
How To Get Rid Of Eczema: 13 Natural Remedies Backed By Research
How To Get Rid Of Eczema: 13 Natural Remedies Backed By Research
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, can affect individuals of all ages, though it is particularly common in young children and infants. It manifests in various forms, most of which cause red, itchy skin rashes. Persistent flare-ups can lead to thickened, scaly skin, and sometimes even fluid-oozing, blister-like bumps that form crusty scabs.
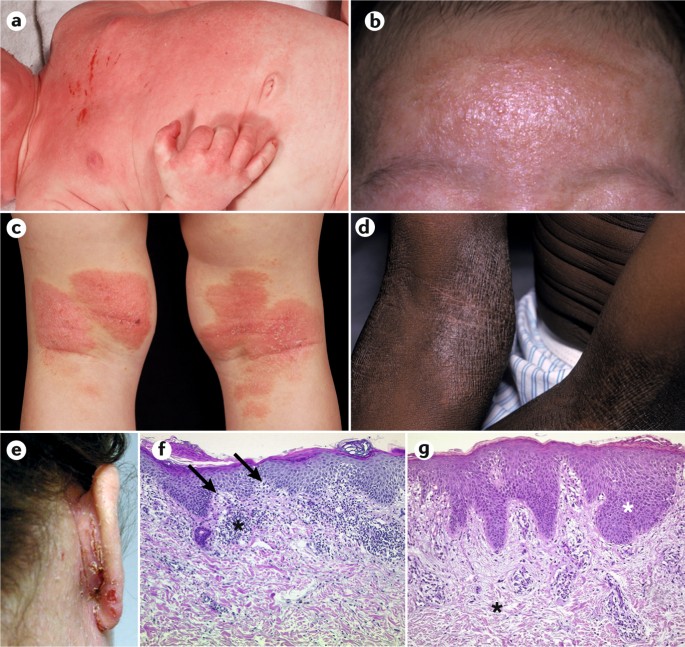
Atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema, can appear anywhere on the body. It frequently causes itchy patches on the hands, feet, upper chest, around the neck and face, and even on the scalp. The condition can be especially painful and irritating when it occurs in the creases of the elbows and knees due to constant skin movement and stretching. In infants, eczema often affects the face and scalp.
The intense itching associated with inflamed skin can provoke severe scratching, further damaging the skin and potentially leading to bacterial infections. For those suffering from this uncomfortable skin condition, numerous natural remedies can help alleviate symptoms and accelerate healing.
This article will explore 13 research-backed home remedies for eczema, offering relief from dry skin, itchiness, and red rashes. We will also delve into the underlying causes of eczema flare-ups, providing insights on prevention and management, including natural treatments for atopic dermatitis.
/assets/images/provider/photos/2705220.jpg)
Understanding Eczema: Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms of Eczema: Almost all types of eczema are characterized by itching, ranging from a mild tickle to an intense, severe itch. Often, the skin can become itchy even before a rash appears. Eczema is also a common cause of itchy bumps on the elbows.
According to respected dermatologist Dr. Debra Jaliman, dry skin is a hallmark of eczema. Affected skin typically develops a rash, becoming thickened or scaly. These reddened patches may turn a brownish-gray color and develop a leathery texture (1).
Symptoms can worsen with scratching, as it can break the skin, allowing Staphylococcus aureus bacteria to cause secondary infections. This can lead to raw, swollen, and highly sensitive skin, often oozing fluid that dries into crusty patches.
Eczema in Infants and Children: It is deeply distressing for parents to witness toddlers and infants suffering from eczema. The National Eczema Association reports that approximately 10% of all infants in the U.S. experience some form of infant eczema (2). The appearance of infant eczema differs from that in older children and adults, varying with the child's age:
-
Babies under 6 months: Red patches of "weepy" skin typically appear on the face and scalp.
-
Babies from 6 to 12 months: Eczema patches develop around the elbows and knees. If infected, these can form "pus bumps" that turn crusty when they dry.
-
Toddlers from 2 to 5 years: Eczema patches become thicker, appearing as dry, scaly, and inflamed skin. Outbreaks may be more common around the mouth and eyelids (2).
Causes of Eczema: The exact cause of eczema remains unknown, according to doctors at the Mayo Clinic. However, its frequent co-occurrence with allergies and asthma suggests a connection to an overactive immune system (3). Other potential contributing factors include dry skin, a compromised skin barrier, or environmental conditions. Eczema often has a familial component.
The Best Home Remedies to Get Rid of Eczema
Natural remedies are an excellent approach to treating eczema and preventing itching by maintaining skin moisture and hydration. This method helps reduce the urge to scratch and prevents the skin from becoming dry and scaly.
Let's explore some of the best research-backed home remedies for managing eczema symptoms:
