He Is the Least Likely to Have This Health Problem, According to Researchers
When it comes to health risks, genetics can play a much bigger role than many people realize. While lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and smoking remain critical, scientists have also been exploring more unexpected influences—one of them being blood type.
Surprisingly, multiple large-scale studies suggest that one blood group may be less likely to develop certain types of cancer compared to others. This has sparked growing interest among researchers and the general public alike.
So, who fits this description?
According to current evidence, men with blood type O appear to have a consistently lower risk for several major cancers when compared with men who have blood types A, B, or AB.
Let’s take a closer look at what the research actually shows, why this connection may exist, and what it really means for everyday health.
The Connection Between Blood Type and Cancer Risk
Blood type is determined by specific antigens found on the surface of red blood cells. While these antigens are best known for their importance in blood transfusions, they also influence several biological processes that are closely linked to cancer development, including:
-
Immune system responses
-
Levels of chronic inflammation
-
Cell adhesion, or how cells stick together
-
The ability of abnormal cells to spread within the body
Because cancer involves uncontrolled cell growth, immune evasion, and metastasis, scientists have long suspected that blood type antigens could play a role in influencing cancer risk.
In recent years, growing epidemiological data has begun to support this theory.
Why Blood Type O Stands Out
Across multiple international studies, individuals with blood type O—particularly men—have shown:
-
A lower risk of stomach (gastric) cancer
-
A reduced risk of pancreatic cancer
-
A slightly lower risk of colorectal cancer
-
In some populations, lower overall cancer-related mortality
These findings do not suggest that blood type O offers complete protection. However, statistically speaking, men with blood type O appear to be less likely to develop certain cancers compared to those with other blood groups.
In other words, he is not immune—but his baseline risk may be lower.
What Makes Blood Type O Different?
Researchers believe several biological mechanisms may help explain this apparent protective effect.
1. Lower Levels of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic, low-grade inflammation is a known driver of cancer development. Some studies indicate that people with blood type O tend to have lower baseline inflammatory markers, which may reduce long-term cancer risk.
2. More Effective Immune Surveillance
The immune system plays a crucial role in identifying and destroying abnormal or pre-cancerous cells. Type O individuals may have a more robust immune response, allowing their bodies to detect and eliminate problematic cells earlier.
3. Reduced Cell Adhesion and Tumor Spread
Cancer cells spread by detaching from their original site and reattaching elsewhere in the body. Certain blood type antigens influence how easily cells adhere to tissues. Some evidence suggests that blood type O may make it harder for tumor cells to spread and establish new growths.
Which Blood Types May Have Higher Cancer Risk?
While blood type O appears to have a relative advantage, research has also identified elevated risks associated with other blood groups:
-
Blood type A has been linked to a higher risk of stomach and pancreatic cancer
-
Blood type AB may be associated with a higher overall cancer susceptibility in some studies
-
Blood type B shows mixed results, with risk varying by cancer type and population
It’s important to emphasize that these are statistical associations, not predictions for individuals.
A Critical Reality Check
Even if he has blood type O, that does not mean he is protected from cancer.
Lifestyle and environmental factors still play a far greater role in determining overall risk, including:
-
Smoking or tobacco exposure
-
Diet quality and nutrient intake
-
Physical activity levels
-
Body weight and metabolic health
-
Sleep patterns
-
Stress and environmental exposures
Blood type acts as a risk modifier, not a guarantee of protection or disease.
What He Can Do to Lower Cancer Risk Even Further
Regardless of blood type, the strongest defense against cancer remains daily lifestyle choices. Evidence-based strategies include:
-
Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fiber
-
Limiting processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks
-
Staying physically active on a regular basis
-
Maintaining a healthy weight
-
Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol
-
Getting regular medical check-ups and recommended screenings
When favorable genetics are combined with healthy habits, the protective effect becomes even stronger.
Why This Research Is Getting So Much Attention
This topic has gained popularity because it feels personal and easy to understand—most people know their blood type. Headlines suggesting “he is the least likely to have this health problem” naturally grab attention.
But the real value of this research lies in awareness, not reassurance.
Understanding relative risk can help people:
-
Take prevention more seriously
-
Make informed lifestyle decisions
-
Seek earlier screening and medical advice when appropriate
Those outcomes benefit everyone, regardless of blood type.
Final Thoughts
So, who is the least likely to have this health problem?
Based on current research, men with blood type O appear to have a lower risk of developing certain cancers compared to other blood groups. However, cancer risk is shaped by a complex interaction of genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Blood type may influence the odds—but daily choices still matter far more.
News in the same category

Eat Garlic Daily, But Avoid These 8 Common Mistakes That Ruin Its Benefits

The Leaf Everyone’s Talking About: Soursop Leaves and Their Potential Wellness Benefits

