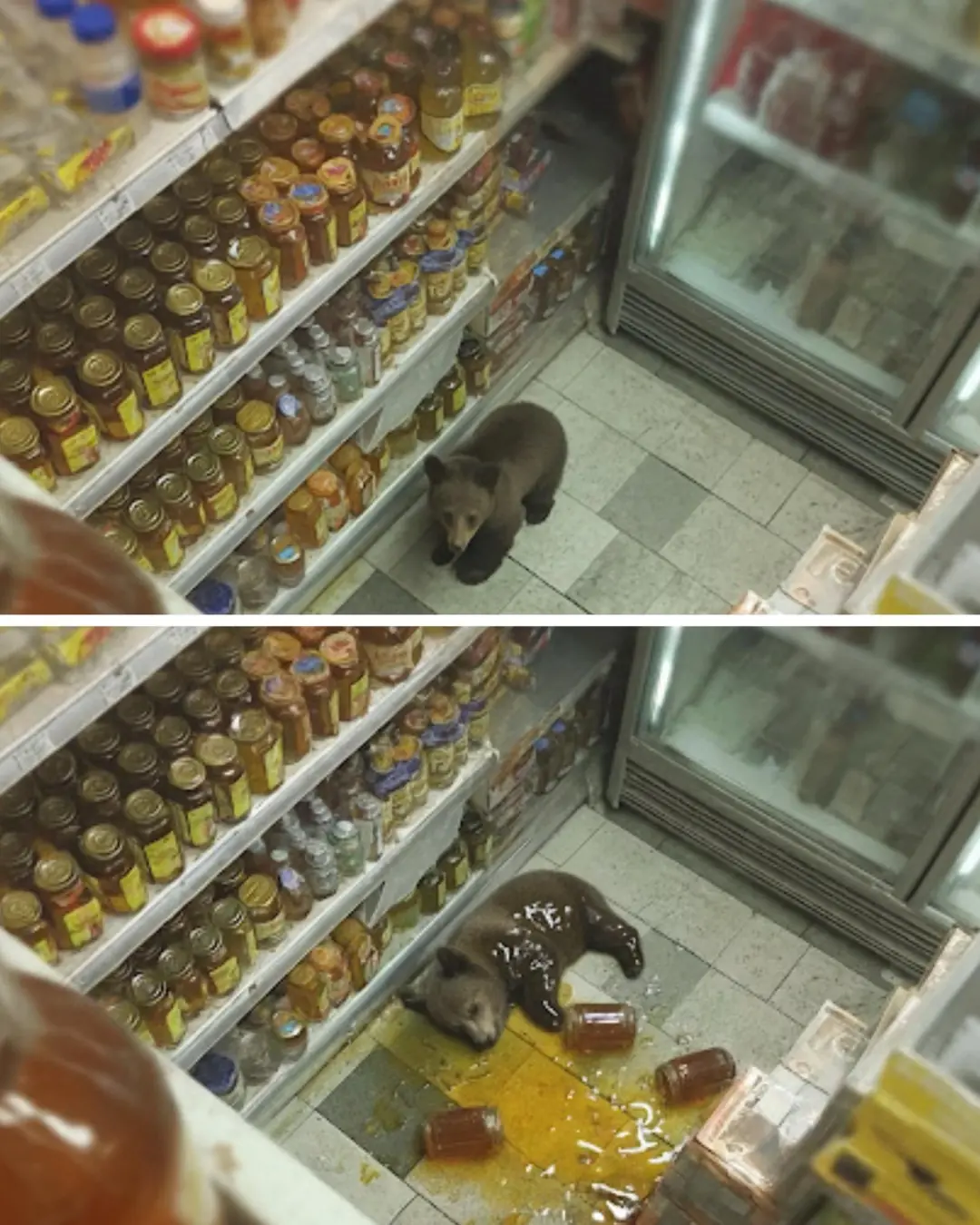

The Honey Heist: Bear Cub Breaks Into Store and Naps After Feast
