
NASA Spots Giant Butterfly-Shaped Coronal Hole Sending Solar Wind Toward Earth
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) has captured an extraordinary butterfly-shaped coronal hole on the Sun that spans roughly 500,000 kilometers across — a colossal structure carved into the solar atmosphere. This remarkable formation, with two distinct lobes resembling wings, immediately drew attention from researchers observing the Sun’s magnetic activity and atmospheric behavior.
What Is a Coronal Hole, and How Does It Form?
Coronal holes are regions in the Sun’s outer atmosphere where magnetic field lines open outward into space rather than looping back toward the surface. These open-field areas allow high-speed streams of charged particles — known as the solar wind — to escape into the solar system. Because the plasma within these regions is cooler and less dense, coronal holes appear much darker in ultraviolet and X-ray imagery captured by observatories monitoring the Sun.
The butterfly-shaped coronal hole is a visually striking example of this phenomenon. Instruments aboard NASA missions and international solar observatories have identified similar features before, but the scale and symmetry of this one make it particularly noteworthy.
Size and Comparison to Earth
At nearly half a million kilometers wide, this coronal hole is enormous — about 23 times the diameter of Earth. Such a comparison highlights the vastness and dynamic nature of the Sun’s magnetic environment. Coronal holes of this magnitude often align with heightened solar activity during the solar cycle’s active phases, offering scientists valuable insights into the Sun’s evolving magnetic structure.
Solar Wind, Forecast, and Potential Impact
From this massive opening, a high-speed stream of solar wind is currently flowing into space and is expected to reach Earth. Forecasts from global space-weather monitoring agencies predict that it may trigger geomagnetic storms ranging from G1 (minor) to G2 (moderate). These storms occur when the charged particles from the Sun interact with Earth’s magnetic field, and their intensity depends on how the solar wind’s magnetic orientation aligns with our planet’s.
Although the expected geomagnetic activity is not considered severe, scientists caution that fluctuating magnetic conditions could briefly enhance the strength of the storm, especially if the solar wind’s magnetic field aligns in a way that promotes stronger energy transfer into Earth’s magnetosphere.
Effects on Earth: Auroras and Technological Systems
One of the most visually captivating effects of such solar wind events is the enhancement of auroras — the northern and southern lights. When energetic particles from the solar wind collide with atmospheric gases such as oxygen and nitrogen, they produce shimmering curtains of light across the polar skies. During moderate geomagnetic storms, auroras may become brighter and more widespread, offering spectacular displays for observers at higher latitudes.
In addition to auroras, minor disturbances to satellite navigation, radio communications, and electrical power systems may occur. While these effects are typically limited during G1 or G2 storms, space-weather agencies and satellite operators remain on alert whenever high-speed solar wind streams are headed toward Earth.
Timing and the Russell-McPherron Effect
The timing of this event coincides with a period when Earth is more susceptible to magnetic disturbances due to the Russell-McPherron effect. Around the equinoxes, the geometry of Earth’s magnetic field relative to the Sun’s magnetic field becomes more favorable for strong magnetic coupling, meaning that geomagnetic storms can intensify even when solar wind conditions are not extreme. This makes the arrival of the solar wind from the butterfly-shaped coronal hole particularly interesting to researchers studying space-weather interactions.
Scientific Importance and Ongoing Monitoring
Beyond its dramatic appearance, this butterfly-shaped coronal hole offers an important opportunity for scientists to refine space-weather forecasting models. High-speed solar wind streams from coronal holes are a major driver of geomagnetic storms, and observing their evolution helps scientists better predict when and how these storms will affect Earth.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, along with other international missions equipped with ultraviolet and X-ray instruments, continues to monitor the event closely. Data collected from these observations support ongoing research into the Sun’s magnetic behavior, solar wind acceleration, and the mechanisms behind space-weather disturbances.
News in the same category


Why Some Children Don’t Visit Their Parents Often

Will Americans Receive $2,000 Stimulus Checks? What You Need to Know

14 Reasons to Drink Lemon Water First Thing in the Morning

Meet the Owners Behind Baltimore’s First Black & Woman-Owned Bodega

Quinta Brunson to Receive Keys to Hometown City of Philadelphia

Bethann Hardison & Andrew J. Young Honored at Gordon Parks Foundation Gala

Jay-Z & Luther Vandross’ First Albums Inducted Into GRAMMY Hall of Fame

Sheryl Lee Ralph Gets Emotional After Learning Her Ancestors Were Free People on ‘Finding Your Roots’

Philadelphia Entrepreneur Becomes The First Queer Black Woman To Lead A Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Company

‘Tia Don’t Piss Me Off’: Tia Mowry’s Selfie with Mystery Man Has Folks Noticing He Looks Nothing Like Ex Cory Hardrict Despite Reunion Chatter

Todd Tucker vs. Kandi Burruss: Prenup Could Make or Break a $30M Empire

HBCU Grad Rajah Caruth Secures Second Career NASCAR Truck Series Win

NPR’s Tiny Desk Celebrates Black Music Month With Performances by Amerie, Beenie Man, CeCe Winans & More

