
Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutrition Facts (Evidence Based)

Celery is a crunchy, refreshing vegetable that is naturally low in carbohydrates and calories, yet rich in nutrients that support overall health. Whether consumed as celery stalks, ribs, leaves, seeds, or juice, this versatile vegetable offers a wide range of health-promoting properties. Celery supports weight loss, helps regulate blood pressure, improves liver function, and plays a role in managing diabetes. In addition, it contains essential vitamins, minerals, and powerful antioxidants that strengthen the immune system and protect the body against disease.
There are numerous ways to incorporate celery into your daily diet. You can drink freshly made celery juice, add chopped celery stalks or leaves to soups and salads, or simply enjoy a raw celery stick as a light, low-calorie snack. Regardless of how you consume it, celery provides an impressive combination of hydration, fiber, and bioactive compounds that contribute to long-term wellness.
In this article, you will explore the many scientifically supported health benefits of celery. You will also learn how celery juice, celery leaves, and celery seeds can help maintain heart health, support liver function, enhance digestion, and promote overall vitality.
What Is Celery?
Celery (Apium graveolens) is a widely cultivated vegetable grown in many regions around the world. It belongs to the Apiaceae family, which also includes parsley, fennel, and carrots. Celery is best known for its long, fibrous green stalks, although every part of the plant—including the leaves, seeds, and root—can be used for culinary or medicinal purposes.
The stalks are often called celery sticks or celery ribs, while the entire plant is referred to as a celery head. The celery heart consists of the tender inner stalks located at the center of the head and is especially mild in flavor.
Researchers recognize celery as a nutrient-rich, diuretic plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. Celery contains beneficial plant compounds such as limonene, selinene, flavonoids, and antioxidants, as well as vitamins A and C. Thanks to its high fiber and water content, celery supports healthy digestion and can aid in weight management.
Celery seeds are particularly valued for their essential oils and fatty acids, which help protect cardiovascular health. Meanwhile, celery leaves are packed with vitamins and minerals and can be eaten fresh or cooked. They add both flavor and nutritional value to soups, salads, and other dishes.
Nutritional Value of Celery
The health benefits of celery stem largely from its impressive nutritional profile. According to data from the United States Department of Agriculture, one celery stalk contains only 6 to 9 calories and virtually no fat, making it one of the healthiest snack options for those trying to lose or maintain weight.
Celery is also rich in dietary fiber. Two large stalks provide approximately 2 grams of fiber, which is about 8% of the recommended daily intake. This fiber content helps reduce hunger between meals, supports gut health, and promotes feelings of fullness without excess calories.
Celery is especially suitable for low-carbohydrate and ketogenic diets. One cup of chopped celery contains only 3.5 grams of carbohydrates and has a very low glycemic load, meaning it has minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
In addition to fiber, celery supplies a variety of essential vitamins and minerals. It is an excellent source of vitamin K and also provides vitamins A, C, and several B vitamins. Minerals found in celery—including potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese—support bone health, muscle function, and cardiovascular balance.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Celery
Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to many serious health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods such as celery may help reduce this risk.
Studies show that celery contains bioactive compounds with strong anti-inflammatory effects. Both celery stalks and leaves help reduce inflammatory markers in the body, while celery seed extracts have been shown to calm inflammatory responses and protect gastrointestinal health. These properties make celery particularly valuable for long-term disease prevention.
Rich in Antioxidants
Celery is also a powerful source of antioxidants, which protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants such as luteolin, apigenin, tannins, and flavonoids play an essential role in preventing premature aging and chronic disease.
Extracts from celery seeds, roots, and leaves have been studied for their potential benefits in managing conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Regular consumption of antioxidant-rich vegetables like celery can contribute to stronger immunity and improved cellular health.
Major Health Benefits of Celery
Supports Weight Loss
Celery is classified as a low-energy-dense food, meaning it provides volume and satiety without excess calories. This makes it an ideal snack or meal addition for people trying to lose weight. Its fiber content slows digestion, reduces cravings, and helps regulate appetite while supplying key nutrients.
Improves Heart Health
Celery supports cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, lowering cholesterol levels, and helping regulate blood pressure. Its antioxidants protect blood vessels from oxidative stress, while compounds such as luteolin improve vascular function.
Helps Lower Blood Pressure
Celery contains compounds that relax blood vessel walls and improve circulation. Both celery stalks and celery seed extracts have been shown to reduce hypertension. Celery’s natural diuretic effect also helps remove excess sodium and water from the body, further supporting healthy blood pressure levels.
Lowers Cholesterol
Research suggests that celery contains unique compounds that reduce total cholesterol and blood lipid levels. Regular consumption may lower the risk of coronary heart disease and support long-term heart health.
Supports Liver Health
Celery juice and extracts help protect the liver from oxidative damage and toxin buildup. Studies show that celery’s antioxidants can reduce liver enzyme levels and support detoxification. Including celery in the diet may help lower the risk of fatty liver disease and improve overall liver function.
Improves Digestion and Gut Health
Celery’s fiber content promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. Additionally, compounds in celery help protect the stomach lining, reduce ulcer risk, and combat harmful gut bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori. This makes celery beneficial for overall digestive health.
Helps Manage Diabetes
Because celery is low in carbohydrates and has minimal impact on blood sugar levels, it is a safe and beneficial food for people with diabetes. Celery leaf extracts have been shown to help regulate blood glucose without increasing insulin levels.
Reduces Joint Pain and Inflammation
Thanks to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, celery may help relieve symptoms of arthritis. Celery seed extract, in particular, has been shown to reduce joint swelling and pain, with effects comparable to some anti-inflammatory medications.
Supports Male Fertility
Traditional medicine has long used celery to enhance male reproductive health. Research suggests that celery leaf extract may improve sperm count and overall fertility parameters.
Enhances Brain and Cognitive Function
Celery contains compounds such as luteolin and apigenin that protect brain cells and reduce neuroinflammation. Certain compounds in celery seeds may also help slow cognitive decline and protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Benefits During Menopause
Celery contains phytoestrogens that may help ease some menopausal symptoms. Its antioxidants also support bone health and may reduce the risk of osteoporosis and certain hormone-related cancers.
Anti-Cancer Potential
Celery contains compounds such as apigenin that exhibit anti-cancer properties. Research suggests these compounds may help inhibit tumor growth and reduce the spread of certain cancer cells, although more studies are needed.
Health Benefits of Celery Seeds
Celery seeds are highly concentrated sources of beneficial compounds. They may help:
-
Lower blood pressure
-
Protect the stomach lining and prevent ulcers
-
Reduce inflammation and arthritic pain
Precautions and Safety Considerations
While celery is highly nutritious, some individuals may experience allergic reactions, particularly to celery root or seeds. Symptoms can include skin irritation, asthma, or digestive discomfort.
It is also recommended to choose organic celery whenever possible, as conventionally grown celery often contains pesticide residues.
Final Thoughts
Celery is a versatile, nutrient-dense vegetable with a wide range of scientifically supported health benefits. From weight management and heart health to digestion, liver support, and cognitive protection, celery is a valuable addition to a balanced diet. When consumed regularly and responsibly, it can play an important role in supporting long-term health and wellness.
News in the same category

