
Germany’s 95% Renewable Power Day: Progress, Challenges, and Lessons for the Future
On May 8, 2016, Germany reached a symbolic turning point in its transition toward a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. On that day, the country’s rapidly expanding network of wind turbines and solar arrays produced an unprecedented amount of electricity, pushing renewable generation to cover up to 95% of Germany’s total power demand. This extraordinary achievement was more than an impressive statistic — it demonstrated the capabilities of a modern grid powered primarily by renewable sources.
The abundance of natural energy created a unique situation: supply surged far beyond national consumption. Because the electrical grid must remain perfectly balanced between production and demand, operators were forced to make rapid adjustments. As a result, wholesale electricity prices didn’t simply fall — they plunged into negative territory for several consecutive hours. In practical terms, this meant that instead of paying for power, certain large-scale consumers were paid to use it.
Industrial plants, manufacturing facilities, and other energy-intensive operations benefited the most. They were encouraged to ramp up consumption to help absorb the surplus, stabilizing the grid at a time when renewable generation was peaking. While consumers receiving money to use electricity may sound unusual, events like this highlight the complex realities of integrating massive amounts of renewable energy into traditional power systems.
Germany’s milestone also revealed the logistical challenges of a renewable-powered grid. Wind and solar energy fluctuate with the weather, making it difficult to match production precisely to real-time demand. Without sufficient energy storage, flexible consumption strategies, or advanced digital grid management, oversupply can occur — leading to market distortions such as negative pricing.
Energy analysts stress that the 2016 event was not merely a curiosity. Instead, they view it as an early glimpse into the future of electricity markets worldwide. As countries continue to expand their renewable capacities, episodes of oversupply and negative prices are expected to become more common. This makes smart grids, large-scale battery storage, and dynamic load-shifting technologies increasingly essential for maintaining stability and maximizing the benefits of clean energy.
May 8, 2016 remains a landmark moment in Germany’s Energiewende, the country’s long-term strategy to phase out fossil fuels and nuclear power. The day Germany effectively paid people to use electricity illustrated both the remarkable potential of renewables and the need for innovation in energy management. It stands as a powerful example of how nations can move toward a cleaner future — and the evolving challenges that come with it.
News in the same category


Why Pineapple Skin Can Withstand a 1,000°C Metal Ball

Stanford Scientists Achieve Breakthrough in Curing Type 1 Diabetes in Mice, Paving the Way for a Permanent Cure

The Healing Power of a Woman’s Voice: How Sound Affects the Nervous System

How Recurrent UTIs Can Lead to Serious Kidney Complications and What You Can Do About It