The Forgotten 100-Year-Old Golden Tea That Melts Cholesterol, Balances Blood Sugar, and Restores Kidneys

7 Benefits and Uses of Castor Oil

10 Reasons to pick purple dead nettle this spring

Discover How a Simple Cup of Rosemary and Ginger Tea Can Warm Your Body and Transform Your Daily Comfort

The One Bitter Leaf That’s Quietly Making Pillboxes Obsolete for Americans Over 60

7 Amazing Health Benefits of Banana Blossoms

7 Benefits of Corn Silk and How to Use It

Cocklebur Uncovered: The Surprising Traditional Uses of Xanthium Strumarium

Why Everyone’s Talking About Moringa : The Nutrient-Packed “Miracle Tree” That Could Transform Your Daily Wellness

7 benefits and uses of Plantago Major

12 Powerful Benefits of Moringa Seeds

Exploring the Traditional Uses and Potential Wellness Benefits of Prickly Lettuce Leaves (Lactuca serriola)

Pumpkin Seeds for Health: Natural Remedies, Recipes, and Benefits
11 Benefits of Dandelion Roots

7 Essential Leaves to Naturally Improve Your Eye Health

Green Smoothies and Weight Management: What Cucumber and Lemon Drinks Can Realistically Do
News Post

She Thought He Was Just a Cop—Until She Found the Key That Changed Everything

I Married a Rich Old Man to Save My Father—On Our Wedding Night, He Removed His Mask

She Didn’t Come Home for 10 Years—Then She Heard the Pilot’s Voice and Broke Down in Tears

My Husband Planned a Romantic Dinner for His Mistress—So I Reserved the Next Table and Brought Her Husband

My Husband Was Cheating—and the Pool Gave Him Away

He Walked Into Court With His Lover—Then the Judge Spoke, and Everything Became Hers
🚨 Recurrent Yeast Infections? STOP Doing These Things Immediately!
Doctors Are Amazed: Two Vegetables That Boost Collagen in the Knees and Relieve Joint Pain
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Dust cinnamon lightly on your lips. It works so fast it feels wrong

Longevity doctor who ‘reversed his biological age’ shares advice for people over 30

Doctors warn 5 everyday habits are slowly killing your kidneys
Eliminate Mucus, Phlegm in the Throat and Nose, and Rhinitis Naturally: Powerful Home Remedies
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Eliminate Fungal Infections (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Naturally and Fast