Tiffany Derry Makes History as MasterChef’s First Black Full-Time Judge

Kwame Onwuachi to Open New Restaurant ‘Maroon,’ the First Black Chef-Led Restaurant on the Las Vegas Strip

How Artists and Engineers Are Confusing Facial Recognition AI

Tesla Faces Slump: Over 10,000 Cybertrucks Remain Unsold Amid Weak Demand

Over a Million ‘Giant Eggs’ Discovered Near Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents
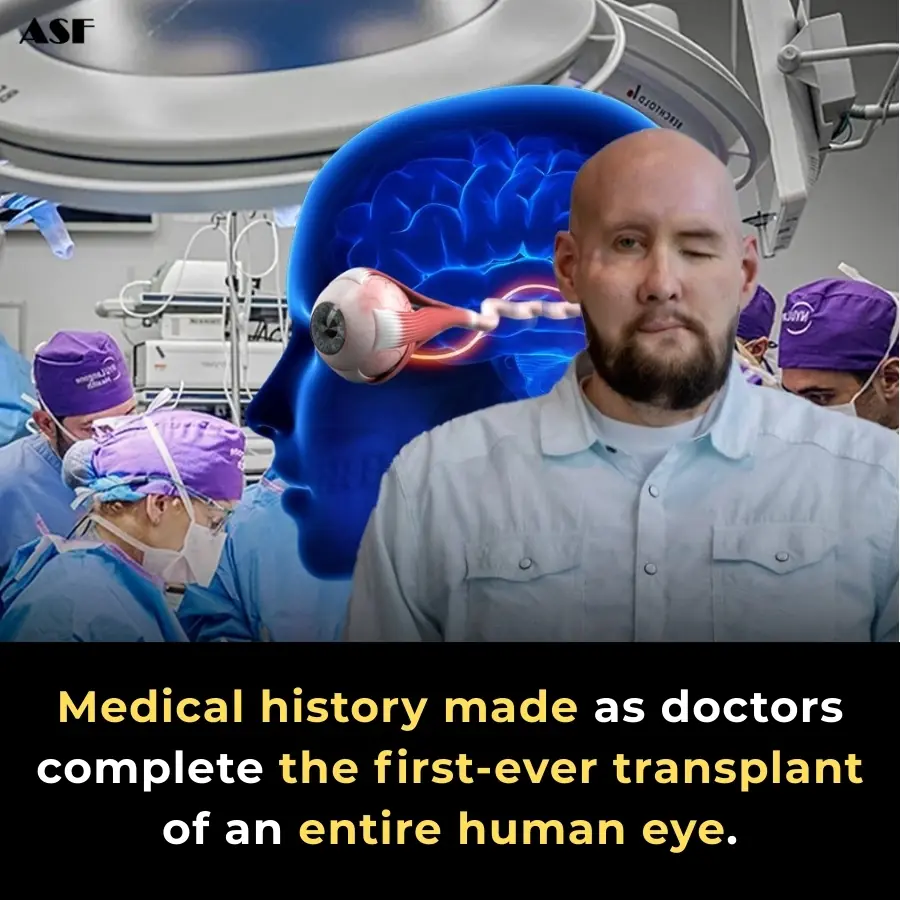
World’s First Full Human Eye Transplant Shows Promising Survival
News Post

Unlock Radiant Skin: The Ultimate Guide to Using Beetroot Gel for Glowing, Spotless Skin

Fenugreek Seeds for Hair Growth: The Power of Fenugreek Hair Rinse and Its Benefits for Hair

Japanese Milk Wax To Get Rid Of Unwanted Facial Hair

When Will I Outgrow My Acne? The Difference Between Adult and Teen Acne

5 Mascara Tips For Short Lashes

LEVEL UP YOUR LASH GAME: Top 5 Tips for Eyelash Extension Success!

Forehead Acne and What to Do About It

11 Common Eyebrow Mistakes Women Make in Their 60s (And How to Fix Them!)

How to Prevent and Treat Age Spots: Expert Tips for Radiant Skin

5 Ways Your Skin Changes as You Age and How to Keep It Vibrant

DIY Fenugreek Oil for Hair Growth – Get Thick Hair

Brow Boosting Serum: The Natural Way to Achieve Full, Thick Eyebrows

Why You Should Be Putting Salt in Your Toilet

Why Some Children Don’t Visit Their Parents Often

DIY Vaseline Cream: The 4-Ingredient Glow Hack That Makes Your Skin Baby-Soft Overnight

DIY Fenugreek Hair Masks for Hair Growth & Reducing Hair Fall

Will Americans Receive $2,000 Stimulus Checks? What You Need to Know

Revolutionary Miniature Implant Offers New Hope for Restoring Vision in Macular Degeneration Patients

A Simple Superfood That Enhances Your Baby's Brain Development During Pregnancy