How Playing a Musical Instrument Boosts Brain Power and Cognitive Health
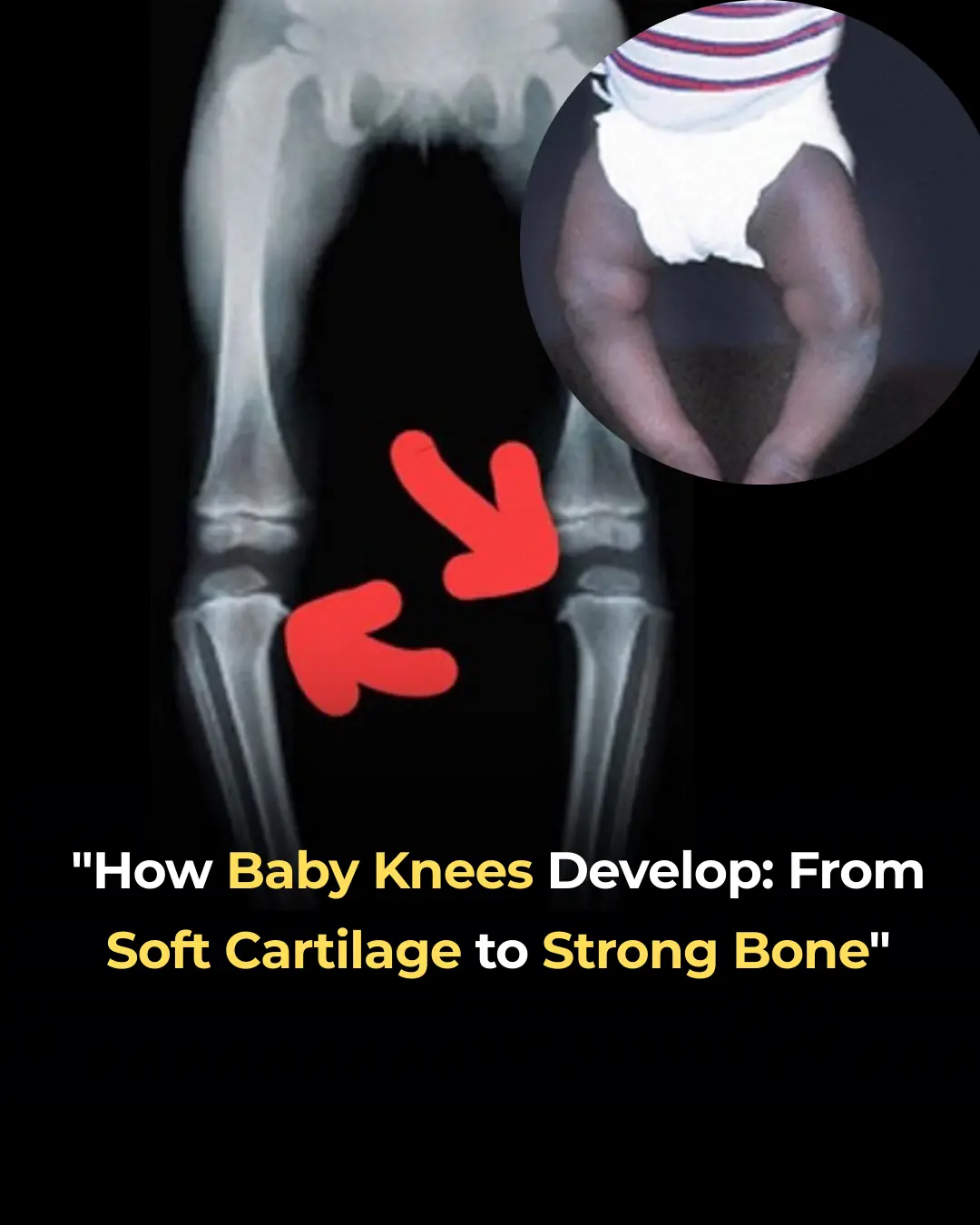
How Baby Knees Develop: From Soft Cartilage to Strong Bone

