
The Hidden Dangers of Eating Leftover Food Stored Overnight
In daily life, many people have the habit of storing leftover food in the refrigerator to eat later. Some even cook once and eat the same food for several days due to busy schedules. While this may seem convenient and economical, it can pose serious health risks if done improperly.
Recently, a case reported online raised public concern. A man in his 50s in China suffered from severe diarrhea after consuming leftover food that had been stored at home. Despite being hospitalized and receiving intravenous treatment, he suddenly lost consciousness. He was transferred to a higher-level hospital for emergency care, but upon arrival, his heart and breathing had stopped. After nearly 40 minutes of resuscitation, doctors were unable to save him.
Medical Explanation
According to doctors, the patient likely developed acute enteritis after consuming food that had been stored in the refrigerator for too long. Severe diarrhea led to electrolyte imbalance, which in turn caused metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels in the blood). These conditions can be life-threatening and may result in cardiac arrest if not treated promptly.
How Dangerous Is Overnight Food?
“Overnight food” does not only refer to food kept from one night to the next, but also to food that has been left for more than 8–10 hours. In everyday life, many foods fall into this category even if they are not technically kept overnight.
To assess the health impact of leftover food, the Ningbo Institute for Food Inspection and Testing conducted an experiment. Researchers purchased common ingredients such as meat, fish, and vegetables from local markets and prepared 30 dishes using typical household cooking methods. These dishes were categorized into meat-based, mixed meat and vegetable, vegetarian, and cold dishes, then stored at 4°C (refrigeration temperature) and 25°C (room temperature).
Key Findings
-
Vegetables stored at 4°C for less than 6 hours: Nitrite levels showed little change, and microbial growth was minimal.
-
Vegetables stored at 25°C for more than 6 hours: Although nitrite levels did not increase significantly, microbial growth increased substantially.
Overall, if cooked food is stored at low temperatures, properly sealed, and kept at around 4°C for no more than 24 hours, nitrite levels and microbial growth generally remain within safe limits. Under these conditions, the food may still be safe to eat.
Therefore, leftover food is only associated with serious health risks, including cancer, when it is stored improperly and consumed repeatedly over long periods. Even though vegetables stored overnight under controlled conditions may not immediately harm health, this does not mean they are completely risk-free.
Foods That Should Never Be Eaten After Being Left Overnight
Some foods are particularly unsafe to reheat or consume after being stored overnight:
-
Mushrooms and wood ear fungus
These foods contain complex proteins that can become harmful to the digestive system when reheated. They also contain high levels of nitrates, which may convert into toxic substances if stored too long. Mushrooms are best consumed on the same day they are cooked. -
Leafy green vegetables
Leafy greens are high in nitrates. When stored for long periods, especially at room temperature, nitrate levels can convert into nitrites, while nutrients are significantly lost. These vegetables are best eaten fresh. -
Soy products (tofu, soy milk)
Soy-based foods are rich in protein and nutrients, making them an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. If stored improperly, they may become contaminated with Clostridium botulinum, a bacterium that can cause nerve paralysis and even death. -
Soft-boiled or runny eggs
Eggs with undercooked yolks are not fully sterilized. Due to their high nutrient content, bacteria can multiply rapidly if they are stored for too long. -
Seafood
Some bacteria in seafood are not completely eliminated during cooking. When stored in the refrigerator, these bacteria may multiply again and produce harmful protein breakdown products, which can damage the liver and kidneys.
How to Store Leftover Food More Safely
-
Store food at low temperatures; avoid leaving cooked food at room temperature.
-
Separate vegetables and meat, and store them in airtight containers or wrap them tightly.
-
Pay close attention to storage duration for cooked food.
-
Do not store leftovers for more than 24 hours.
-
Avoid reheating food multiple times; leftovers should be reheated only once.
Final Note
While eating leftover food may seem harmless, improper storage and repeated consumption can pose serious health risks. Freshly prepared food remains the safest and healthiest choice whenever possible.
News in the same category


The Best Proven Ways to Heal Scars Naturally (Evidence Based)
16 Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation and How to Treat It
The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

Daily Step Counts Combined With Genetic Risk Can Better Predict Type 2 Diabetes

Gestational Diabetes Rates Surge Across the United States

Why Does Lung Cancer Affect Non-Smokers? A Hidden Culprit in the Kitchen That Many People Overlook
6 Foods You Absolutely Need To Avoid If You Suffer From a Thyroid Disorder
Gastroenterologist says this is the #1 drink for gut health
Top 5 drinks to INSTANTLY improve leg circulation and blood flow

Five Morning Habits That May Quietly Increase Cancer Risk

Natural Home Remedies for Cough and Sore Throat
People with weak kidneys often do these 4 things every day: If you don't stop soon, it can easily damage your kidneys
I spent a couple of nights at my friend’s previous apartment and saw these unusual bumps
10 Unusual Signs Your Blood Sugar Is Constantly Too High

Five Simple Drinks That Help Eliminate Uric Acid and Prevent Gout Flare-Ups

Red and Processed Meat Consumption Increases Cancer Risk, Experts Warn

Two Rare Neurologic Disorders Added to US Newborn Screening Panel
News Post

Say Goodbye to Varicose Veins Naturally: A Simple Garlic, Onion, and Olive Oil Remedy That May Offer Relief