Eat Garlic Daily, But Avoid These 8 Common Mistakes That Ruin Its Benefits
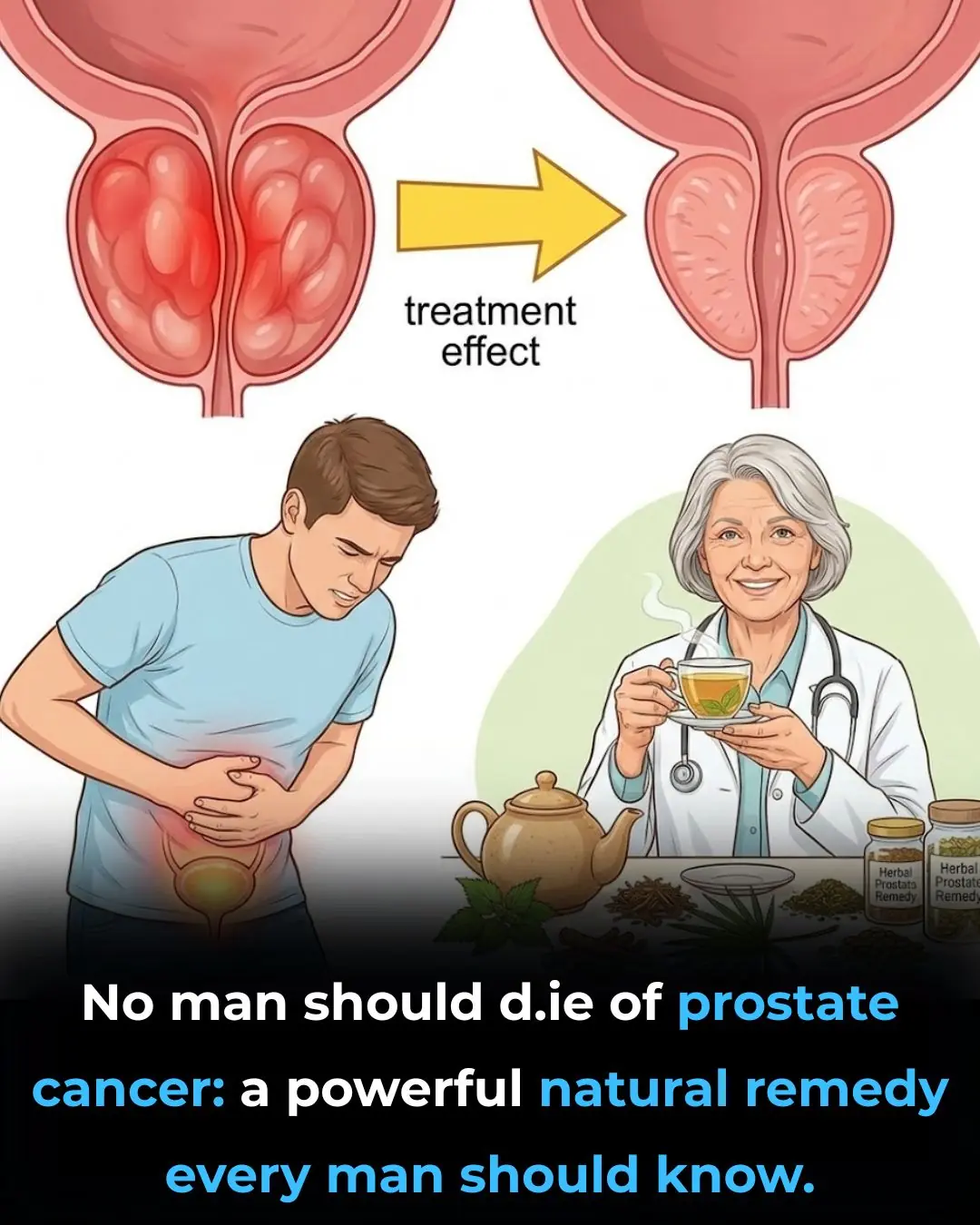
Natural Prostate Remedy: An Effective Herbal Option for Urinary Health
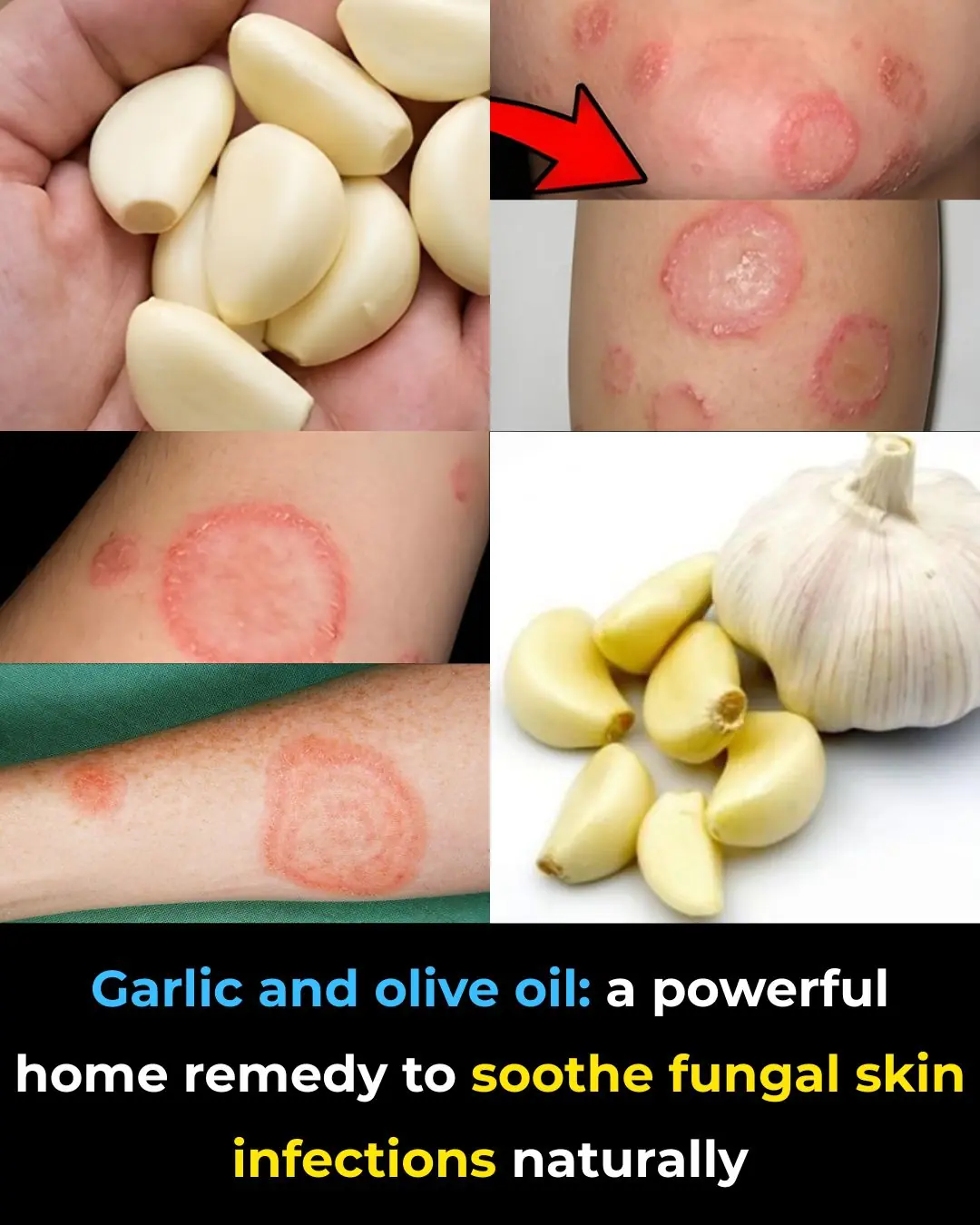