How Daily Kefir Consumption Can Help Alleviate Lactose Intolerance and Improve Gut Health
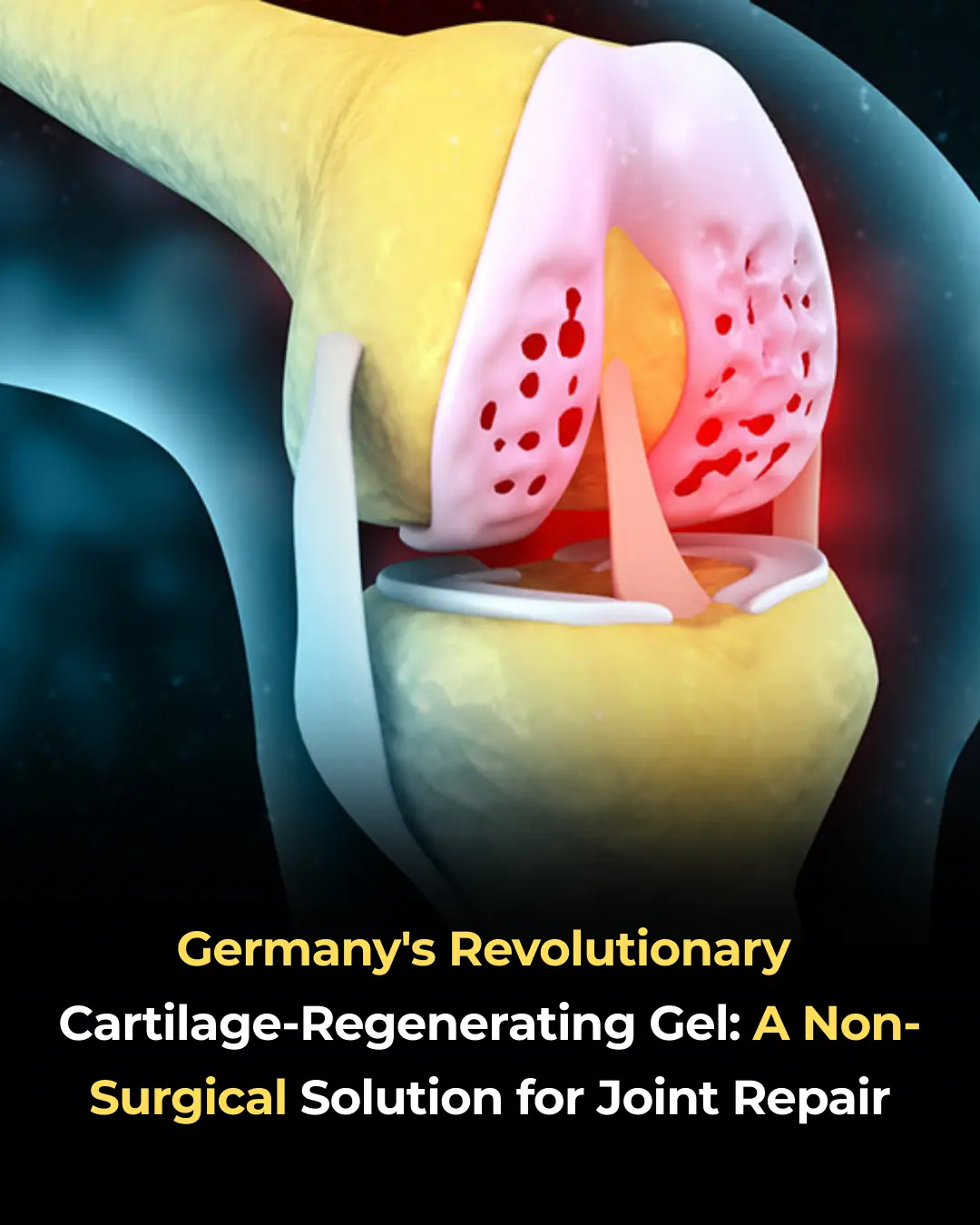
Germany's Revolutionary Cartilage-Regenerating Gel: A Non-Surgical Solution for Joint Repair