1. Coconut Oil for Treating Eczema
Virgin coconut oil is a soothing natural remedy for preventing and treating eczema. It deeply hydrates the skin, protecting it from dryness and flaking. Its effectiveness stems from its antimicrobial, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties (7).
Research highlights coconut oil's antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. A study in the journal Dermatitis found that coconut oil acts as an emollient to moisturize dry skin and combat bacteria that cause skin infections, describing it as "useful in the proactive treatment of atopic dermatitis colonization" (8).
Gentle enough for infants, virgin coconut oil has been shown to effectively reduce redness on inflamed infant skin while hydrating and soothing dryness, according to the International Journal of Dermatology (9).
Many eczema sufferers attest that organic unrefined virgin coconut oil helps control their outbreaks more effectively than expensive commercial products.
Application: Apply virgin coconut oil directly to the affected area several times a day and before bed. Continue daily until the reddish, itchy patches completely disappear.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)
Raw, unprocessed apple cider vinegar can reduce inflammation and relieve the itching of eczema due to its high acetic acid content, which helps kill bacterial skin infections and reduce itchiness. Eczema-affected skin often has a higher pH, contributing to itching and inflammation (4). ACV's acidity helps lower skin pH, alleviating the urge to scratch.
Clinical research supports the effectiveness of acetic acid on damaged, inflamed skin. A Medscape review found it effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in wounds (5). Other studies suggest that bathing affected skin in acidic water can reduce inflammation from atopic dermatitis (6).
Application Methods:
-
Topical Application: Mix equal parts raw unprocessed ACV and water. Apply with a cotton ball or spray bottle directly to eczema patches twice daily (morning and night). For sensitive skin, dilute further. Always moisturize afterward (e.g., with coconut oil or jojoba oil).
-
Bath Soak: Add 2 cups of ACV to warm bathwater. Soak for at least 30 minutes, 3 times a week, to soothe irritated skin and relieve body-wide itching.
-
Internal Consumption: Mix 1-2 tablespoons of ACV into a cup of water (add honey for taste). Drink once or twice daily to help reduce eczema signs and prevent flare-ups.
3. Chamomile for Eczema
Chamomile is an excellent natural therapeutic agent for eczema due to its soothing, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial compounds, which help calm infected red skin patches. Research indicates that chamomile extracts can reduce skin inflammation, showing a similar anti-eczema effect to hydrocortisone ointments (10).
Application Methods:
-
Tea Bag Compress: Make a cup of chamomile tea, then use the cooled tea bag to soothe itchy skin. Drinking the tea can also promote relaxation.
-
Chamomile Ointment: Add 2-3 drops of chamomile essential oil to a tablespoon of virgin coconut oil. Gently massage into scaly, red skin 2-3 times daily to speed healing and prevent bacterial infection.
4. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel's astringent and anti-inflammatory properties make it a helpful home remedy for eczema, as well as acne, cuts, and psoriasis. Its tannins help contract skin cells and accelerate healing. This astringent activity alleviates eczema-induced inflammation and prevents skin cell damage. Its powerful antioxidant and antibacterial effects also help prevent infection in damaged skin (11).
Application: Soak a cotton ball in witch hazel and gently apply directly to eczema-affected areas, especially weeping sores. Repeat as needed daily for relief.