World-First Breakthrough: Base-Edited Gene Therapy Reverses "Incurable" T-Cell Leukemia
Daily Tefillin Use Linked to Improved Blood Flow and Lower Inflammation

Daily Whole Orange Consumption Associated with 30% Reduction in Fatty Liver Prevalence

Phase I Trial: White Button Mushroom Powder Induces Long-Lasting PSA Responses in Prostate Cancer

Tea Supports Bone Density While High Coffee Intake Linked to Bone Loss in Older Women

Rapamycin Reduces Lung Tumor Count by Up to 90% in Tobacco-Exposed Models
51-Year-Old Man Declared Cured of HIV Following Stem Cell Transplant for Leukaemia
Modified CAR T-Cell Therapy Successfully Eliminates Solid Prostate Tumors in Mice

The Gut-First Approach: Berberine’s Impact on Microbiome Balance and Barrier Integrity

Living Near a Golf Course Linked to Nearly Triple the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease

High-Dose Nattokinase Reduces Carotid Plaque Size and Arterial Thickness in 12-Month Clinical Study
A 65-year-old man passed away in the middle of the night: Doctors warn against 4 types of drinks to avoid before bed

Diagnosed with late-stage stomach cancer after a sore throat examination, the enraged man threw the two "culprits" from his kitchen onto the street

Cooking with Aluminum Foil: Why It’s Dangerous and Safer Alternatives

3 habits that silently "poison" the uterus, the last one costing many women dearly