Garlic and Olive Oil: A Natural Way to Soothe Annoying Fungal Skin Infections at Home
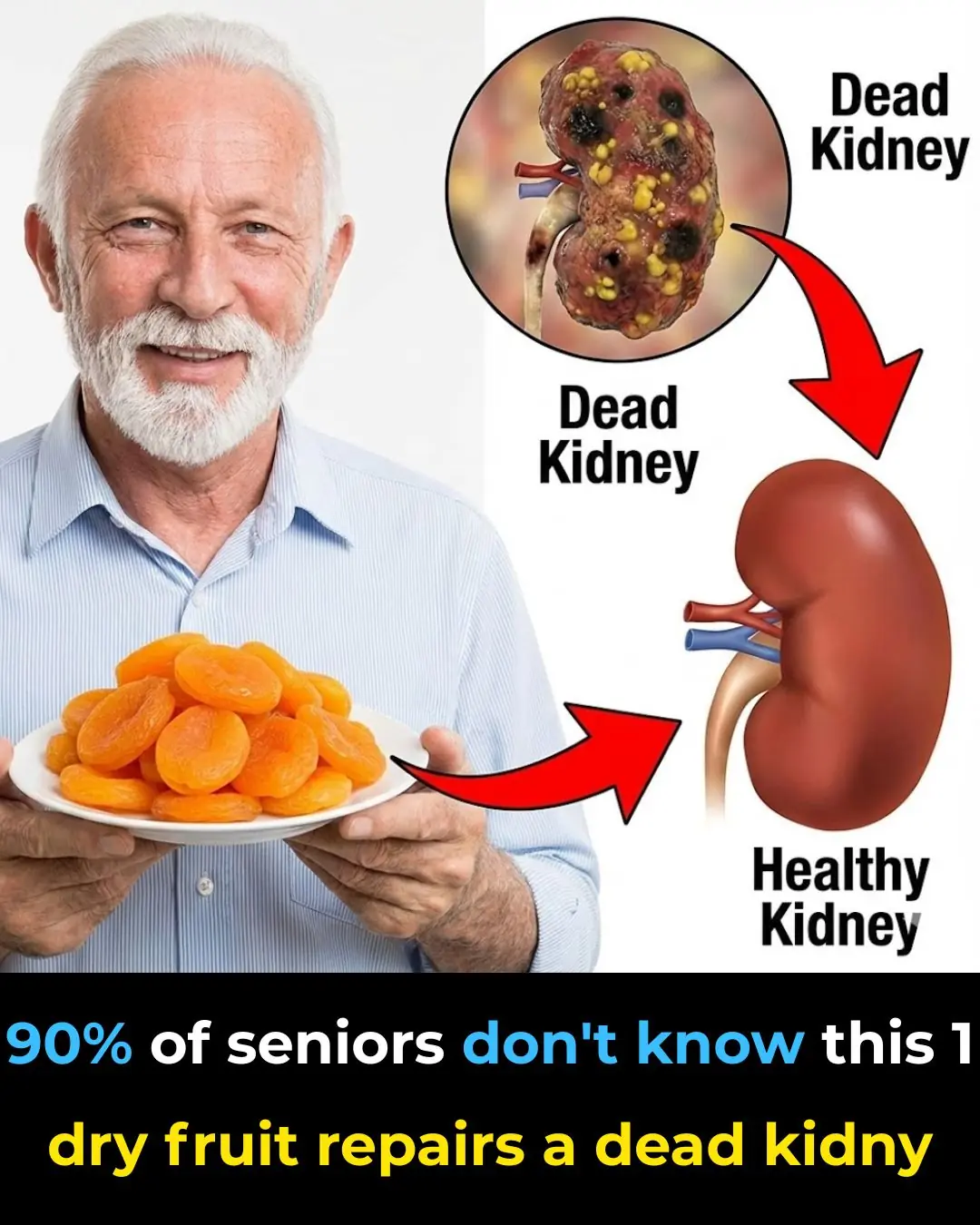
Top 5 Dried Fruits to Explore for Supporting Kidney Health After Age 60