5. Colloidal Oatmeal Bath
For quick relief from flaky, dry, itchy eczema skin, oatmeal is highly effective. Dermatologist Dr. David Lim recommends oatmeal for various skin disorders, noting its moisturizing and antioxidant properties that combat itchiness, dryness, and inflammation (12). Colloidal oatmeal is gentle enough for babies and infants with eczema. A comprehensive report confirmed its effectiveness and good tolerability in all age groups with atopic dermatitis (13).
Application (Soothing Oatmeal Bath):
-
Grind 2 cups of oatmeal and place them in a clean pantyhose, tied loosely.
-
Draw a warm bath, ensuring the oatmeal sock is under the faucet so water flows through it.
-
Occasionally squeeze the sock to release more oat liquid.
-
Soak for 15 minutes, dabbing the oat sock onto eczema patches for relief. Take this bath before bed, as eczema itchiness often worsens at night.
6. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a great home remedy for relieving painful eczema symptoms and repairing damaged skin. Known for its healing properties for burns and itchy skin, it contains anti-inflammatory compounds and vitamins that nourish and protect the skin. Its antibacterial activities also help reduce or eliminate bacterial skin infections.
A 2014 study found that applying aloe vera directly to itchy, inflammatory skin greatly improved conditions, successfully treating long-term eczema due to its anti-inflammatory effect (14). An article in Pharmacognosy Review explained that aloe vera speeds healing by increasing blood circulation to affected areas and preventing cell death (15).
Application: Apply pure aloe vera gel to affected areas 2-3 times daily, gently massaging until the itchy rash is cured.
7. Baking Soda
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is an easy and inexpensive treatment for atopic dermatitis. Its anti-inflammatory properties can relieve dry, scaly, itchy skin conditions. The National Eczema Association recommends baking soda baths as an effective home remedy, especially for large areas of eczema (17).
Application Methods:
-
Baking Soda Bath: Add half a cup of baking soda to a full warm bath. Soak for 20 minutes. Remember to apply a mild moisturizer afterward.
-
Baking Soda Paste: For small patches, mix 1-2 tablespoons of baking soda with enough water to form a thick paste. Apply to the affected area for fast itch relief. Leave for a few minutes, then rinse with warm water and moisturize.
8. Licorice Cream
Licorice is known to help skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis due to its ability to soothe inflamed skin. Research published in The Journal of Dermatological Treatment showed that licorice has anti-inflammatory activity, and when applied as a 2% gel, it effectively relieved itching, swelling, and redness (18).
Application: Licorice cream can be purchased online or in drugstores. Follow product instructions.
9. Turmeric for Eczema
Turmeric possesses numerous therapeutic benefits for inflammatory conditions, including eczema. Its active ingredient, curcumin, provides anti-inflammatory properties. Many studies show curcumin helps maintain healthy skin, free from itchy red patches. The journal Phytotherapy Research found that both oral and topical curcumin supplements offer therapeutic benefits for atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and acne (19).
Application: While incorporating turmeric into your diet is beneficial, regular curcumin supplements are best for treating eczema. Look for supplements that include piperine to enhance absorption, as curcumin is poorly absorbed on its own. A natural turmeric face mask can also be used for facial eczema.
10. Evening Primrose Oil for Atopic Dermatitis