Why Seniors Are Turning to Honey and Cloves for Everyday Comfort After 60

Can Garlic and Lemon Really Support Better Vision? Kitchen Staples Your Eyes Might Appreciate

Banana Flower: The Underrated Superfood Taking Over in 2025

Fears of a Texas Serial Killer Intensify After Three More Bodies Are Recovered from Houston Bayous

From Casual Drinking to Dependence: A Recovering Alcoholic Reveals Seven Warning Signs of Addiction

Why Americans Were Shocked by the British Way of Washing Dishes

No one told me
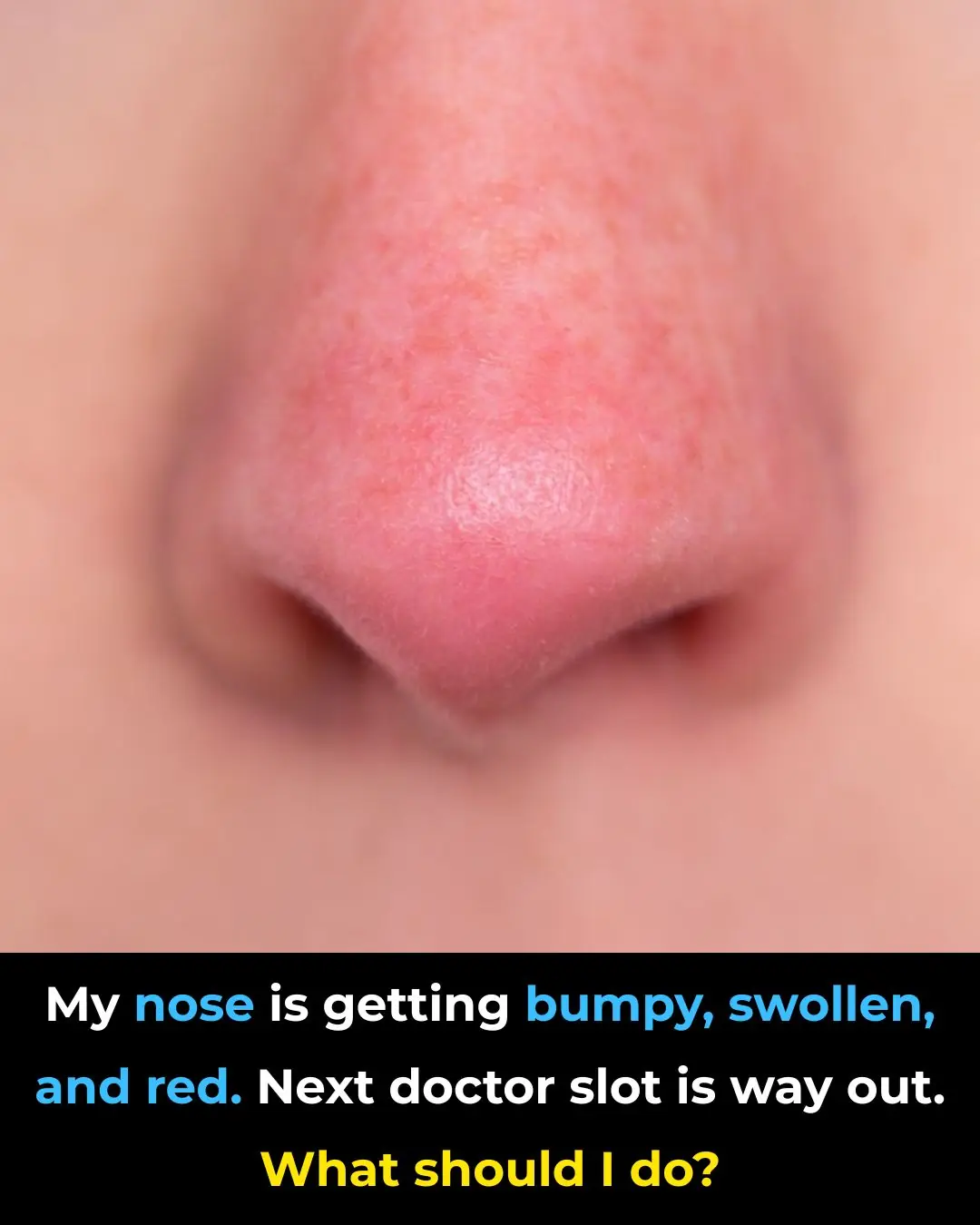
My nose is getting bumpy, swollen, and red. Next doctor slot is way out. What should I do?

Can You Spot It? The Viral “Sniper Vision” Challenge That’s Testing Human Perception

Most Doctors Won’t Tell You, But This Can Cut Heart Attack & Stroke Risk By 80%

The Best Proven Ways to Heal Scars Naturally (Evidence Based)

How Japan Preserves Nature by Relocating Trees Instead of Cutting Them Down

16 Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation and How to Treat It

The Best Home Remedies For Getting Rid of Ear Infection

A Simple Act of Kindness That Turned a Lifelong Dream into Reality

Soap Left on Plates? British Dishwashing Method Sparks International Debate

A Hero on Four Paws: How a Cat’s Instincts Saved a Baby from an Alligator

Florida’s Trooper’s Law: A Landmark Step Toward Protecting Pets During Natural Disasters