David Choe’s Gamble and the Impact of Childhood Trauma on the Brain

A Forgotten Car’s Journey: Rediscovered, Remembered, and Recycled
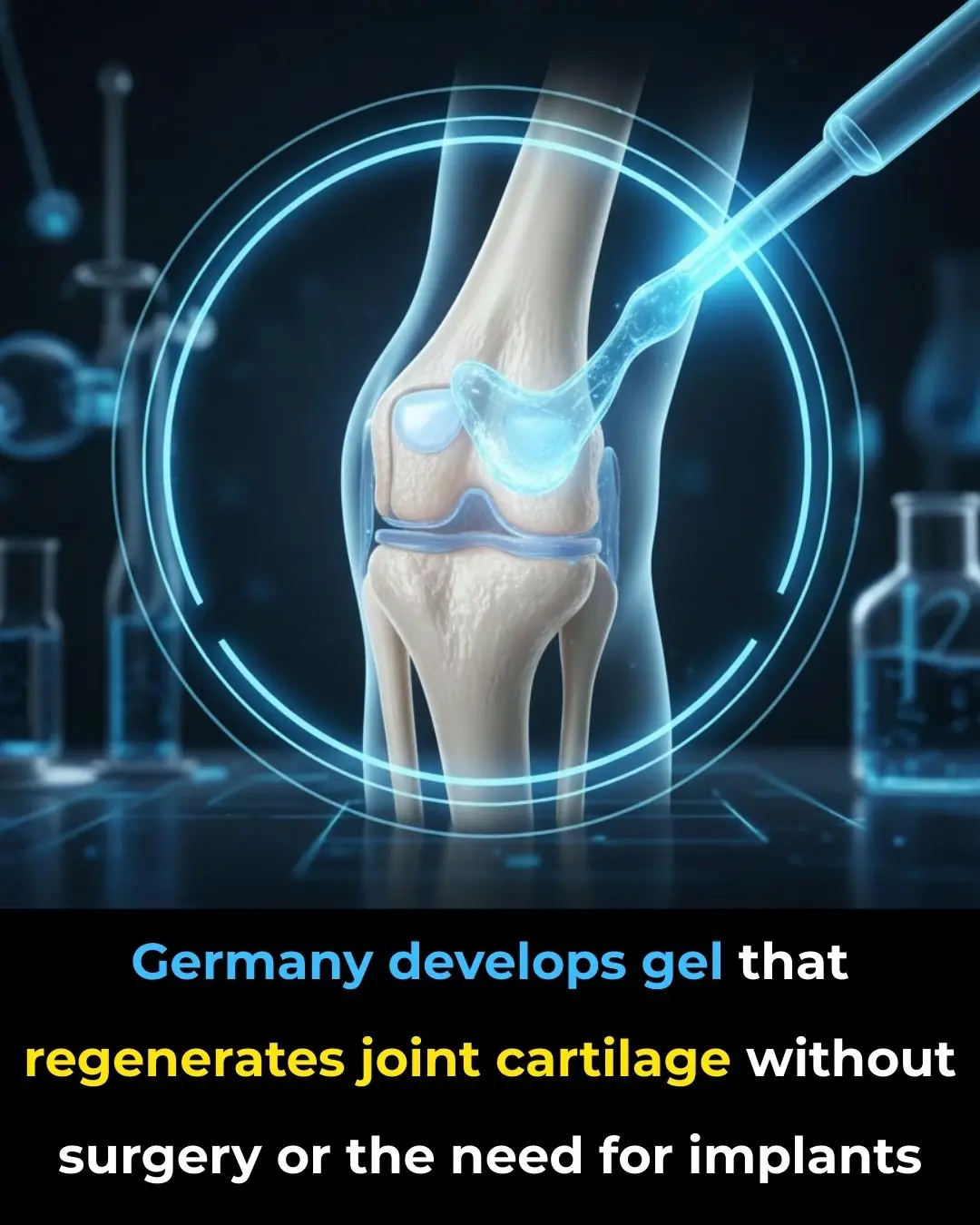
Revolutionary Gel from Germany Offers Non-Surgical Solution for Cartilage Regeneration

From Playground to Graduation: The Enduring Power of Childhood Friendship

The Spruce Pets – Creative ways to feature cats and dogs in weddings.

The Water Man of Tsavo: A Hero's Mission to Save Wildlife from Drought

Better Sleep, Healthier Spine: Why You Should Avoid Stomach Sleeping

Plumbing Mayhem on Brown Friday: How Holiday Feasts Overload Pipes

Health Alert: Contaminated DermaRite Products Recalled Across U.S. and Puerto Rico

Into the Darkness: A Bioluminescent Jellyfish Illuminates the Deep Ocean
News Post

Rosemary: The Ancient Herb With Powerful, Underestimated Benefits for the Human Body

Doctors Reveal What Eating Peanuts Can Really Do to Your Body

Mexico frees 350 captive dolphins

Why Pineapple Skin Can Withstand a 1,000°C Metal Ball

Tradescantia zebrina: The Colorful Healer Hidden in Plain Sight

Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia): 14 Surprising Benefits and How to Use It at Home

Stanford Scientists Achieve Breakthrough in Curing Type 1 Diabetes in Mice, Paving the Way for a Permanent Cure

Papaya Seeds for Gut Health: The Simple Secret Inside Your Fruit

The Healing Power of a Woman’s Voice: How Sound Affects the Nervous System

How Long Can Frozen Meat Be Stored? Here’s the Answer

My nana swears by applying baking soda to her face. Here's her 3 methods and how they work

Vinegar is the key to streak-free windows and shiny surfaces, but most use it wrong. Here's the right way to use it