Evening primrose oil can be taken as a supplement or applied topically as an effective natural treatment for eczema. Its extracts contain essential fatty acids beneficial for the skin. The University of Maryland reports that treating painful eczema symptoms is its most scientifically proven medical use. A study involving over 1,000 people found relief from eczema, with evening primrose oil reducing itching, swelling, and crusting in both adults and children with atopic dermatitis (20).
Application: Create a topical application by adding a few drops of chamomile oil to a tablespoon of evening primrose oil. Apply 2-3 times daily to dry, flaky skin. Taking evening primrose oil as a supplement may also alleviate irritation.
11. Urea Cream
Although not entirely natural (as it contains other ingredients), urea cream is highly effective for treating and preventing eczema outbreaks due to its powerful moisturizing and soothing properties for dry, cracked, and thickened skin. It also helps remove dead and scaly skin cells.
Application: Follow the instructions on the urea cream product, available at drugstores or online.
Other Ways to Get Rid of Eczema Naturally
Certain supplements have also shown effectiveness in treating eczema symptoms:
12. GLA Supplement
GLA (Gamma-Linolenic Acid) supplements have proven very beneficial for eczema. Some studies suggest that eczema may stem from a lack of an enzyme needed to create GLA, an omega-6 fatty acid. A study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that modest doses of GLA improved itching from atopic dermatitis (21). It's recommended to take GLA supplements for at least 4 weeks for gradual symptom improvement.
13. Probiotics
A balanced gut microbiome with "good" bacteria is crucial for proper digestion. An imbalanced digestive system can increase sensitivity to allergies and skin irritations. Studies suggest that taking probiotic supplements can help prevent eczema in children (22).
How to Prevent Eczema Flare-ups
Eczema is a chronic condition, meaning it can only be managed, not permanently cured. Therefore, preventing flare-ups is key to long-term management. Dermatologist Dr. Debra Jaliman offers these simple tips to reduce the frequency of outbreaks:
-
Moisturize Regularly: Apply moisturizer throughout the day to maintain a protective skin barrier and prevent itchiness.
-
Avoid Temperature Changes: Try to avoid sudden shifts in temperature.
-
Manage Stress: Stress can trigger eczema, so find effective ways to manage it.
-
Choose Fabrics Carefully: Avoid clothing and fabrics that irritate sensitive skin prone to eczema.
-
Gentle Cleansing: Steer clear of harsh soaps and detergents that strip the skin of its natural protective oils.
Dr. Jaliman also notes that certain foods can trigger outbreaks.
Avoid Trigger Foods that Cause Eczema: Keeping a food diary to identify foods that aggravate your eczema symptoms is crucial. Once identified, eliminate them from your diet. Some individuals have found success with a raw food diet for eczema.
According to Dr. Tim Kenny on Patient.info, common trigger foods include cow’s milk, eggs, soy, wheat, peanuts, cheese, fish, chocolate, artificial food colors, and tomatoes. Begin by observing foods you consume regularly and, through a process of elimination, identify which ones trigger your itchy breakouts.
Eczema vs. Psoriasis – What’s the Difference?
Both eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that cause significant discomfort and are challenging to manage. They share symptoms like itchy patches of dry, thickened, and inflamed skin, and both are linked to the immune system and triggered by similar conditions. However, psoriasis affects fewer people than eczema and typically presents symptoms after the age of 16. Psoriasis patches are usually much thicker and covered with silvery scales.
The good news is that many natural home remedies successfully treat both psoriasis and eczema. Experiment to find what works best for you.
News in the same category