Scientifically Proven Health Benefits of Avocado and Avocado Seeds
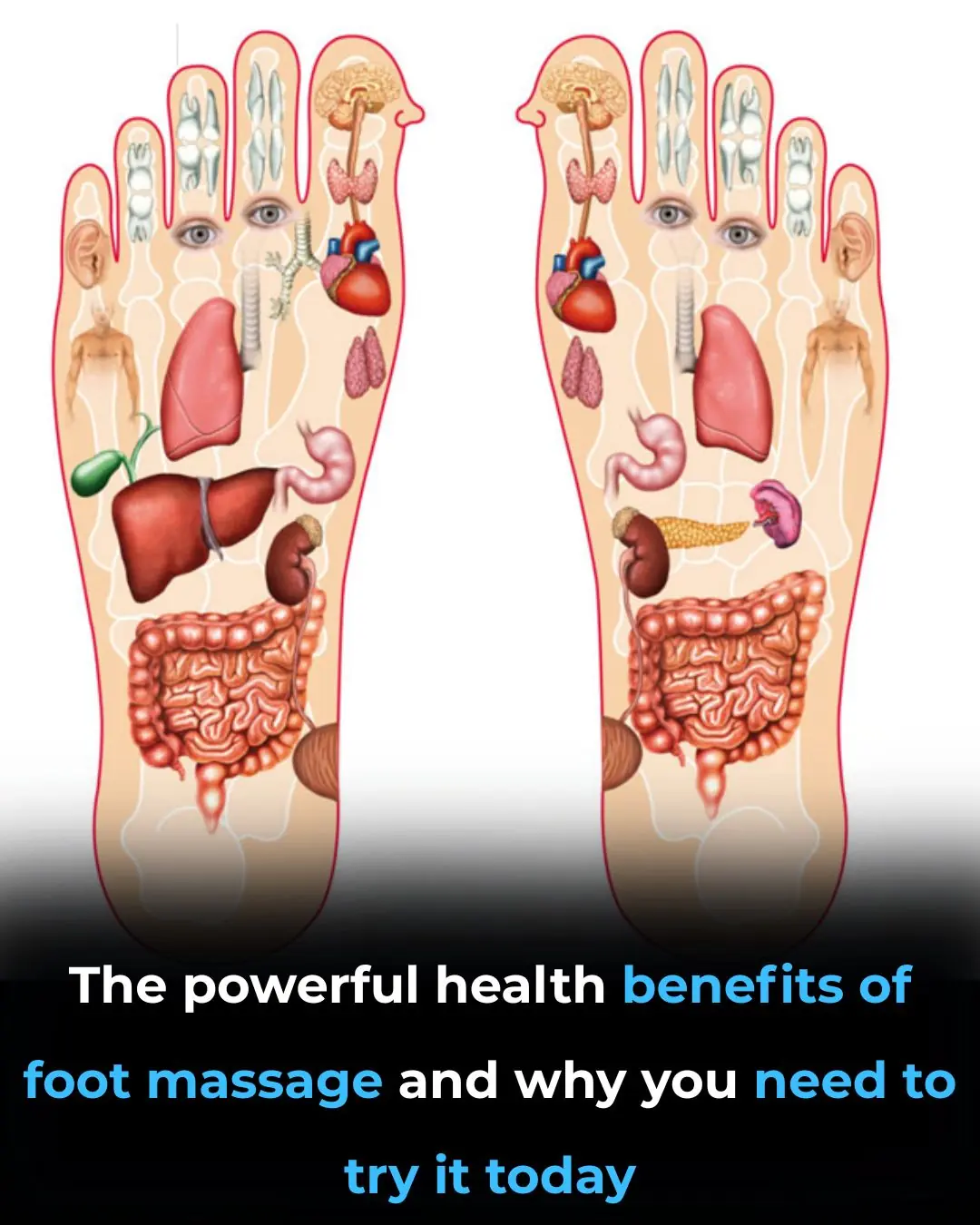
Foot Massage: Proven Health Benefits and How to Give It (Video)

Brazil Nuts: Proven Benefits, How Many to Eat Per Day, Nutrition Facts, Calories
News Post

Ultra-Processed Foods Linked to Increased Psoriasis Flare-Ups, Study Finds

Giant Pandas Officially Move Off the Endangered Species List: A Historic Conservation Triumph

Twin Study Reveals Gut Microbiome's Role in Multiple Sclerosis Development

Mexico City Passes Landmark Law Banning Violent Practices in Bullfighting: A Controversial Move Toward "Bullfighting Without Violence"

World-First Breakthrough: Base-Edited Gene Therapy Reverses "Incurable" T-Cell Leukemia

Daily Tefillin Use Linked to Improved Blood Flow and Lower Inflammation

A Magical Bond: The Unlikely Friendship Between a Blind Dog and a Stray Cat in Wales

Daily Whole Orange Consumption Associated with 30% Reduction in Fatty Liver Prevalence

Phase I Trial: White Button Mushroom Powder Induces Long-Lasting PSA Responses in Prostate Cancer
Chronic Gut and Metabolic Disorders May Signal Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Years in Advance

Tea Supports Bone Density While High Coffee Intake Linked to Bone Loss in Older Women

Syros Cats: A Sanctuary for Feline Rescue and Compassion in Greece

Rapamycin Reduces Lung Tumor Count by Up to 90% in Tobacco-Exposed Models

51-Year-Old Man Declared Cured of HIV Following Stem Cell Transplant for Leukaemia

Modified CAR T-Cell Therapy Successfully Eliminates Solid Prostate Tumors in Mice

The World Bids Farewell to Bobi, the World's Oldest Dog, at the Age of 31

The Gut-First Approach: Berberine’s Impact on Microbiome Balance and Barrier Integrity

Living Near a Golf Course Linked to Nearly Triple the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease

The Cost of a Trip to Tokyo Disney is Now Cheaper Than Going to Disney in Florida