How Recurrent UTIs Can Lead to Serious Kidney Complications and What You Can Do About It
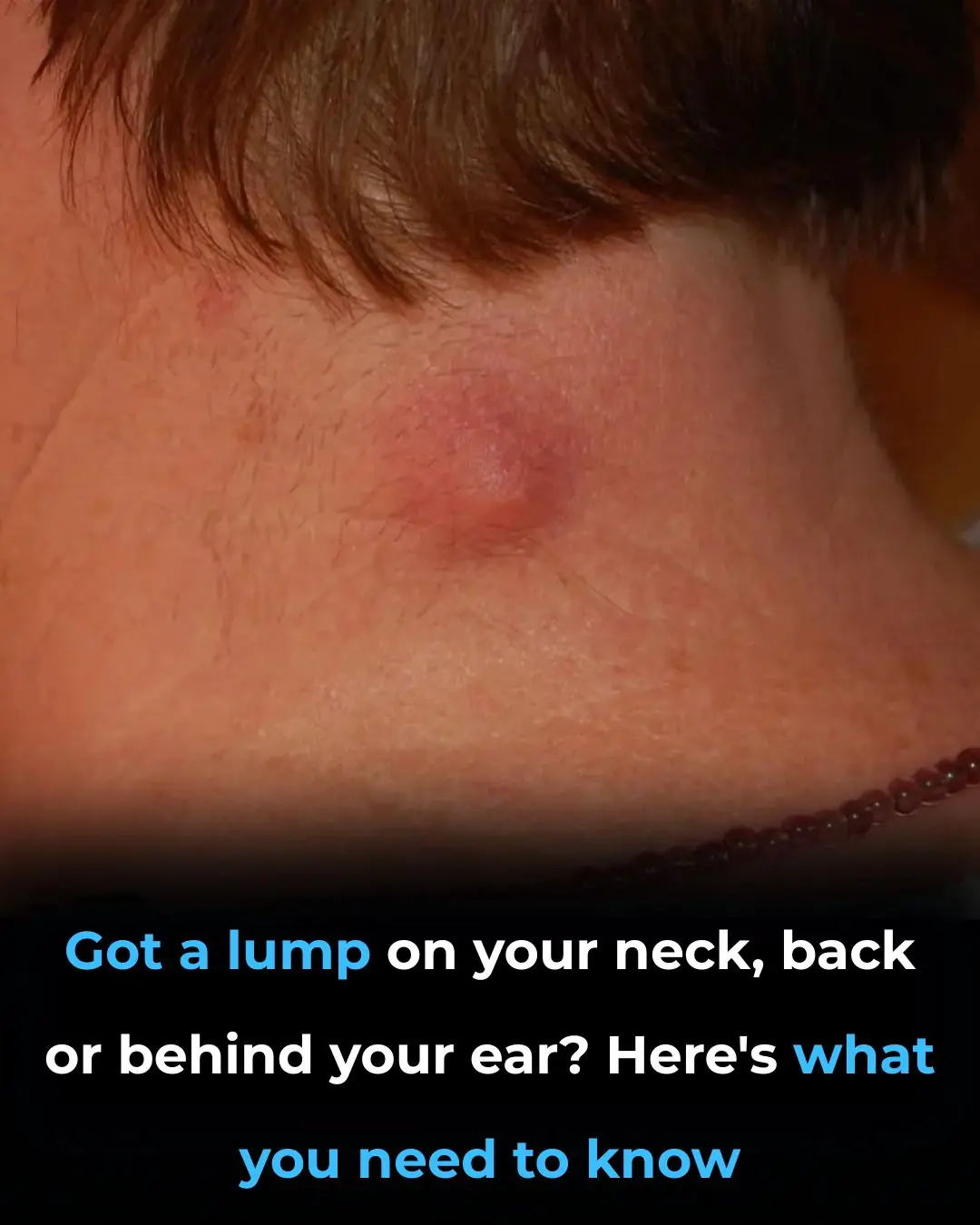
Got a lump on your neck, back or behind your ear? Here’s what you need to know

Kettles Covered in Limescale? Add This One Ingredient, Boil Once, and It Comes Out Spotless—No Scrubbing Needed

My nana taught me this hack to strengthen nails in 3 mins with 0 work. Here’s how it works

How Playing a Musical Instrument Boosts Brain Power and Cognitive Health
Nail salons don’t tell you this. What you should know before you apply your nail polish
3 Nighttime Warning Signs of Kidney Disease: Ignoring Them Could Cost You for Life