Warning Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency and How to Fix It
Tingling Sensation In Your Body: Why Does It Happen

High Blood Sugar Warning Signs
Top Signs of Iron Deficiency and How To Increase Iron Levels In Your Blood

Doctors Suspected Baby Had Mouth Tumor—The Shocking Truth Left Them Speechless
Why Some People Never Break A Bone—3 Wild Theories Explained
JAW DROPPING SIMULATION SHOWS WHAT HAPPENS TO YOUR BODY WHILE FASTING FOR 36 HOURS TO ACHIEVE 'FULL RESET'

6 Health Benefits of Sleeping In a Cold Room and How to Make it Cooler- And Why You May Not Want to Use a Fan
Dentists Explain What Those Black Triangles Are Between Your Teeth

This optical illusion may help identify autistic traits in seconds
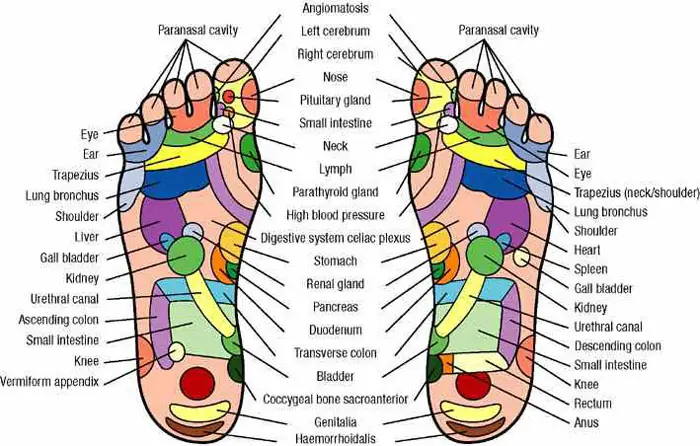
Pressure Points in Your Feet: Use This Foot Massage Chart for Pain Relief
8 Ways To Get Rid Of Phlegm And Mucus In Chest And Throat

Doctor Reveals Surprising Thing That Occurs When You Don’t Eat – and It’s The ‘Opposite’ of What Most People Think
10 Signs You May Have Kidney Disease

This is what sleeping on the left side does for our brain, stomach & glymphatic health

This Is What Happens When You Eat Too Much Sugar—#7 Will Sh0ck You!
Learn to recognize the red flags of sugar overload before it sabotages your health
Heart Surgeon Reveals 4 Foods You Should ‘Always Avoid’ That Will ‘Poison’ Your Body
Natural Skin Care: What Can You Try To Remove Age Spots, Moles, Skin Tags, Warts, And Blackheads?
10 Signs You’re Living With Clogged Arteries
News Post
Parents plan funeral for 10-yr-old with cancer – She then opens her eyes and says something that leaves them stunned

After I Saw The Baby My Wife Gave Birth To, I Was Ready To Leave Her — But Then She Said, “There’s Something I Need To Tell You.”

Medicinal Health Benefits of Garlic (Raw, Supplement) – Science Based

Mom Sells Old Stroller to Feed 4 Kids, Finds It on Her Doorstep the Next Day with Note Inside – Story of the Day
A pregnant mother of three needs to sell her stroller to feed her three children after she was abandoned by her husband.

A Father’s Redemption: How One Dad’s Love Gave His Disabled Daughter a Future Beyond Her Dreams
Prom Night Miracle: Devoted Dad Takes Disabled Daughter to Prom—Then Finds a $10K ‘Dad of the Year’ Surprise!

He Wouldn’t Take Off His Hat In Class—But When I Found Out Why, Everything Changed

THEY SAID I COULDN’T KEEP MY JOB AND RAISE HER—SO I TOOK HER ON THE ROAD

A Stranger Yelled At My Daughter In Public—So I Made Sure She Got What She Deserved

My Cousin Got A Job At My Ex’s Restaurant—And Then Sent Me A Photo Of What He Found In The Walk-In

Warning Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency and How to Fix It

Tingling Sensation In Your Body: Why Does It Happen

High Blood Sugar Warning Signs

Earth Plunged Into Darkness For Six Minutes In Rare Event Not Seen In A Century

The Hidden Meaning Behind Leg-crossing — It’s More Than Just Comfort

Scientists Warn: Universe’s ‘Self-Destruct Button’ Could Trigger Without Warning

WORLD'S FIRST DATE SOFT DRINK

We weren’t the only humans just the last ones left to tell the tale

Japanese “Baba Vanga” Meme Resurfaces After July 2025 Tsunami Triggers Alerts

Top Signs of Iron Deficiency and How To Increase Iron Levels In Your Blood
